Rotational grazing of goats for pasture conservation and improvement. [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: betty adoch
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: JOY TUKAHIRWA
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Renate Fleiner, Stephanie Jaquet, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano
Gwoko Dyel
technologies_2147 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Mwaka Abel
Omoro district, Bobi subcounty, Paidwe parish, Pato village.
ยูกันดา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Improves biodiversity in the grazing fields and improvement of soil fertility through rotational grazing where the goats wastes enhances soil fertility which enables the regeneration of natural pastures in the different paddocks.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Rotational grazing by improved goats variety enhances/ increases soil fertility, biodiversity and production of pastures and generates farmyard manure applied on cropland.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
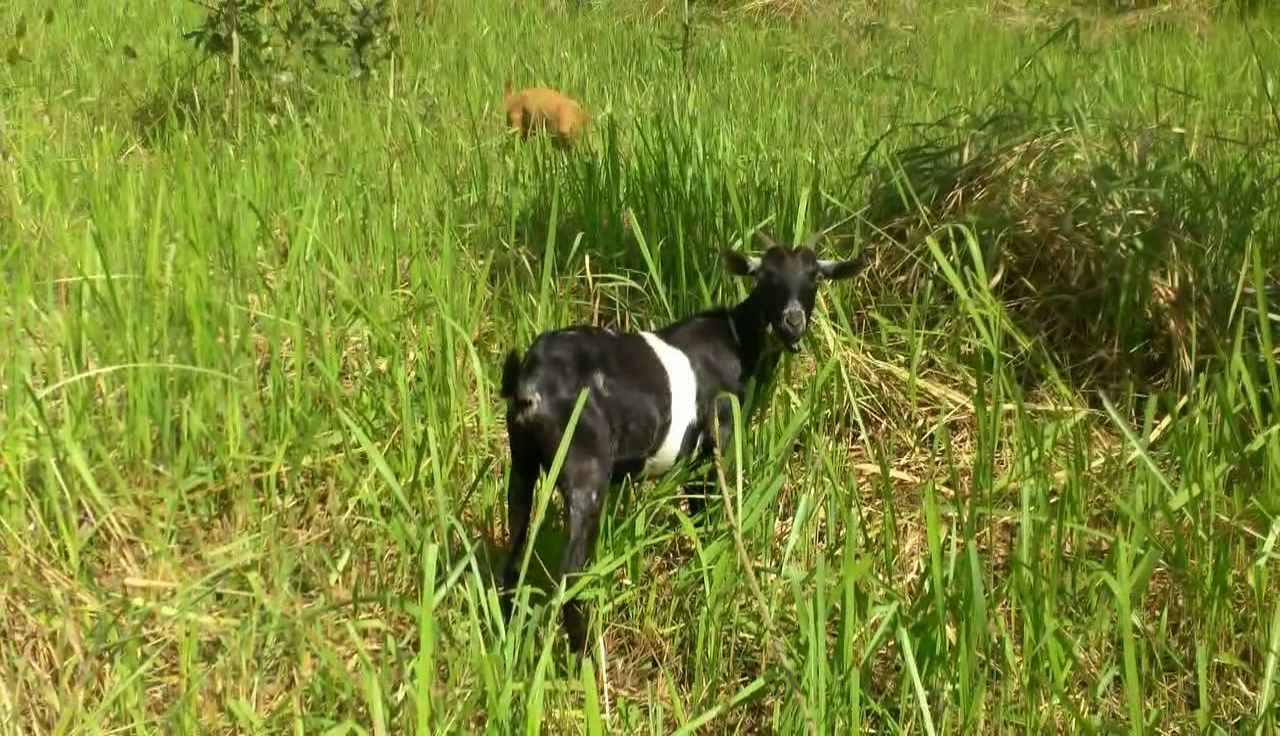
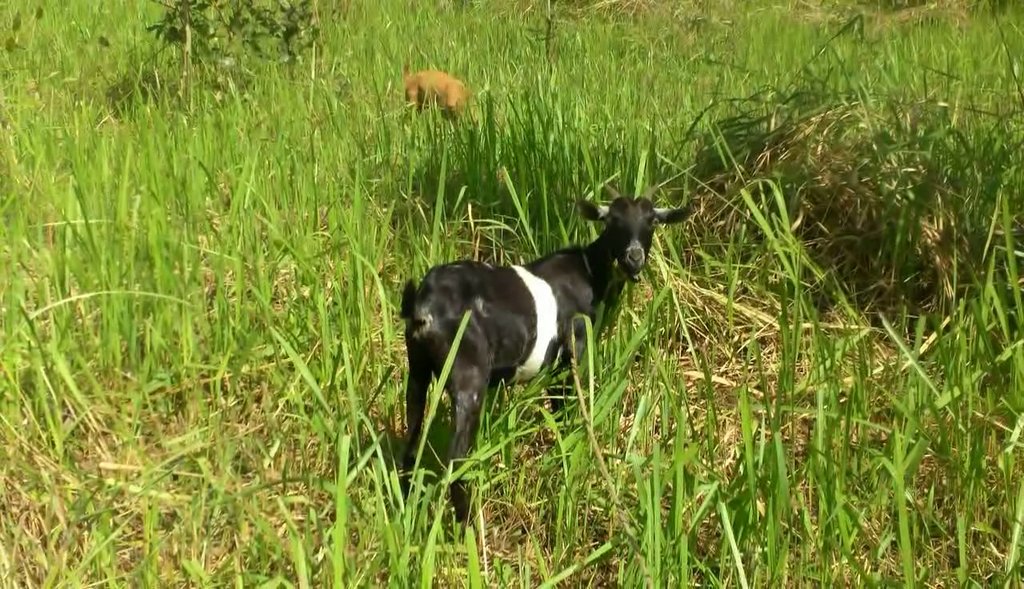
Rotational grazing is the shifting of livestock to different units of a pasture or range in regular sequence to permit the recovery and regrowth of the pasture plants after grazing, which increased forage production. Forage that are over-grazed or are less healthy from being grazed every few days have smaller root mass, which leads to less soil organic matter. Northern Uganda has tropical savannah climate characterized by moderate rainfall of 750-1000mm per annum. This region also experiences prolonged dry spells from June to July and also November to March characterised by wild fire outbreaks which retards pasture growth. Because of this, land user has to conserve pastures through rotational grazing in a paddock system. The land is gently sloping with moderate soil humus that has also supported the growth of pastures. The land user is a subsistence farmer who graze goat in a paddock system for pasture conservations, manure generation for cropland, and goats for home consumptions and sale. About 90% of his income is from on farm activities.
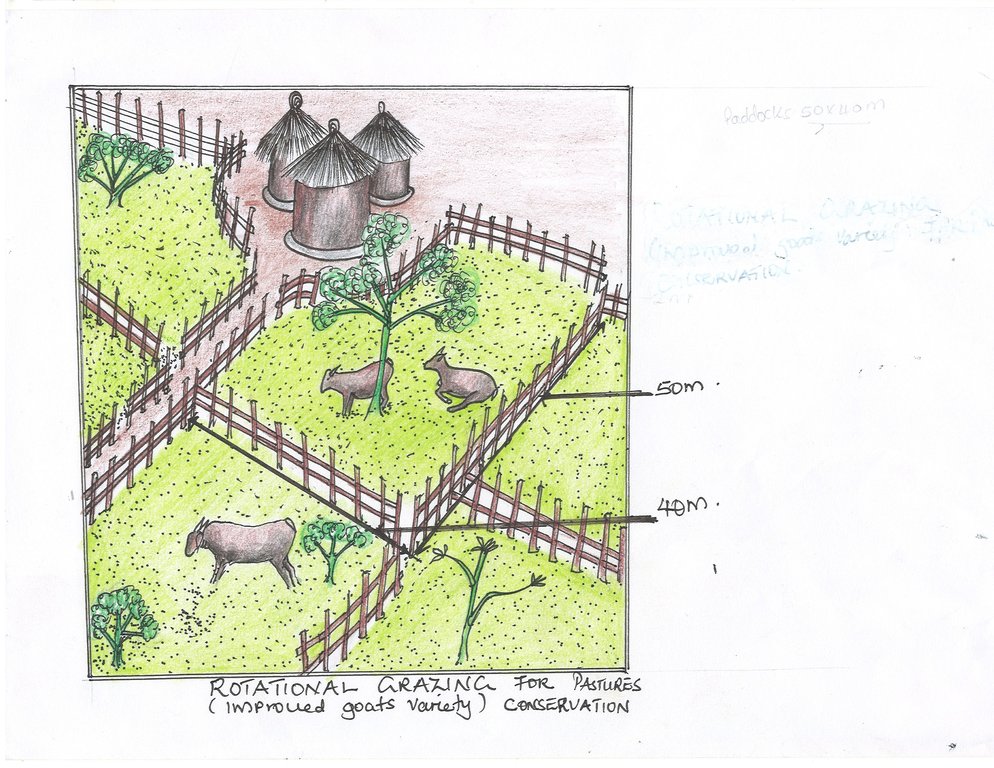
A well-managed controlled grazing program can increase quality forage production by 30-70% each year. Much of this increase in forage production is accomplished by minimizing overgrazing. In this technology, six paddocks were created measuring 40x50meters on a five acres’ piece of land. Goats are shifted from one paddock to another in an interval of one month and later shifted to another section. The water tank is also moved as the goats are shifted to another paddocks. The shifting is to reduce on overgrazing. The land user has 40 goats. Two paddocks are grazed at the same time with each having a carrying capacity of 20goats to minimize on overcrowding and congestion at the water point. controlled grazing is practiced in order to protect the area from the damages of grazing that is digging up roots and everything in the field since this will de-grass an area and make it susceptible for erosion. By limiting graze time, fields can produce all year round instead of being a one-time harvest. Goats are not allowed to graze a paddock until it is at least 10 to 12 inches in height. If grazed any shorter, this compromises root recovery, energy storage in the roots, and grass' ability to depend on photosynthesis alone. This is why the land user preferred rotational grazing to prevent overgrazing, and allow the forage plenty of time to recover.
The inputs needed for the establishment of this technology are pangas, hand hoes, slashers, poles, and labour force to carry out the work of paddock constructions. To main the technology, the over grown grass is slashed to a height of 10 to 12 inches in height which is consumable by goats, water point is cleaned every two weeks to avoid contamination, paddocks repaired and goats constantly checked for treatment
The technology provides beneficial impacts like improvement of organic matter content and pasture soil fertility as a result of spreading manure around the whole pasture while grazing and browsing. Grazing goats typically return to the water tanks or a single favourite shade tree. The manure deposited around water tanks/tree shade is collected and used as farmyard manure for the seasonal crop production like cereals, vegetables, and legumes.
The technology is disliked because it is tedious to look after so many goats, wild animal attacks and drought affects water supply and pasture growth for the goats.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Goats grazing in the natural pastures
วันที่:
28/04/2017
สถานที่:
Omoro District, Bobi Sub County, Paidwe Parish, Pato Village.
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Betty Adoch
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Northern Uganda.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Omoro District.
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The GPS point shows the land user grazing ground. Rotational grazing.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2003
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Diversify source of income, improve on nutrition and improve soil fertility.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - sorghum
- simsim
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Rainfall is moderate which sustains pasture growth.

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
- Rotational grazing
Animal type:
- cattle - non-dairy beef
- goats
- poultry
- The goats graze the paddocks twice a year.
Species:
cattle - non-dairy beef
Count:
8
Species:
goats
Count:
40
Species:
poultry
Count:
50
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
conservation of pastures
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Rainfall is moderate which sustains pasture growth.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์

มาตรการอื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The mixed cropland is easily managed with livestock which provides manures to the cropland leading to high crop yields and pasture conservation.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
high risks of fire outbreaks and prolonged dry spells.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
To promote diversification and prevent land degradation.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Five acres of land under paddock system of rotational grazing. The paddocks measures 40x50meter. Poles of about 1meter high are used to fenced the paddocks.
ผู้เขียน:
Betty Adoch
วันที่:
28/04/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
5acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UGX
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
3718.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1000shs
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearning the bush through digging and slashing | Dry season. |
| 2. | Marking the paddocks and planting poles | Dry season |
| 3. | Fencing the area | Dry season |
| 4. | Installing the water tank | Dry season |
| 5. | Introducing the goats into the paddock | Rainy season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Easy to eastablish rotational grazing.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost is manageable by the land user.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing the over grown grass | wet season |
| 2. | cleaning the water tank | wet and dry season |
| 3. | Refilling the water tank | wet and dry season |
| 4. | Repairing the paddock | Dry season |
| 5. | Creating firelines | dry season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land user protects his farm from the danger of fire outbreaks and pests.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Record keeping is not done by the farmer.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The labour costs for fencing the paddocks, and the high costs of fencing materials.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The rainfall is moderate and unreliable.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Gulu meterological station.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Climate is suitable for pasture growth.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The landscape is generally gentle easy to practice rotational grazing.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
suitable for human consuptions and animals .
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Different species of plants and animals coexist in the environment.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
He totally depends on farming for livelihood.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technologies secure the land from land grabbers within the community. The land user has full right over his land.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to conserved pastures.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Source of water is secured by the land user.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
slightly negative
หลังจาก SLM:
very positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water filled in a tank for goats consumption.
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Goats fenced off which avoid water contamination.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Rotational grazing has saved the land user from purchasing animal feeds which would be very expensive.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
very positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Land user is aware of climate smart agriculture which has a lots of site benefits in terms of increased animal productions.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
very positive
หลังจาก SLM:
very negative
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass cover the soil from effects of evaporation.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass covers the soil from erosion.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
slightly negative
หลังจาก SLM:
very positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass covers the soil from being exposed to agents of erosion.
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
very positive
หลังจาก SLM:
very negative
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The grass covers the soil from erosion.
การอัดแน่นของดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
very positive
หลังจาก SLM:
very negative
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grazing goats loosen the soil particles which helps in fertile soil formation.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
very positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Dry grass decompose to form humus.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Different vegetation covers exist in the grazing fields.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
very positive
หลังจาก SLM:
very negative
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fire lines are created during dry seasons to prevent wildfire spread to the grazing fields.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
negative
หลังจาก SLM:
positive
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass roots filters and purifies the surface water.
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
positive
หลังจาก SLM:
negative
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Goats are fenced off from crop land reducing unnecessary destruction.
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
conserved vegetation acts as carbon sink
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The technology is highly sustainable.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is sustainable.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The farmer has been able to generate income to improve his standard of living.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology has inspired many community members to engage in sustainable land management practices.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
indegineous pastures are conserved for the goats.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Conserve indegineous pastures. |
| The vegetation roots filters the surface water. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Availability of pastures for the goats through out the year. |
| The paddocks protects the land from land wrangles. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Limited capital to establish the paddocks. | Extenal support from doners. |
| Prolonged dry spells that retards pastures growth. | Practice climate smart agriculture like rotational grazing. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Limited labour force to look after the goats. | Employing farm workers. |
| Pests and diseases that disturb the goats. | Technical services from the extension workers. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
one
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
28/04/2017
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mixed crop-livestock farming - FAO
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
www.fao.org/docrep/004/Y0501E/y0501e03.htm
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Mixed farming | ClimateTechWiki
URL:
www.climatetechwiki.org/content/mixed-farming
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล