Slope cross barier in banana combined with common agronomical measures production [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Godfrey Baraba
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Makinganga maji mchanganyiko
technologies_1216 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kakilla Samuel
TCRS-Ngara
แทนซาเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Chitege Daudi
Magereza Rusoma Primary School
แทนซาเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Masikundima Iddi
Ngara District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
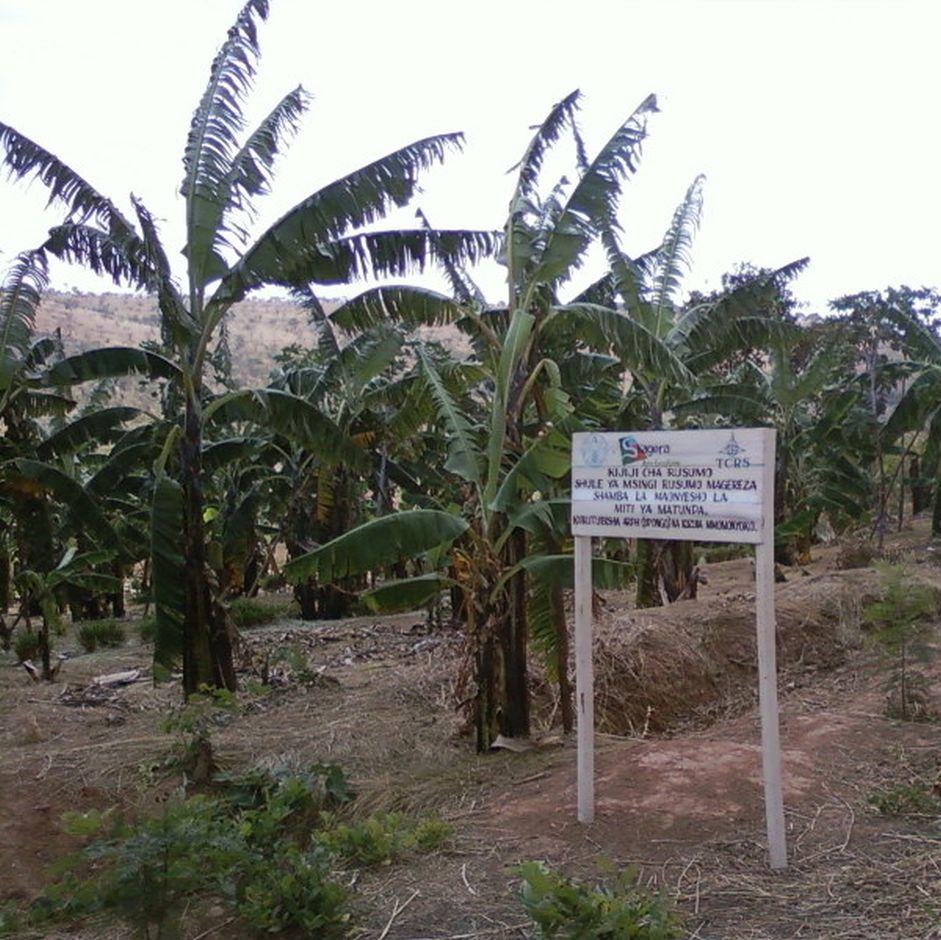
Is the embanked soils on the lower side of the furrow, lemon grass and vetiver grass strips along the contour lines combined with Farm yard manures and grass mulch application in banana production.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The slope cross barrier technology in banana production is a 2m deep by 0.6 wide furrow at the less slope combined with lemon grass, vetiver grass contour strips at the greater slopes.. The lemon grasses and vertiver grass are planted in single row spaced 0.3m plant to plant. The distance between strips is about 18m at the slope category of 2%. The technology is applied on the cropland in the tropics, sub humid, dissected plain to flood plains, sandy clay loam over sand clay and deep to moderate deep soils. The land is cultivated manually using hand hoes in a mixed production system. The land ownership is communal and individual not titled. The establishment procedures includes planting of banana suckers, lemon grass, vetiver grass, fruit trees, construction of fanya chini and planting gravelia spps along the boundaries. The maintenance procedures require application of FYM at the rate of 24-36kg per plant. Grass mulch is spread across the slope at the thickness of 0.15m. The average establishment costs is US$ 3,531.42 per hectare while maintenance costs on average is US$ 351.77 per hectare. The technology was introduced fifteen months past ( March 2013) using Demonstration plots methodology. Common agronomic measures such as using improved banana suckers and banana weevils trapping can add extra effectiveness to the main technology.
Purpose of the Technology: The general purpose of the technology is to reduce soil erosion, reduce soil moisture stress and increase soil nutrient cycling and soil organic matters.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment activities includes first, clearing and cultivation of land in May done manually using machete and hand hoes. Second, harrowing in May done manually using fork handhoes. Third is identification and demarcation of contour lines doneusing A-frame. Fourth is spacing and digging of holes for banana and fruit trees done manually done. Fifth is planting of banana suckers and fruit trees done manually. Sixth is planting of vertiver and lemon grasses along the demarcated contour lines done manually, seventh is digging the farrow and excavating soils to be placed at the lower side of the furrow done manually. The maintenance activities include; first, weeding the entire field using hands done in twice April and October. Second is manure application using plastic buskets done. Third is spreading grass mulch done manually, fourth is desuckering using chisel hand hoes done twice in April and October. Fourth is detrushing using machete and local made tools (rwabyo) done twice (May and January). Last but not least is harvesting of banana, lemon grass and fruits done on market demand.
Natural / human environment: The land ownership is communal and individual not entitled while the water use right is open access. The natural environments are 1184mm of rainfall.The technology is tolerant to drought and seasonal rainfall decrease. Soil fertility is low to moderate. Top soil organic matter is medium, Soil drainage is medium. Soil water storage capacity is medium.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tanzania
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Bukoba
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A demonstration plot for pupils self-reliance education studies established a plot measured 2 acres where the technology is applied.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In February 2013 TAMP -Kagera, Tanzania introduced the technology through demonstration sites for cross slope beerier technology at Magereza Rusumo Primary School.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - sorghum
- lemon grass, vertiver grass
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- fruit trees, oranges, Pawpaw
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: March to May; Second longest growing period in days: 60;Second longest growing period from month to month: November to December
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problems were soil erosion, moistture stress, declining soil nutrients and organic matters.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The major land use problems were reduced soil fertility.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A6: Residue management

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, temporary trashlines, manure / compost / residues, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope), change of seasonal rainfall (decreased rainfall intensity.), droughts (Increased length of dry spell.), population pressure (Increased population density had forced to cultivate slope land to meet the social economical requirements.), poverty / wealth (Land users cant afford to invest in land concervations.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate staffing limits effective support services for land users to access land concervation knowledge.), governance / institutional (Environment policy implimentation is weak at lower levels.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Basic priciples are taught at colleges.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The new technology should be taught first for a better innovation and adoption processes.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: Panic grasses
Quantity/ density: 1500
Remarks: 0.15m thickness across the slope.
Temporary trashlines
Material/ species: banana dry leaves abd old pseudostems.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Trushlines
Quantity/ density: 7.5t0nes
Remarks: A 2m X2mX3m pit is dug at the centre of foor banana stools and pilled.
Pits
Material/ species: .
Remarks: a 0.3m depth is left un covered with soil below the soil surface level
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 700
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 70
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 715
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 625
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
In blocks
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: gravelia spps
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Pawpaw and oranges
Perennial crops species: Banana
Grass species: lemon grass and vetiver
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Structural measure: Fanya chini
Vertical interval between structures (m): E
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 105
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.9
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 105
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.88
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughoing | May |
| 2. | Harrowing | may |
| 3. | Digging holes | |
| 4. | Demarcating contour lines | |
| 5. | Digging holes for planting banana suckers | |
| 6. | Demacarting banana spacings. | |
| 7. | Mixing FYM | |
| 8. | Plating banana suckers | |
| 9. | Planting vetiver grass and lemon grass. | May |
| 10. | Planting mango, pawpaw, orange and gravelia | January |
| 11. | Demarcation of contour line using F-frame. | March |
| 12. | Digging the furrow and excavating soils. | May |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 541.18 | 541.18 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 134.31 | 134.31 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedling | ha | 1.0 | 2032.4 | 2032.4 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost / manure | ha | 1.0 | 823.53 | 823.53 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3531.42 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 3531.42 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | april |
| 2. | Desuckering and detrushing | January and may |
| 3. | Mulch grass application | May |
| 4. | Pr-oping (anchor poles placement) | routeenly |
| 5. | Harvesting banana fruits. | routeenly |
| 6. | Planting ricinus communis | February |
| 7. | Trees Pruning | |
| 8. | Harvesting fruits | |
| 9. | To remove soil sediments from the furrow and place the in the space between. | May and January |
| 10. | To cvlear fire-break along the bounderies | May |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 153.73 | 153.73 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Grass mulch | ha | 1.0 | 196.08 | 196.08 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 351.77 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 351.77 | |||||
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Highet precipitation March to May and second precipitation November to December.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months is above 18°C
LGP 60dys to 90dys
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: 3 adption land users are found in the flat areas and a 1.5 acre is demonstration plot site where thye adoption plots found elsewhere.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Redish brown/dark brown sandy clay loam over sandy clay
Soil fertilityis low and DP Low to moderate
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium and DP well drained
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: Bordering Kagera river.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Earthworms, black ants etc.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Market orientation of production system: Fruits intededed for sale and banana are dual purposes.
Level of mechanization: Hand hoes are used.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- Institutions
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
- village goverment
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- village goverment
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
5
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Banana first harvest
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulch reduced moisture stress
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved seeds and seedlings, FYM & grass mulch
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Orchad as comlimentary enterprises
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FYM and mulch applications demanded extra labour
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Conseved land ensured soil improvement to ensure food availability, accessility and utilizations
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
AESA conducted during FFS
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Equal chances for different gender considered in FFS formulation
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The effective technology duration is too short to obeserve impacts, but we can say that, there is hope for the technology to contribute highly on livelihod and human wellbeing
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulching
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulching
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Pitt and furrows
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulching
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Contours
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FYM
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trushlines
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Ditches traped running water down the slope
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farrow and bunds along contour lines minimized water run off in the area
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology can be modified to become more tolerant by meter drain construction from the contour furrow into drainage ditches to collect excess water during heavy rainfall events. This excess water should be used for small scale irrigation.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
8 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Only the primary school received external materials to establish a 1.5 acre demonstration plots.
4 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Three teachers applied the technology at their own lands bearing their full cost of implimentation.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A 75% adption rate within a less than two years effective duration implies a strong adoption trend.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Easy to learn and practice. |
| social economic and production very feasible at increasing return to scale. |
| Ecological benefits should maintain constant returns to scale |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Increased farm input costs. | |
| Highly extension services demand to learn new technology. | |
| Thieving attractions |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
07/08/2014
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล