Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Supplemental Irrigation Purpose in Dry Season [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kabita Nhemhafuki
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Isabelle Providoli
Mato, Baluwa ra Cement bata Nirmit Sinchai Pokhari - Nepali
technologies_5684 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Shah Ram Deo
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED)
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Gautam Laxmi
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
K.C Prashuram
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Neupane Kumar
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Adhikari Apsara
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Shrestha Jay Ram
เนปาล
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Resilient Mountain Solutions Initiative, ICIMOD (RMS initiative)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
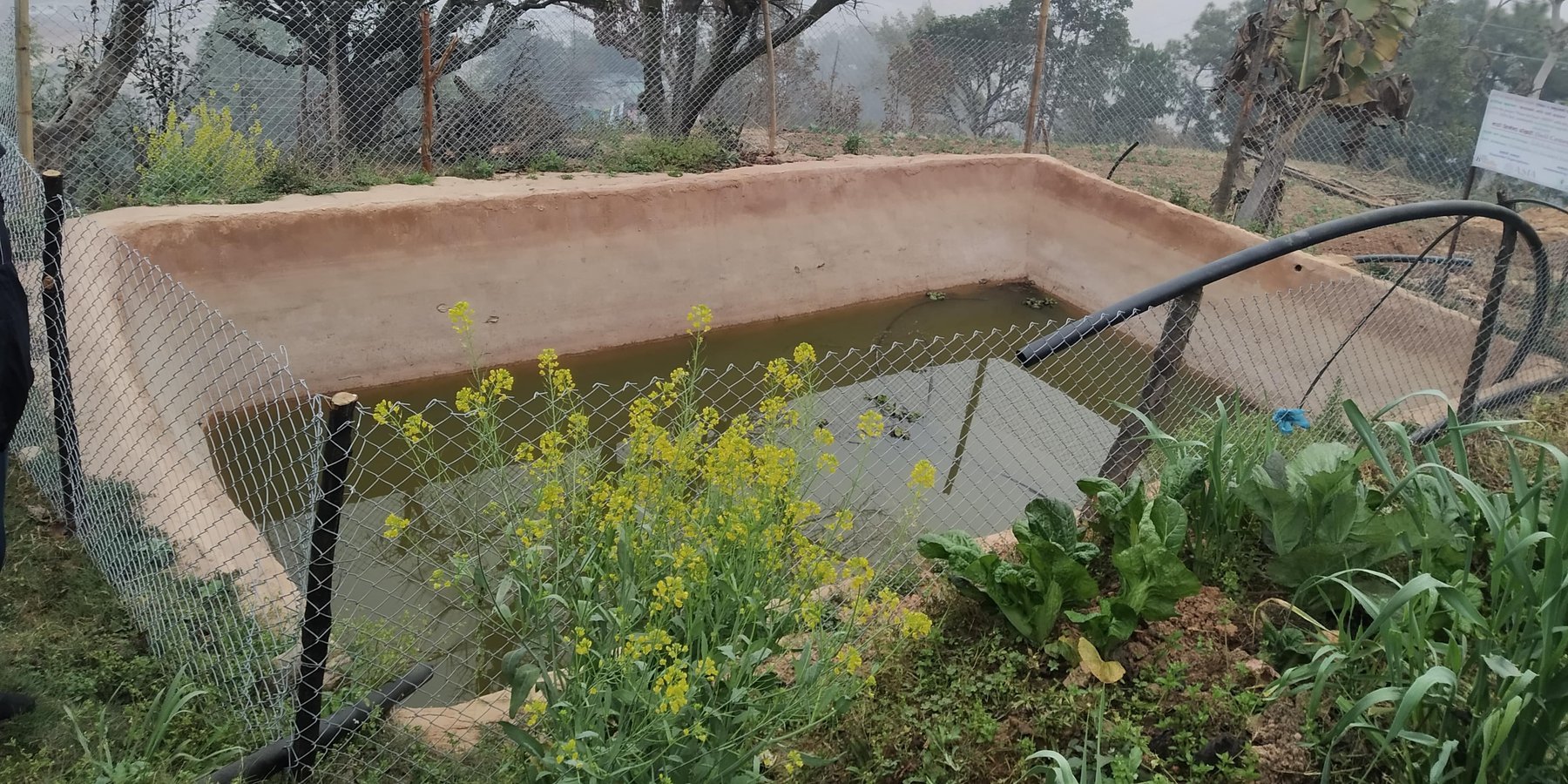
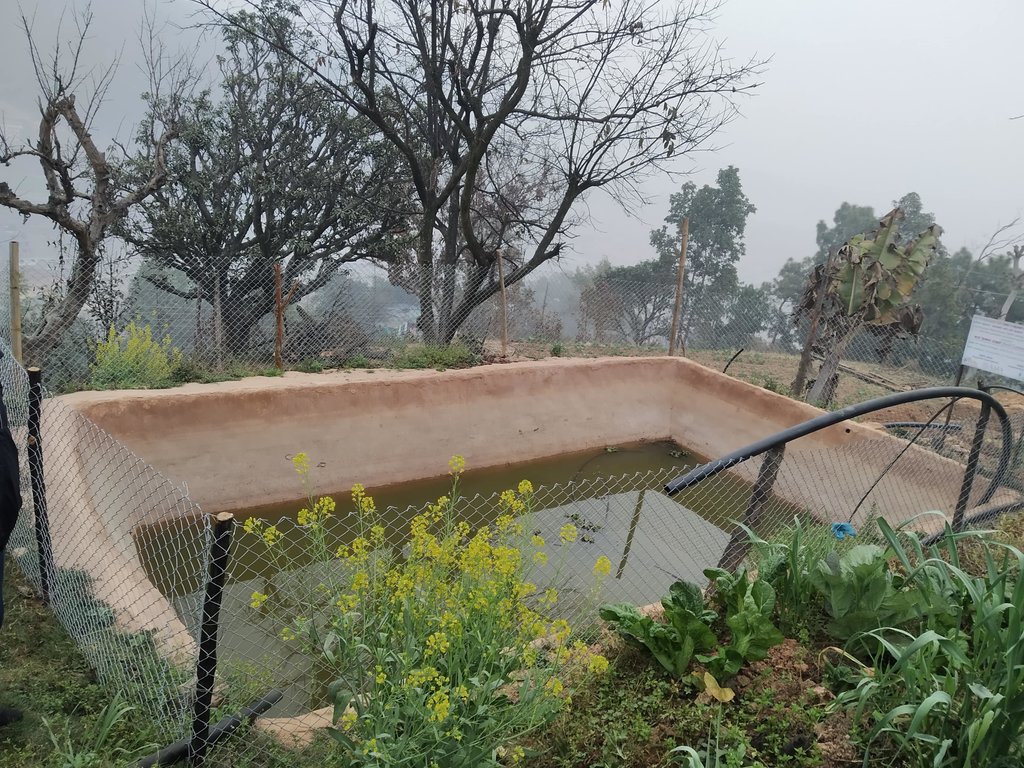
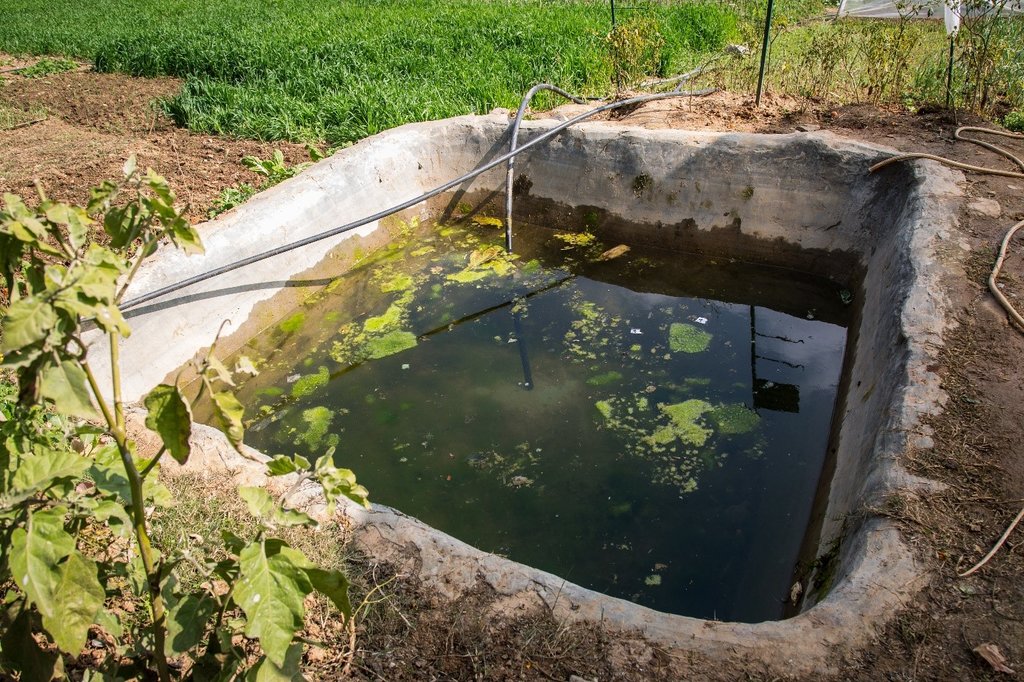
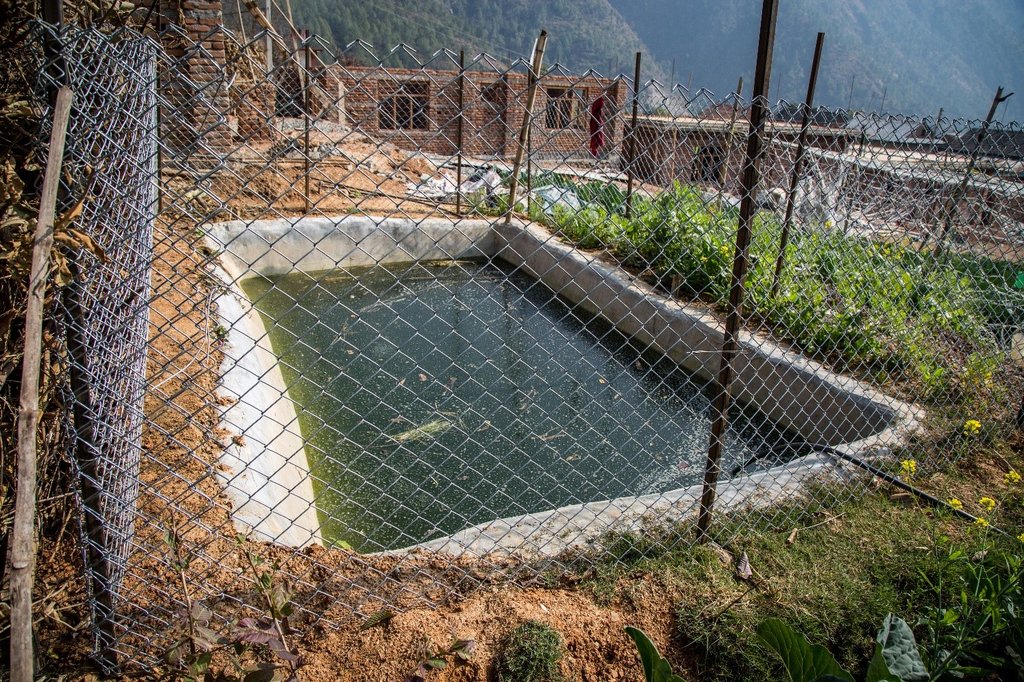
A soil cement water collection pond to store rainwater, runoff and household kitchen waste water free from soap and detergent for supplemental irrigation purpose during dry seasons.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
In Nepal's mid-hills mountain farmers face problems during dry seasons to irrigate their fields, as they entirely depend on rain- water. Soil cement water collection pond are ideal to tackle this challenge, as they can capture excess rainfall during monsoon, which is later available during prolonged seasonal water shortage.
The Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project of ICIMOD together with its local partner, CEAPRED tested and demonstrated soil cement ponds with a capacity of 24000 liters. The conservation ponds were used for irrigating high value off-season horticultural crops (vegetables, fruit, and spices). These crops were irrigated with drip irrigation and micro sprinklers. The ponds were fed from rainwater, upland springs and taps, and household wastewater from kitchen free from soap and detergent. They were established during the dry season during 3 months. They were prepared by selecting a suitable site with a sufficient catchment; mapping out the area and depth of the pond; digging out the soil; removing protruding stones and roots; and compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond. Then gravel and pebbles were used for the base and the floor and side walls were leveled off. Initial mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1) was applied to roughly plaster all the side walls and gravel was mixed in the mixture while plastering the floor. The following day, the roughly plastered pond was watered and was covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This was continued for 3-4 days. Then again a second mixture of soil, sand and cement (2:2:1) was applied to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. The pond was watered for the next 3-4 days and was covered with wet jute sacks. Around 4-5 days after the second plaster, the pond was filled with water. For safety, pond was enclosed with a gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using any locally available material). The total establishment cost for a soil cement pond with 24000 liters capacity was USD 311.
The main maintenance activity was to maintain the gabion wire/bamboo fence to prevent livestock and people from entering the pond, and to remove the sediment that accumulates in the pond. The sediment has to be removed once a year carefully by hand and if cracks occur, it should be sealed with a mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1). The total annual maintenance cost for 24000 liters soil cement tank was USD 68.
This technology has somehow helped small-land holding farmers to irrigate their rain-fed land during dry months which has increased the crop production and their income as well.
Land user's particularly liked that their production increased and that they were able to grow up to three crops per year. Trough this the farmers were able to diversify their crops, and they were less vulnerable to the dry season. In addition, soil cement water ponds are more efficient than plastic-lined conservation ponds which are easily damaged by rats. Although cost effective, the fixed price for this technology is quite high, particularly for smallholder farmers. To lessen this financial burden, local governments can provide subsidies to women and marginalized groups interested in this technology. Self-help groups with a revolving grants system would help expand the use of these ponds and ensure sustained use across Nepal.
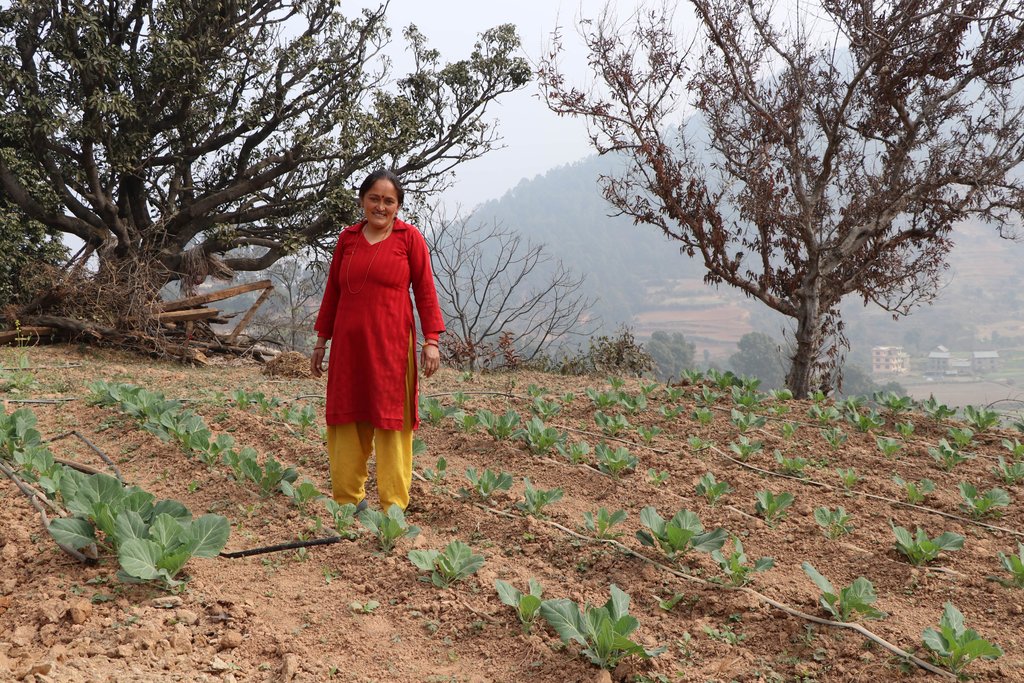
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
Size of soil cement pond depends upon the area of land to be irrigated.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Province no: 3
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk District, Nepal
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
ICIMOD demonstrated this technology through the program of Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) with the help of its implementing local partner, The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) in its pilot project sites in Kavrepalanchok district.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- Improve water availability during dry seasons
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rice (upland)
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- seed crops - sesame, poppy, mustard, other
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 3
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Tomato and raddish
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
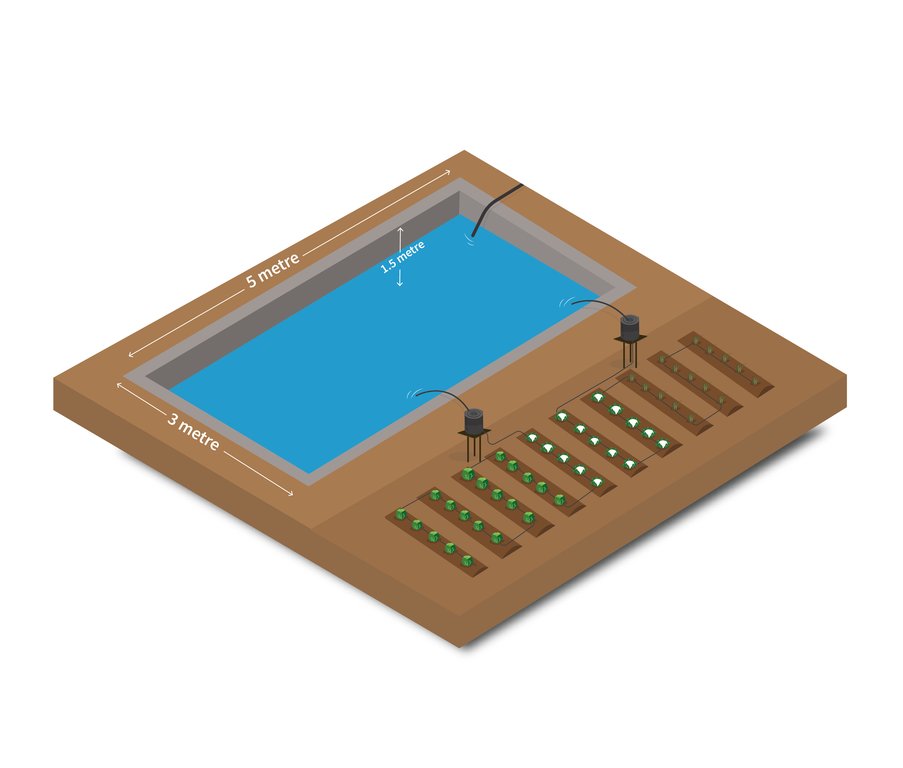
Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Irrigation Purpose in Dry Seasons
Location: Charange fedi, 03, Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5
Capacity of the tank= 24000 litres.
Construction material (earth): Clay
Construction material (other): Cement, sand and water-proofing liquid
ผู้เขียน:
Kabita Nhemhafuki, Ram Dev Shah
วันที่:
01/12/2020
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
0.0024 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 10000 square metres
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.68
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a preferably stable ground with a sufficient catchment area | dry months |
| 2. | Measure the area to be irrigated and estimate the size of the pond | dry months |
| 3. | Measure and mark out the pond | 1st day |
| 4. | Dig out the soil to the pre-determined depth and remove protruding stones and roots | 1st day |
| 5. | Compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond | 2nd day |
| 6. | Apply initial mixture of soil, sand, cement (3:3:1) to roughly plaster all the the side walls and mix gravel in the mixture while plastering the floor. | 2nd day |
| 7. | The following day, the roughly plastered pond should be watered and covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This should be continued for 3-4 days. | 3rd day |
| 8. | Apply a second mixture of soil, sand, and cement (2:2:1) to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. | 5th day |
| 9. | Water the pond for the next 3-4 days and cover with wet jute sack. | 8th day |
| 10. | Around 4-5 days of second plaster, fill the pond with water. | 13th day |
| 11. | For safety, the pond can be enclosed with gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using other locally available materials) | 14th day |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Dig out pond | persons/unit | 7.0 | 5.68 | 39.76 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Stone soiling | persons/unit | 1.0 | 8.74 | 8.74 | |
| แรงงาน | Cementing | persons/unit | 10.0 | 8.74 | 87.4 | |
| แรงงาน | Wiring | persons/unit | 2.0 | 8.74 | 17.48 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | piece | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Measuring tape | piece | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Shovel | piece | 3.0 | 7.0 | 21.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hammer | piece | 3.0 | 4.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Cement mixing iron pan | piece | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Trowel | piece | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Sand | bags | 24.0 | 0.87 | 20.88 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Cement | bags | 6.0 | 7.43 | 44.58 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Water proofing liquid | bottle | 1.0 | 2.62 | 2.62 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gabion wire sheets | sq.ft | 120.0 | 0.31 | 37.2 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 311.66 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 311.66 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) covered the remaining cost
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintain and repair wire fence to prevent livestock and humans from entering the pond | once in a year |
| 2. | Removing accumulated sediment once a year carefully by hand | dry months/once in a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Clean and maintaining the pond | persons/unit | 3.0 | 5.68 | 17.04 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Maintain and repair wire fence | persons/unit | 2.0 | 7.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gabion wire | sq.ft | 120.0 | 0.31 | 37.2 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 68.24 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 68.24 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost given above is for unit technology having 24000 liters capacity as in 2020.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Cost of cement and sand
Members of a household contributed as labour in all sites.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
1584.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Water source is mainly spring.
More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: spring
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Nepal harbors 3.2 % and 1.1 % world's known flora and fauna respectively despite occupying only 0.1 % of global area. Particularly, beta diversity is high in Nepal (BCN and DNPWC, 2011).
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 154 - 453 persons per km2 ( Census, 2011)
Annual population growth : 2% - 3%
Among 100% land users, 80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (ranked by land users). 20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification:
Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages.
Due to loss of farmland and increasing urbanization and loss of farmlands many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns.
The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi.
Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Vegetables- commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labor consists of planting, irrigation , harvesting, while field preparation is carried out by animals, also machines but just in valley bottom.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
Waste management:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Health facilities: There are nine health facilities centre in Namobuddha municipality, Kavre. The main health facilities are Methinkot Hospital, which is a 15-bed district level government hospital, and Dapcha Health Center, which is run by Kathmandu.
Education: There are eight academic institutes for higher studies ( higher secondary schools and colleges). The main academic institutes are:
Dapcha Krishna
Multiple Campus (community), Dapcha;
Janahit Secondary School (public), Khanalthok
Janak Multiple Campus (community), Methinkot
Janak Secondary School (public), Methinkot
Kanpur Campus(community), Kanpur and
Kanpur Secondary School
(public), Kanpur.
Employment ( off-farm): Due to loss of farmlands and increasing urbanization, many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns. The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi. Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Market: Bhakundebesi is the emerging marketplace due to its strategic location in the middle of the municipality astrid the BP Highway. Most local business activities in the municipality take place in Bhakundebesi bazaar. It is a major place for local people to purchase consumer goods.
Energy
Cooking fuel:
In 2011, 88% of households mainly used firewood for cooking, followed by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) (4.92%). In Puranogaun Dapcha, almost all households (99.8%) relied on firewood for cooking. LPG was relatively popular in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (10.3%) and Khanalthok (11.5%). Less than 6% of households used biogas for cooking, with its use relatively high in Mathurapati Fulbari (19.3%) and Methinkot (15.9%) (CBS, 2011).
Lighting :
93% of households used electricity for lighting while 5% depended on kerosene. Dependency on kerosene was relatively high in Khanalthok (8.1%) and Methinkot (7.4%). There was little solar lighting except for in Khanalthok where 3% of households relied on it (CBS, 2011).
Roads and Transportation:
Namobuddha Municipality is easily accessible by motorable road from neighboring areas via the BP Highway, which splits the municipality into almost two equal halves . The highway, which runs from Banepa to Bardibas in the Terai, is the shortest route from the Kathmandu Valley to the eastern hills and Terai. The limited width of the road and its sharp bends mean that public transportation along the BP Highway is mostly by small buses and jeeps.
Drinking water and Sanitation:
In 2011, about 60% of households had access to taps or piped water with accessibility varying across the municipality. While about 80% of PuranogauDapcha households had taps or piped water, only 37.5% of households in Simalchour Syampati enjoyed such services. Other sources of drinking water were covered wells (12.3%), uncovered wells (20.2%) and water spouts (6.3%). Methinkot (40.8%) and Simalchour Syampati (31.4%) residents were most reliant on uncovered wells. Covered wells served sizeable household populations in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (35.3%) and Simalchour Syampati (23%) (CBS, 2011).
Toilet facilities: In 2011, about 63% of households had accessto toilet facilities, with about 40% overall having flushtoilets. The least toilet coverage was in Kanpur Kalapaniand Simalchour Syampati VDCs where 63% and 58% ofhouseholds respectively did not have their own toilets. Almost all households in Puranogaun Dapcha had their own toilets, mostly flush toilets (CBS, 2011).
Waste Management: – Namobuddha is in the early phase of urbanization with no systematic waste management.The Municipality Office is searching for a landfill site.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before they used to plant only one crop per year but now due to adoption of this technology, crop production has increased as they plant three crops per year.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop quality has become good due to availability of more water for irrigation and integration of this technology with bio-pesticide jholmol and mulching.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to availability of water for irrigation, farmers have turned many fallow land into agricultural land.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water needed for irrigation has increased as all the waste water from households, rainwater and taps waters are stored in this tank for irrigation in dry seasons.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Irrigation water availability has increased crop production in turn farmer income has increased by selling those crops in market.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers are becoming more self sufficient due to high production of crops.
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to informal network of farmers with pond has strengthened community institutions.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers share their knowledge and experiences with each other and discuss on how they can overcome the challenges they have been facing recently.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to availability of more irrigation water.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Most of the fallow land are turned into crop land.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to trapped runoff
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ) อื่น ๆ
| อื่น ๆ (ระบุ) | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร |
|---|---|
| reducing growing period | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Till now 24 land user families of Namobuddha Municipality have adopted this technology.
Among 24 land user families, 18 have adopted this technology with external material support through Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project and 6 land users families have adopted this technology without any external support.
Comments on spontaneous adoption (Through survey results) : There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the technology because this technology is quiet expensive, compared to plastic- lined conservation pond.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Water stored in this tank is sufficient to irrigate 2-3 ropani (1 ropani = 508 sq.m.) land in one season. |
| This technology can be enhanced by sharing the advantages of this technology with large number of people. |
| It is more sustainable and efficient than plastic-lined conservation pond. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Good income can be achieved even from a small piece of land by sales of vegetables in the dry season . |
| These ponds are fed with rainwater and household kitchen wastewater free from soap and detergent and from springs and taps. The pond water was mainly used for micro irrigation including drip irrigation and micro-sprinkler. |
| It helps to promote the use of other water conserving techniques like mulching when using the harvested water. |
| It has reduced the dependence on large scale water supply schemes. |
| How can they be sustained / enhanced? Harvest all possible sources of water. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil cement tank is expensive for poor farmers. | Subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| It is unsafe for small children. | Protection structures should be constructed. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Cement and sand rate is very expensive for poor farmers. | Make it available in the local market at a subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| The ponds attract insects, mainly mosquitoes, that cause disease; and the ponds are unsafe for small children. | Regularly clean the pond and fence them. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
6
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
5
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
1
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
2
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
20/02/2020
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
ICIMOD (2018) Building Mountain Resilience: Solutions from the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
ICIMOD
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SCWMC (2004) Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Measures and Low Cost Techniques. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Component - Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
DSCWM, Kathmandu
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Namobuddha Municipality, Nepal Situation Analysis for Green Municipal Development, 2018
URL:
https://gggi.org/site/assets/uploads/2018/07/GGGI_GMD-Assessment_Namobuddha.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Farmers in Kavre reaping benefits from soil cement tanks, 2021
URL:
https://www.icimod.org/article/farmers-in-kavre-reaping-the-benefits-of-soil-cement-tanks/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล