Manure separation to better distribute organic matter at farm level [เนเธอร์แลนด์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Simone Verzandvoort
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Mestscheiding om organische stof op bedrijfsniveau beter te verdelen (NL)
technologies_1256 - เนเธอร์แลนด์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
เนเธอร์แลนด์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Leever Henk
HOEDuurzaam
เนเธอร์แลนด์
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
เนเธอร์แลนด์
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Hoe Duurzaam - เนเธอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ROM3D - เนเธอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - เนเธอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Provincie Gelderland - เนเธอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - เนเธอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Separation of cow manure is a common practice on dairy farms in The Netherlands to improve the nutrient use efficiency.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
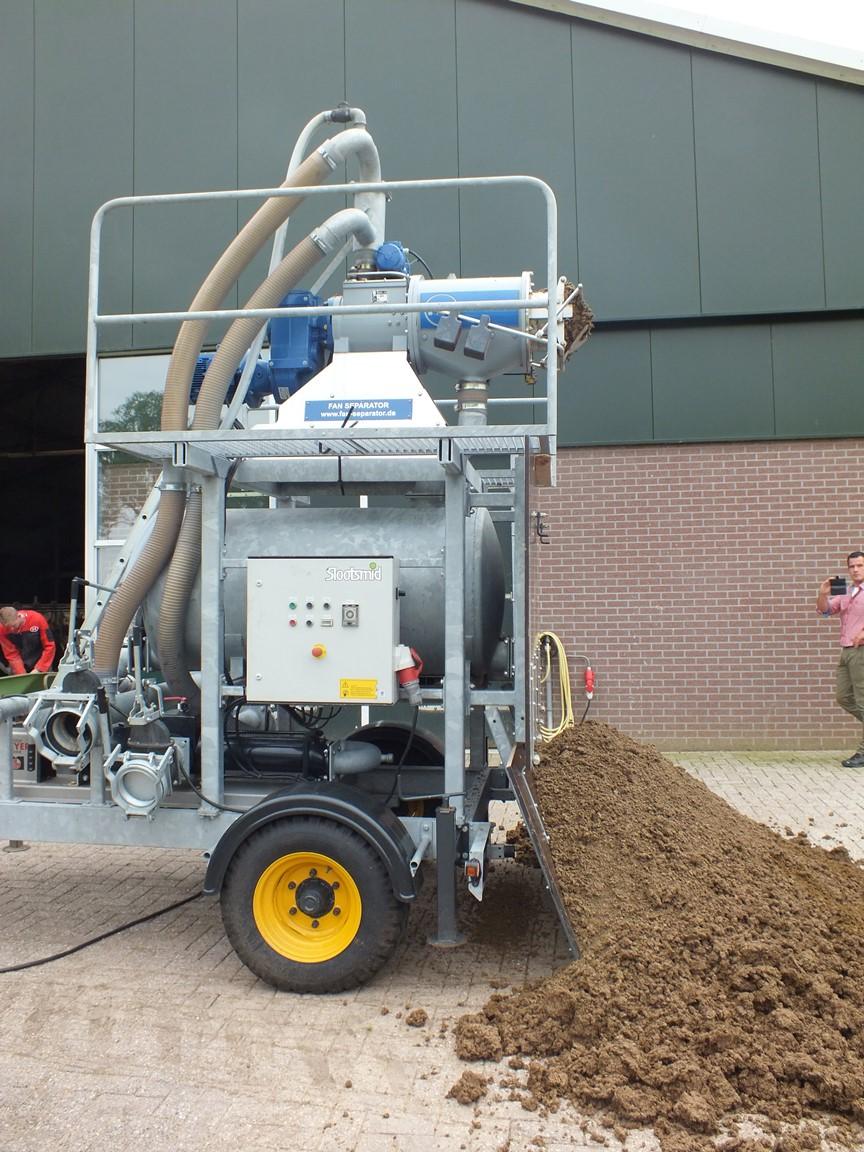
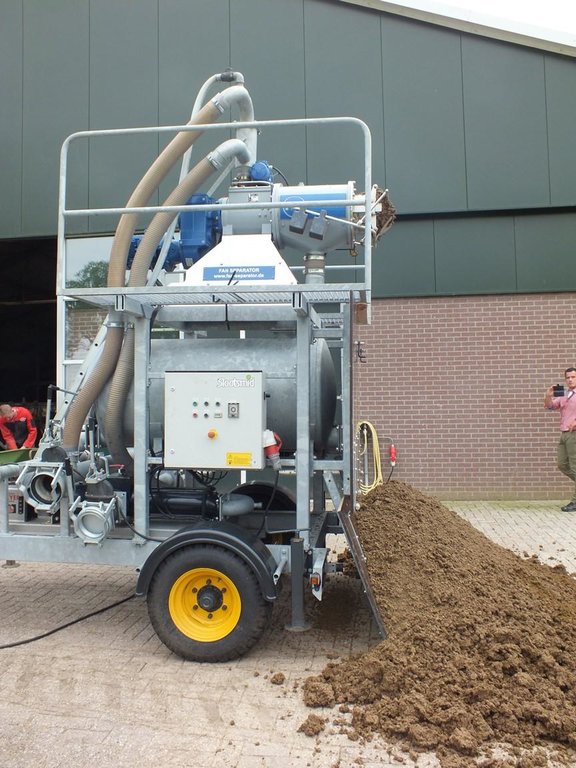
คำอธิบาย:
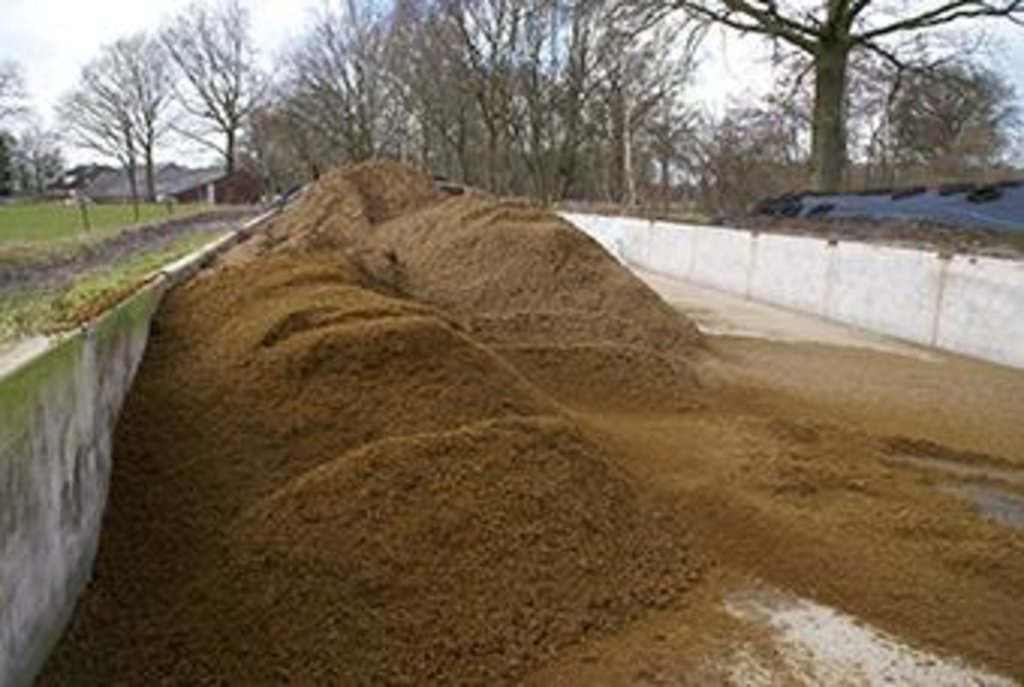
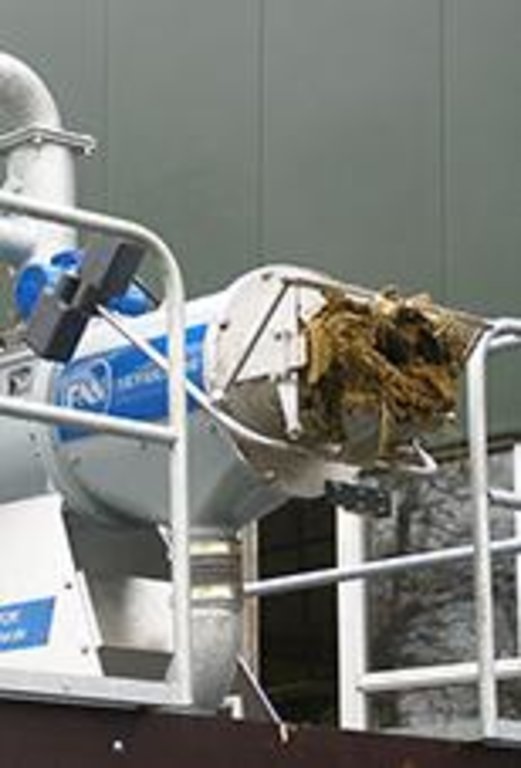
Het primaire doel van mestscheiding is de productie van een dikke
fractie met hoge gehalten aan organische stof en mineralen en een laag vochtgehalte. Een dergelijke geconcentreerde
fosfaatrijke fractie is een waardevolle organische meststof en kan over grote afstand vervoerd worden. De
dunne waterige fractie, met daarin het grootste deel van de stikstof, kan op eigen grond of in de nabije omgeving als
meststof worden aangewend of verder worden gezuiverd tot loosbaar water.
Slurry manure is fed through a manure separator that separates much of the thick material from the liquid portion. These fractions differ in the proportion between P and N; the thick fraction contains relatively more P than the thin fraction.
The thick fraction is used on maize fields or as substrate in cow stables; the thin fraction, with the larger part of the nitrogen, can be used on other parts of the farm or is exported from the farm to be treated for discharge in the environment. Due to stricter regulations for the application of N and P to crop land and grassland, less manure may be applied to the land. If manure must be exported because the threshold for P is reached, this implies that also N is exported from the farm.
Purpose of the Technology: Slurry from livestock consists of more than 90% of water. The primary purpose of manure separation is to produce a thick fraction with high contents of organic matter and nutrients and a low moisture content. The thick fraction is a valuable fertiliser and can be transported over large distances. The thin fraction, with the larger part of the nitrogen, can be applied as fertiliser on the farm, on farmland in the proximity, or can be treated into a quality suitable for discharge in the environment or water drainage system.
Manure separation allows farmers to use organic matter from manure more efficiently at the farm level. Manure separation increases the efficiency of processing and using manure in 5 ways:
1. By concentrating phosphorus in the thick fraction the volume of manure to be exported can be decreased, and also the export of nitrogen from the farm.
2. Manure separation creates three types of manure (thick, thin and mixed), which allows for differentiated application to different fields and crops, and reductions on requirements for artificial fertiliser.
3. Manure separation decreases the volume of manure to be exported from farms, and therefore saves energy and transport costs.
4. The thick fraction can be stored in stacks, taking up less space.
5. The thick fraction can be used as substrate in stables, replacing costly sawdust.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Purchase a manure separator. Periodically feed your collected slurry manure through the separator and then apply the thick portion to your fields. Discard the liquid portion.
Natural / human environment: Dairy farming on sandy soils in the eastern part of The Netherlands. Stricter manure regulation originting from the Nitrates Directive sets a limit on the amounts of animal manure for farms on sandy and loess soils in the eastern and southern part of The Netherlands.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนเธอร์แลนด์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Gelderland
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The thick manure fraction is applied to corn fields. There is 240 ha of corn in the area amongst 44 farmers. Only 2 farmers are applying this technology.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The land users's initiative was through the application for the project Healthy Sand by a group of farmers. During the Gezond Zand Project the group organised themselves in the Foundation HOEDuurzaam. The project ran from 2012-2014 and is followed by the new project BodemRijk.
The external initiative was from the drinking water company Vitens and the Province of Gelderland in the same period.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - other
- fodder crops - grasses
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 250Longest growing period from month to month: March-November

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major cash crop annual cropping: Potatoes
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, cereals
Major food crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Grass
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decrease of soil organic matter content.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area expeience decreasing organic matter content in soil.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: feeding in stables
Improved pasture: feeding in field
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Intensive ploughing)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Intensive crop management)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Slurry manure is the influent placed into the separator. A drill-press pushes the slurry and pressure squeezes out the liquid portion (Liqour). The thick manure (cake) is pressed out the end. The screen holds the solid material in the drill press.
Location: not applicable. not applicable
Date: 13-01-2008
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The agricultural advisor should advise on options for application of the thick fraction of manure based on composition.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Farmer has to calculate and strategize distribution of thick manure fractions and RDM(slurry) to reach balanced application rates and consider impact between fields.)
Technical knowledge required for technical advisor from machine company: moderate (Technical advisor should advise on type of manure separator (screw or roller) depending on the intended use of the thick and thin fractions.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Thick fraction obtained by separation of manure from dairy cows.
Quantity/ density: 10 t/ha
Remarks: The thick fraction is applied separately from the slurry.
ผู้เขียน:
Extension, http://www.extension.org/pages/27470/solids-separation-in-swine-manure-handling-systems#.VU9uDk0cRoI
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.94
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
255.70
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a seperator |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Seperator | Machine | 1.0 | 5320.0 | 5320.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 5320.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 5659.57 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Life span of the seperator: 6 years
Number of parties sharing: 44
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Operating separator | once per year |
| 2. | Applying both thick fraction manure and RDM manure | once per year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 127.68 | 127.68 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Sampling manure | ha | 1.0 | 21.28 | 21.28 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 308.56 | 308.56 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | rent of manure separator | h | 1.0 | 16.5 | 16.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | depreciation costs | m3 | 1.0 | 0.65 | 0.65 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | maintenance | machine | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Electricity | ha | 1.0 | 3.72 | 3.72 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Extra Potassium | ha | 1.0 | 10.64 | 10.64 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 489.33 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 520.56 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Separator, truck, loader, tractor
Cost of everything per hour was multiplied by totals and divided by hectares applied so costs per hectare are given. The establishment cost of the separator is the total unit. It was purchased by the farmer's foundation. It can not be given in a cost per hectare.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour. Equipment.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
182 days of precipitation annually
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperature varies between 2-17 °C ( LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperature varies between 2-17 °C)
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Flat and gentle (only incidentally.)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Deep (A and B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area). Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm.) and very deep (deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area).)
Soil texture is coarse/light (most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (Soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (Most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area)) and very high (in Fimic Anthrosols originated due to application of farmyard manure since medieval times (12% of the area))
Topsoil organic matter is medium (the purpose of the technology is to increase soil organic matter at farm level)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep groundwater table (H>40-80 cm; L>120 cm) in the sandy soils on thick substrate of cover sands (in 65% of the area)) and medium (shallow groundwater tables in the Umbric Gleysols (35% of the area).
Soil water storage capacity is medium (in the other soils, varying with the soil organic matter content) and very high (in the Fimic Anthrosols with high SOM in the topsoil.)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: <5m (in all soil types the highest level of the groundwater table during the year is <140 cm below the soil surface. The lowest level can be lower than 120 cm)
Availability of surface water is medium (From small rivers (De Berkel) and creeks)
Water quality (untreated) is poor drinking water (levels of the pesticides Bentazon and MCPP in the groundwater have incidentally exceeded the norms for drinking water production between 1985 and 2009)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Soil biodiversity is high in the Fimic Anthrolsols.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men. Women often have jobs outside the farm.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality or craft work. Farms do not provide B&B or educational services.
Market orientation of cropland production system is mixed ( Maize is completely used to feed cows (max 20% of the area is allowd under maize); other arable crops are sold to the market. Dairy production is commercial. )
Market orientation of grazing land production system is commercial/market (dairy farmers grow feed crops for their livestock)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
Cropland per household: 15-50 ha (6 land owners (situation in 2014)) and 50-100 ha (15 land owners, situation in 2014)
Grazing land per household: 5-15 ha (average grassland is 7.8 ha per household)
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- Other forms of exploitation
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Many fields have other forms of exploitation than individual ownership or lease.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
expected, based on better targeted fertiliser application
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
expected due to increase of SOM
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On artificial fertiliser (30-80% reduction on N fertiliser) and substrate for cow stables. But since the thick fraction contains less N per kg of P2O5 than the original mix, farners applying the thick fraction (for maize as described in this QT) may need to apply more articial N-fertilizer
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Decreased costs for manure export from the farm: A smaller part of the total manure mix needs to be exported (ca 35% less N-export than without manure separation; 10-30% less net energy use)
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Ease of manure storage
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Thick fraction is less voluminous and can be stacked
Manure processing
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Thick fraction can be more easily stored and transported; thin fraction takes up less volume and does not need to be transported.
Energy use
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
4-7 GJ/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
3-5 GJ/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Energy use for manure transport, processing, digestion and fertiliser use
Expenses on machinery
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
For farms with less than 1000-2000 tons of manure to be separated expenses on manure separation become larger than benefits. Such farms could better hire a mobile separator, as in the descirption of this SLM technology.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil and manure management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
expected: reduction in leaching of nitrate and phosphorus due to better targeted manuring to plant needs
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to increased SOM
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to improved manure composition for crop growth and build-up of SOM
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to better targeted fertiliser use to needs of crops and reduced use of artificial fertiliser (30-80% less supply of N-fertiliser required)
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Emission of NH3
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
18
หลังจาก SLM:
20
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
NH3 loss in kg/ha, for dairy farms with 1.75 cows/ha, manure prod of 255 kg N/haand other assumptions; model estimate
P2O5 surplus
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1
หลังจาก SLM:
4
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
P2O5 surplus in kg/ha, same conditions
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
12.5
หลังจาก SLM:
10.4
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced leaching of nitrate from fields where manure is applied due to less surplus of N in thin fraction(NO3-N in groundwater in mg/lfor farm with 1.75 dairy cows/ha)
Energy use
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
4-7 GJ/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
3-5 GJ/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Energy use for transport of manure from farms, processing, digestion, fertiliser use
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is almost independent on environmental change, since it depends on the availability of manure. It is strongly dependent on the farming system (supply of manure and possibility to apply the separated fractions on farm).
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is no evidence yet on economic and agronomic effects of using the manure separator in the area, so the land user's perspective cannot be given. Assessments of costs, effects and energy use based on modelling are available in the literature for dairy and arable farming in the NL in Schroder et al. (2009). These reveal that for farms with 1.75 to 2.18 dairy cows/ha and under conditions of manure production and application and manure regulations for this part of The Netherlands, the required export of N-manure could decrease by 35%, required N-fertiliser by 30-80%, and net energy use by 10-30%.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The Foundation HOEDuurzaam purchased the manure separator. Farmers can use the machine for 15 euros/hour, and can apply for a subsidy from the Province when applying the technology. Two farmers were actively using the machine in 2014.
Comments on adoption trend: We do not have information on how many farmers were using the manure separator in 2015. This information will become available in 2016.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued application of the measure and subsidy for maintenance of the manure separator by the Foundation; support to farmers in calculating parameters for manure separation specific for their farm (type of manure, concentrations, fields to apply to, livestock intensity) |
| energy saving and reduced loss of N while maintaining equal levels of crop production |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued application of the measure and subsidy for maintenance of the manure separator by the Foundation; support to farmers in calculating parameters for manure separation specific for their farm (type of manure, concentrations, fields to apply to, livestock intensity) |
| increases available soil moisture |
| reduces leaching of nitrate to the groundwater |
| reduces energy use for manure handling and transport |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| there is still little experience with manure separation and there are many uncertainties relating to separation efficiency and financial aspects |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Mestscheiding: relaties tussen techniek, kosten, milieu en landbouwkundige waarde - Jaap Schröder, Fridtjof de Buisonjé, Gerrit Kasper, Nico Verdoes & Koos Verloop, Plant and Animal Sciences Groups Wageningen UR, 2009.
URL:
http://edepot.wur.nl/50884
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล