Orchard establishment on a former wheat plot, by planting fruit tree seedlings in combination with sowing Alfalfa [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Malgorzata Conder
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1138 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Conversion of wheat monocropping into an Alfalfa plot with the aim to establish an orchard
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
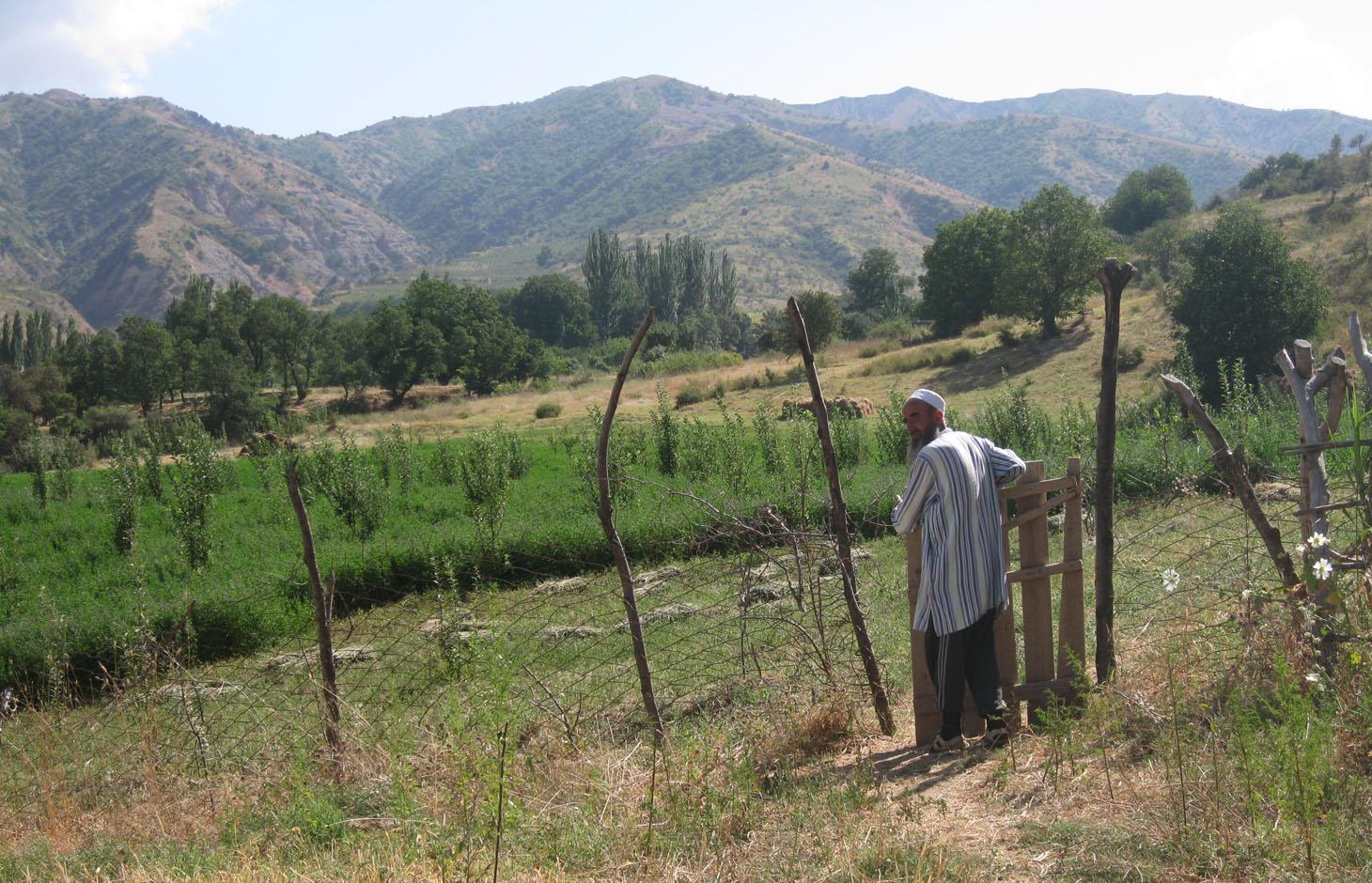
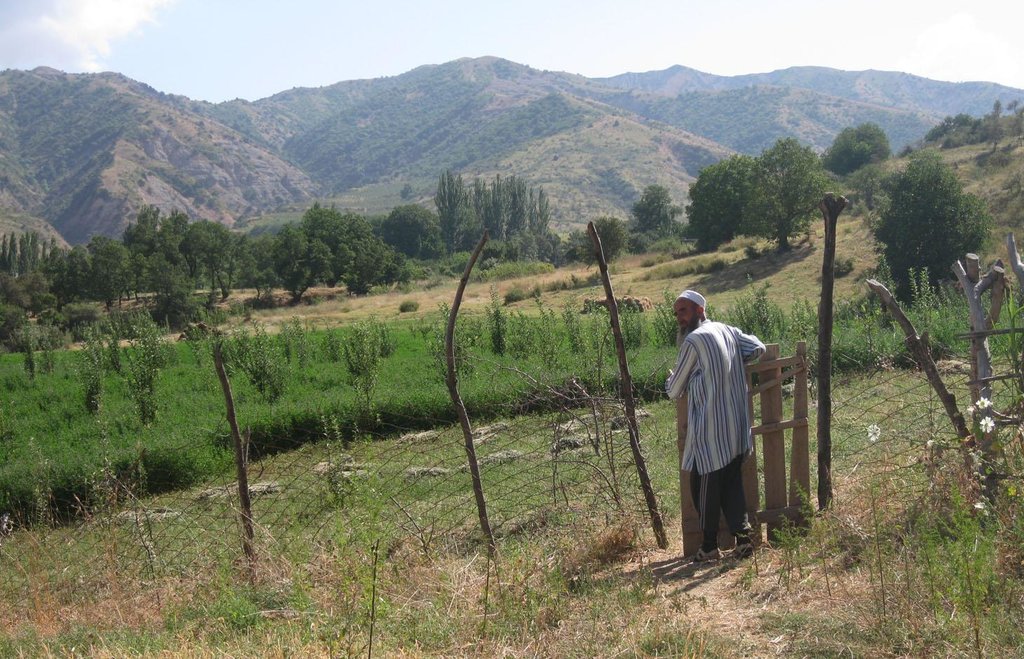
In 2009 the farmer changed his wheat plot into an Alfalfa plot where he also planted fruit tree seedlings in between to establish an orchard. One hectare is used for the perennial cropping of Alfalfa. Alfalfa cropping supplements beneficial soil functions which are crucial for the establishment of an orchard. The plot lies on a narrow plateau next to other wheat crops. The plot is mainly bordered by fruit and nut orchards on a gentle slope, and by a steep slope of the riverbed. A solid fence prevents boars from entering the area through the nut orchard. The plot is not accessible by the steep slope. Two fences are built from the side of the neighboring wheat plots. One fence works like an entrance gate to all the plots on that plateau. A second fence indicates the boundaries between the farmers' Alfalfa crop and the wheat plots belonging to other farmers. The whole family is working on the farm land, consisting of several plots which are distributed over the valley. The children are mainly guarding the cropland.
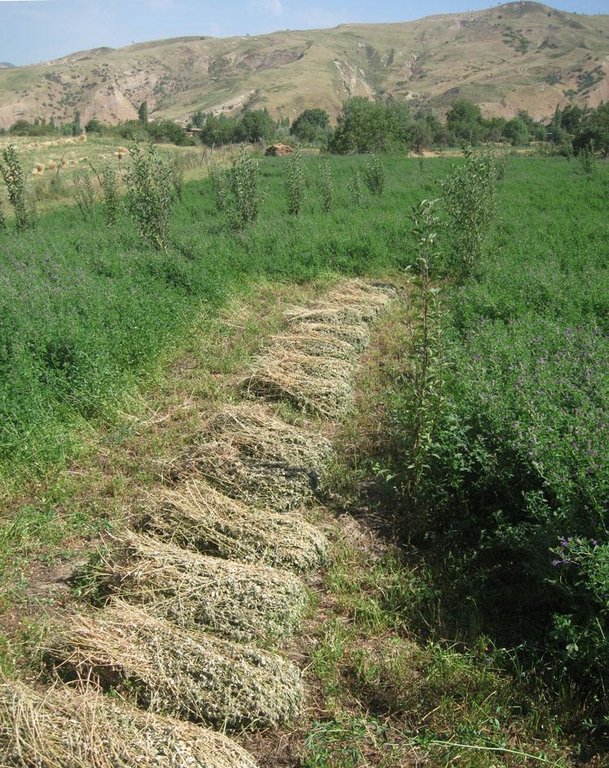
Purpose of the Technology: In order to establish an orchard, first the farmer planted Alfalfa, which maintains more moisture in the soil and hence creates favorable conditions for tree growth. The wheat cropping was drying out the soil. Therefore during heavy rainfall events water infiltration was limited, and the strong runoff washed away the wheat crop. It was the farmer’s initiative to change the crop management, but Caritas Switzerland supported him with a financial grant. Alfalfa can be harvested several times a year, which he can use as fodder for the livestock or as cash crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The first year after the crop rotation there was no benefit, as the Alfalfa did not give any harvest yet. According to the farmer, Alfalfa seeds were relatively cheap (15 TJS per kg) and result in a good harvest. Currently he is harvesting Alfalfa three times a year, wheat could only be harvested once a year. The whole family was involved in the establishment of the alfalfa crop and tree planting, by ploughing, sawing Alfalfa, planting the seedlings and constructing the fence. Despite the fence, the crop is often guarded by the farmer or his children because boars enter his property. After the first year some seedlings dried out which he had to replace. Presently, little maintenance is required, only guarding and cutting Alfalfa.
Natural / human environment: The farmer’s plot is situated on a plateau on the other side of the riverbed, from where the village of Momandion is located. It takes some 15 minutes to get from their house to the plot. One of his neighbors adopted the technology of sowing Alfalfa and planting fruit tree seedlings.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muminabad
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
Total crop size is around 1.5 ha, lucerne crop is around 1 ha. The remaining area is a small wheat plot and meadow with some sparse walnut trees. A fruit and nut tree orchard is above the fenced crop.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Farmers idea, one third was payed by himself, the rest was supported by Caritas
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fodder crops - alfalfa
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- fruits, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, poor nutrient and moisture availability in the soil, high runoff
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, poor soil moisture availability, high runoff, declining yields
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Fruits of growing orchard will be food and probably cash crop in future
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), poverty / wealth (Fear of food insecurity pushed farmer to plant wheat, year by year)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (No knowledge about alternative and beneficial land management)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
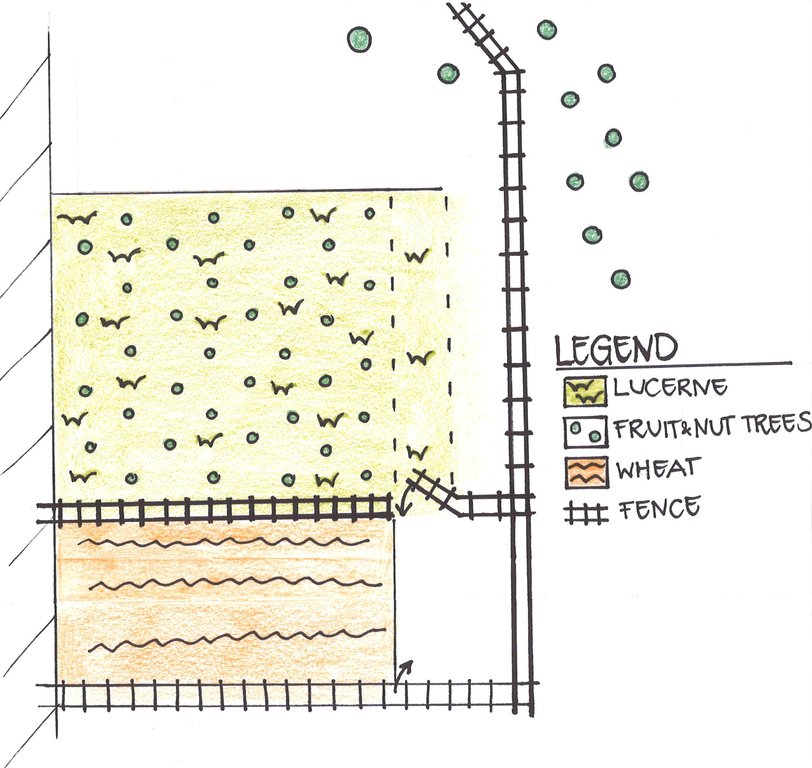
The farmer’s property is located on a plateau, surrounded by an upper orchard on a slope (in the top right corner on the figure) and delimited by a steep embankment (on the left on the figure). The Lucerne plot is protected by a fence and the embankment to hinder intrusions of boars. There is a well locked entrance to get to the crop. A second fence protects the adjacent wheat crops and the Lucerne plot. Around 600 fruit trees are planted in the crop leaving a buffer strip of Lucerne.
Location: Momandion, Obishur watershed. Muminabad, Kathlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Alfalfa to recover soil for orchard
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Change of land use type: Conversion from wheat to fenced Alfalfa crop and orchard
Alfalfa crop has a twofold function, as a crop which is harvested several times a year and as cover crop to reestablish soil properties
ผู้เขียน:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
12.40
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying and planting 600 trees: 10 Min/ tree for digging | once |
| 2. | After first year: 100 trees dried out | once |
| 3. | Fencing 400 m, by 6-7 pers, 10-11 days (8 h a day) | once (spring) |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting trees | Persons/day | 12.5 | 12.4 | 155.0 | 37.0 |
| แรงงาน | Planting trees for replacment | Persons/day | 2.1 | 12.4 | 26.04 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Plowing labour | Persons/day | 1.0 | 12.4 | 12.4 | |
| แรงงาน | Sowing | Persons/day | 0.27 | 12.4 | 3.35 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Plowing machine | days | 1.0 | 103.5 | 103.5 | 37.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Petrol | litres | 120.0 | 1.1383333 | 136.6 | 37.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Buying trees | trees | 600.0 | 0.62116666 | 372.7 | 37.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Buying tree replacments | trees | 100.0 | 1.035 | 103.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | kg | 20.0 | 3.1 | 62.0 | 37.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Fence | area | 1.0 | 1490.7 | 1490.7 | 37.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2465.79 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2465.79 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Caritas
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting/Cutting Alfalfa 3 times and seeds 1 time, 8 Pers one week (first cut) | 4 times a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around 600 trees | spring/ once |
| 3. | Looking after the orchard, 2 or 5 hours per day | every day |
| 4. | Pruning after 5 years (in future), one month | spring/ once every five years |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Soil loosening | Persons/day | 9.375 | 12.4 | 116.25 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Looking after orchard | days | 365.0 | 100.0 | ||
| แรงงาน | Pruning after 5 years | Persons/day | 25.0 | 12.4 | 310.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Harvesting/Cutting Alfalfa | Persons/day | 192.0 | 12.4 | 2380.8 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2807.05 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2807.05 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
2.5.4.2 Harvesting and cutting labour input is estimated proportinally to the expected yield. The first cut has a max. yield, the second yield amounts up to 70%, the third some 50% of the initial yield. Labour input for harvest might be to high as it was not indicated by hours, but by days. The farmer paid only a part of the initial costs, which amount some 37% of the total costs.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Fencing is very expensive due to high material costs. It is a very laborious and time consuming work.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200mm asl, wheater station Muminabad)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms hill slopes: Nut and fruit orchard right above the crop
Landforms foot slopes: Plateau
Slopes on average: 12-16%
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: High
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water medium: Winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm)
Availability of surface water poor/none: no rainfall from July to August
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Level of mechanization manual labour: Everything except plowing
Level of mechanization mechanised: Plowing
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
1.4 ha, if 7.7 pers per household
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No fertlizer, less controlling
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
Livelihood and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Alfalfa seeds are more expensive than other seeds (e.g. wheat) and in the first year just one cut can be done. In the second year already several cuts are possible and assure a high yield. It is expensive to establish an orchard and in the first 5 years there is no harvest.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Neighboring farmer adopted Technology on one of his plots (even though less technical), other is interested.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
After one time sowing, several cuts are possible from the second year on. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread the experience of the farmer. |
|
Perennial crops are beneficial to soil and increases the income of the farmer. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread technology through demonstrations, work shops etc. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Alfalfa gives good yield and is a good conservation measure for soil and water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Workshops or institutional incentives for farmers to promote perennial crops. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| First year might result in more input than output because just one cut is possible and an orchard must grow at least 5 years to give fruits. | Raise awareness about long-term benefits or give incentives in the establishment phase. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล