Conservation Agriculture in a semi-arid area [นามิเบีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Alexander Groengroeft
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Lima nawa (Vambo/Rukwangali)
technologies_1297 - นามิเบีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Simfukwe Maxon
CEDP
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kowalski Benjamin
เยอรมนี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Future of Okavango (TFO / GLUES)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Conservation agriculture using permanent water-harvesting planting basins, or rip-lines and fertilizer/manure application on low fertility dryland soils.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
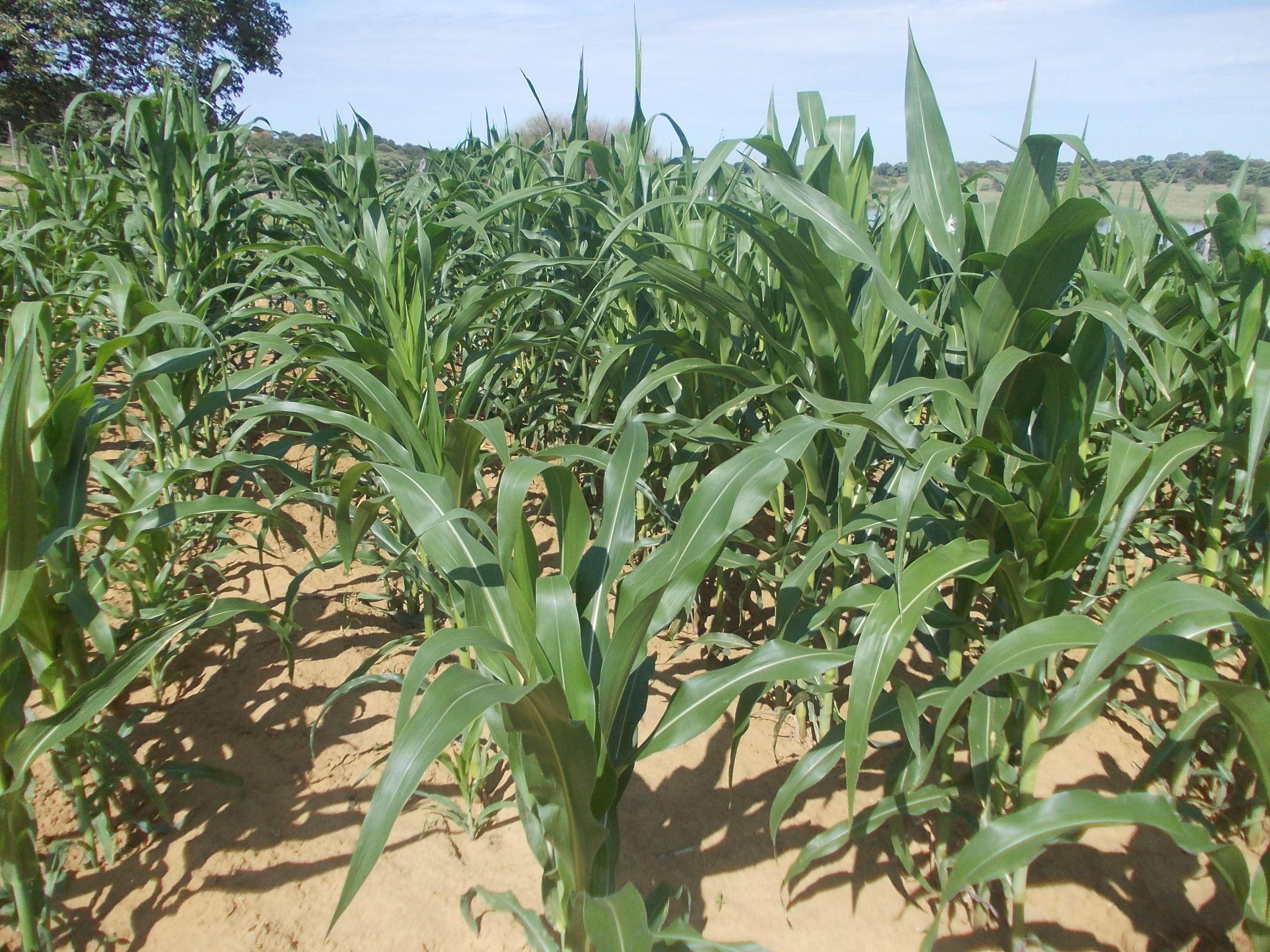
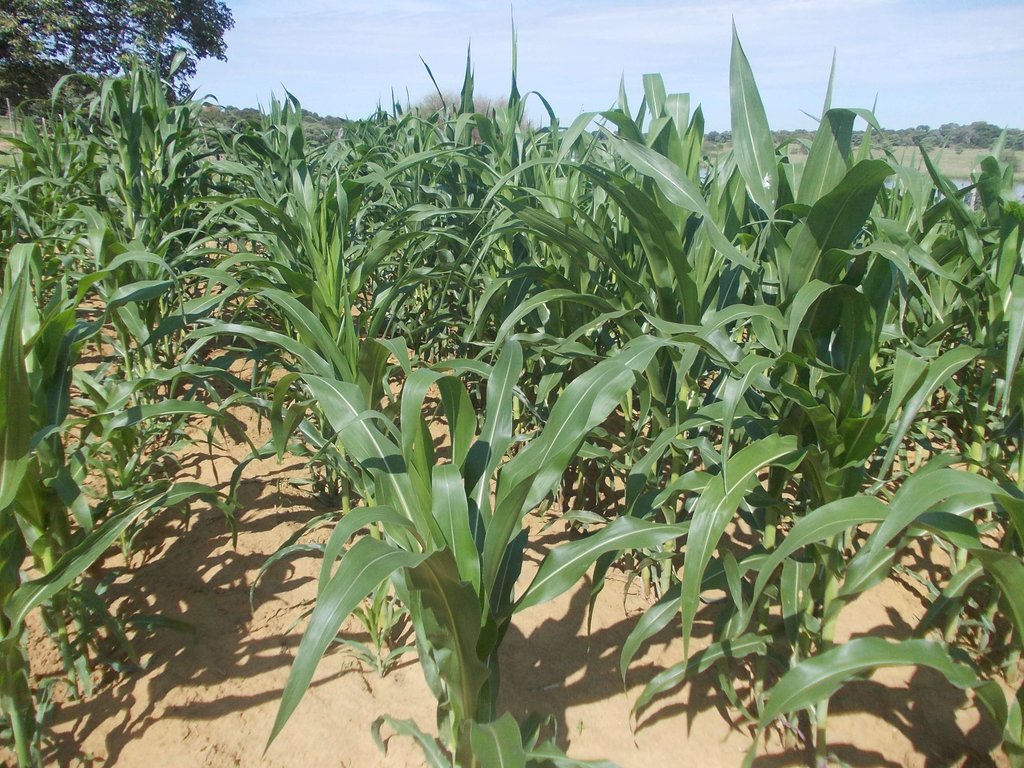
Farmers in north-eastern Namibia practice shifting/semi-permanent subsistence cropping, concentrating on pearl millet cultivation. Here, conservation agriculture (CA) was promoted to sustain and improve production and to reduce conversion of woodland to crops. CA comprises the three principles of minimum soil disturbance, permanent soil cover, and rotation. CA was tested on small plots with volunteers trained by a local NGO. The technology was characterized here by: (i) Early (pre-rains) preparation of the land with two alternative techniques; either: a) basins with a defined spacing opened by a hand hoe, with composted manure added (biochar has also been tested), or b) rip-lines prepared with oxen in lines and with manure application within the rip lines; (ii) Mulching the soil with crop residues, branches or sunnhemp, specially grown for the purpose; (iii) Protection against grazing of crop and mulch by livestock; (iv) Intercropping with vegetables or legumes. (v) Weeding.
CA has been promoted for four seasons, and now trained farmers are transferring their knowledge to others. The technology was promoted to substantially improve the low yields of traditionally practiced agriculture by improving fertility and soil structure as well as better capturing runoff. It was also aimed at avoiding further expansion of croplands into dry woodlands on low fertility arenosols. Eventually it is hoped that the well-being of local subsistence cropping communities will be improved and outmigration reduced.
Knowledge about CA comes from Zambia, where it has been has been practiced successfully for many years by small-scale farmers. A local NGO was engaged by an international project (www.future-okavango.org) which searched for volunteer farmers in the Kavango area. The first CA planting took place in 2011/12. These pioneer farmers were backstopped regularly and the number of farmers trained increased. The NGO monitored crops with contact farmers. 45 more farmers showed interest and were then trained by the contact farmers. Training and backstopping continued until August 2015.
The natural environment is semi-arid. Rainfall is concentrated from November to March. Mean annual precipitation is 570 mm, and mean air temperature is 26.2°C in the hottest month (October) and 16.2°C in the coldest month (July). The landscape forms part of the extended Kalahari basin in central-southern Africa. Deep and extended sands restrict people to living in areas close to surface water. Villages are located along the Okavango on the elevated river terraces – where they produce crops. Here, sedimentation of fine-grained soils, the accumulation of calcium carbonates in the subsoil and the activity of termites have resulted in soils of medium fertility which could potentially ensure yields of 500 kg/ha of millet, if well managed, and assuming good rainfall. Due to the growing population and restricted land availability, cultivation patterns have changed from shifting to semi-permanent and expanded to the adjacent woodlands on the deep Kalahari sands. Here, rapid degradation of soil fertility has caused further expansion and reduced crop yields to very low levels (ca. 150 kg/ha on average). Livestock graze and browse vegetation on the floodplains and in the woodlands. Due to night-time kraaling of livestock, manure is available as fertilizer: thus sustained cropping can be supported. The importance of the woodlands for ecosystem services including timber and firewood, for thatching grass, medicinal plants and biodiversity means they must be conserved and this acts as a reason to support the search for alternative crop production systems such as CA.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
นามิเบีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kavango East
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mashare
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -17.92 / 20.0 -17.89 / 20.28
SLM technology was applied by trained smallholders on small plots
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Introduction in the area by Community Economic Development Programme (CEDP) TFO-project in 2011
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 135, Longest growing period from month to month: Nov to March

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low and very variable yields per ha; ongoing expansion of fields to less fertile woodlands due to nutrient depletion of originally fertile plots; years with dry spells.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop wilting and poor yields, opening new areas in search of better fields, cutting down trees, slushing and burning residues
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Under CA, sunhemp for residue and nitrogen fixing has been grown as green manure and fodder for livestock.
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, green manure, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage, pits
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bf (Detrimenta leffects of fires): ผลเสียหายจากไฟ
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Missing nutrient returns)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Grazing and burning of crop residues), population pressure (Expansion of croplands to less fertile soils)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Scheme of CA field with basins
Within the fenced area, basins are dug per hand-hoe in lines with about 15 cm width, 35 cm length and 15 cm depth and in 70 cm distance. To keep the line and position, a rope with knots every 70 cm is used. Each basin is refilled with 2 cans of manure mixed with part of the soil material. Maize or pearl millet - two stages shown on the graph
Location: Mashare. Kavano East/Namibia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Early planting
Remarks: Planting basins prepared in dry season, planting can occur by first rainfalls (earlier than plough-d
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Maize / Millet /Cowpea
Remarks: Cultivated in parallel lines
Mulching
Material/ species: Grasses & crop residues & sunhemp
Remarks: sunhemp cultivated on the CA field and cut to produce mulch
Green manure
Material/ species: branches of fertilizer tree
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Composted manure from cattle post
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: Maize / Millet /Cowpea
Remarks: Planted in lines and shifted annually
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Riplines by oxen
Pits
Material/ species: planting basins by hand hoe
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 0.7
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.35
Structural measure: ripline
Spacing between structures (m): 0.7
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:8,3
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More specific soil management; crop protection by fencing; earlier seeding
Major change in timing of activities: To a large part, land preparation can be carried out throughout dry season, independent of rainfall level
ผู้เขียน:
Maxon Simfukwe
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Nam $
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
15.5
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | dry season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 1104.0 | 1104.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wire for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 224.0 | 224.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | sticks & poles | ha | 1.0 | 1114.0 | 1114.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2442.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 157.55 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing fences and de-bushing of the fields | (May - July) |
| 2. | Gatering and spreading of mulch cover | July - Dec |
| 3. | Cutting sunhemp and applying as additional mulch | Feb-Mar |
| 4. | Re-digging the planting basins | August |
| 5. | Manure collection, Planting & fertilizer application | September - December |
| 6. | Sowing of main crops and sunnhemp and fertilizer application | November - December |
| 7. | Intercropping with legumes like groundnuts and cowpeas normally two weeks after germination of cereals. | |
| 8. | Weeding | |
| 9. | Harvesting | April - May |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 848.0 | 848.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 276.0 | 276.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wire for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 220.0 | 220.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1525.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 98.39 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Values above are for manual CA using a hoe; an external worker earns 4 N-$ per working hour; above, family labour was multiplied by 4 to estimate the “value” of the family labour invested
The costs are based on labour needs of one year and 500 kg/ha of fertilizer
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
CA was designed to require minimal financial investments; theoretically, everything apart from wire for the fences and inorganic fertilizer can be created or gather by the household. This turns CA into a very labour intensive farming practice. The high Dollar values above result from multiplying the (free) family labour invested in farming with the typical hourly wage rate of an external worker
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2% (One farmer to our knowledge could be considered wealthy). (Few average farmers). (Mostly CA farmers are poor).
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
parallel existence of state and communal laws
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Envy and gossip were observed
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
contribution to human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved and stabilized yields help rural families to adapt to modern lifestyles. However, the long-term contribution of CA to the well-being of the local farmers cannot be foreseen. The establishment of family-owned fenced areas for crop production is likely to have an influence on the social structure of the rural communities.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
not measured but assumed
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Dig basins at 20cm (0.20m) deep; and extra water harvesting basins at 0.45m in-between the rows. For the ox-ripped lines, use ripper wings to open a wider farrow for water harvesting
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
SLM Technology has been applied by own interest of smallholders
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Saves labour over time |
| Can use less land compared to conventional system for the same harvest/yield |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| A strength of the system is the timely land preparation |
| The advantage of permanent planting stations results from the higher availability of nutrients to crop roots. |
| The moisture retention within the rooting space is improved by the surface structure and the increase in soil organic matter |
| The rotations of crop rotations is encouraged |
| All inputs can be used precicely, there is less wastage of inputs |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The weed management is labour intensive and the impact of pests might be a future challange. | The application of more mulch and the weeding regularly in the first part of the season is supposed to reduce weeds. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| To start with this technology is labour intensive at the beginning. In this moment, the hard pan caused by years of ploughing has to be loosened. | Because the basins/riplines are permanently maintained in CA, the preceding land preparations become easier. Also since land preparation starts before on-set of rains, one can spread labour by starting just after harvesting crop |
| There is a general problem of constructing fences around fields in communal lands, as state authorities declare this land as being owned by the state. | By agreeing with the local leadership to allow those doing CA to fence off their fields for proper keeping of residues and basins/riplines that might be prone to free livestock grazing after crop harvests. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/03/2001
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Groengroeft, A., et al. (2013) A method for yield assessment on rainfeld dryland agricultural fields.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Biodiversity & Ecology 5:279 - 286
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kowalski, B. et al. (2013) Mashare - The People.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Biodiversity & Ecology 5:121-128
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Pröpper, M. et al. (2010) Causes and perspectives of land-cover change through expanding cultivation in Kavango.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Biodiversity in southern Africa. Volume 3: Implications for landuse and management, eds. M. T. Hoffman, U. Schmiedel and N. Jürgens. Göttingen & Windhoek: Klaus Hess Publishers.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Pröpper, M. et al. (2015) The Future Okavango – Findings, Scenarios and Recommendations for Action.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Research Project Final Synthesis Report 2010-2015, 190. Windhoek: University of Hamburg
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล