System of rice intensification (SRI) [มาลี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Dieter Nill
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Système de riziculture intensification (French)
technologies_1654 - มาลี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kouyate Djiguiba
IICEM
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Traore Minamba
IICEM
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - เยอรมนีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Intgrated Initiative for Economic Growth in Mali (IICEM) - มาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The objective of a system of rice intensification (SRI) is increased yields.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
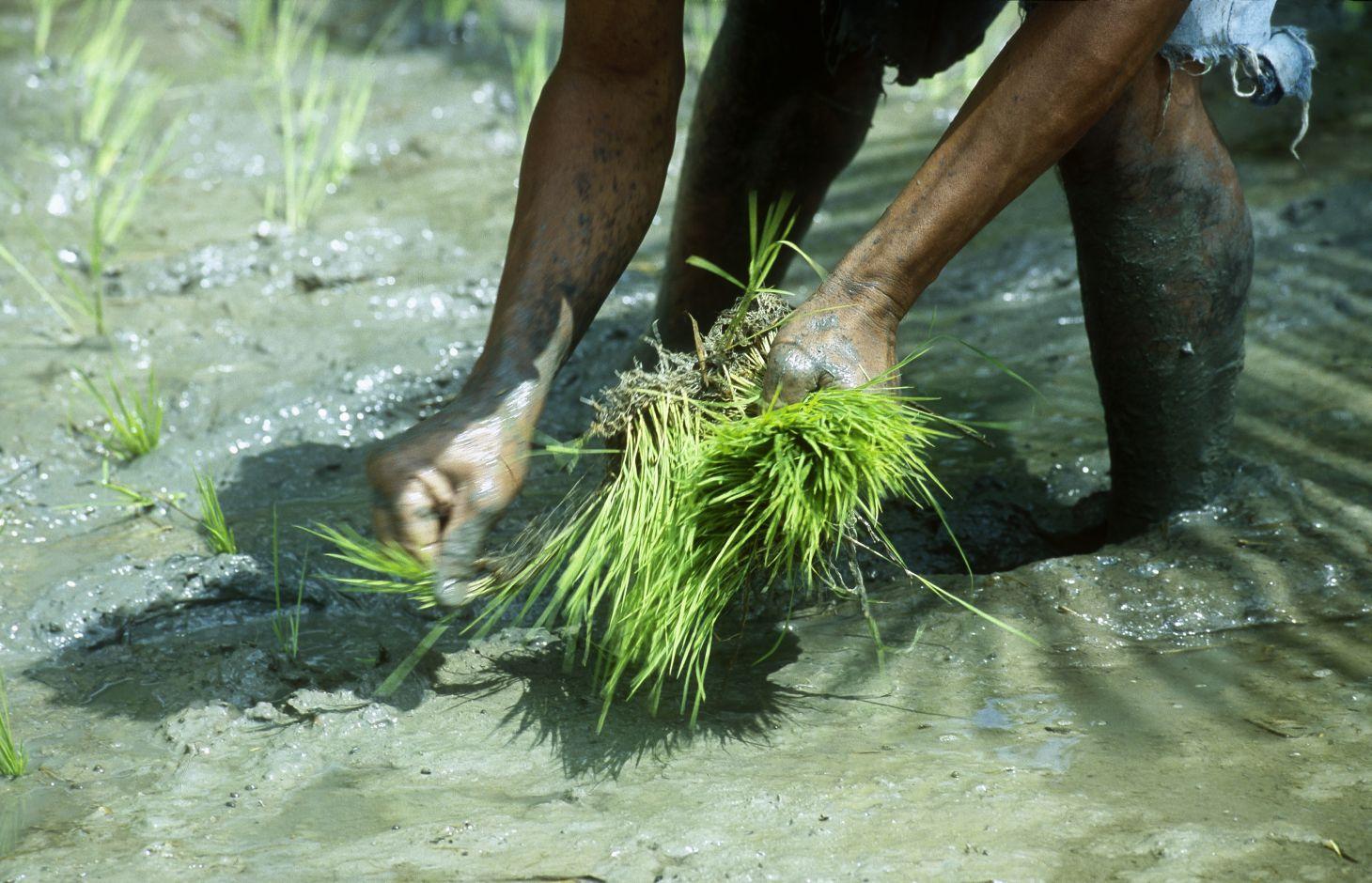
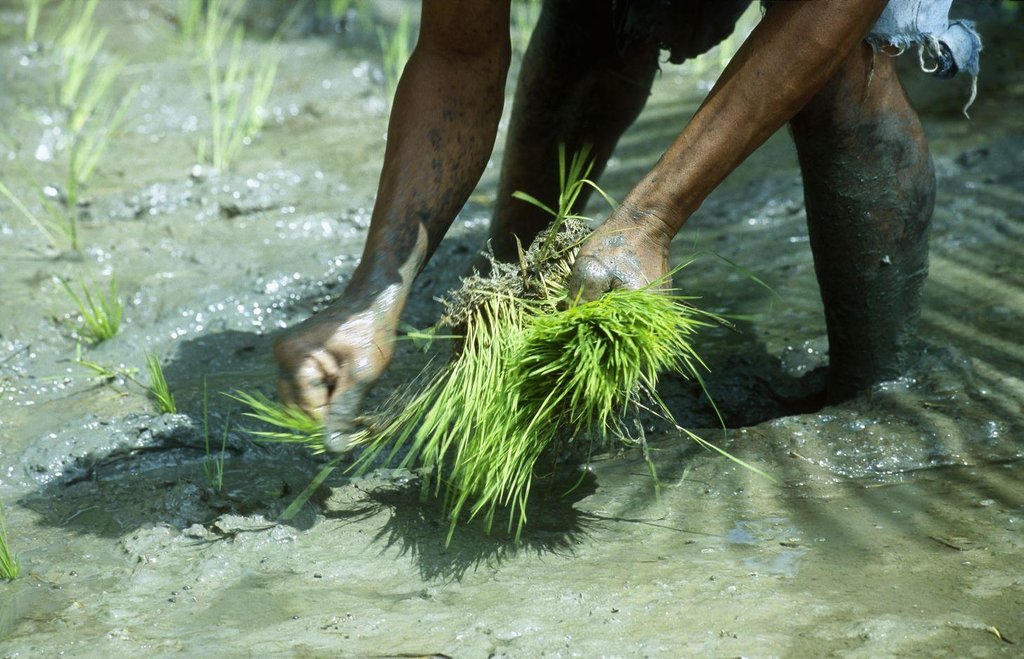
คำอธิบาย:
This can be achieved when rice plants are provided with sufficient air and space for their ripening process. Irrigation water supply requirements are lower, which means the approach can be deployed in low-rainfall areas or the rice growing areas can be extended using the same quantity of water (climate change adaptation). The technique requires less seed and fertiliser.
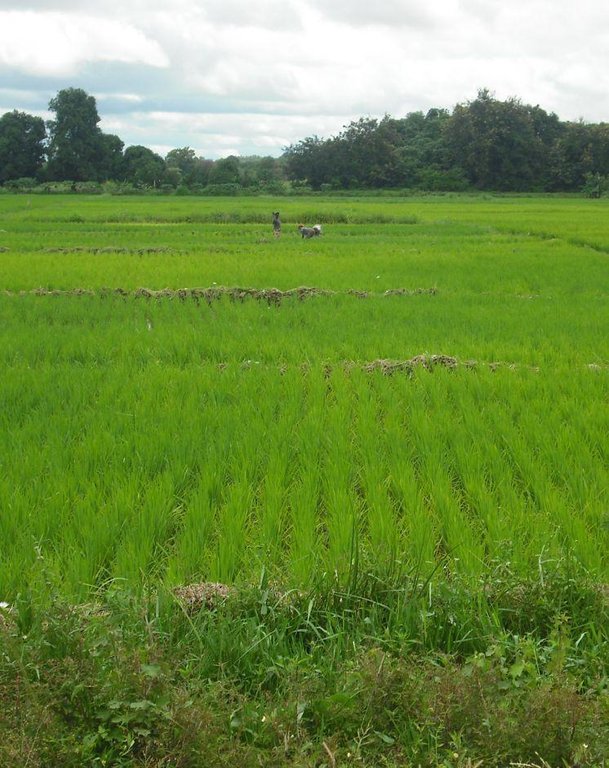
SRI optimises the soil-water-plant relationship. It increases the plants’ potential for production by correcting disadvantageous practices. In practical terms, this involves growing rice on lowlands and plains using fewer seeds (with the rice variety selected according to the water regime) and less fertiliser.
The system of rice intensification proves that rice is not strictly speaking an aquatic crop. Rice growing simply requires a very humid environment. The water level is maintained considerably lower down the rice stalk than it is in traditional rice paddies, where water levels range from 10 to 25 centimetres.
SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days). Growers reduce seed use by 8 to 10 kilograms per hectare. Water use drops by around 35%, given that the rice is not constantly submerged and water levels in the paddy are low.
Implementation: Firstly, the growers are sensitised and informed about the principles and benefits of SRI in terms of yields and production costs, and are given the opportunity to sign up for technical training in SRI. IICEM takes charge of monitoring the proper application of the SRI methods over the
growing season. Seedlings are planted out individually to ensure each plant has sufficient space to grow. The rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier.
Operation: 1) Selecting the most appropriate rice varieties according to the water regime of the area in question (rainfed rice and lowland rice). SRI rice crops adapt well to flood and recession waters, meaning rising and falling water source levels can be managed. 2) Respecting the irrigation cycles developed with the planner: An irrigation cycle is drawn up with a planner. Training is then provided to the growers managing the irrigation system to ensure they adhere strictly to the cycle. It is important for growers in the same hydraulic area to plant out at the same time so their irrigation supply needs correspond. This ensures that the water requirements of the rice crops are met and reduces pumping costs.
Roles of the actors involved: IICEM delivers training to raise awareness about SRI and provide the relevant skills. Conscious of the need to increase yields, IICEM ensures that this learning is applied in the field. Sometimes local NGOs are tasked with providing training and monitoring. Growers apply the SRI approach and monitor inputs and yields so that operations can be effectively evaluated.
The practice was rolled out in the Mopti, Timbuktu and Gao regions of northern Mali and in Sikasso in the south. Two very small-scale rice fields were installed: one in Deibata in Youwarou Circle and one in Mopti. Farmer organisations supported by IICEM are benefiting from the technique. The practice has been carried out since 2009 by IICEM. It was deployed in Madagascar prior to its introduction in Mali.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มาลี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Mali
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao, Sikasso
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The practice was rolled out in the Mopti, Timbuktu and Gao regions of northern Mali and in Sikasso in the south.
Two very small-scale rice fields were installed: one in Deibata in Youwarou Circle and one in Mopti. Farmer organisations supported by IICEM are benefiting from the technique.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - rice (wetland)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August to November
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low rice production, high amount of seeds, fertilizer and water required, high production costs
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, improved plant management, improved water management, increases the plants’ potential for production
Change of land use practices / intensity level: system of rice intensification (SRI)
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
CFA Franc
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Growers are sensitised and informed about the principles and benefits of SRI | |
| 2. | Opportunity to sign up for technical training in SRI | |
| 3. | Selecting rice varieties according to the water regime | |
| 4. | Seedlings are planted out individually to ensure each plant has sufficient space to grow. rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier. | |
| 5. | irrigation cycle is drawn up with a planner |
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Species diversity: medium, low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduced demand for seeds and fertilizer, shorter growing season
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
Contribution to human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days).
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The practice has been carried out since 2009 by IICEM. It was deployed in Madagascar prior to its introduction in Mali. Growers who have been trained in SRI continue using the technique as they value its effects;
namely, achieving higher productivity without incurring excessive costs related to inputs, pump unit consumables, etc.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. |
| It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days). |
| Growers reduce seed use by 8 to 10 kilograms per hectare. |
| Water use drops by around 35%, given that the rice is not constantly submerged and water levels in the paddy are low. |
| Growers who have been trained in SRI continue using the technique as they value its effects; namely, achieving higher productivity without incurring excessive costs related to inputs, pump unit consumables, etc. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
|
SRI growers are strongly advised to use organic fertilisers to supplement soil nutrient levels. Organic fertiliser is not, however, available. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2012
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Farmer Returns to Rice, IICEM
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
IICEM leaflet on SRI
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล