Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Donia Mühlematter, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
elyeshero ne elyato (Haya tribe)
technologies_1157 - แทนซาเนีย
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 29 ธันวาคม 2016 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 5 มิถุนายน 2017 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 28 มิถุนายน 2018 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 6 สิงหาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
government:
Kagaruki Annagrace
Misseny District Council
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
government:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
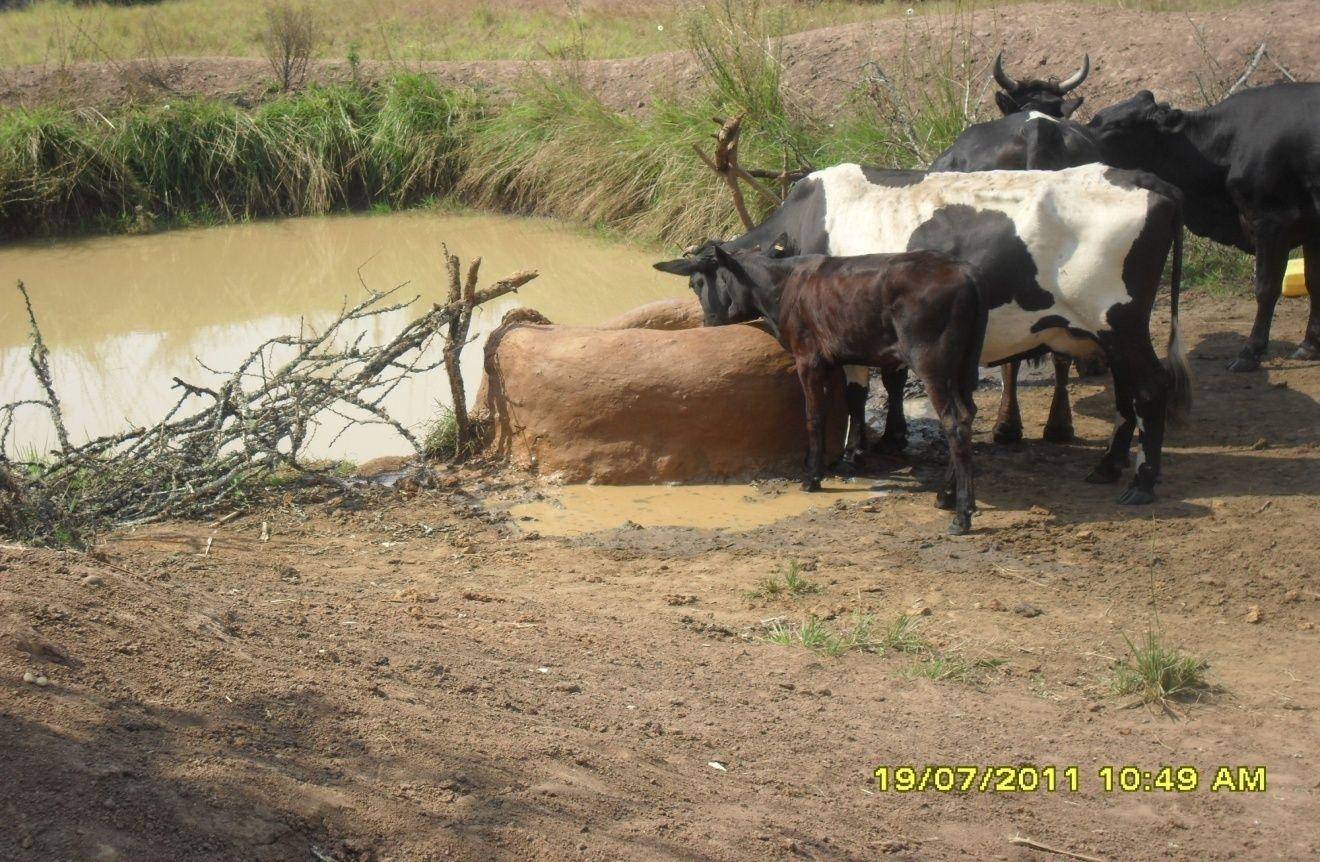
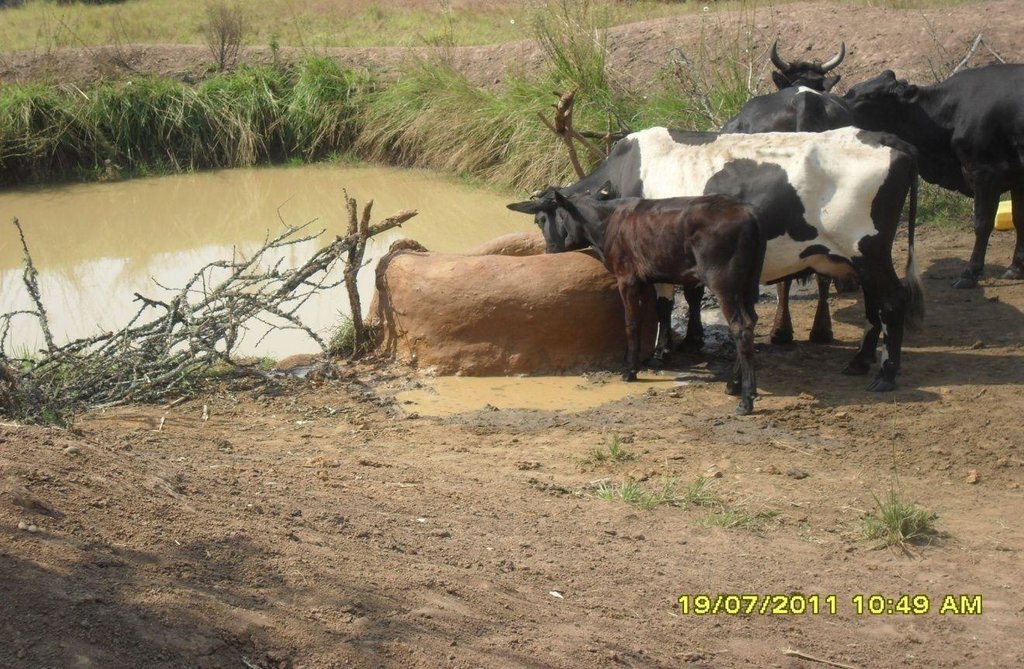
Construction of indigenous water pond and a livestock watering trough along an underground water source.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
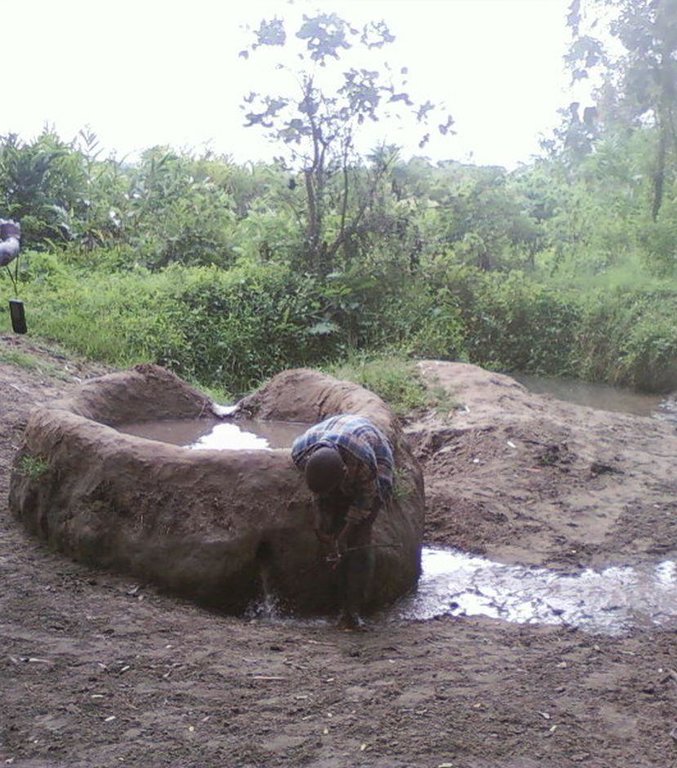
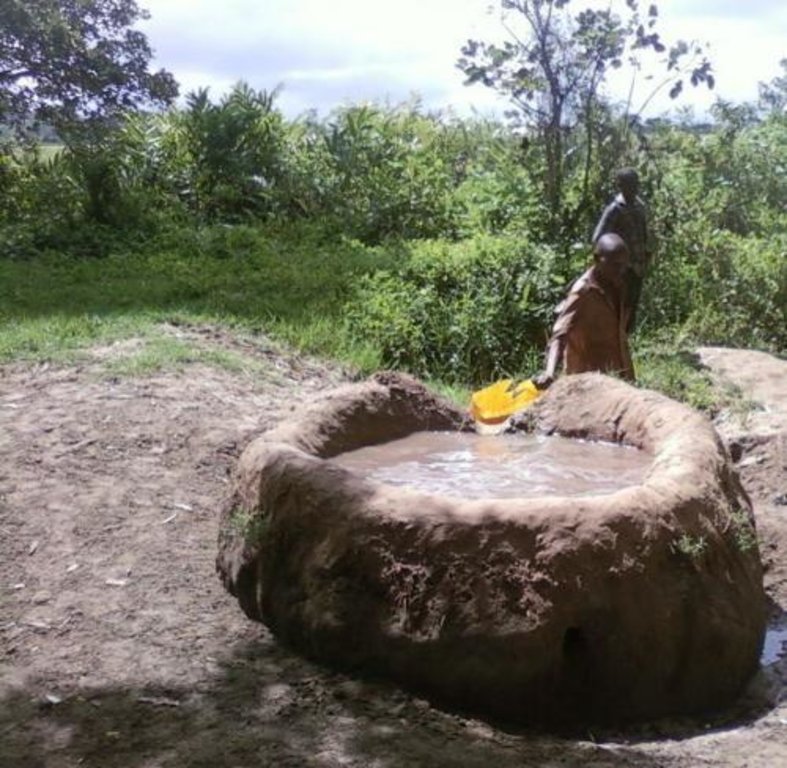
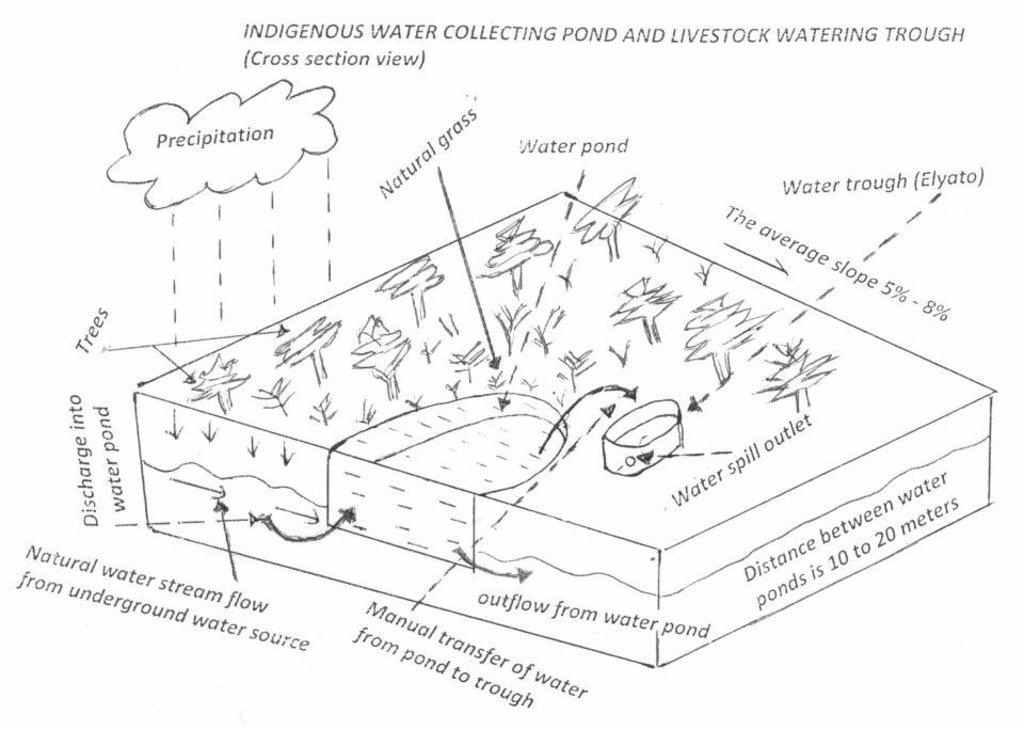
This technology is used during the dry seasons and where ground water level is high and there is natural water stream flowing from underground water source. Water pond is excavated along the naturally flowing water stream and is recharged by natural ground water. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available, groundwater table, slope and soil characteristic. Groundwater collection ponds described in this technology on average are 4m long, 3m wide and 1m deep of 12m3 (12 000 liter) capacity and the slope is moderate 5% to 8% and soil characteristics is clay loam with deep soil. Water troughs (Elyato by local name) are constructed adjacent to the water pond to allow livestock to access clean drinking water. The number of troughs per pond is usually 1 to 2. Materials used in construction of water trough include clay, red termite mound soil, grass and wooden poles. The number of ponds needed usually depends on the expected number of animals and are arranged at irregular intervals ranging from 10 to 20 meters apart. The average size of a water trough is 0.14 m3 and can cater for 5 cattle at a time. The Pond is stabilized by naturally growing grass on its banks. Common pond stabilizer species are Leodicatiar digitalia and Hyperrhenia rufa. Management of the natural water source is through preventive village/customary by-laws which prohibit tree and grass cutting around the water source. The dominant indicator tree species normally found are Erythrina abysinica, Ficus thorgii and Phoenix recrinata. The animal watering troughs are usually used in the dry period. Before watering the troughs are coated (smeared) with red termite mound soil (normally hand carried by herders) to provide a good taste which is attractive to animals. Water is transferred from the pond to the water trough manually using cans or buckets. Animals drink directly from the troughs. This water from the trough is rich in iron (Fe) from red termite mound soil. The troughs are constructed with outlets used to spill out water immediately after drinking in order to prevent their damage through excessive water saturation.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is preferred by livestock keepers as it provides for animals to drink clean and mineralized water and for health improvement. User fee payed to land owners also enable them to expand and diversify there income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment: Land clearing, excavation and shaping of water pond and construction of animal watering trough.
Maintenance: repair of water pond and water trough (de-siltation, grass slashing and gap refilling).
Inputs: labour, implements (machete, spade, hand hoe, sickle), clay, red termite mound soil, wooden poles, buckets, grass and tying rope. Average establishment cost for one pond and its water trough is 41.27 American dollars. Average annual maintenance and recurrent costs (filling and emptying of water trough) for one pond and its water trough stands at 458.76 dollars and labour is a core cost determinant factor.
Natural / human environment: Natural environment: Extensive grazing land. The technology is largely structural (excavation and shaping of water ponds and construction of water troughs) supported by the use of by-laws which prohibit destruction of the protective natural and indicative trees and grasses around. The technology is common in sub-humid climatic zone.
Social economic environment: Level of mechanization is handy tools with subsistence production systems on individual fields.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tanzania
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Missenyi District (Minziro)
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.11472, 31.655 ; -1,09972, 31.70194
The area is owned by individual farmer. The area is found adjacent to extensive grazing land. Water table is high and there is a permanent underground natural water flows.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
the technology has been in use for about 80 years ago
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September to DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- goats
- sheep

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Eutrophication, siltation, water shortage, deforestation and wildfire outbreaks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Drying of the underground water source.
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M7: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other structural measures: water collection pond and animal watering trough
Specification of other management measures: protect water source enclosure by naturally regenerating vegetation
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (cutting of natural tree and removal of grass along the natural water flow way), overgrazing (Compaction by trampling animals, rainfall runoff, siltation of water collection point and disapearence of vegatative cover.), discharges (point contamination of water) (spoilage and contamination of surface water by human and livestock feaces.), population pressure (Overstocking due to increase in the number of livestock), poverty / wealth (low capacity to invest in enviromental friendly energy sources), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Unavailable improved and reliable water ponds and animal watering troughs), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited knowledge on sustainable use of natural water sources), governance / institutional (limited enforcement of existing environmental regulatory systems.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (excavation and layout that contradict the natural environment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fire wood collection from the natural water source), industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, labour availability, war and conflicts
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Water pond and water trough cross section view.
The water pond has an average internal capacity of size of 12m3 (4m length, 3m width and 1m depth).
Water troughs are constructed on the side of the water ponds. The water trough outside height is 0.2 - 0.4m above ground, inner depth is 0.5m, and diameter varies from 0.6 to 1m. It is made of cylindrical walls whose average width is 0.1m.
The average slope of the water catchment is 5% to 8%.
Location: Minziro village, Minziro ward, Missenyi division. Missenyi Dist, Kagera Reg, United Rep of Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (At least primary school leaver with the basic indigenous technical knowledge.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 10 to 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Structural measure: water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): mostry used clay soil and red termite mound soil.
Construction material (wood): for water pond and trough stabilization
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10.6m3
Catchment area: 4 acresm2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:4
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ผู้เขียน:
Allan Bubelwa, Box 38 Kyaka Missenyi
วันที่:
28/8/2012
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tanzanian shillings
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1600.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.13
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for pond excavation | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of pond | During dry period |
| 3. | Construction of water trough | During dry season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land preparation for pond excavation | person/day | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of pond | person/day | 1.0 | 21.88 | 21.88 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of water trough | person/day | 1.0 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | piece | 1.0 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | piece | 3.0 | 9.38 | 28.14 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | pieces | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | kg | 20.0 | 1.25 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 85.03 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.05 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiltation | During dry season |
| 2. | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | During dry season |
| 3. | Water trough repairing | dry season |
| 4. | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Desiltation | person days | 5.0 | 6.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | person days | 5.0 | 6.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Water trough repairing | person days | 8.0 | 10.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | person days | 450.0 | 1.25 | 562.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | pieces | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Water can | pieces | 2.0 | 1.88 | 3.76 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | pieces | 6.0 | 3.75 | 22.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | kg | 60.0 | 3.75 | 225.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 966.26 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.6 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost is calculated per one water pond and its one trough and as per 28 August 2012
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. all months temperature is above 18
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: little involvement of women because at large/traditionally livestock rearing is done by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (the techology is used by rich and average livestock keepers who have the animal).
75% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (the village poors usually do not have the animals though most of them are cattle herders).
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
การผลิตพลังงาน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Improving structure on the pond (use impermeable materials to prevent seepage, use concrete as a building material)
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology requires low establishment and maintenance cost and benefit surpass the costs.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
All livestock keepers use the technology to water their animals voluntary and through self mobilization.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is cheap and requires low investment costs.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Income generation due to water use fee. How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve service to water users. . |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Reduce conflict between livestock keepers and domestic water users. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws reinforcement, Area enclosure and Demarcation |
|
Improve accessibility of water to animals (improved animal water intake) How can they be sustained / enhanced? sensitization on regular maintenance. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Not durable and requires frequent and regular maintenance | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| not durable | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| high labor demand to fill the troughs | Use simple leverage pump |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล