Semi-circular bunds (for crops and forest/rangeland) [ไนเจอร์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Dieter Nill
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Demi-lunes (French)
technologies_1614 - ไนเจอร์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Sani Mamadou Abdou
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP), Niamey, Niger
ไนเจอร์
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
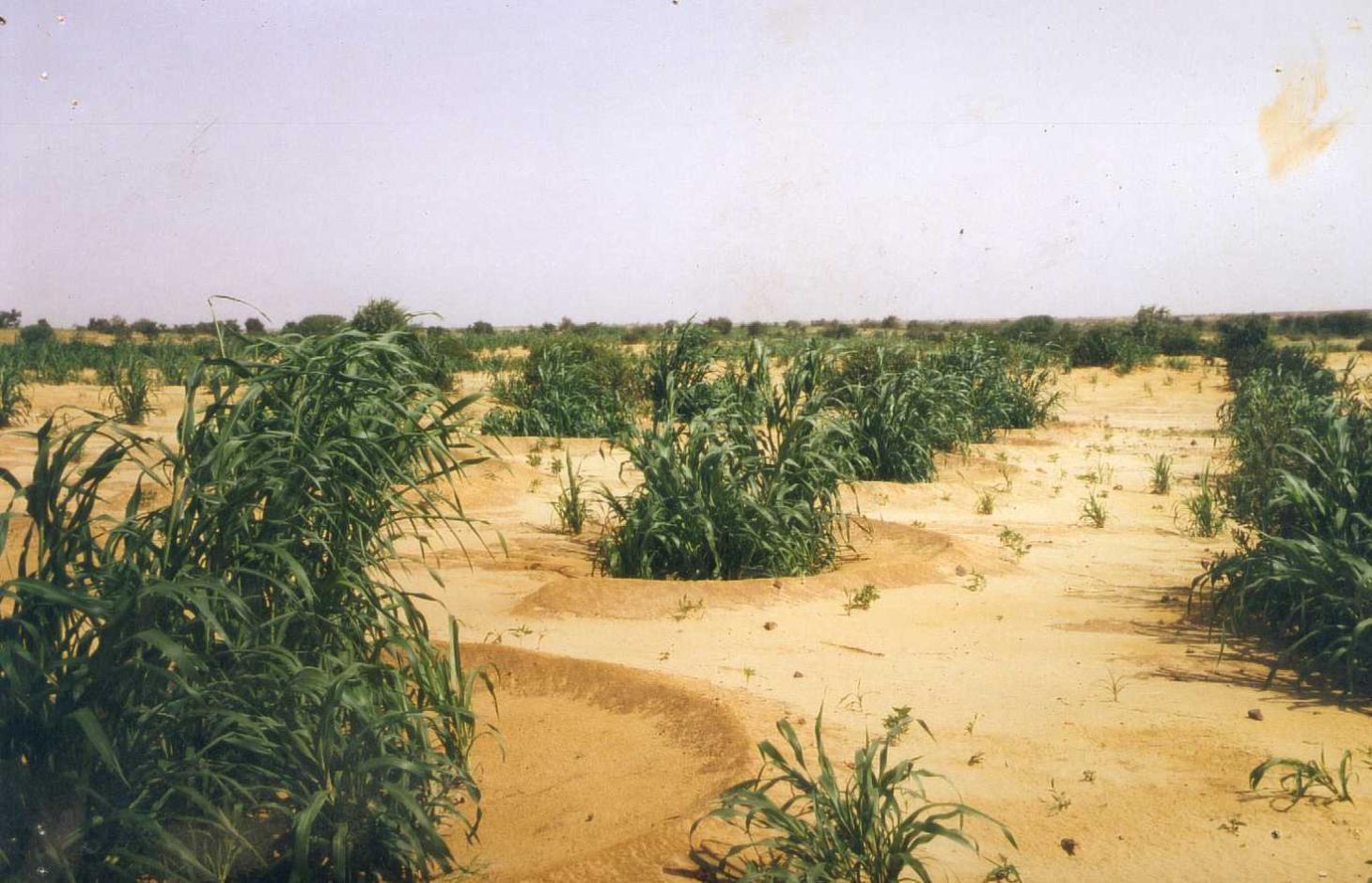
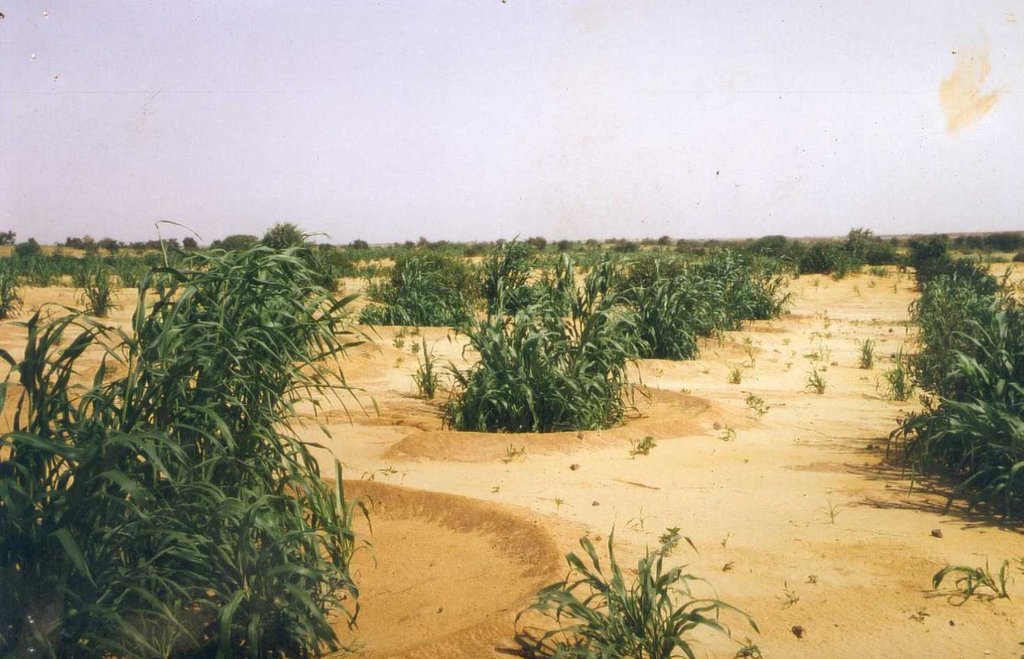
Semi-circular bunds are used to rehabilitate degraded, denuded and hardened land for crop growing, grazing or forestry.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
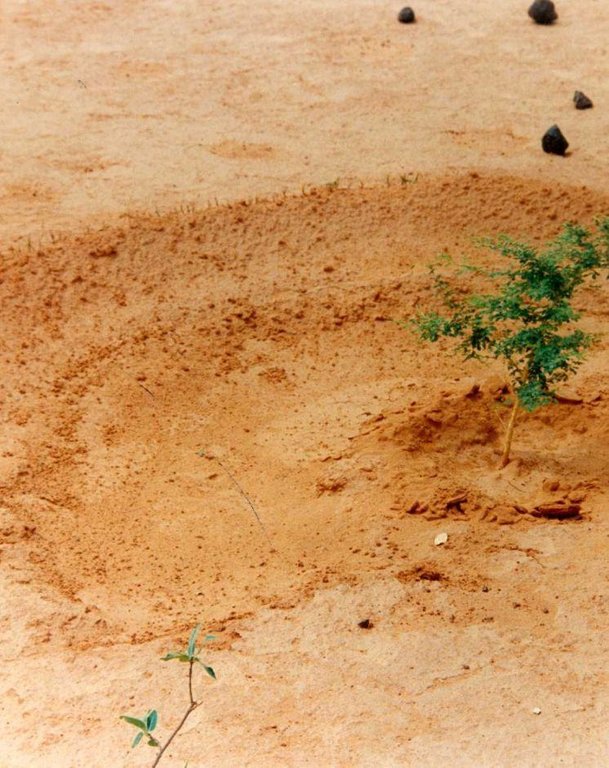
This technique involves building low embankments with compacted earth or stones in the form of a semi-circle with the opening perpendicular to the flow of water and arranged in staggered rows. They are constructed on gently to moderately sloping pediments and plateau areas in order to rehabilitate areas that are degraded, denuded and/or affected by soil crusting.
Depending on their purpose, the areas inside the semi-circular bunds, enriched with organic fertiliser, are used for growing cereals (crop crescents) and for planting trees, bushes and/or grasses (forestry and pastoral crescents). Semi-circular bunds slow down and capture runoff, providing the plants inside them with the water they need. They therefore reduce the loss of water and the fertile layers of the soil. This is particularly advantageous when rain is scarce, as the semi-circular bunds channel water towards the plants, increasing the moisture available to them. In the medium term, rich sediment builds up behind the semi-circular bunds, which helps to protect and restore the land. The bunds ensure that the manure placed around the plants inside them is not washed away by heavy rains, and the ridge of the bund protects young plants from the wind and wind erosion. When they are used for reforestation, they increase the rate of survival of the trees planted in them. Cropland bunds enable crops to survive dry spells. Earthen bunds are not, however, suitable in a scenario with heavy rainfall. They do not allow water to filter through, which can result in the soil inside them becoming waterlogged and the plants being flooded. This can lower yields in the case of crops that do not tolerate excess water. In such conditions, stone bunds are preferable.
To establish semi-circular bunds on cropland, the following activities are required: marking out the contour line, laying out the lines of the semi-circular bunds in staggered rows, digging the microcatchment, forming the ridge downhill of the microcatchment, applying organic fertiliser (around 1 t per ha per year).
To establish semi-circular bunds on forestland the same steps are required, however instead of applying fertilizer, other steps include digging the holes, planting the trees, and sowing grass on the ridges. The earthen ridges around cropland bunds need to be rebuilt each year. It is recommended that the ridges of forest/rangeland bunds be maintained each year and raised if overflowing has occurred. Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. This requires good community organisation. After dry years, forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds may have to be re-sown with grasses and replanted with trees.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events. The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไนเจอร์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Niger, Burkina Faso, Chad
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa in Niger; Bam region in Burkina Faso
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Also implemented in Burkina Faso and Chad
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa in Niger; Bam region in Burkina Faso
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การตัดไม้ที่มีคัดเลือก (Selective felling)
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- การแทะเล็มหญ้า / การเก็บกินหญ้า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): droughts, soil erosion, lack of water, surface runoff, soil crusting, unadapted land use methods, rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land, reduced or abandoned fallow periods, soil erosion, insecure access to land.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing, Improved pasture, agropastolralism
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population, increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed community land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
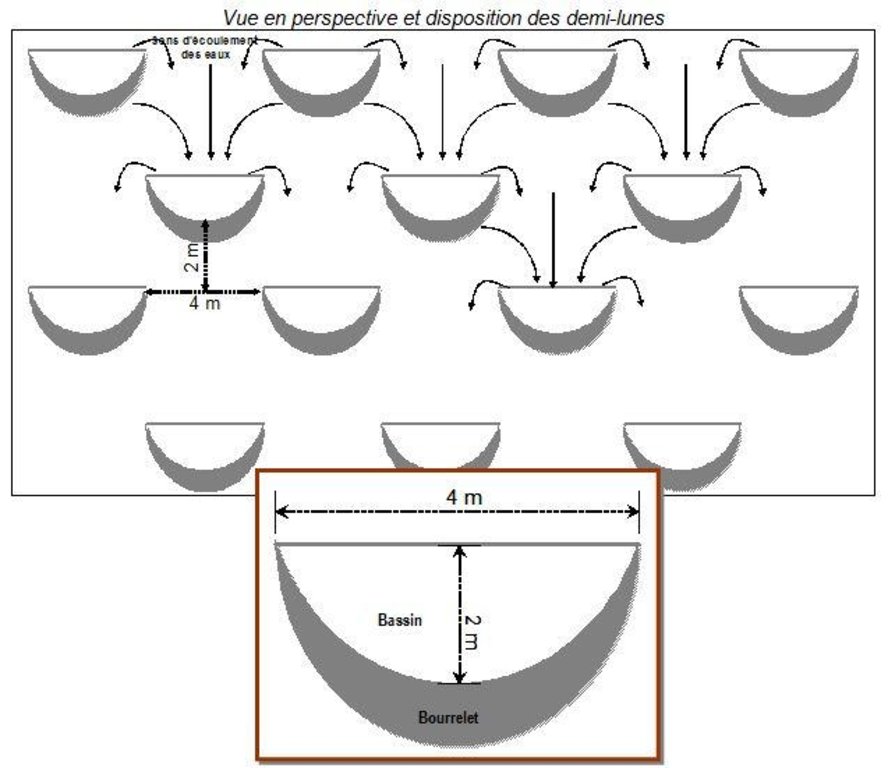
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Source: Ministère du Développement Agricole Niger (without date): Recueil des fiches techniques en gestion des ressources naturelles et de productions agro-sylvo-pastorales.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,15-0,20
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
CFA Franc
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
521.18
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the contour line | |
| 2. | laying out the lines of the semi-circular bunds in stag- gered rows | |
| 3. | digging the microcatchment | |
| 4. | forming the ridge downhill of the microcatchment | |
| 5. | applying organic fertiliser (around 1 t per ha per year) (only on cropland, this step is not required on forestland) | |
| 6. | digging the holes (only on forestland) | |
| 7. | planting the trees (only on forestland) | |
| 8. | sowing grass on the ridges (only on forestland) |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 201.5 | 201.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | tools | ha | 1.0 | 17.3 | 17.3 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 218.8 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.42 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The earthen ridges around cropland bunds need to be rebuilt each year | each year |
| 2. | the ridges of forest/rangeland bunds be maintained each year and raised if overflowing has occurred. | each year |
| 3. | After dry years, forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds may have to be re-sown with grasses and replanted with trees. | after dry years |
| 4. | Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. | in the first two to three years |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
other costs for cropland semi-circular bunds: 10 cartloads of manure.
other costs for forestland semi-circular bunds:
• 625 tree seedlings
• 15 kg of grass seed
• cost of transporting 625 tree seedlings (2 cartloads)
• 120 seedlings to replace trees that die.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
In the case of forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds, the availability of tree and grass seeds and seedlings is a vital factor. In the PDRT and PASP projects in Niger, the villages had nurseries, and members of the village land manage- ment committees collected grass seeds from rangelands to sow in the semi-circular bunds.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seaonally carry out paid farm labour
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
traditional land use rights are prevailing. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cropland bunds constructed on abandoned farmland increase millet yields by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. This requires good community organisation.
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sites improved with semi-circular bunds for reforestation produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
contribution to human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
notably increses production of food, fodder and forest products
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
survival of planted trees
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ทราบ |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Physical structures can be biologically stabilized through planting of grass, bushes or trees. Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. Semi-circular bunds on forest/rangeland can achieve a remarkable regreening of the environment and promote biodiversity. Cropland bunds constructed on abandoned farmland increase millet yields by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year. Sites improved with semi-circular bunds for reforestation produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The techniques were implemented with food for work in the 1990s to 2000. Between 2000 and 2012 the work provided by land users was not compensated. Only small equipment and transportation were provided for free.
40% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support. Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Semi-circular bunds are applied for example in Niger, Burkina Faso, and Chad.
Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Semi-circular bunds slow down runoff and enable the harvested water to be used to good effect. Soil moisture increases and the loss of fertile layers of the soil is reduced. |
| Cropland bunds enable crops to survive dry spells. On abandoned farmland millet yields may increase by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year. |
| Semi-circular bunds on forest/rangeland can achieve a remarkable regreening of the environment and promote biodiversity. When they are used for reforestation, they increase the rate of survival of the trees planted in them. Sites improved with semi-circular bunds produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare. |
| In the medium term, rich sediment builds up behind the semi-circular bunds, which helps to protect and restore the land. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| In the event of heavy runoff, a considerable amount of water accumulates inside the semi-circular bunds, and the ridges must be strong enough to withstand its weight. If the water overflows, it can create gaps in the bunds or cut out channels around the sides of them. | The land must be hoed each year. |
| At some sites, rainwater infiltration increases in the first year after the semi-circular bunds have been constructed, but if the land is not hoed, this effect declines considerably in successive years. | In such conditions, stone bunds are preferable. |
| Earthen bunds are not suitable in a scenario with heavy rainfall. They do not allow water to filter through, which can result in the soil inside them becoming waterlogged and the plants being flooded. This can lower yields in the case of crops that do not tolerate excess water (e.g. millet). | |
| Animal production may be reduced because forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. | |
| Labour-intensive work |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2012
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล