Area closure [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Bota Klela (Tigrigna)
technologies_1414 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Project (LLPPA) [เอธิโอเปีย]
It is a local level participatory planning approach.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
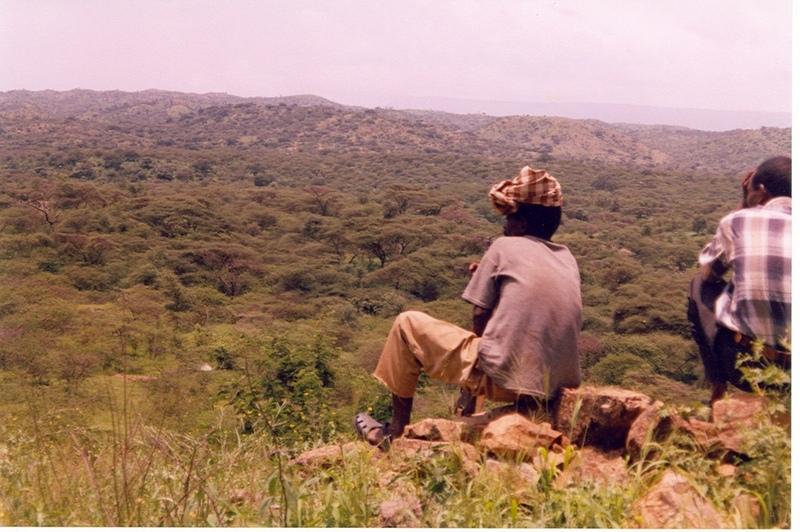
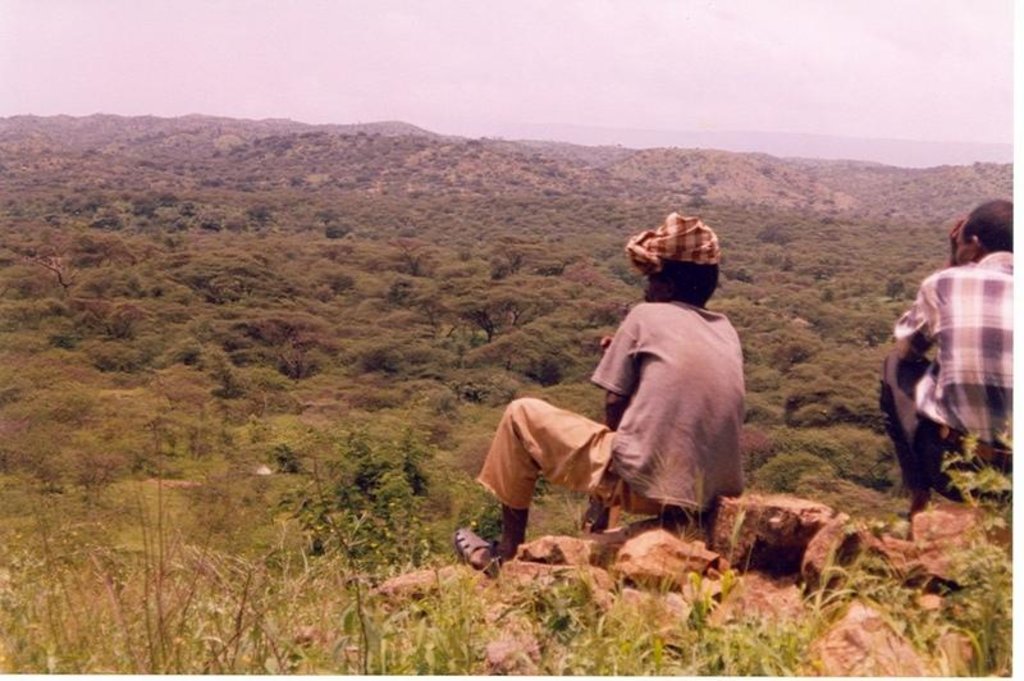
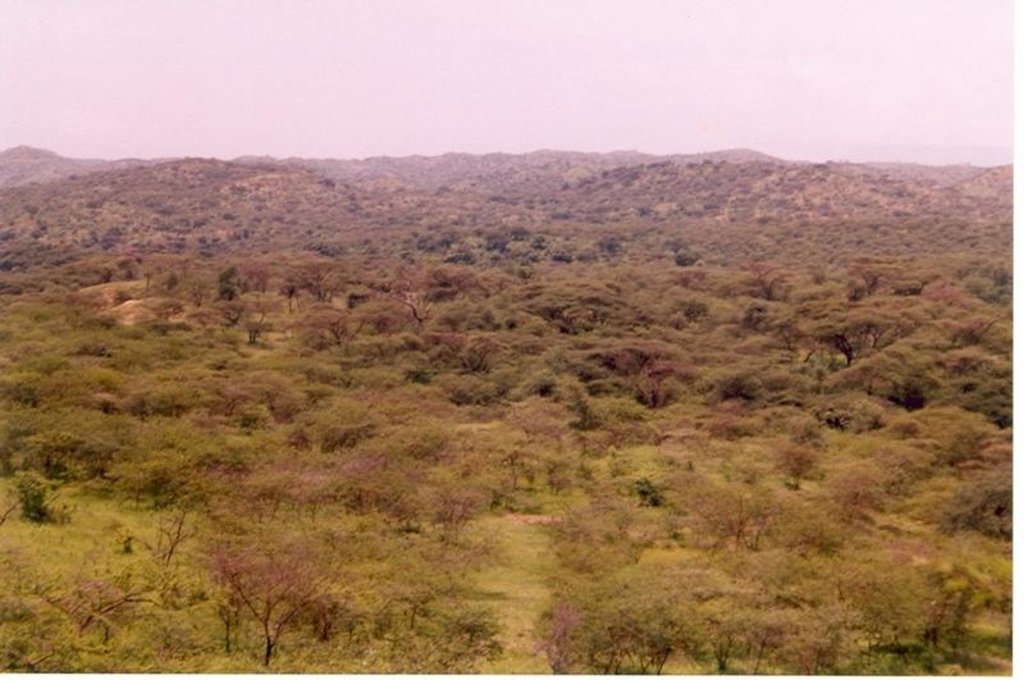
Closure of degraded land is made on land that has lost vegetation cover, has low soil fertility . To speed up the regeneration process applying some SWC activities and enrichment plantation will be necessary.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The degraded land is closed from human and animal interfrances for at least 3-5 years. Inorder to enhance the rehabilitation rate of the degraded land SWC activities, such as terracing, enrichment plantation and oversowing of grass species is considered. These practices enhances growth of natural vegetation and enriches biodiversity.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tigray
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Ahferom
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 54.6 km2.
The bush land are closed and in some areas SWC activities were made and enrichment plantation has been done.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
From churches and other religious areas
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
- Rhodes grass, local grasses
- Acacia saligna, grevellia, schinesmolle
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- free grazing

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, deforestation, degradation, loss of biodiversity, reduction in land productivity
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity and decline of soil fertility.
Other grazingland: free grazing
Other type of forest: area rehabilitation: lack of awarness
Problems / comments regarding forest use: In the closed forests enrichment plantation is undertaken. Individual woodlots are planted at homesteads. Currently individuals considered land less, poor and women are given land from the hillsides to plant and enclose them. The purpose is to enable individuals to generate income from it.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปิดล้อมพื้นที่ (หยุดการใช้ประโยชน์ สนับสนุนการฟื้นฟู)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (wood cutting), overgrazing (trampling, degraded cover-plant), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (heavy rainfalls), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), land policy
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Also: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia saligna, grevellia, schinesmolle
Grass species: Rhodes grass, local grasses
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 5-8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 300
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: area closure
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Birr
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.88
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedling Production | Januray-June |
| 2. | Pitting | May |
| 3. | Planting | Jully |
| 4. | Layout and survey | September |
| 5. | Stone collection | December-may |
| 6. | Foundation excavation and construction | December-may |
| 7. | Awarness creation and site selection | January |
| 8. | Area closed | |
| 9. | Site guard | throughout the year |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 154.0 | 154.0 | 10.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Person days | ha | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 190.5 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 23.81 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting | Jully /yearly |
| 2. | Weeding | end of August /once |
| 3. | Stone collection | July-august/annual |
| 4. | Construction | July-august/annual |
| 5. | Enrichment plantation | July / annual |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 15.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1.88 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
length of structure, site guard/ha, number of seedlings
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
labour, slope
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
650.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1000-2500 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also plateua/plains and hill slopes
Slopes on avereage: Also moderate and steep
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep, deep and very shallow
Soil texture also coarse/light and fine/heavy
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium-good
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Food for work
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cut and carry
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction of grazing land
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Wild life increase. On the other hand this also led to danger of wild life on crops and domestic animals
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
Soil fertility
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
180000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: because the benefits obtained are convincing and many land usrs want to practice it either individually, in groups or at a community level.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Rehabilitating the degraded land |
| Increase grass and fodder for livestock |
| Obtain wood for fuel |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Rehabilitation of the degraded land How can they be sustained / enhanced? Developing bylaws to keep the area and to use benefits out of it |
|
Increase biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enrichment plantation |
|
Decrease soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constructing SWC techniques wherever necessary |
| Increasing feed and forage |
| Habitate for wild animals |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of land use policy | facilitate to develop and implement national policy |
| Lack of awarness | creat awarness of stackholders at various level |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Meret
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Project (LLPPA) [เอธิโอเปีย]
It is a local level participatory planning approach.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล