Sub-surface drainage on irrigated lands [แอฟริกาใต้]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Hans Edward King
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ondergrondse dreinering, brakdreinering, natdreinering (Afrikaans)
technologies_1126 - แอฟริกาใต้
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Richter Francois
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Wellington
แอฟริกาใต้
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Smit Jan
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Wellington
แอฟริกาใต้
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Steyn Francis
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, George
แอฟริกาใต้
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Oliver Gert
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Moorreesburg
แอฟริกาใต้
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Dept. of Agriculture, Western Cape (Dept. of Agriculture, Western Cape) - แอฟริกาใต้1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Drainage of saturated and salinised soils by means of sub-soil drainage pipes
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
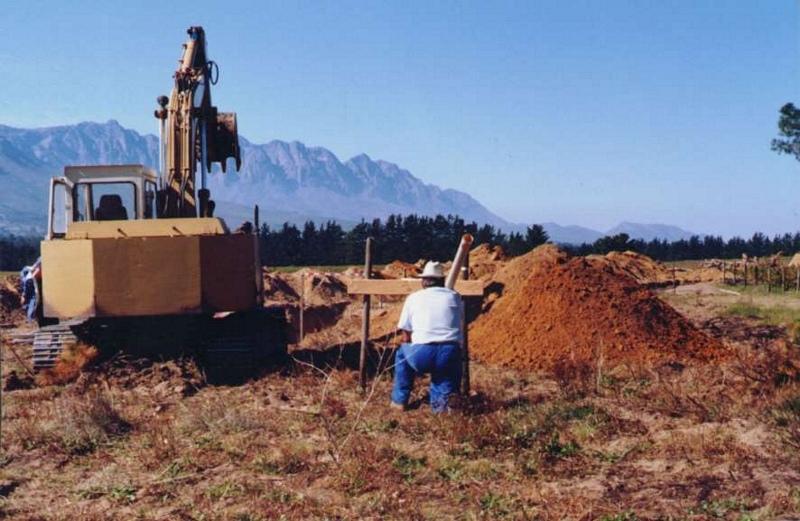
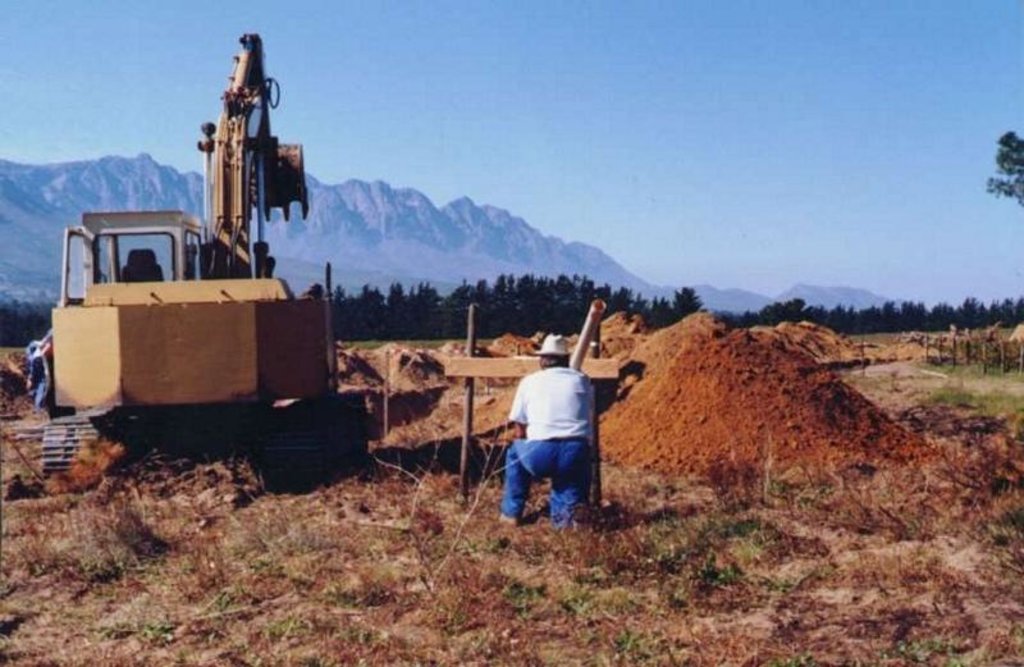
คำอธิบาย:
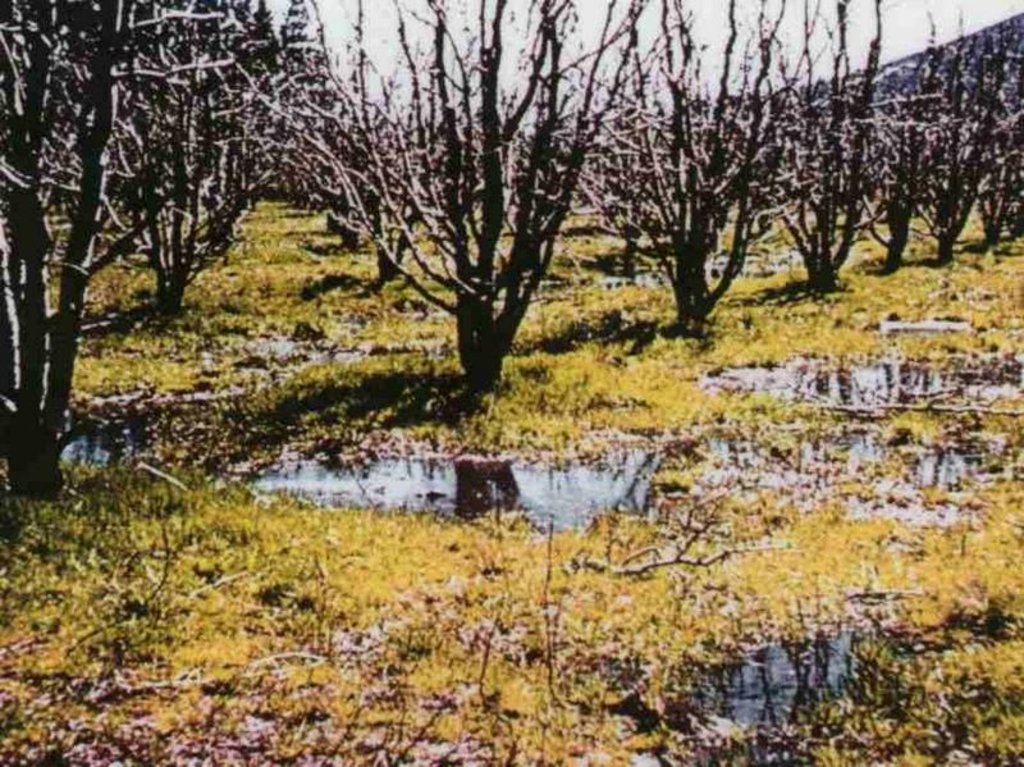
There is a lot of soil, wind and water erosion in this area. River erosion, not related to this SWC, is a problem over the whole area (on average 20 t/ha/y). Sheet and gully erosion occurs on commercial land. The whole area along the rivers varies up to 50 km.
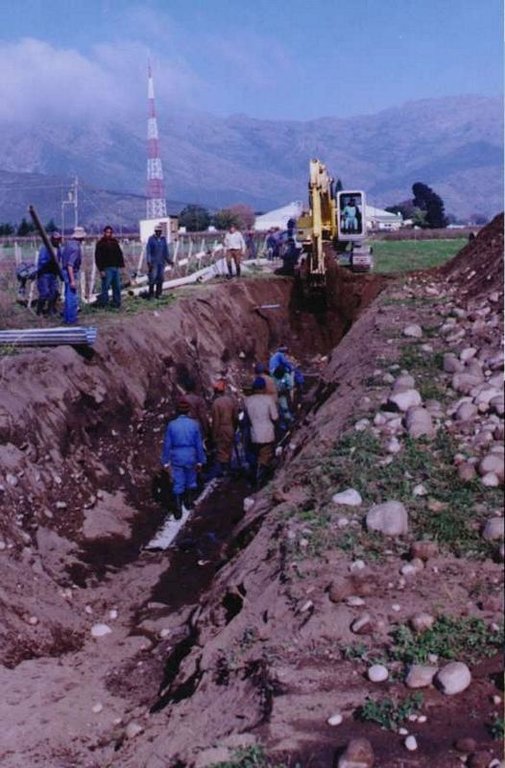
In some places drainage is inadequate and water-logging occurs. A system of sub-soil perforated pipes with surrounding filters was installed. Pipes laid at spacing determined according to the site conditions.
The overall purpose was to limit the level of the water table in the soil profile and remove salts, to provide an adequately aerated zone in the soil for a crops’ root system.
The system must be planned by a suitably trained person and constructed by an expert.
Drainage pipes must be flushed at least annually and roots removed whenever present.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แอฟริกาใต้
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Western Cape Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Southern Cape, Boland, Swartland
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
240.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 240 km2.
Technology also applied in other provinces. Boland 60% under agriculture and from this 20% under this technology. Swartland mainly wheat, 10% under irrigation and from this 20% is already drained. Southern Cape: 20% irrigated of which 20% is drained, 95% commercial farmers. Other parts in SA: KwaZulu/Natal (Pongola), Free state (Rietriver, Orange River), Northern Cape (Vaalharts, Douglas, Upington), Eastern Cape (Fish River, Sundays River, Langkloof)
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Holland, USA - literature
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- citrus
- grapes
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Mar
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
major food crop: Deciduous fruit/citrus
other: Grapes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Bad management (over irrigation). The washing of soil from one land to the other. High winter rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of crop production due to saturation/salinisation of soil. Not putting money back what would be expect, because not enough growth, reduced crop roots deeper in soil and no growth in the area, slanted growth - salinised soils.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pw (Waterlogging): ภาวะชุ่มน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Rising water tables - As result of over irrigation, leaking dams and canals)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - Build dams & canals that leak, over irrigation)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Removal of salts from soils, Decrease water table, Increase of soil aeration
Structural measure: subsurface drains
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 40-80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300
Construction material (other): Plastic perforated pipe with crushed stone filter
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
15.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig trench | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 2. | Lay pipe | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 3. | Place filter material | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 4. | Build manholes | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 5. | Backfill trench | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Install drainage system | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 15.0 | 150.0 | 75.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 75.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 75.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Pipes | ha | 1.0 | 240.0 | 240.0 | 75.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Manholes | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 75.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Contractor overheads | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 75.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1390.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1390.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flush pipes with water | All year/2 times a year |
| 2. | Cut roots in pipes | When required/ |
| 3. | Clean manholes | All year/2 times a year (was reduced) |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Maintenance | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 25.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 25.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Length of pipe (grid at 60 m spacing - i.e. pipe that average team lays in one day)
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Suitability of soil for drainage (greater depth and permeability = lower costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
501-750 mm is closer to the mountain
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of them are only farmers.
Level of mechanization: Tractors, trailer, plough, crop sprayers
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 100-500 ha, but production capacity on all is really the same
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- กลุ่ม
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During rainy season (winter) tractor can drive on field without getting stuck in the mud, but construction process and maintenance of intercrops farming activities (negligble)
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
on farm employment
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
due to higher workload
input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Construction must be financed
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less bare soil
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil fertility
restoration of original topsoil aeration
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Most of this soils have originally been saturated
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
downslope salinatation
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
50 percent of all households in this area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more farmers are coming to do ditch drainage because there's more money available, if waiting period is more than 3 months the service from government is free of charge.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Greatly improved crop yield |
| Improved access for mechanisation |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Greatly improved crop yield |
| Improved access for mechanisation |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Initial capital outlay | |
| Slight decreased in run-off water quality | |
| Insufficient information on soil properties |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Initial capital outlay | |
| Slight decreased in run-off water quality | |
| Insufficient information on soil properties |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Drainage Works for Western Cape (Afrikaans). July 1988.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
HE King
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
National Drainage Manual (Afrikaans)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
NDA - photostat costs
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล