Rehabilitation of ancient terraces [เปรู]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Andenes / Anchacas / Patapatas
technologies_1506 - เปรู
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Marquina Rodolfo
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo – DESCO
เปรู
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo (DESCO) - เปรู1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [เปรู]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Repair of ancient stone wall bench terraces, and of an associated irrigation and drainage system.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
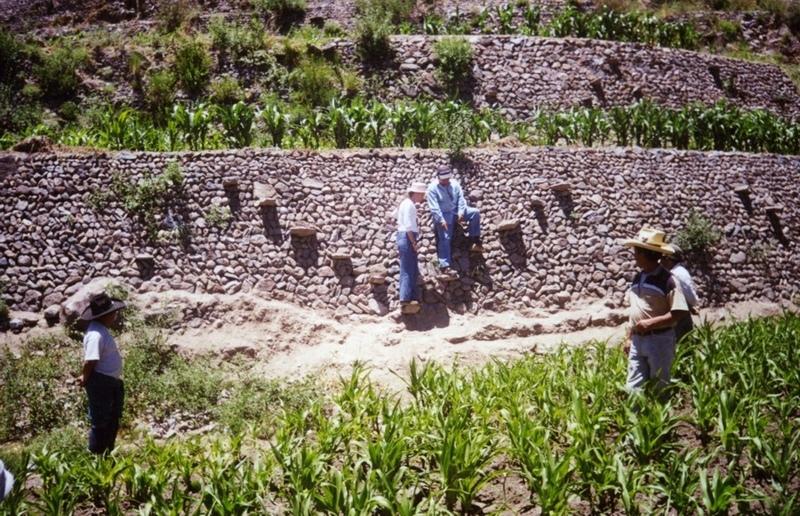
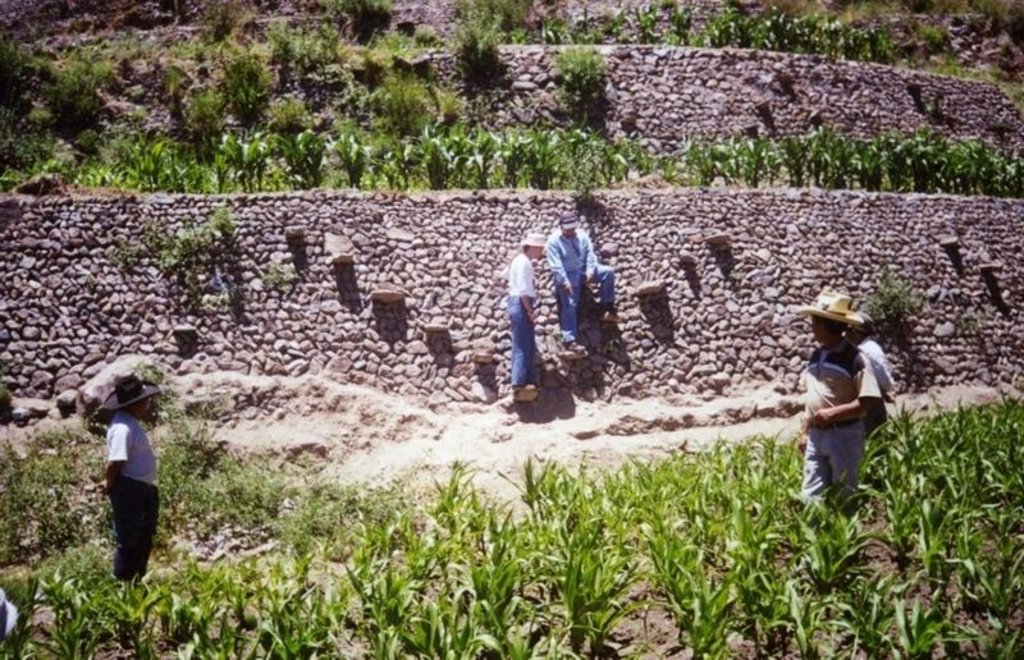
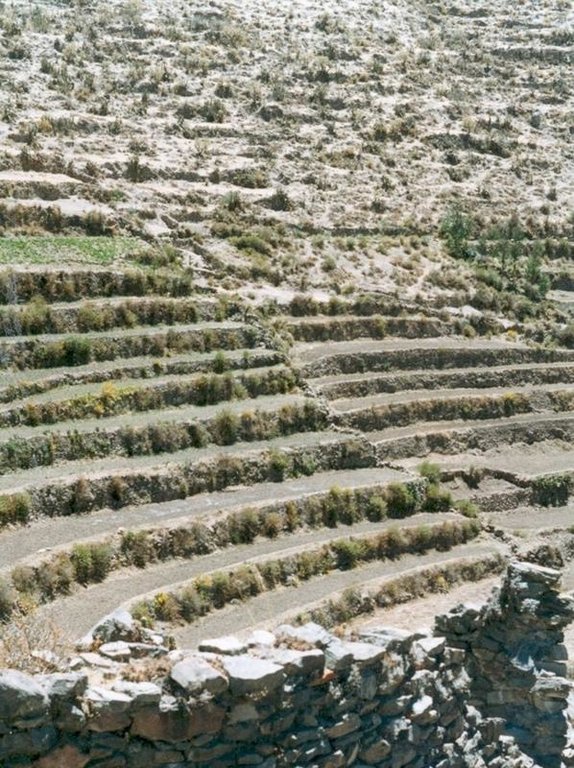
The level bench terrace system in the Colca valley of Peru dates back to 600 years AD. Since then the terraces have been continuously used for crop production, but due to lack of maintenance they have deteriorated, and the population has lost its traditional knowledge of repair.
The rehabilitation of the terraces recreates their original structural design. Broken sections are cleared and the various materials - stones, topsoil, subsoil and weeds - are removed and separated. The foundation is re-established, followed by construction of the stone wall (the ‘riser’). Backfilling with subsoil then takes place; this is consolidated and finally covered with topsoil. Simultaneously the complementary irrigation and drainage systems are reconstructed.
The rehabilitated terraces efficiently conserve soil and water on steep slopes, and they create a favourable microclimate for crops, reducing loss of stored heat at night by minimising air movement (preventing frosts) and mitigating dry conditions through moisture conservation. The main economic benefits are from increased yields and crop diversification.
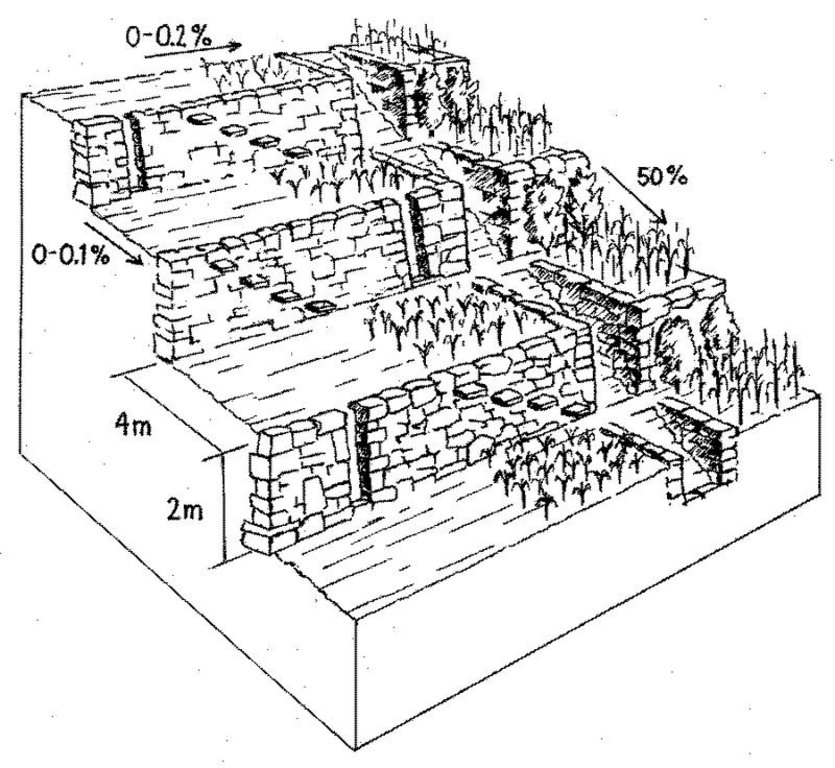
Terraces are spaced and sized according to slope, eg on a 50% slope, terraces are 4 m wide with a 2 m high riser between terrace beds. Stones of ancient terraces had been widely used to build walls for boundary marking after privatisation of land, therefore a large amount of stone had to be provided by splitting rocks and transporting from other locations.
The area is characterised by steep slopes with loamy-sandy, moderately deep soils (on the terrace beds). Most of the annual precipitation (ca. 350 mm) falls within a period of 3 months, which makes irrigation necessary. The farmers in the area own, on average, 1.2 hectares of arable land, divided into around six plots in different agro-ecological zones. Production is mainly for subsistence. Important supportive technologies include agronomic measures such as improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping. Tree and shrub planting at the base of terrace walls is an optional measure with the aim of stabilising the walls, diversifying production and again ensuring a good microclimate. On average 250 trees/ha are planted; these are mainly native species such as c’olle (Buddleia spp.), mutuy (Cassia sp.), molle (Schinus molle: the ‘pepper tree’) and various fruit trees including capulí (Prunus salicifolia).
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เปรู
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Río Colca,Caylloma, Arequipa
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 km2.
Map
×2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- fodder crops - alfalfa
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Major food crop: Potatoes, maize,beans, etc
Main animal species and products: Alfalfa (cut and carry)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - Loss of productive capacity: 30% of the agricultural land lost due to degraded terraces, severe deforestation (through
cutting for fuelwood), overgrazing and burning of grazing areas.
- Inefficient irrigation practices (flooding) due to poor maintenance of irrigation system (and drainage system in poor
condition), flood irrigation leads to deterioration of terraces.
- Loss of traditional knowledge of ancestral crop management practices (abandonment of appropriate rotation practices, lack of residue incorporation/recycling, unsystematic crop layout).
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated and rainfed
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Rehabilitated ancient terraces with high stone risers. Two options for irrigation and drainage of excess water are shown: outlets in the risers (left) and a broad water channel cutting perpendicularly through the terraces (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of microclimate
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
ผู้เขียน:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Separation of materials of collapsed wall: subsoil, topsoil, stone, weeds. | dry period. |
| 2. | Cleaning and re-establishment of the foundation according to originalstructure. | dry period. |
| 3. | Cutting stones from rocks (blasting and splitting); transporting. | dry period. |
| 4. | Reconstruction of the stone wall, building on the basis of remainingintact structures of ancient terraces; simultaneous reconstructionof irrigation channels and complementary structures. | dry period. |
| 5. | Backfilling with subsoil, moistening soil and consolidation with motor | dry period. |
| 6. | Covering with fertile topsoil. | dry period. |
| 7. | Levelling of terrace bed and completion of riser edge (lip). | dry period. |
| 8. | Planting of trees below terrace walls (optional). | dry period. |
| 9. | Improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping (supportivemeasures). | dry period. |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 560.0 | 560.0 | 40.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction supervisor (days) | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 40.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 40.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 40.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1400.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1400.0 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation system cleaning. | |
| 2. | Clearing weeds from stone wall | (dry season)./ |
| 3. | Inspection of the stone walls’ stability | (before sowing)./ |
| 4. | Repair structures | (rainy season)./ |
| 5. | Tree and root pruning. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 125.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 125.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: A-frame,tape measure,motor drill,wheelbarrow,shovel,pick,steel bar,sledgehammer,hoe,hand compressor.
Person days needed for rehabilitation of 1 ha of ancient terrace system depend on degree of deterioration, the dimensions of the wall, slope angle (the steeper the more terraces) and availability of stones. In the case of the project, under a typical situation, for physical rehabilitation of 1 ha with 6 terraces, each ca 600 m long, 3–4 m wide and 2 m high, with one third of the main structures in disrepair, 18 men and 7 women work for 5 days; shrub planting is extra. Land users bear 35% of the overall costs: they also provide food for the group during work. The programme pays the rest. 450 m3 of additional stones are required to repair the broken parts, the cost includes blasting/splitting rocks and transport to the construction site.
Supportive agronomic measures and agricultural inputs (seeds and manure) are not included. Maintenance costs vary considerably, depending on the specific situation: an average is taken here.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and footslopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1, used for maize) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (low recycling of organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Off-farm income specification: main source is wage labour in the valleys
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1) and mixed (ranked 2, 30% for market)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1, complementary to crop production) and commercial/market (ranked 2, income generation to meet basic needs)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Average 30%
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Careful management required (water and livestock)
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Easier crop management (level bench, alignment of crops). On the other hand increased labour constraints: heavy work, const. Maintenance. Heavy work by establishment
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Efficiency
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Efficient use of irrigation water and fertilizers
Input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Tools
Ccarcity of stones (in some places)
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Regular crop growth and development
Improved microclimate
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced wind; conserving heat
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
240
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2160 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
240 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption.
40% of terraces have been rehabilitated in 7 districts (8 micro-watersheds) of the Colca valley.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). |
|
Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification How can they be sustained / enhanced? Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. |
|
Increased yields and food security How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety. |
|
Cultural heritage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation of traditional practices |
| Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc)-->Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). - Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification-->Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. - Increased yields and food security-->Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety Cultural heritage-->Conservation of traditional practices. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Traditional technology is of great value and adapted to local conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness raising of the local population on maintenance of terraces. |
|
Successful implementation is product of evaluation, analysis and documentation of experiences How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further appraisal of the technology. |
|
Soil maintained on steep slopes, no soil loss due to water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and appropriate management through training. |
|
More efficient use of irrigation/rain water, longer storage of soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Permanent maintenance of structure. |
|
Maintenance of soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Recycling of organic matter. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals | Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. |
| Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system | More training on maintenance and conservation. |
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals-->Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. - Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system-->More training on maintenance and conservation. Editors’ comments: Terracing systems on hillsides date back to the beginning of agriculture. Often these feature walls (‘risers’) built of stone, and sometimes they are used for irrigation – as in this case from Peru. While many ancient systems have fallen into disrepair with out-migration of rural populations, this is an example of project-based rehabilitation. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
|
Specialised work, not easy to carry out – complex system of different structures |
Promote applied research and extension. |
|
High rehabilitation costs; increased by loss of traditional forms of reciprocal work, and a trend towards individualism |
Reactivate and strengthen traditional labour systems based on reciprocity and mutual help. |
| Limited availability of stones impedes the rehabilitation process |
Carry stones from adjacent or remote places, give training in rock splitting. |
| Not appropriate for use of agricultural machines | Awareness creation. |
| Private properties, but not titled |
Promote the legalisation of titles to facilitate the access to credit and technical assistance. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mejia Marcacuzco AP Folleto de divulgación: Andenes, construcción y mantenimiento. (undated).
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Treacy, JM (undated) LasChacras de Coporaque: Andenes y riego en el valle del Colca. Instituto de Estudios Peruanos. DESCO
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [เปรู]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล