Zero grazing [ยูกันดา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Wilson Bamwerinde
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okurisiza hamwe
technologies_1188 - ยูกันดา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - ยูกันดา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Stall-fed livestock production is an efficient method to produce organic fertilizers (manure) for the conservation and improvement of soil fertility.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
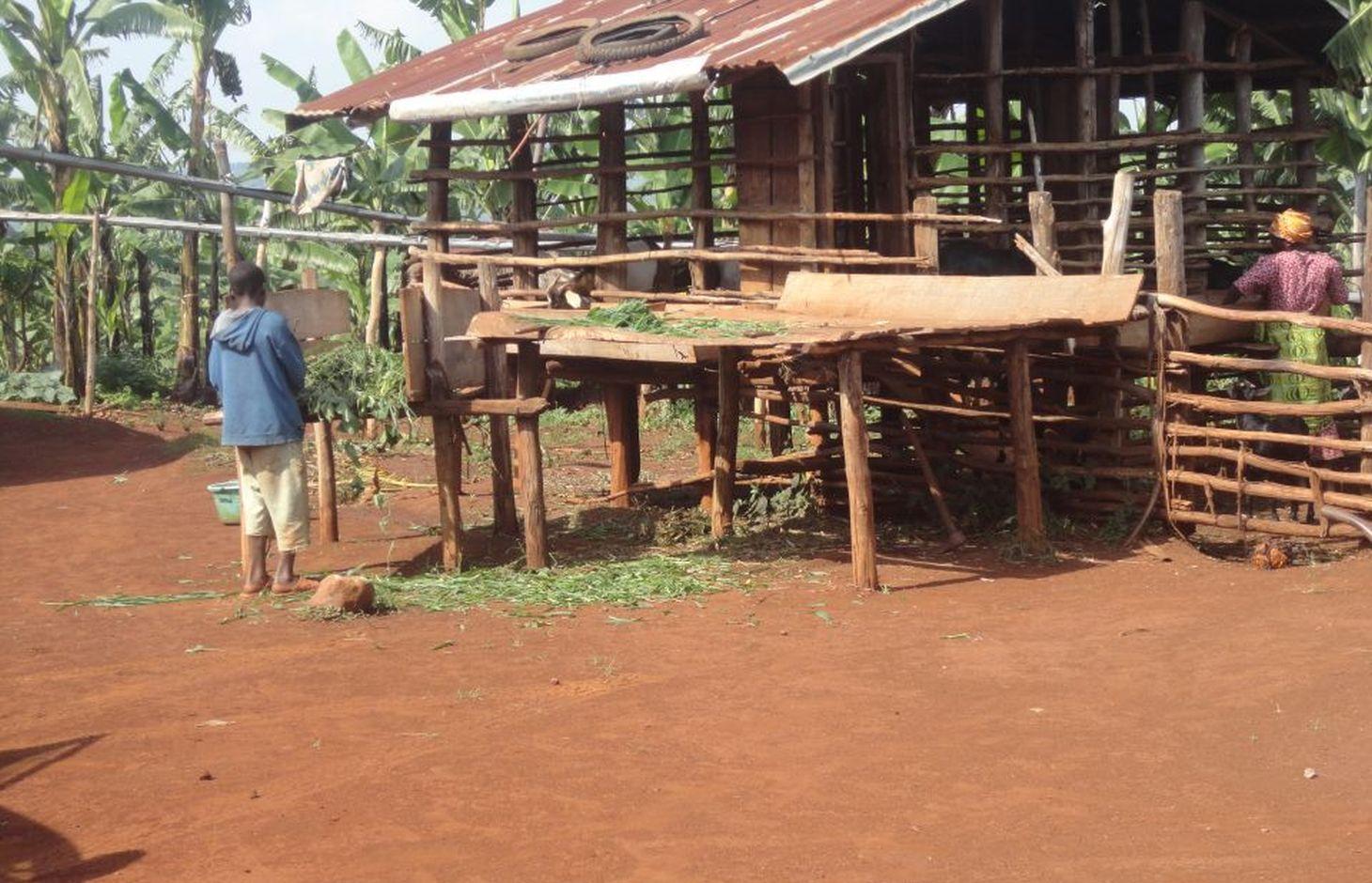
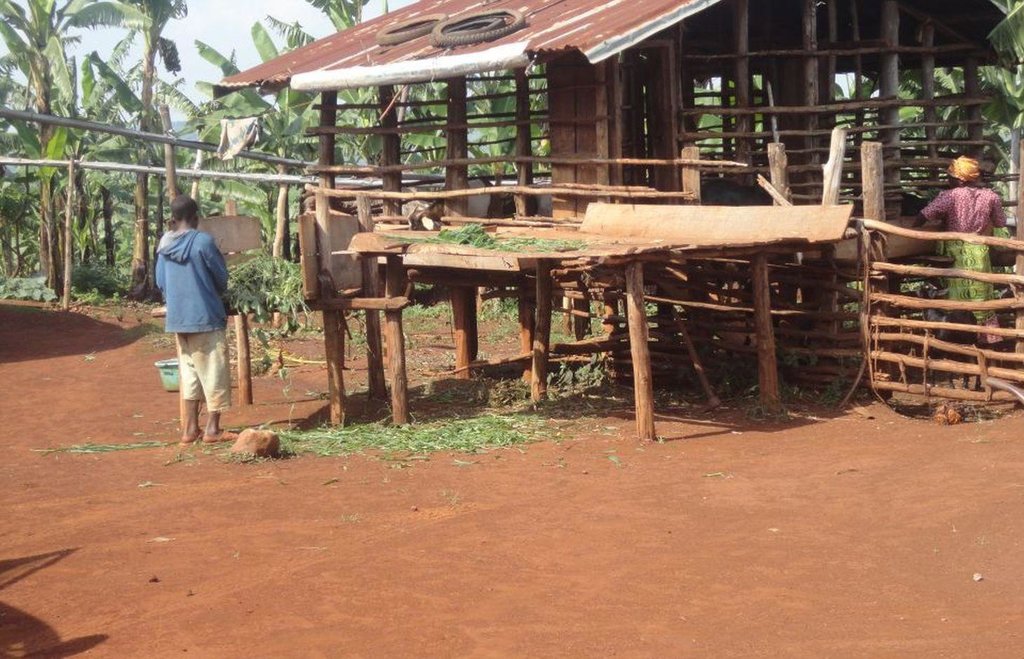
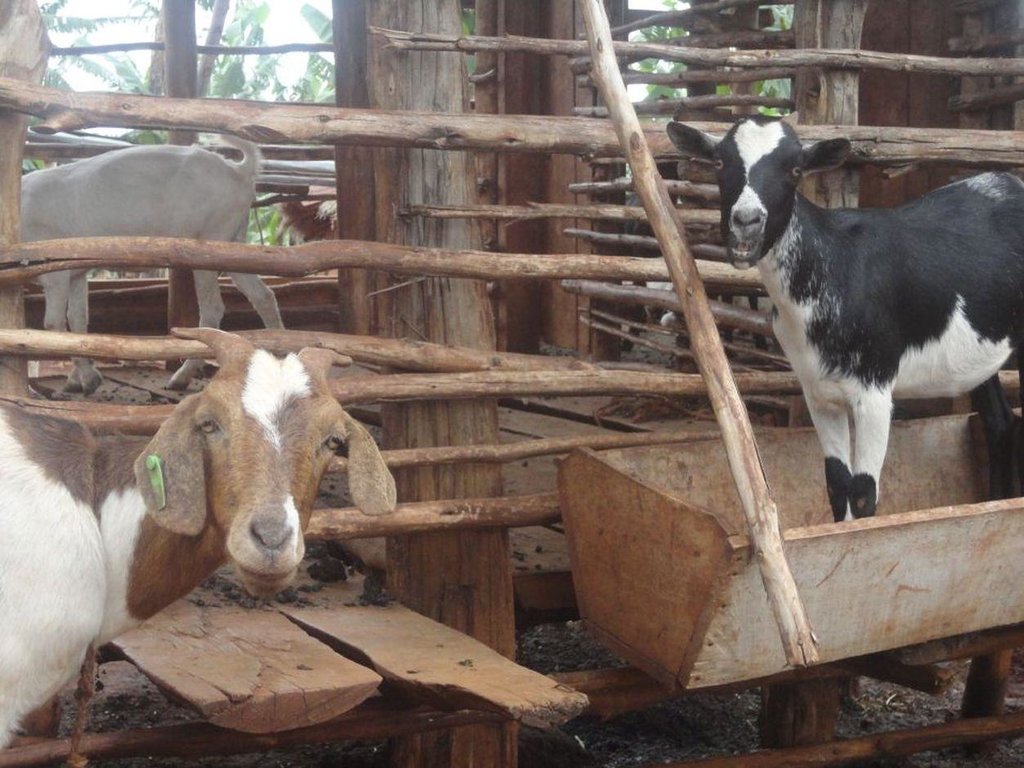
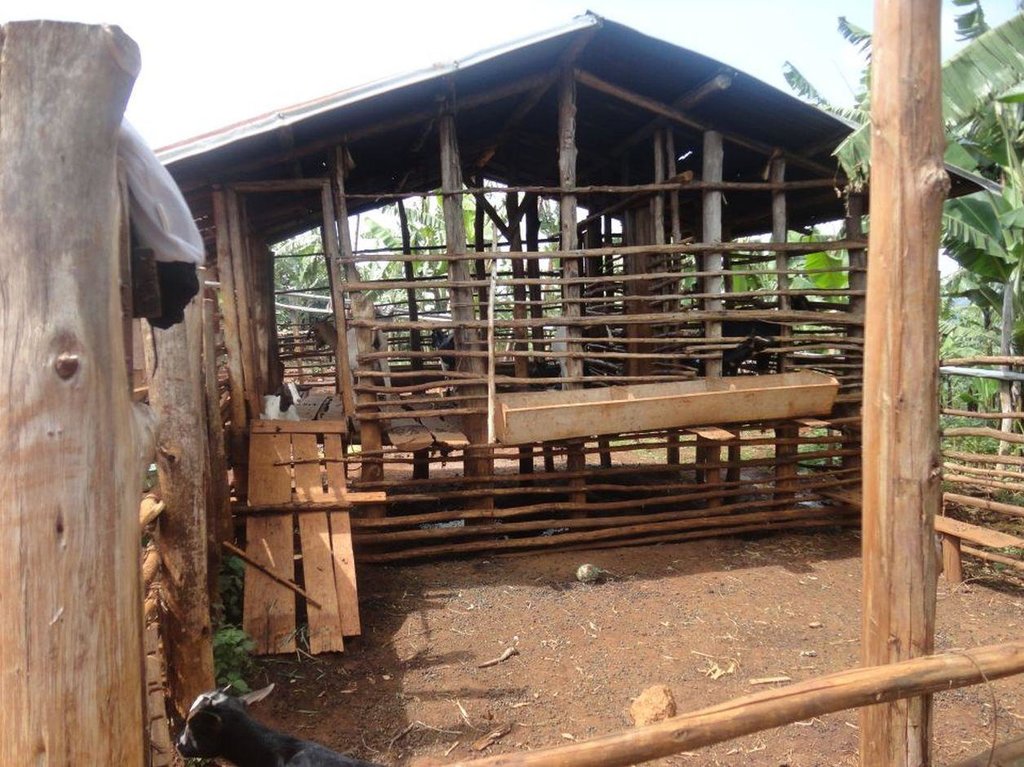
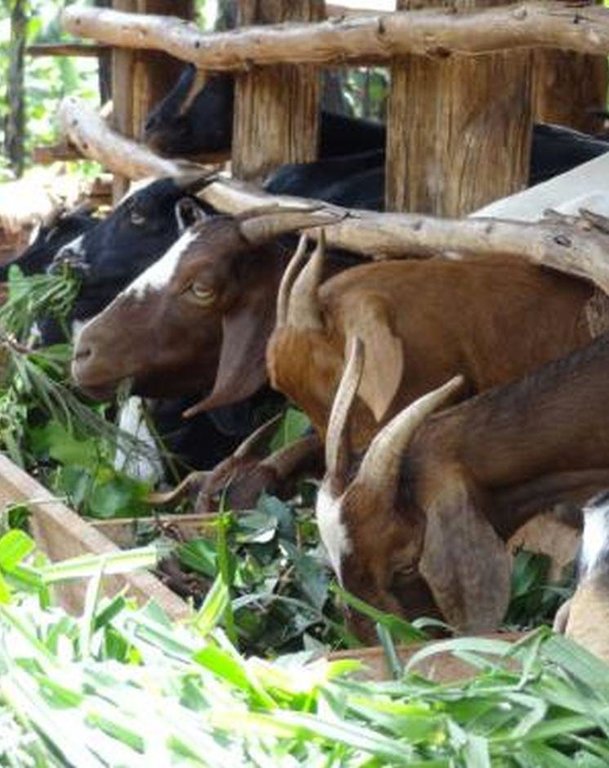
Zero-grazing has been a common livestock (cattle and pigs) management practice in most areas of south-western Uganda due to reduced communal grazing land. In the predominantly annual cropping system communities, free grazing livestock often damage crops and are a major cause of conflict. On the other hand, farmers observe that crop yields have declined season after season. For example, the bunch of bananas has grown smaller, it has smaller fingers, and many banana stands have no fruit during much of the year. The most important ways through which croplands in Rubagano are degraded include nutrient transfer through harvest and crop residue movement and use; nutrient mining whereby continuous cultivation is done with little or no replenishment; and soil and water runoff on steep slopes. Farmers know that one of the most important ways to reverse declining soil fertility is to apply manure, but it is expensive. Therefore farmers acquired goats or pigs primarily for the provision of manure for their cropland, but also as a household income generating enterprise. In stall-fed goat or pig production, The zero-grazing unit is designed in such a way that it is well ventilated and protected from wind, rain and constant direct sunshine to avoid livestock developing coughs, colds and stress. The unit has 3 major parts: the feeding and rest area, the exercise area and the manure collection area. The feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground. Below it is the manure collection area and above it, a corrugated iron roof. There is a feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area in which mixed fodder is fed to the livestock. A wooden food preparation slab for cutting and mixing fodder is in front of the feeding/rest area. The unit for housing 12 goats is 4 m by 8 m on the ground and 3 m high at the feeding area.
Purpose of the Technology: The major objective of stall-feeding is to maximize manure collection for sustaining soil fertility in cropland. Other goals are to improve household income, reduce expenditure on pests and disease management through livestock isolation from other animals and to reduce labor by cutting and storing fodder for use over a period instead of grazing in distant pastures daily.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The materials required for establishment of the zero-grazing unit for goats are wooden posts or poles, cut-off planks, wooden slats/timber, iron sheets and nails. The 4 m by 4 m feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground on strong Eucalyptus or pine posts of diameter 5-10 cm. Its wall is 2 m high and is made of widely spaced cut-off planks or light wooden poles not more than 3 cm diameter nailed to strong upright posts. The floor is made of wooden slats placed 2 cm apart, big enough to allow livestock droppings to fall through but too small for adult goats’ or kids’ hooves pass, in order to avoid injury to livestock. There is a 1.5 m by 0.5 m feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area and a 1 m by 1 m fodder mixing wooden slab at the front. On the ground to one side of the feeding/rest area is the 4m by 4m exercise area. The unit can be constructed at any time of the year.
Natural / human environment: Regular maintenance of the unit is done to ensure the floor does not develop holes that can lead to injury of the livestock, and the roof does not leak when it rains. Increased manure collection and application increases crop yields and supports crop diversification.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ยูกันดา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Uganda
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mbarara District
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86313 30.62564; -0.86314 30.62561; -0.86316 30.62569; -0.86319 30.62567
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002 km2.
There are 20 zero grazing units (goats and pigs) in the area and with a total area of about 2 hectares. The technology is being adopted slowly throughout the community.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
This technology was introduced in 2008 by NAADS and later by Africa2000 with aim to improve manure and compost production in Kagera region. Recently, Kagera TAMP project provided additional support to introduce exotic breeds of the goats and increase livestock productivity.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- goats
- pigs
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Reduction of soil organic matter content
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decline of soil fertility and decreased crop yields
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: other crops like peas, millet, maize and sorghum are also grown.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Extensive grazing land
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor methods of cultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor agronomic practices), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Vegetation destroyed for domestic use (firewood and thatch).)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Details of zero grazing shed structure : A. Overview of the livestock shed with manure colelction area (below) B. View on the feeding arrangement with the fodder vats abouve ground level C. Deatils of the fodder vat D. Overview of the fodder preparation structures
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 29-DEC-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Manure (Pigs or goats)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 900
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Grass species: Pennisetum purpereum (napier grass), Calliandra Spp.)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25-30%
Change of land use type: Mixed crop and livestock husbandry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Planting fodder in addition to traditional annual and perennial crops
ผู้เขียน:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabala
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UGX
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
2600.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.85
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of tools | Wet season |
| 2. | Purchase of construction materials | |
| 3. | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | |
| 4. | Purchase of livestock | |
| 5. | Grass seed procurement and sowing | Wet season |
| 6. | Converting part of the cropland (annual and perrenial crops) into fodder production |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | ha | 1.0 | 115.4 | 115.4 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | Set | 1.0 | 115.4 | 115.4 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1.0 | 38.46 | 38.46 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1.0 | 173.1 | 173.1 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 692.36 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.27 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
Lifespan of:
Tools - 1 year
Construction material - 10 years
Zero grazing shed - 1 year
Livestock - 20 years
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and carrying and application of fodder | Daily |
| 2. | Collection, composting and application of manure | Daily |
| 3. | Purchase of tools and materials for reconstruction/repairs of the shed structure | annual |
| 4. | Weeding and gapping | Seasonal |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 38.46 | 38.46 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 11.54 | 11.54 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1.0 | 3.85 | 3.85 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1.0 | |||
| อื่น ๆ | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 71.85 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.03 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Panga, hoe, tree poles nails, soka jembe, spade, and wheel barrow., Hand hoe, panga.
The costs were calculated for the construction of the shed, acquisition of 3 does and establishment of fodder crops on part of cropland formerly used for annual and perrenial crops. The calculations were done for the technology in August 2011.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The most determinate factors in the establishment of the technology are: labour for planting, maintaining and cutting grass and other pastures and carrying the fodder to the zero-grazing unit; labour for fetching water for the animals; and labour for removing and composting manure and spreading into the garden.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1041.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C.
Rubagano receives at least 6 months of rain in 2 seasons, February to May and September to November
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1740 m.a.s.l)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Fairly steep slopes in places)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (Mother rock easily reached on pitting)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Sand and stones)
Soil fertility: Low (Fertility depleted; being slowly replenished by application of technology)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (Water easily penetrates into the soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (Crops easily dry during the dry spell)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: >50m (Not possible to reach water table)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (No surface water except when it rains)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, muddy water collected by damming runoff in natural rock depressions)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Low, noticed improvements after application of the technology
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No difference in involvement of men and women.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
14% of the land users are rich and own 37% of the land.
48% of the land users are average wealthy and own 42% of the land.
21% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land.
17% of the land users are poor and own 7% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is increased yield where the technology has been applied, increasing the income generated on-site thereby reducing off-farm percentage.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (use hand hoes)
Market orientation: Mixed (Some crops are sold to generate household income. Goats will be mainly for sale)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Some households have more while others have less land.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Individual land ownership. Recent introduction of the water harvesting measures provided land owners with access to own water sources
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10kg
หลังจาก SLM:
60kg
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased yields for beans realised.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
23dollars per yr
หลังจาก SLM:
92 dollars per yr.
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
yields increased from sell of goats
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As there is now a lot more activity on-farm
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Vegetation cover has been improved.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Food security and household income have improved. This has resulted in children in these households having more time for school and in case of illness, there in some money for accessing treatment.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
livestock is confined
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Forage and fodder usually become scorched during seasons of long drought and livestock may die from lack of food. Grass is cut in the wet season while it is plentiful and turned into hay for the time of scarcity. For this, a barn unit needs to be constructed.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The benefits far outweigh the establishment and maintenance costs. The negative on short-term returns is due to the cost of the technology (construction and procuring livestock) which is a little high for the farmers in this area.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
20 on 2 hectares
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The does were supplied to farmers using project funds.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: these farmers are rich and procured the technology without support from the project
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: 20 households in one village have adopted the technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Technology easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the livestock |
|
Helps in soil fertility management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good manure management |
|
Imporove soil cover and reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? using the manure in a proper /recommended way i.e. using it when planting or putting it in the plot before primary cultivation |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Animals are fed on selected pasture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the growing of that pasture |
|
The technology promotes us of organic manure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of compost pits to recycle the wastes into manure |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technology may contribute to loss of vegetation | Planting pasture & other grass for feeding the animals |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล