Gravity type inverted tyre structure [แอฟริกาใต้]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mirjam Staehli
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Swaartekrag tipe omgedopte bande struktuur (Afrikaans)
technologies_1374 - แอฟริกาใต้
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Du Toit Boeta P.
Marico Bushveld Soil Conservation Committee, South Africa
แอฟริกาใต้
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Meiring C. H.
Marico Bushveld Soil Conservation Committee, South Africa
แอฟริกาใต้
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
Community driven Protection of the Molatedi Dam Catchment … [แอฟริกาใต้]
Development and capacity building in participating communities through the implementation of measures to prevent topsoil losses through erosion in the Molatedi dam catchment area.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
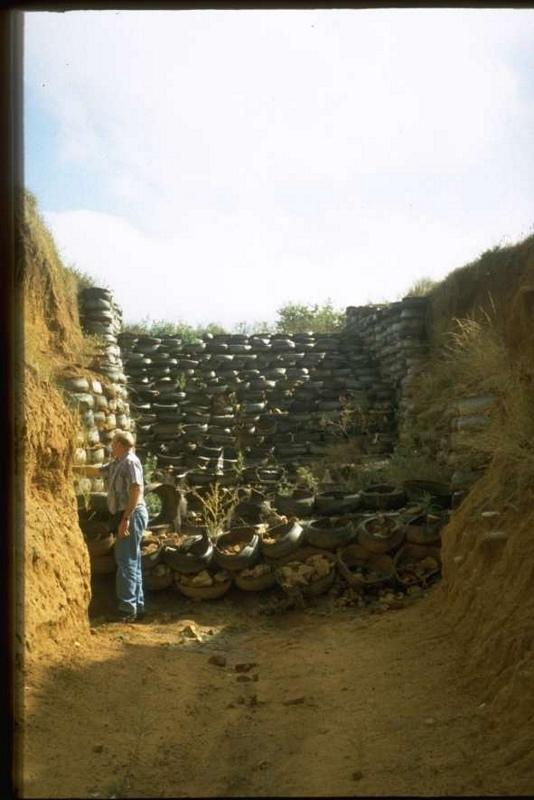
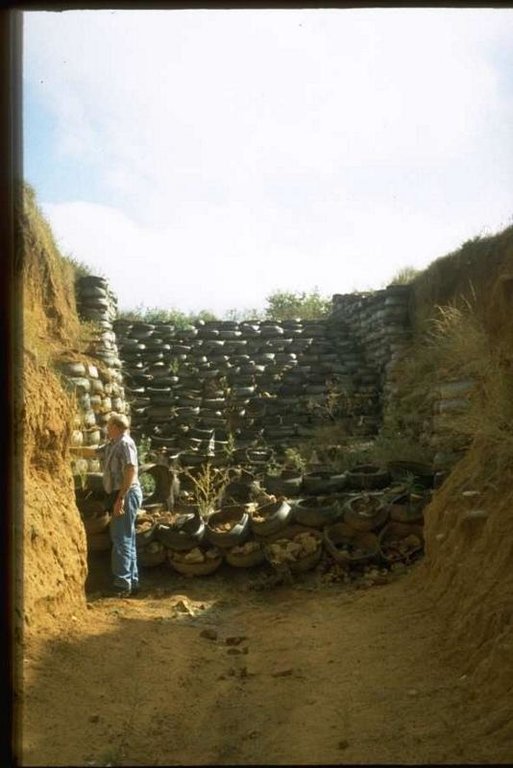
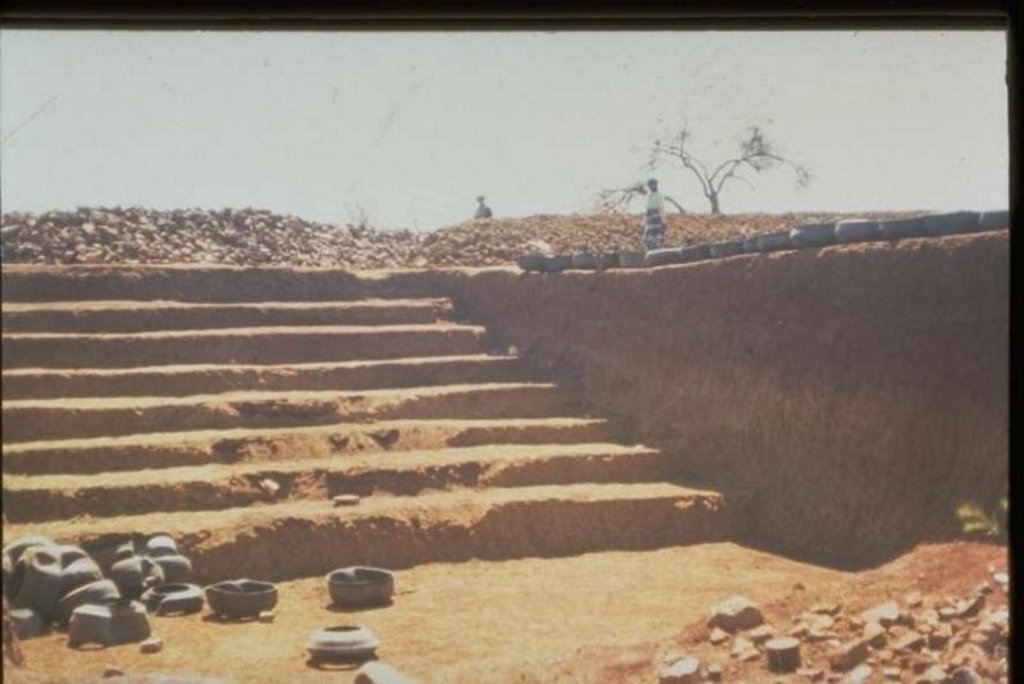
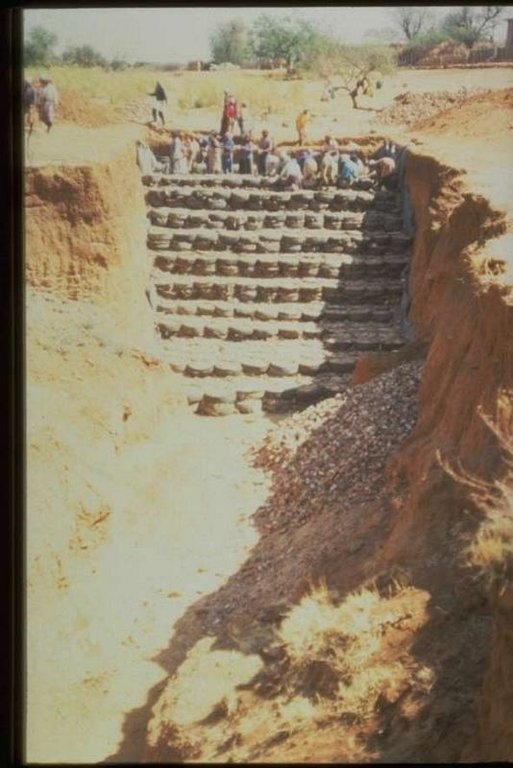
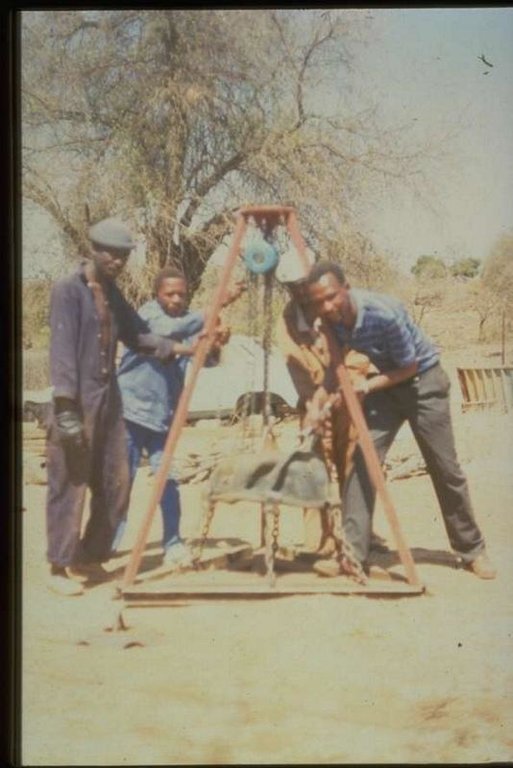
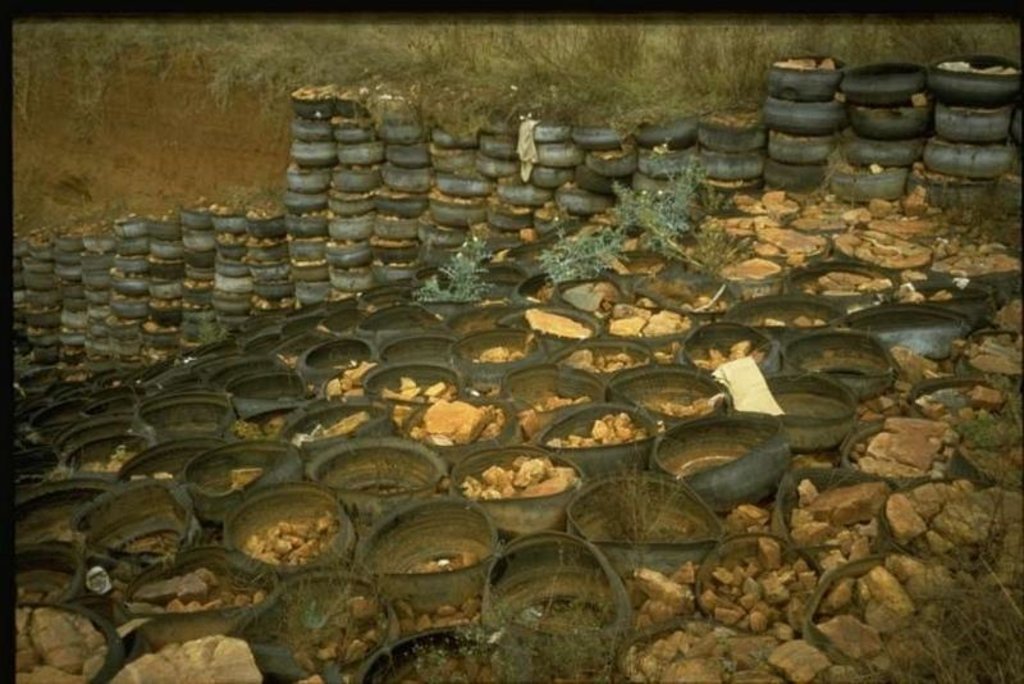
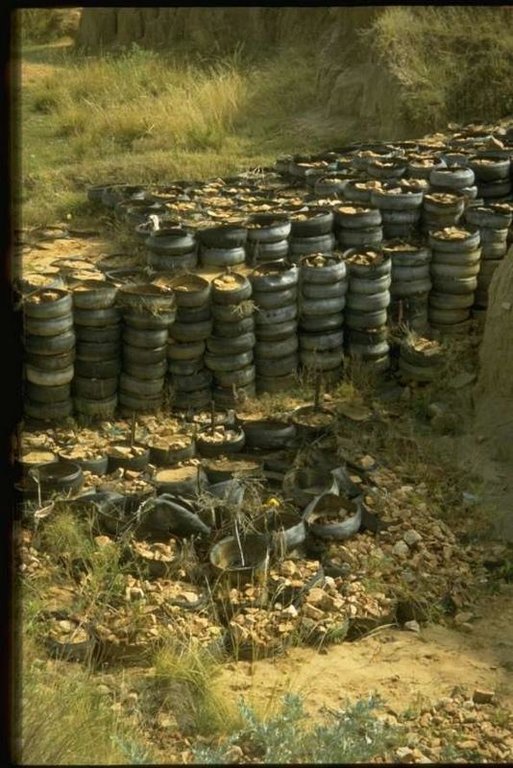
Stabilising of gully erosion by means of gravity type inverted tyre structures filled with stone.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Gravity type inverted tyre structure is bound together with wire and filled with stone.
The valley floor gully head drop is protected to prevent further erosion. Survey planning and design are important for the construction of the structure.
Maintenance includes prevention of leakage alongside the structure. The walls to prevent the erosion of soil are filled in. Ensure that the top layer stones are not washed away.
The structure is situated in a semi-arid area which is highly degraded through overgrazing.
Due to the location of the structure, further erosion was stopped that would have endangered some of the homesteads.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
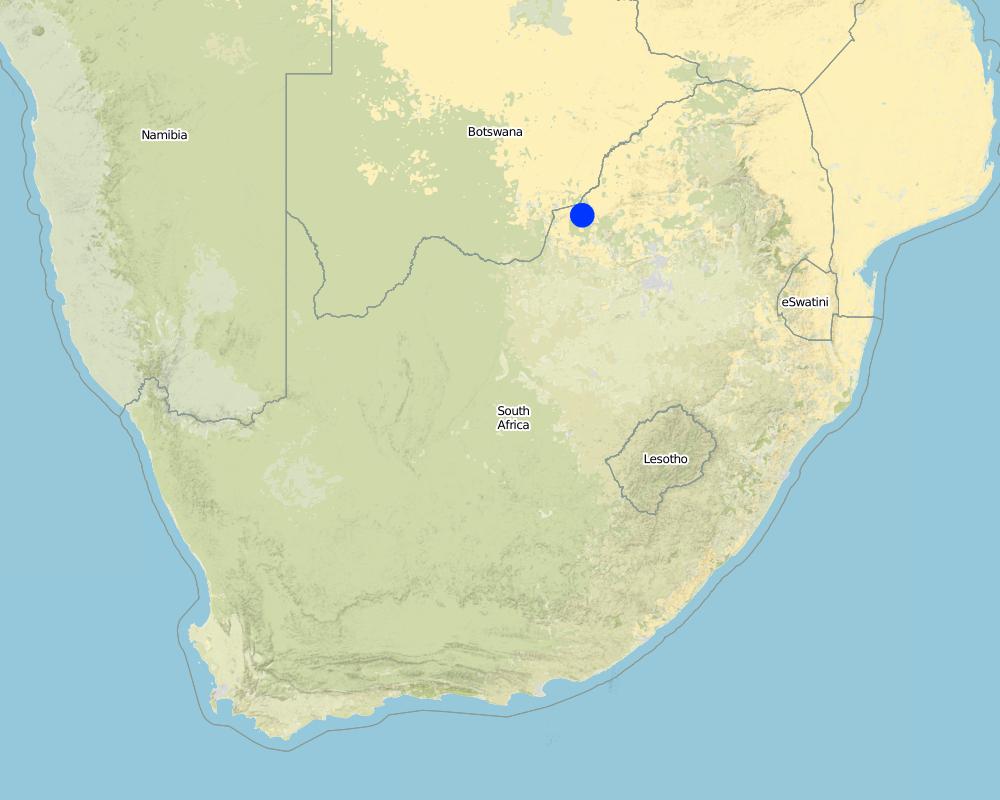
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แอฟริกาใต้
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
North West Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Marico District
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
12.0
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12 km2.
Same technology was also applied in the Molatedi tribal village (70 km away in the same catchment area)
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
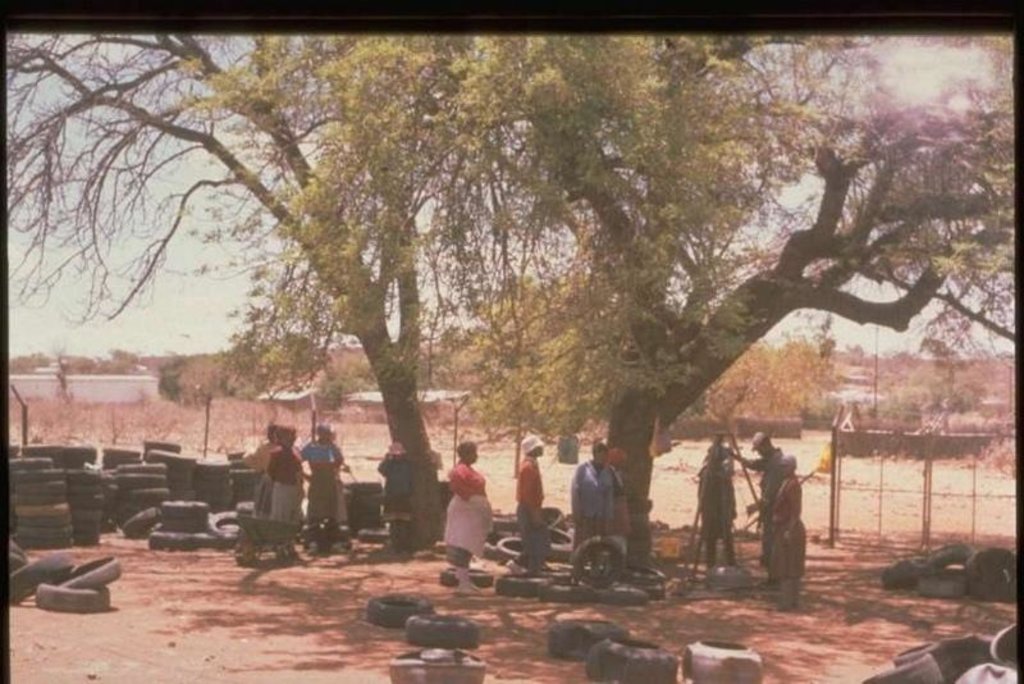
Developed by technician department Resource Conservation and farmer from local conservation committee.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of landuse planning. Overgrazing. Overpopulation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of grazing land, frequent occurrence of droughts.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): Not planning for access roads in the village
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 240; Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Apr
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - Lack of training & awareness)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Lack of extension and planning), land tenure (Land subdivision - Only if someone own land (commercial farmers)), poverty / wealth (Lack of employment), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (Regarding natural resources)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
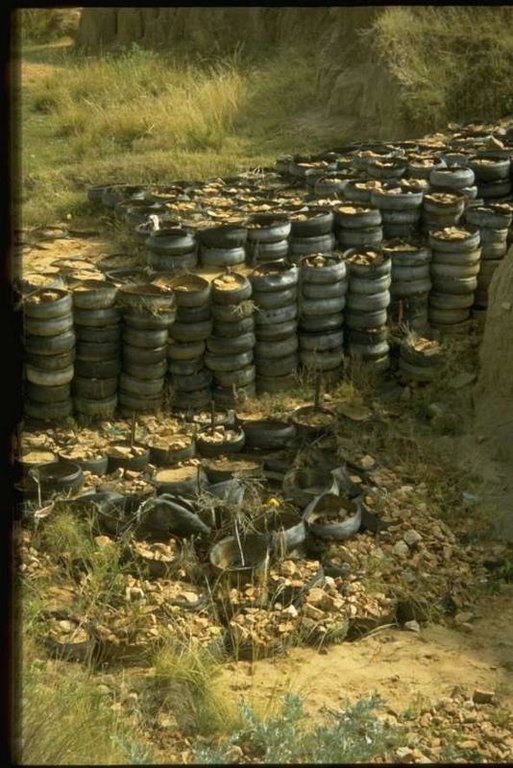
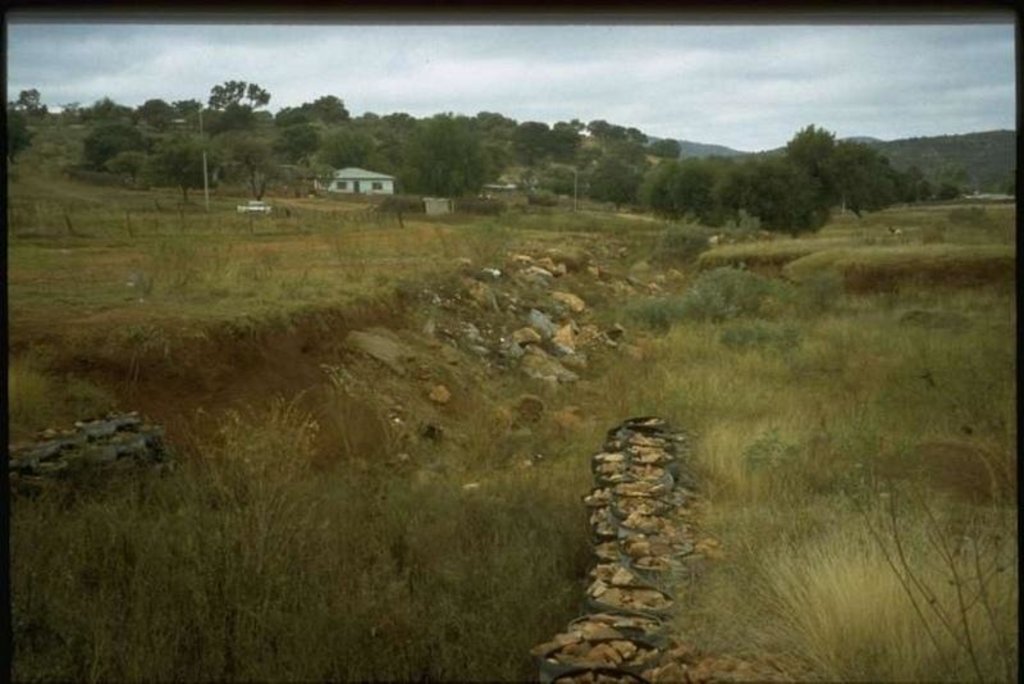
further downstream another tyre construction trapping the silt, behind the structure silting up and vegetation is well growing
North West
Date: April 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Structural measure: Gully head drop structure
Construction material (earth): wire iron posts, plastic material, geotextilemembranes (bidim-kaymat) -water permeable soil exclude
Lateral gradient along the structure: 50%
ผู้เขียน:
Mirjam Staehli, Switzerland
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Rand
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
6.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.50
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 9400.0 | 9400.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tyre averting tool machine | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Geotextile membrane | ha | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wire 2mm (rolls a 50kg) | ha | 1.0 | 330.0 | 330.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Fully galvanised iron | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 12480.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2080.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The complete structure.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour - very low productivity. Transportation of tyres. Tying wire must be cut economically according to need otherwise huge waste take place.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Thunderstorms, heavy rainfall
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Summer rainfall
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 100% of the land (Communal land belongs to the tribe).
Off-farm income specification: State pensions- head of family work elsewhere.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
short term job creation
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
spending on consumer goods in shops in area
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
20 percent of the area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Labour intensive, job creation |
| Received training |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Low cost material |
| Labour intensive can be utilized without machinery |
| Mostly unskilled labour can be used. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Storm water walls are in the way of motor vehicles, travelling in the village | Plan roads properly - construct alternative road around wall. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Costly if manual labour is unproductive | Maintain high productivity. Train workers, work smart, contract work |
| Transport cost of tyres is a big factor. | Utilize tyres from nearby areas. Utilizes big transport trucks with big loading capacity. |
| Need machine to invert tyres | Tool well and practically constructed - operators trained. |
| Must technically be well planned and constructed. | Use skilled technician for planning and to assist workers during construction. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Community driven Protection of the Molatedi Dam Catchment … [แอฟริกาใต้]
Development and capacity building in participating communities through the implementation of measures to prevent topsoil losses through erosion in the Molatedi dam catchment area.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล