Monitoring and Management of Agroforestry using SmartAG [โปรตุเกส]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Patrícia Lourenço
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Joana Eichenberger, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Agroforestry in Montado and Dehesa
technologies_7126 - โปรตุเกส
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Lourenço Patrícia
AgroInsider
โปรตุเกส
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Marques da Silva José Rafael
AgroInsider
โปรตุเกส
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Paixão Luís
AgroInsider
โปรตุเกส
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The Montado/ Dehesa Agroforestry system contributes to carbon sequestration in Spain and Portugal. The SmartAG app helps in monitoring and management of these systems, providing data available to farmers, producers, and stakeholders.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The SmartAG model is mainly applied in the Montado (Portugal) and Dehesa (Spain) agroforestry systems which serve as a biodiversity oasis in the
Mediterranean region. They are currently being heavily impacted by climate change.
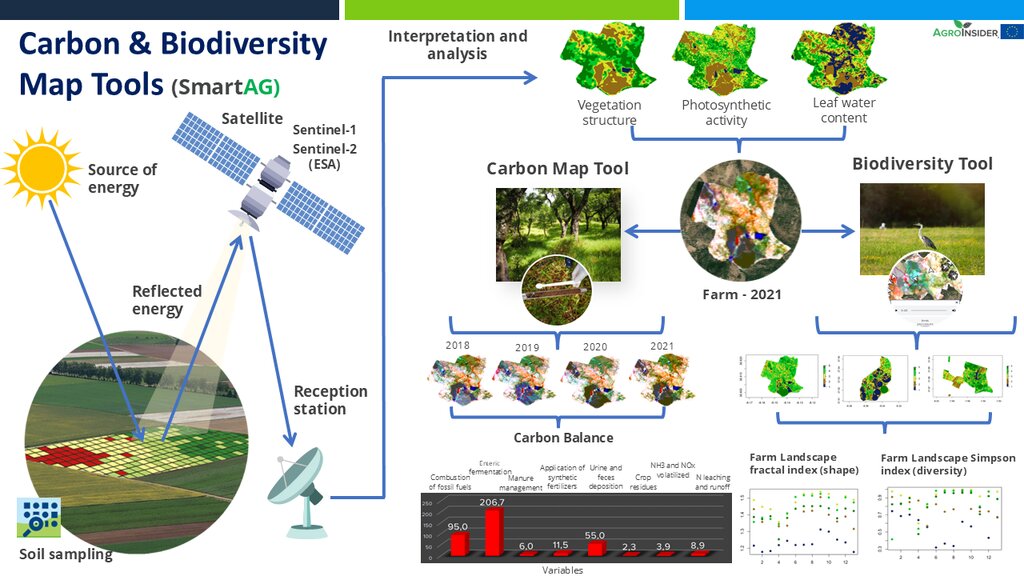
It contributes to achieving carbon sequestration potential. The SmartAG model is also applied in agriculture systems in Portugal, Spain, Greece, The Netherlands, Indonesia and Ukraine. Nevertheless, it can be applied in any part of the world. The SmartAG app provides accurate Agricultural Climate Services on a large-scale, available to farmers, producers, and stakeholders. The model analyzes agronomic anomalies to reduce CO2 emissions and promote CO2 sequestration in the soil, via remote sensing. Additionally, it seeks to remotely analyze farms by evaluating the spatiotemporal dynamics occurring in agroforestry activities for the same purposes.
Through data collection on land use, mapping, remote sensing and in situ data collection, an assessment of the initial state of the farm is carried out, along a carbon balance, to establish a reference scenario (baseline year). Future projections are made, and recommendations formulated.
Users appreciate this methodology because it helps them conserve or increase current carbon stocks, potentially creating a new source of income through the sale
of carbon credits. SmartAG is a highly user-friendly app which records georeferenced evidence of existing conditions and activities. It facilitates a transparent and participatory process in agroforestry ecosystem management.
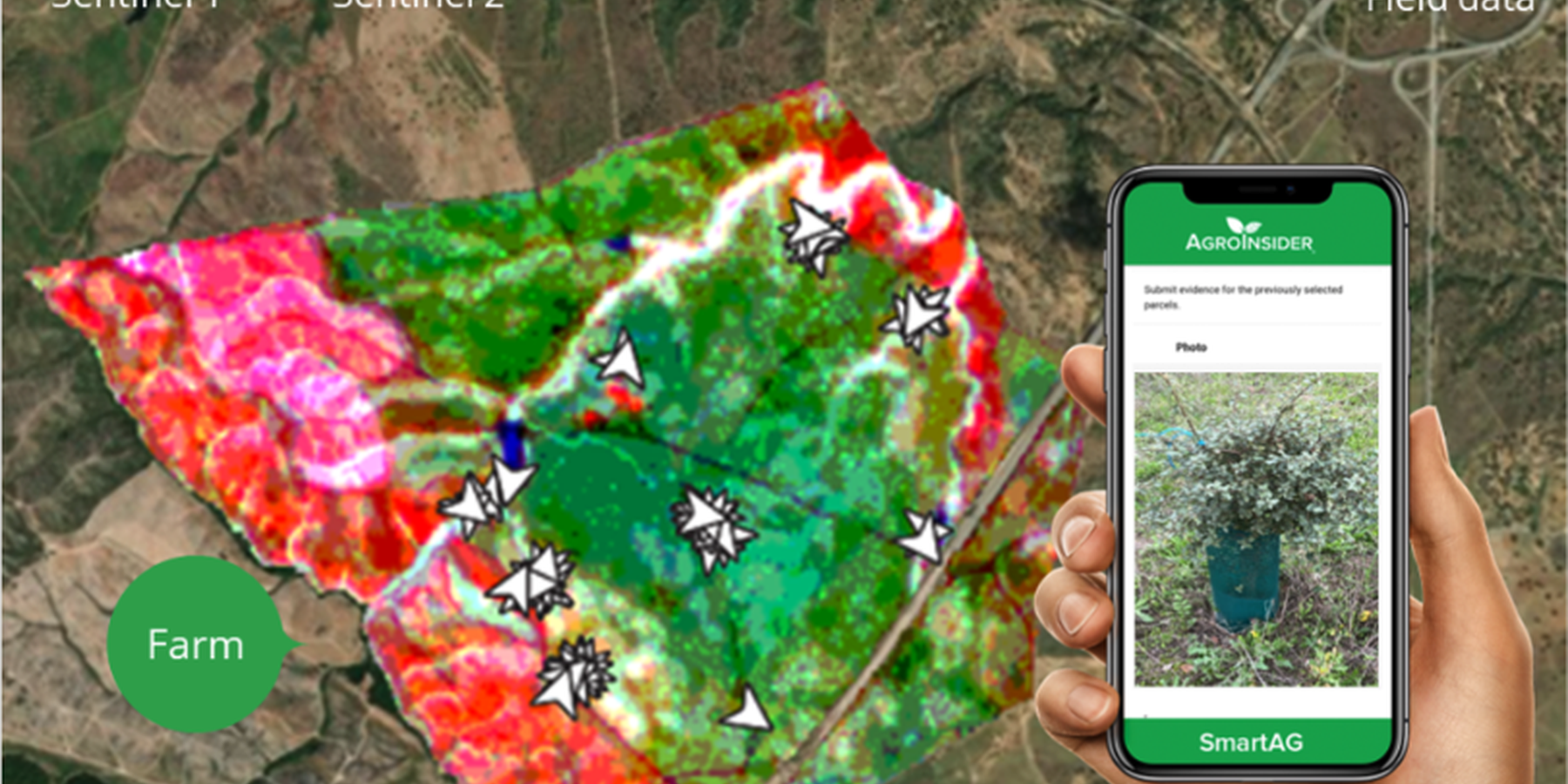
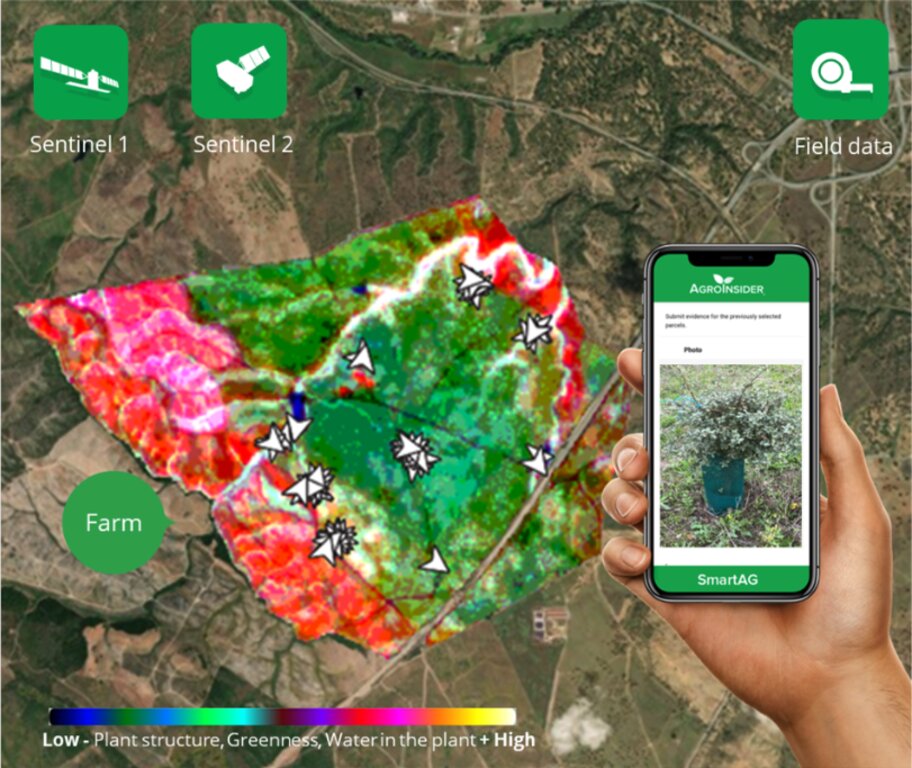
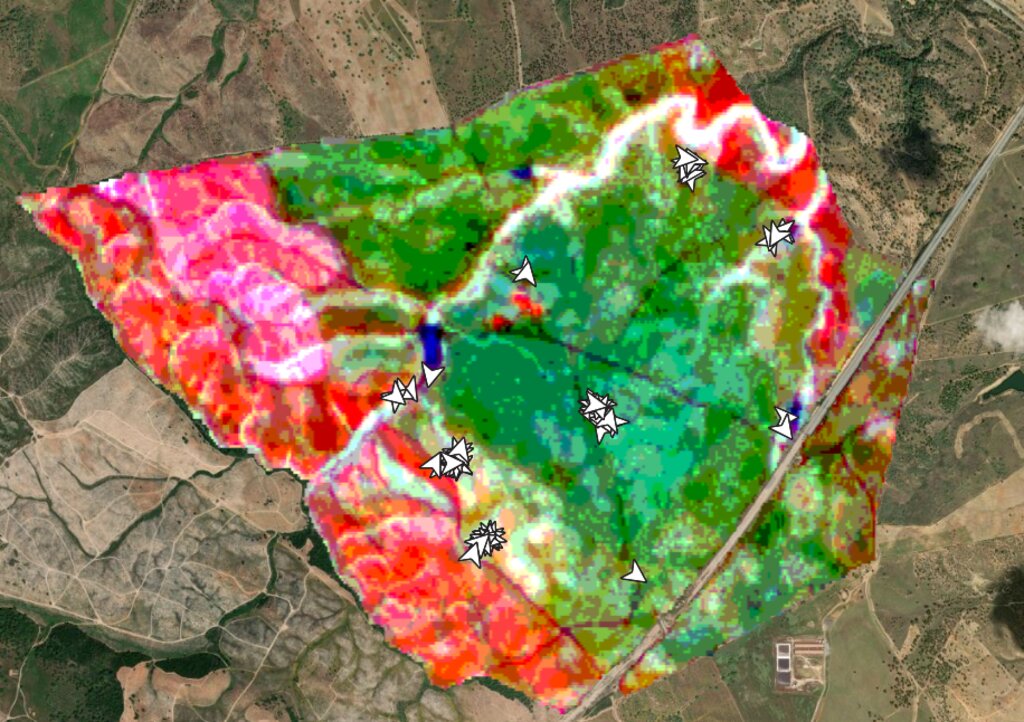
SmartAG automatically processes data from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data, and LST data for thermo-climatic zoning. These data: i) allow monitoring, reporting and verification of farms; ii) provide machine learning capabilities in agroforestry and environmental data.
Based on Sentinel data, spectral vegetation indices are calculated to identify: i) crop anomalies related to soil-water-plant; ii) management zones to define different land uses, the selection of sampling locations and sensor installation sites, water sampling locations, and identification of species for biodiversity quantification.
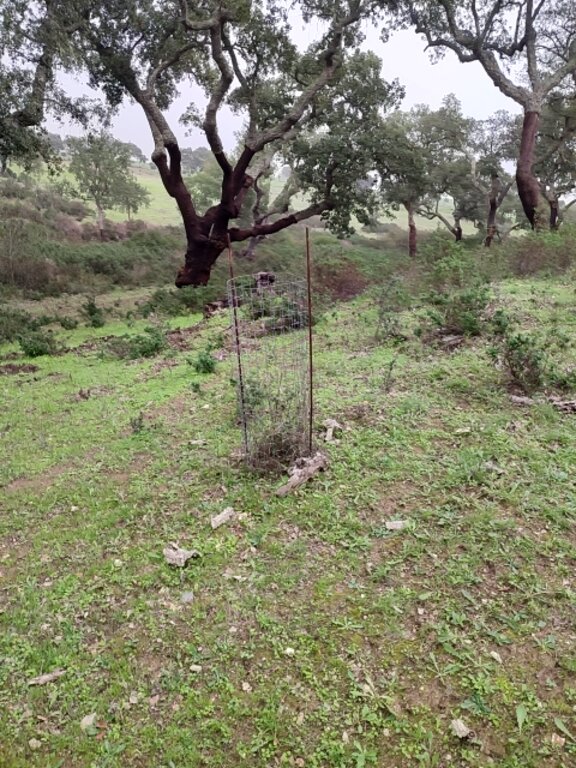
The Montado/Dehesa is a slow-developing and very complex agroforestry system meaning that differences will be observable only at the end of a year or longer. In addition, it is a highly stratified system, consisting of a complex arboreal structure with trees of different ages, shrubs, and herbaceous vegetation. Given the limitations of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 satellites it is essential to record georeferenced evidence of these. Using SmartAG app developed by AgroInsider allows the collection of georeferenced evidence (e.g., photos, audios, and videos) of
the vegetation structures, as well as documenting evidence of processes occurring such as ecosystem services and biodiversity. Georeferenced evidence is automatically uploaded into the system.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zxKjnAAkSI0
วันที่:
16/06/2023
สถานที่:
Évora, Portugal
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Filipa Santos
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
โปรตุเกส
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Alentejo
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
100000.0
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Montado and Dehesa constitute a Very High Nature Value agroforestry system which is under protection.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2023
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In 2023 AgroInsider started the implementation of the LMT and SmartAG monitoring in Agroforestry system case studies in Montado, in Portugal, and Dehesa, in Spain.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
- Transhumant pastoralism
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - non-dairy beef
- poultry
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
- whool
Species:
sheep
Count:
40
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
40

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การเอาไม้ที่ตายแล้วออกไปหรือการตัดแต่งกิ่ง
- Mediterranean Agroforestry System (Montado/Dehesa)
- cork holm, cork oak
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- cork
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Ca (Acidification): การเกิดกรด

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The LMT will be implemented on a farm with montado/dehesa (minimum area of 100 ha). Satellite data is used to characterize land use. After identifying the montado/dehesa area, field sampling is conducted. These data, along with satellite imagery, will be used to calculate the total CO2eq stock (above and below ground biomass) and estimate CO2eq sequestration. Farmers are encouraged to enhance LMT effectiveness, notably by engaging in ecosystem-value activities such as avoiding soil disturbance to preserve soil organic matter, increasing tree density, and maintaining water mirrors. Farmers will record georeferenced evidence of improvement activities and existing biodiversity in the montado and in other areas of the farm using the SmartAG developed by AgroInsider. This app will allow to monitor, report and verify carbon stocks through weekly alert reports, enabling the identification of carbon anomalies/losses over time and space.
ผู้เขียน:
Patrícia Lourenço
วันที่:
23/04/2024
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
100 ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euro (€)
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3590 €
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a farm with montado/dehesa (minimum area of 100 ha) | In the baseline year |
| 2. | Characterization of the land use using satellite data in the baseline year | In the baseline year |
| 3. | Field sampling in the montado/dehesa area | In the baseline year |
| 4. | Field data along with satellite imagery will be used to calculate the total CO2eq stock (above and below ground biomass) and estimate CO2eq sequestration | In the baseline year |
| 5. | Farmers are encouraged to enhance LMT effectiveness, notably by engaging in ecosystem-value activities such as avoiding soil disturbance to preserve soil organic matter, increasing tree density, and maintaining water mirrors | In the baseline year |
| 6. | Farmers will record georeferenced evidence of improvement activities and existing biodiversity in the montado and in other areas of the farm using the SmartAG developed by AgroInsider | Whenever farmers go to the field |
| 7. | After calculating the CO2eq stock and CO2eq sequestration estimates for the baseline year, SmartAG will allow to monitor, report and verify (MRV) carbon stocks through weekly alert reports. The MRV will enable the identification of carbon anomalies/losses over time and space | Weekly |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Data preprocessing before heading to the field | Hour | 4.0 | 20.0 | 80.0 | 0.0 |
| แรงงาน | Field data collection | Hour | 24.0 | 20.0 | 480.0 | 0.0 |
| แรงงาน | Post-processing of field and satellite data | Hour | 4.0 | 20.0 | 80.0 | 0.0 |
| แรงงาน | Improvement suggestions | Hour | 8.0 | 20.0 | 160.0 | 0.0 |
| แรงงาน | Emission estimates | Hour | 40.0 | 20.0 | 800.0 | 0.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Car renting | Day | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 0.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Fuel | Km | 350.0 | 0.4 | 140.0 | 0.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Soil sampling | Samples | 3.0 | 70.0 | 210.0 | 0.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | 1.0 | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2010.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2010.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The costs are covered by AgroInsider
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This value varies depending on the distance from AgroInsider's headquarters to the farm, the farm's area, and carbon-emitting farm activities (i.e., agricultural activities).
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Calculate the total CO2eq stock (above and below ground biomass) and estimate CO2eq sequestration | In the baseline year |
| 2. | MRV carbon stocks | Weekly |
| 3. | Record georeferenced evidence | Whenever farmers go to the field |
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Human resources, farm area, and the quantity of carbon-emitting farm activities (i.e., agricultural activities).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Montado/Dehesa is influenced by the Mediterranean climate, characterized by a great variability in precipitation and temperature in each year and between years, presenting a hot summer lasting more than four months, associated with a high irregularity in precipitation, both inter- and intra-annually. In this climate, natural droughts are recurrent.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
More recent data for the agricultural years 2015/2016, 2016/2017, and 2017/2018 report values for cumulative precipitation for the Évora region (Alentejo) of 547 mm, 421 mm, and 612 mm, respectively. However, in the same region, in the 2018/2019 crop year, there was only 315 mm of precipitation, while in the following year, this value already reached 627 mm.
It is common in the Alentejo region to have several days with temperatures above 40 ◦C in summer and with minimum temperatures below 0 ◦C in winter. In the Estremadura region, the average minimum temperature recorded was 3.4 ◦C, and the average maximum temperature was 35.6 ◦C.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
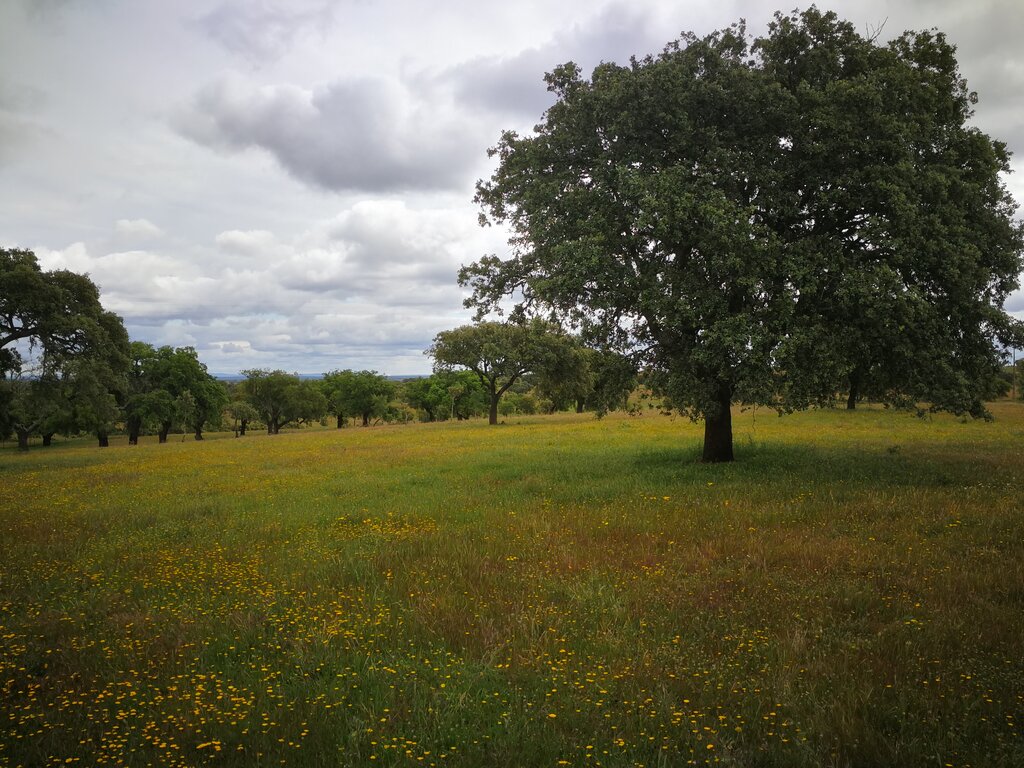
The Agroforestry system Montado, in Portugal, and Dehesa, in Spain, is a High Nature Value system characterized by a high complexity because of the interactions between climate, soil, pasture (natural pastures, fertilized natural pastures, and sown biodiverse permanent pastures rich in legumes), trees (e.g., pure or mix stands of cork oak, holm oak, stone pine), and animals (e.g., sheep, pigs, cows, goats). Montado/Dehesa is one of the most prominent and best preserved low-intensity farming systems in Europe. The integration of traditional land-use and biodiversity conservation that is characteristic of this system is an exemplar for the wise management of the countryside.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- สหกรณ์
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Conservation and preservation of the Montado and Dehesa.
Estimated
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Conservation and preservation of the Montado and Dehesa.
Estimated
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Selling carbon credits in the voluntary market
Estimated
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV, Recording evidence and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Measured
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV, Recording evidence of reforestation of young growth and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV, Recording evidence and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV, Recording evidence, Calculation of emissions and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Measured
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
MRV and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa. Estimated
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
None
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
| ไฟป่า | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Desertification combat efforts. |
| Diversifying income sources |
| Montado/dehesa conservation initiatives |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| New income source |
| Montado/dehesa conservation |
| Maintenance and increase of carbon stock. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Price of carbon credit in the voluntary market | Selling abroad of Portugal |
| Delay in the implementation of the voluntary carbon market |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Delay in the implementation of the voluntary carbon market | Selling abroad of Portugal |
| Certified credits before the entry of the new law on the voluntary carbon market by the European Union | Quantify and recertify. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
One visit per farm
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
4
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
1
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
2022
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Pinto-Correia, T., & Mira Potes, J. (2013). Livro verde dos montados.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://dspace.uevora.pt/rdpc/bitstream/10174/10116/1/Livro%20Verde%20dos%20Montados_Versao%20online%20%202013.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Lourenço, Patrícia, & Silva, José Rafael Marques (2023). How our portfolio of land-use practices might be adopted at scale in Portugal
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5f7b27859c352b2444f4cbd9/t/64a5440ac47212047978bc68/1688552460748/Portugal.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล