Environmentally-friendly rural practices [มอลโดวา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Valentin Ciubotaru
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Valentin Ciubotaru, UNCCD PRAIS
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Practici rurale prietenoase mediului
technologies_1815 - มอลโดวา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
02/06/2014
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
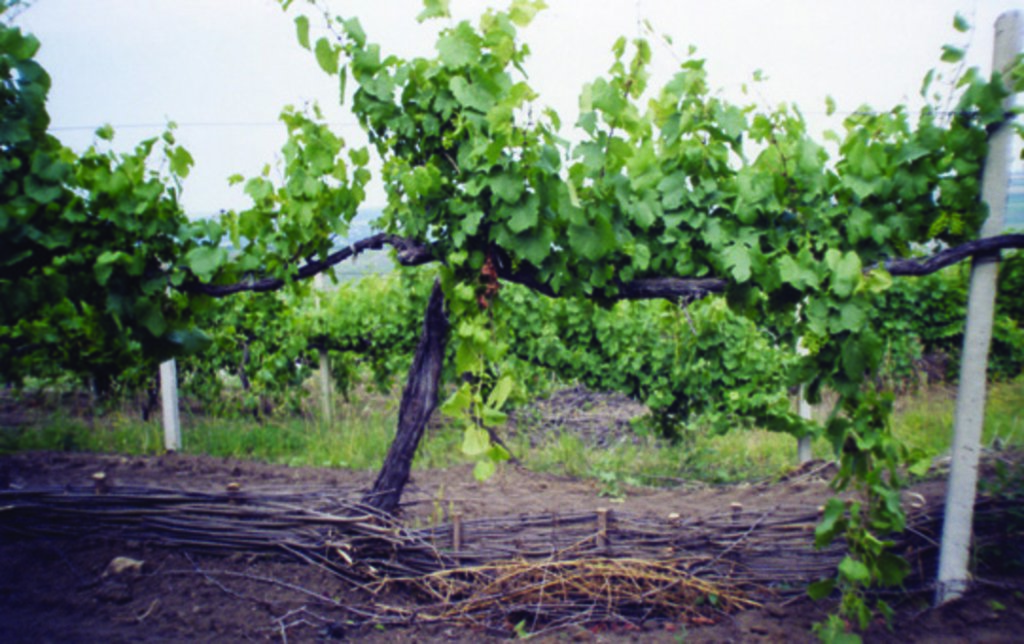
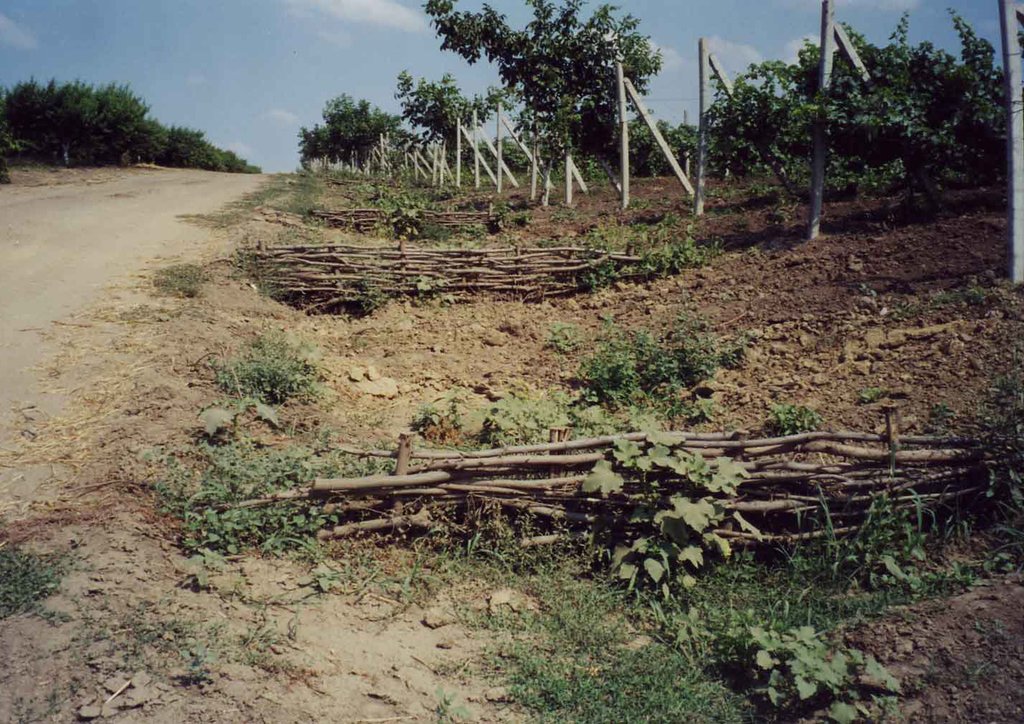
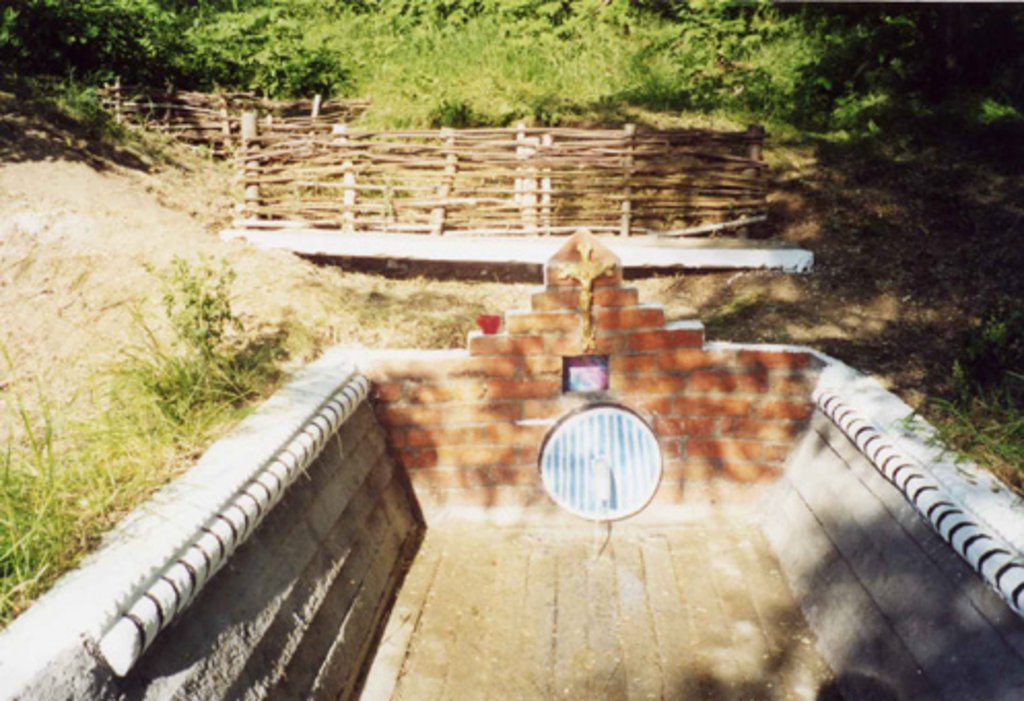
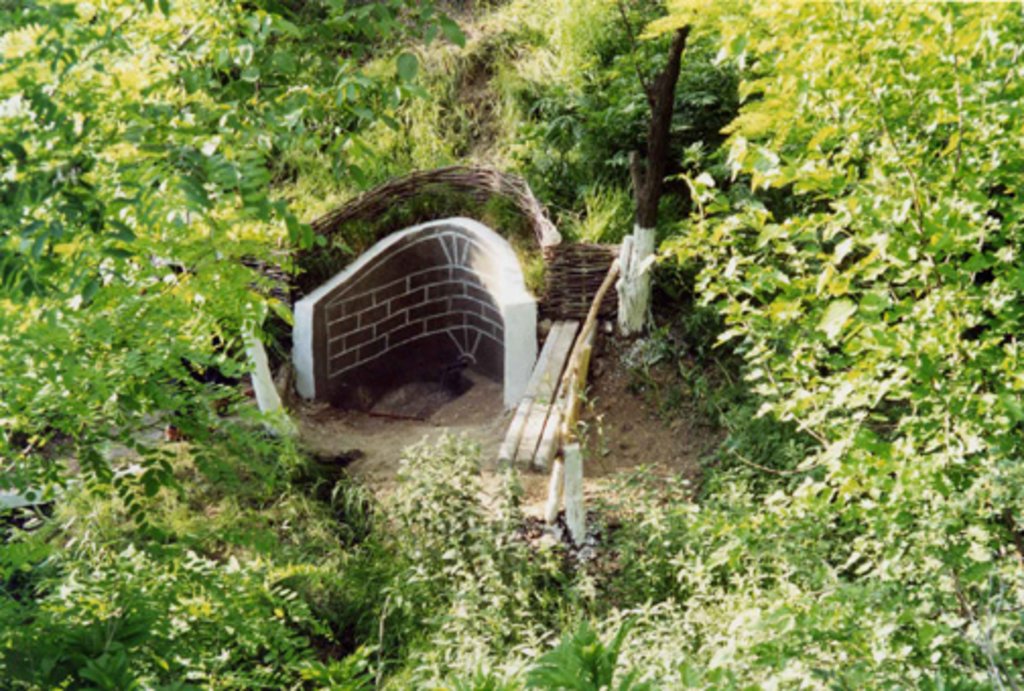
Various environmentally-friendly rural practices have been developed and applied in vineyards and orchards. These included contour tillage, strip cropping and buffer strips, as well as barriers to impede runoff made from straw and brushwood etc. There are also forest belts, channels for water retention and discharge, dams, and grassed waterways; trees are planted on land affected by landslides and soil erosion.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Tartaul de Salcie belongs to the Pri-Danube steppe pedologic region: clay-sandy carbonated chernozem is predominant. Widespread erosion leads to compaction of upper horizons. There is a danger of soil alcalization if irrigated.The landscape is hilly, and very fragmented with a dense network of valleys. Almost 85% of the land is situated on slopes. The climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, and the winters are mild and dry. Annual rainfall ranges around 500 millimetres; long dry spells are not unusual. The sources of income are crops, mainly grapes and walnuts for sale. Vegetables are also grown - for home consumption. People also have cattle and sheep, mainly for consumption. Plots are about 2 to 4 hectares per household, with title deeds and land maps to prove it. The main problem relates to registration and legalization of sale or inheritance of land which is bureaucratized and expensive. Incomes depend closely on the amount of precipitation, and also on market access and prices, but on average, per capita, it is 38 US dollars per month.
Various environmentally-friendly rural practices have been developed and applied in vineyards and orchards. These included contour tillage, strip cropping and buffer strips, as well as barriers to impede runoff made from straw and brushwood etc. Integrated plant protection is carried out, reducing soil and water pollution. There are also forest belts, and trees are planted on land affected by landslides and soil erosion. Cleaning of natural springs is carried out, and their protection is ensured. Forest species trees are planted around homes - and cleaning within around the village is practiced.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://youtu.be/CGgCshNbVkg
วันที่:
02/07/2008
สถานที่:
Tartaul de Salcie village Cahul district, Republic of Moldova
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Viorica Cucereanu
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มอลโดวา
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Tartaul de Salcie village, Cahul district, Republic of Moldova
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2000
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Wheat, maize, sunflower, vineyards, orchards

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้:
- การตัดไม้ที่มีคัดเลือก (Selective felling)
- การเอาไม้ที่ตายแล้วออกไปหรือการตัดแต่งกิ่ง
- การใช้ประโยชน์จากป่า ยกเว้นไม้
ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- การแทะเล็มหญ้า / การเก็บกินหญ้า
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A5: การจัดการเมล็ดพันธุ์ การปรับปรุงพันธุ์

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
- M6: การจัดการของเสีย (การทำ รีไซเคิล การเอากลับมาใช้ใหม่หรือการลดปริมาณ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
- Control of runoff
- Maintain/ increase soil fertility
- Increase/maintain water stored in soil
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Ps (Subsidence of organic soils): การยุบตัวของดินอินทรีย์ การทรุดตัวของดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Development of environmentally friendly rural practices | ด้วยวิธีพืช | After harvest of crops |
| 2. | Public awareness and education | ด้วยวิธีพืช | In winter when farmers have time and during vegetative period - to show the results of the measures |
| 3. | Monitoring and evaluation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | After rainfall and strong winds |
| 4. | Combine income generation with land management | ด้วยวิธีพืช | During establishment and maintenance |
| 5. | Give up unproductive land use practices | ด้วยวิธีพืช | When farmers are convinced about efficiency of tested practices |
| 6. | Development of environmentally friendly rural practices | จัดการพืช | After harvest of crops |
| 7. | Public awareness and education | จัดการพืช | In winter when farmers have time and during vegetative period - to show the results of the actions |
| 8. | Monitoring and evaluation | จัดการพืช | After rainfall and strong winds |
| 9. | Combine income generation with land management | จัดการพืช | During implementation |
| 10. | Give up unproductive land use practices | จัดการพืช | When farmers are convinced about efficiency of tested practices |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Similar activities are performed for structural and management measures
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The project Sustainable Agriculture financed by the Dutch Foundations CORDAID AND NOVIB
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
450.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Cahul
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about 22°C, and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging -2°C. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 500 millimeters; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in summer; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The landscape is hilly, very fragmented with a dense network of valleys. Almost 85% of the land is situated on slopes. About 60% of the land has a gradient from 2 to 6 degree, while 25% of land has an inclination exceeding 6 degrees. Water erosion processes are widespread and quite intense. The predominant length of the hillsides in Tartaul de Salcie is over 1000 m.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Tartaul de Salcie belongs to the Pri-Danube steppe pedologic region. Clay-sandy carbonated chernozem is predominant on the territory of the village.The intensification of the erosion process leads to compaction of the upper horizons. The drainage porosity is high in the weakly and moderately eroded soils, and medium in heavily eroded soils. There is a large impact of erosion on penetrability. There is a danger of soil alkalization if irrigated
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Water mineralization is high: 1 mg/l
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The sources of income are agricultural crops, mainly grapes and walnuts for sale, but also vegetables for home consumption. People also have cattle and sheep in their households, mainly for own consumption and some extra for sale.|
People in the community have land plots of about 2 to 4 hectares per household - which belongs to them - and they have title deeds and land maps to prove it. The main problem relates to registration and legalization of sale or inheritance of land which is bureaucratized and expensive. The principal landowner in the village is the association of shareholders “TarSalAgro”.
Income in the area depends much on the amount of precipitation and also on market access and prices, but on the average for the last 3 years the estimated income per capita per month was 38 US dollars.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- บริษัท
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตไม้
การจัดการที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The forest close to the village (22 ha) was transformed into a recreational site. A lake was built for recreation purposes. Natural springs in the forest were cleaned and arranged. Currently both the local population and the population from neighbouring villages use the forest for recreation.
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved capacities of LPA and school
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SLM knowledge is improved not only among the local population, but also people in the from South region. Students from Comrat University visited several times to view the SLM practices in Tartaul de Salcie.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
While illegal cutting of trees still occurs, people started planting forest species of trees on all spare spaces in the village, which has improved the environment and compensates for earlier loss through tree cutting without replacement planting. |
Community cohesion has improved. People became less isolated through participation in meetings, training events, they exchange opinions more frequently and assist each other. |
Productivity is paramount, since it guarantees future income. For the soil to be productive for many years ahead, sustainable technologies were proposed and implemented. Thus, while the crops have not increased much, the replacement of mineral nutrients with manure diminished expenditures and needs. Changes included a cleaner community area and cleaner households, better use of existing resources, and more attention to hygiene.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Environmentally friendly rural practices implemented in Tartaul de Salcie improved soil properties, water quality, restored forests, planted forest belts, i.e. they create very good conditions for the development of agricultural biodiversity and wild biodiversity in farming landscapes. |
Environmentally friendly rural practices are one of the main sinks of carbon dioxide. Thus, they have a positively impact on climate change mitigation. |
Environmentally friendly rural practices are in harmony with nature and they positively impact on climate change adaptation.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
The area covered is over 1000 ha
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 10-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Reduce soil loss and runoff from the slopes |
| The project used local knowledge and people are happy that their ideas are implemented in their own village. |
| Almost all village the population was involved to some extent in the development and implementation of activities, and they are proud that their village has become better than others, and outsiders come and learn how to improve their own situation. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Show sincere interest in people's life and their problems. Seek expertise among wise village people and encourage them to share it. Accept people as they are and provide assistance for their growth |
| Teach people to save and plan. Advise them that wise investment always pays off. Teach them to invest more in things they treasure most (family, health, land, local forests, etc.). |
| Try out and experiment with new things on a small scale, so that failure does not affect income significantly. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to cover maintenance costs after end of project | Possibility to apply for additional funding to National Environmental Fund and to motivate the private sector to cover better the respective expenses. |
| Lack of interest of new LPA to continue to implement the SLM practices on communal land. | Awareness building workshops with farmers who implement SLM practices. |
| Lack of substantial difference in profit. | Although there is a small difference in the short term, nevertheless the soil quality and water storage capacity will be improved, and as a result, the yields and profits will be increased in the long term. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
10
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
4
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Making a Difference. Secretariat of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.recoveryplatform.org/assets/submissions/200909020934_recovery_from_desertification.pdf
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Elena Bivol, Valentin Ciubotaru. Farmer’s Book (Cartea fermierului)/ NGO BIOS, Chisinau, 2005, 264 p. ISBN: 978-9975-9901-4-1
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
NGO BIOS. 72/3 Columna str. # 3, Chisinau, MD-2001, Republic of Moldova
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล