Stone Wall Bench Terraces [ซีเรีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Michael Zoebisch
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Mudarrajad Hajaria (Arabic)
technologies_1411 - ซีเรีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Salem Salwa
ICARDA Syria
ซีเรีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - เลบานอน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
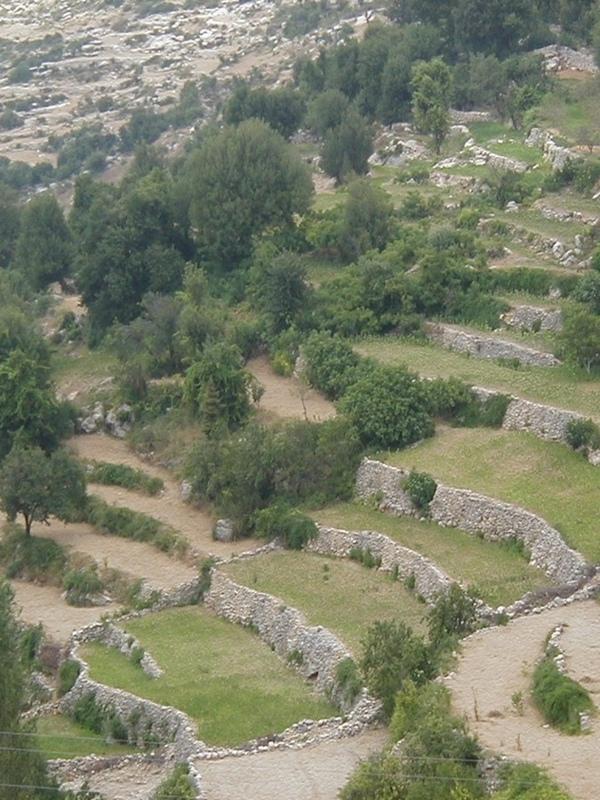
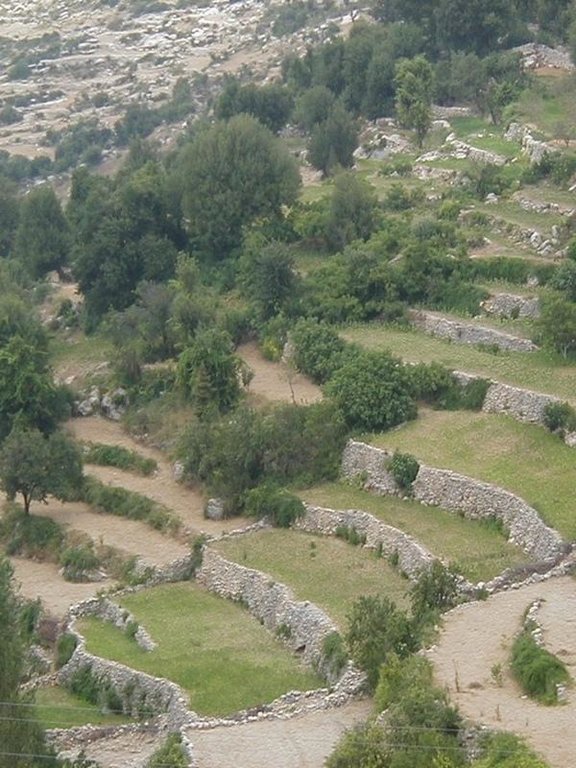
Ancient level bench terraces with stone walls, built to stabilise slopes, retain moisture, and create a suitable environment for horticulture.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
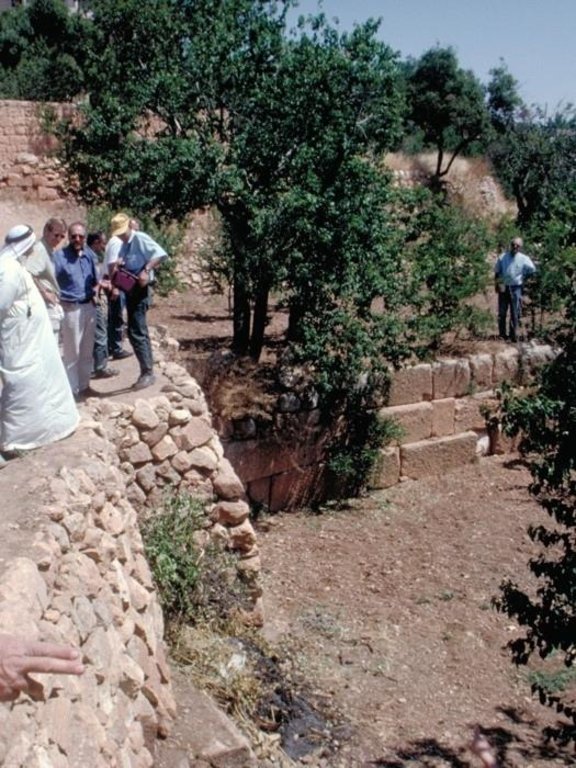
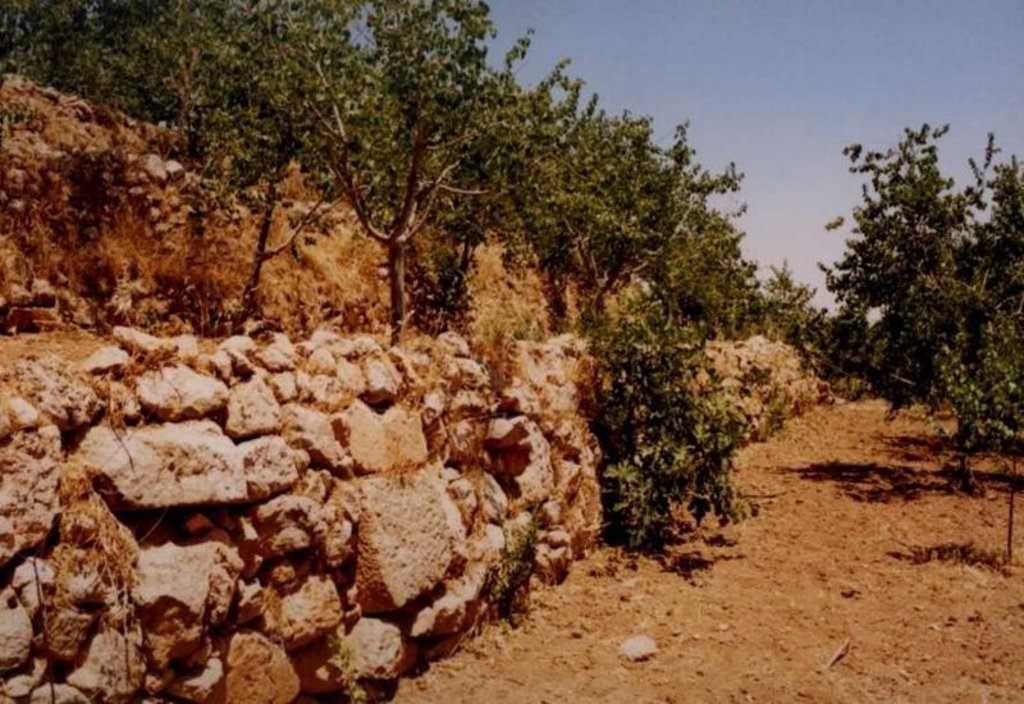
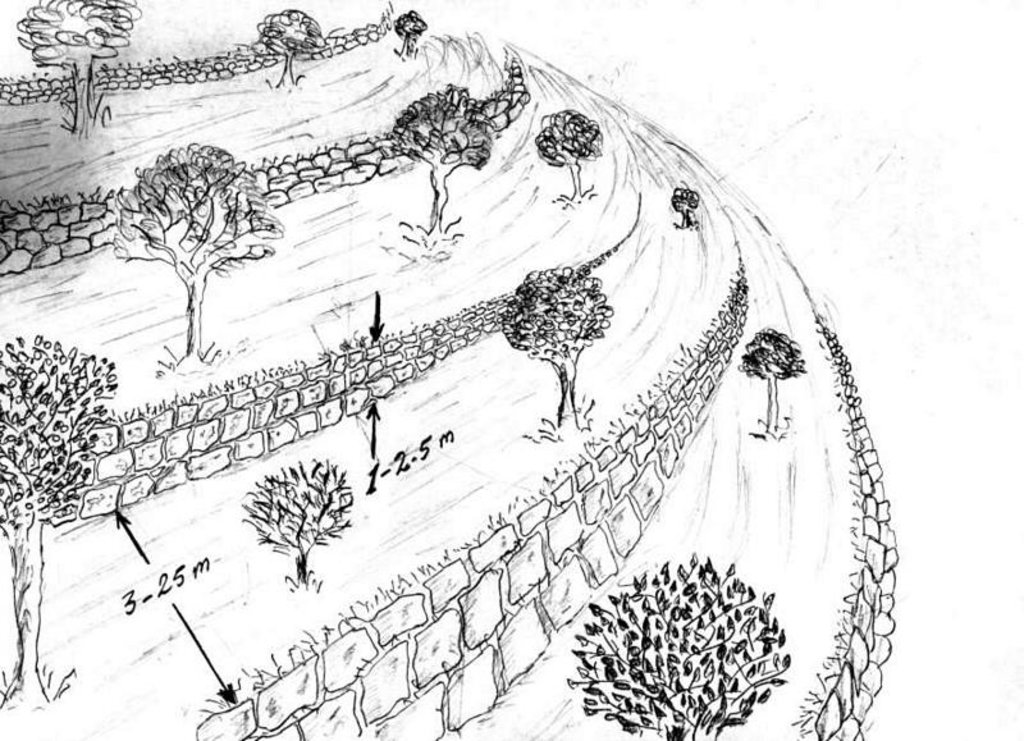
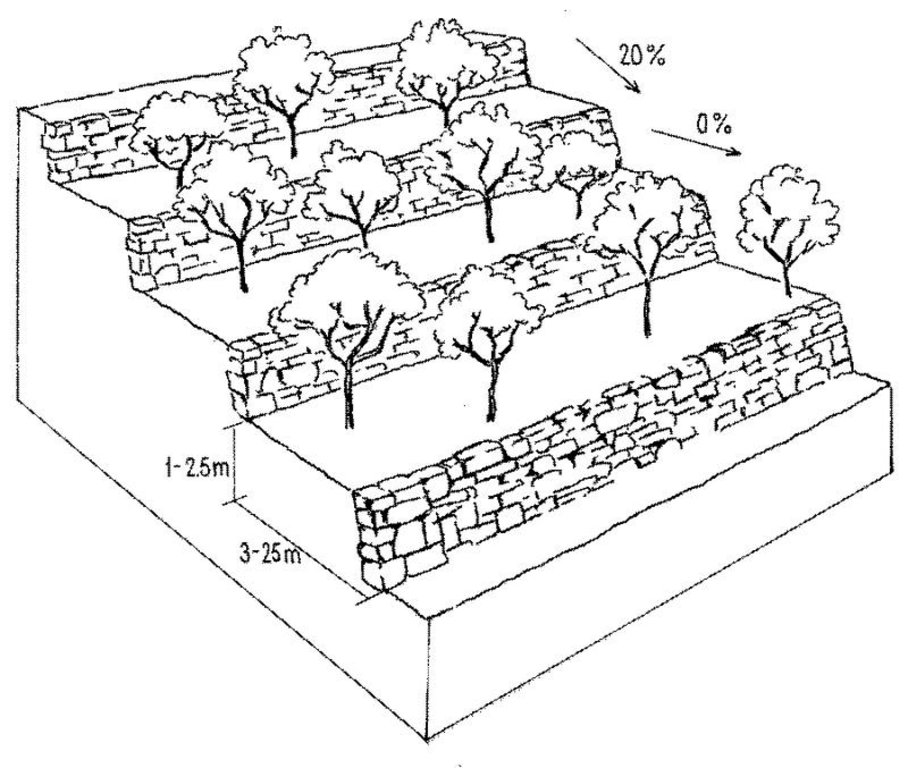
Stone wall bench terraces in the hill ranges of western Syria comprise an ancient indigenous technology, introduced by the Romans and Byzantines about 2,000 years ago. Some new terraces are, however, still being built. The walls are constructed with limestone, largely found on site. The terraces are located in steep terrain (usually on slopes more than 25%) under low (and erratic) rainfall regimes of between 250 and 500 mm per annum. The terrace walls are 1-2.5 m high and the level beds 3-25 m wide, depending on slope.
Deep soil profiles (more than 2 m) have developed on steep slopes, where original soil depth was only shallow to medium. The terraces are very efficient in preventing soil erosion and in the retention of rainfall. They support trees and annual crops where they could not otherwise be grown.
These terraces are usually found near settlements. Construction is very labour intensive, considering how little land is effectively protected from erosion and brought into cultivation. High labour investment makes the construction process slow and retards further extension of the technology. However, if soundly constructed, maintenance requirements are low. Underlining this point, a large number of very ancient terraces can still be found intact, supporting a productive crop. Sometimes localised collapse of a terrace occurs due to concentrated runoff. In that case, the terrace in question may need to be rebuilt. To prevent such breaches, it is important to allow for discharge of excess runoff along drainage lines.
Currently, most terraces are used to grow fruit trees. These include olives, cherries, almonds, plums, pomegranates, apricots, and peaches. Husbandry practices are normally carried out by hand. Where space permits, however, draft animals are used for tillage. The curves of the terraces and access to the steep slopes make it very difficult/impossible to use tractors. Animal power is more versatile in this irregular landscape, but it is more expensive than tractor power, due to shortage of fodder.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ซีเรีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
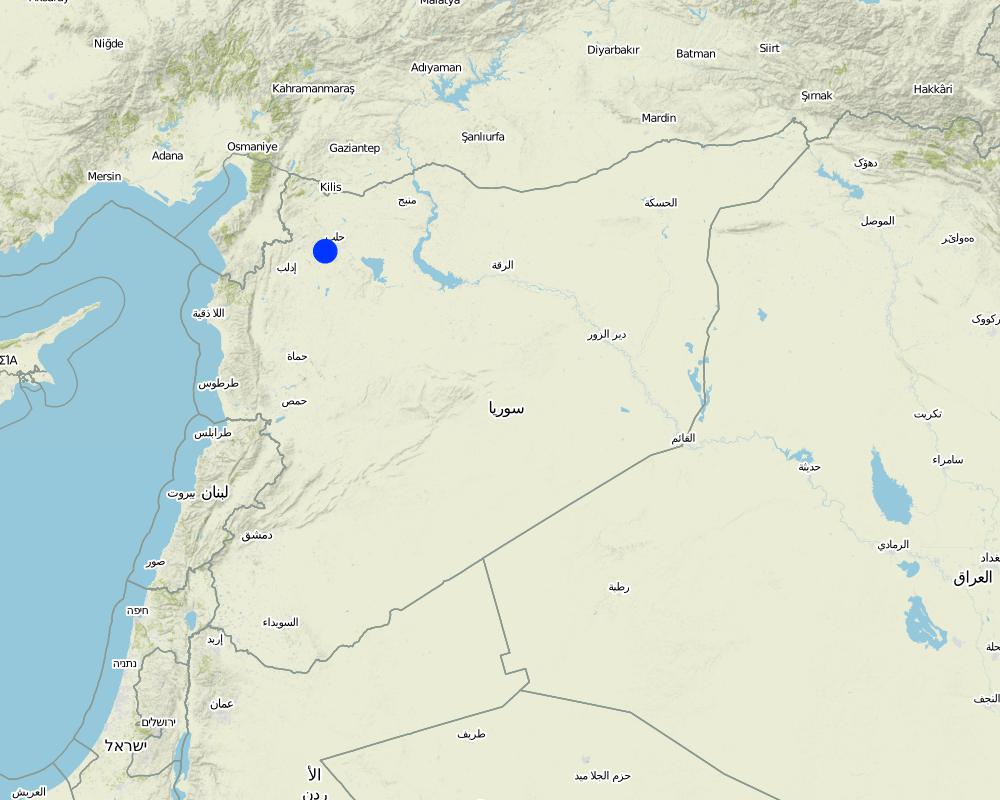
Idleb Province, Ariha District
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Tal Lata Village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology was most probably developed and introduced during the Roman/Byzantine period, 200-400 AD
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- olive
- stone fruits (peach, apricot, cherry, plum, etc)
- tree nuts (brazil nuts, pistachio, walnuts, almonds, etc.)
- pomegranates
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Apr
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Before terracing, water erosion resulted in shallow to medium colluvial soils. Terracing made cultivation possible, but the
beds tend to be very narrow and/or irregularly shaped, with large boulders set in them, making tractor cultivation (which is cheap) impossible.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): (1) Soil tillage - mechanization is difficult; animal power is up to 5 times more expensive than tractor power.
(2) Rockiness of the soil - large and very large stones make cultivation difficult.
(3) Accessibility - inadequate road network to reach fields
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Ha: aridification
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
other/ national currency (specify):
Syrian Pounds
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
50.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
ผู้เขียน:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Syrian Pounds
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
50.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Levelling the terrace bed by bulldozers where necessary. | 0.35-0.7 persondays/m for all activities |
| 2. | Blasting rocks in the field | |
| 3. | Collecting stones for wall building – which are available locally. | |
| 4. | Building the stone walls with 1–2.5 m vertical interval (and therefore | |
| 5. | Levelling land between stone walls. |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1260.0 | 1260.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Stone collection | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Drill | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Ammonium nitrate(kg) | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | |||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Detonators | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Fuses (m) | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1460.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 29.2 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing (replacing stones) | 5 persondays required/every year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | |||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 20.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.4 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Manual construction work requires 0.35-0.7 person days per metre length of terrace wall. Establishment costs were calculated for an average of 600 m length of stone wall (height 2 m, width 70 cm) per hectare on a 12% slope, with
terrace beds therefore about 16-17 metres wide. Narrower terraces on steeper slopes are considerably more expensive to construct.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour shortage and labour cost
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Also rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, average, poor
3% of the land users are very rich and own 20% of the land (very few).
7% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (few,).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Many).
50% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land (Many).
Off-farm income specification: On average, 70 % of the income is from off-farm activities
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The overall range is 0.5-7 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mechanisation is not possible
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
But a potential for conflict if the community refuses to participate in joint maintenance activities
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
39
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
37 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The rate of spontaneous adoption is low because of the high costs.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Soil and water is conserved and fruit crop yields are maintained/increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with soil fertility improvement (such as farm yard manure). The prices of the crops grown should remain adequate |
|
The maintenance requirements are low. The terraces need little repair How can they be sustained / enhanced? Natural drainage lines must be prepared/maintained to prevent collapse during heavy rainfall. |
| The terraces make the cultivation of trees on hill slopes possible. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The establishment costs are high | Plant high value cash crops. |
| The mechanisation of farm operations is impossible because there is no access to the terraces for tractors, while animal power is constrained by high maintenance costs (fodder). Thus, field operations are limited to hand labour | Subsidise mule ploughing. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mushallah AB. The visible and the hidden in the country of olives. pp 463. 2000.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Akrama Publ. Office. Damascus, Syria.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล