Terraces with improved seed and fertilizer application [อัฟกานิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Bettina Wolfgramm
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano
Palbandi bo tukhmihoi behbudyofta va kud
technologies_607 - อัฟกานิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
อัฟกานิสถาน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Researcher:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [อัฟกานิสถาน]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Bettina Wolfgramm
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
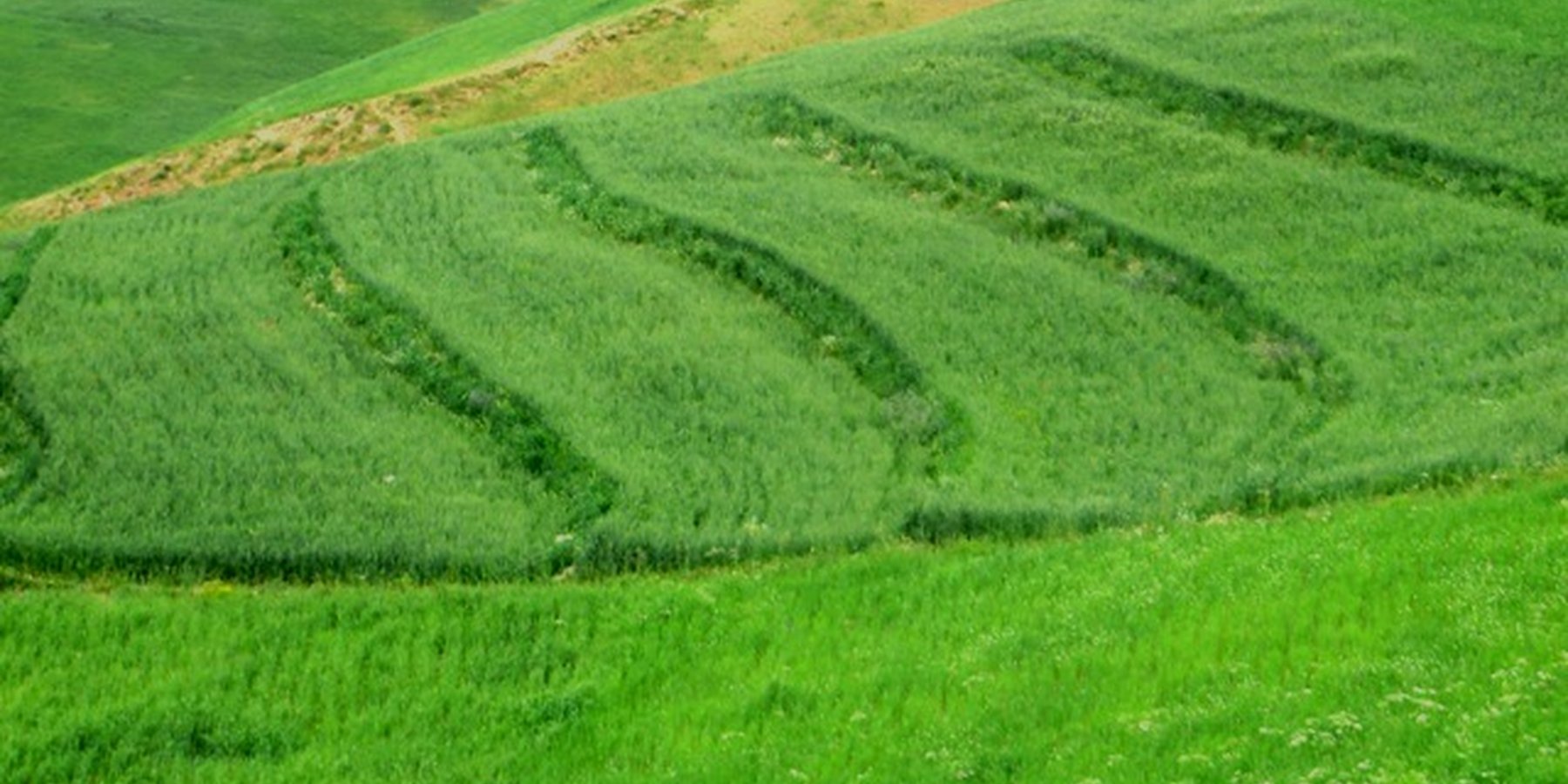
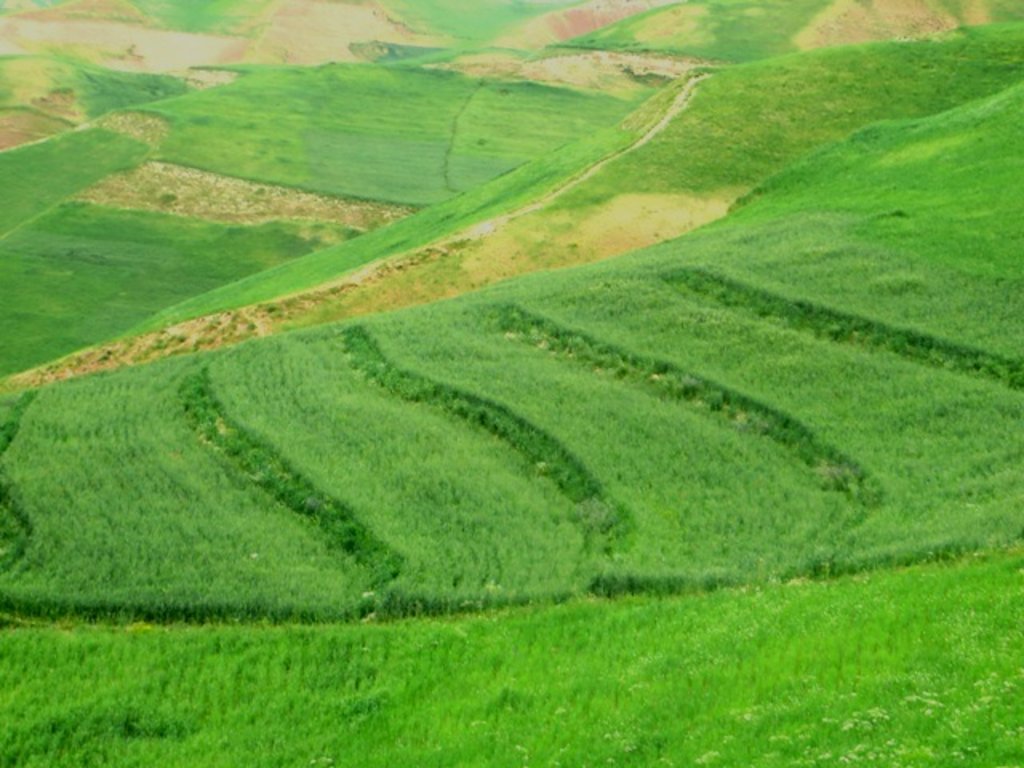
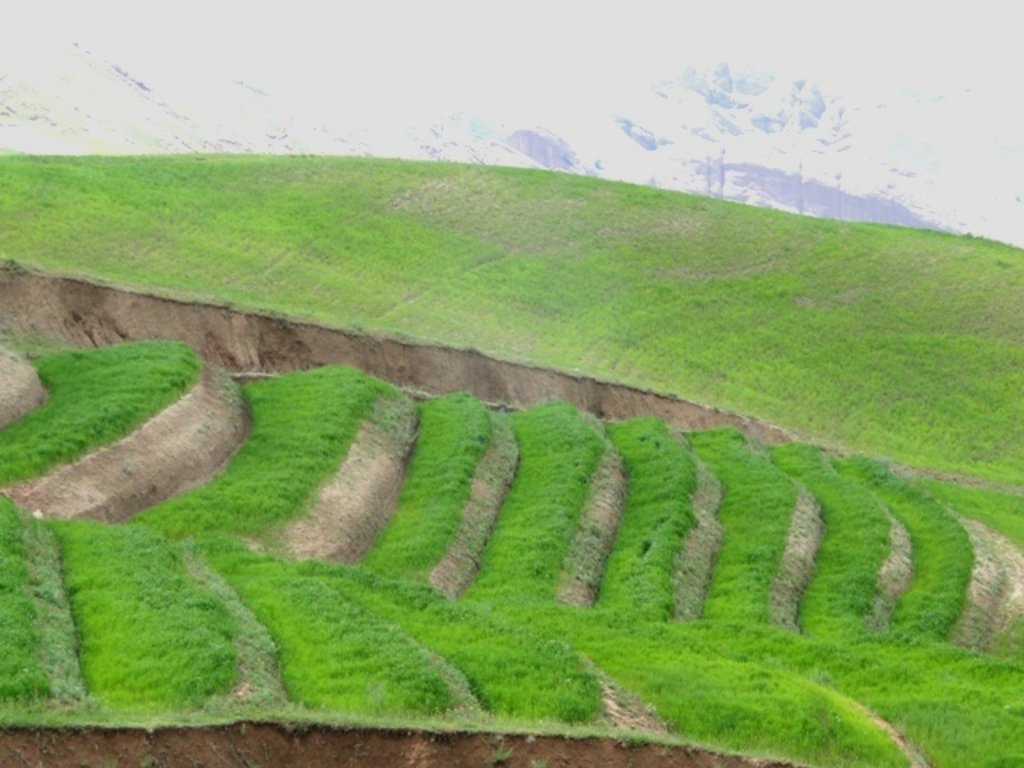
Terraces are established on mountain slopes used mainly for cropping wheat, with the purpose of soil protection from erosion, preserving runoff, sediments and nutrients on-site. Improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on the terraces for increasing crop yield, but also vegetation cover and biomass production, and thus prevent further land degradation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Project supported implementation of terraces with application of improved seeds and fertilizer has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash floods triggered by heavy rainfall.
The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend mainly on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months.
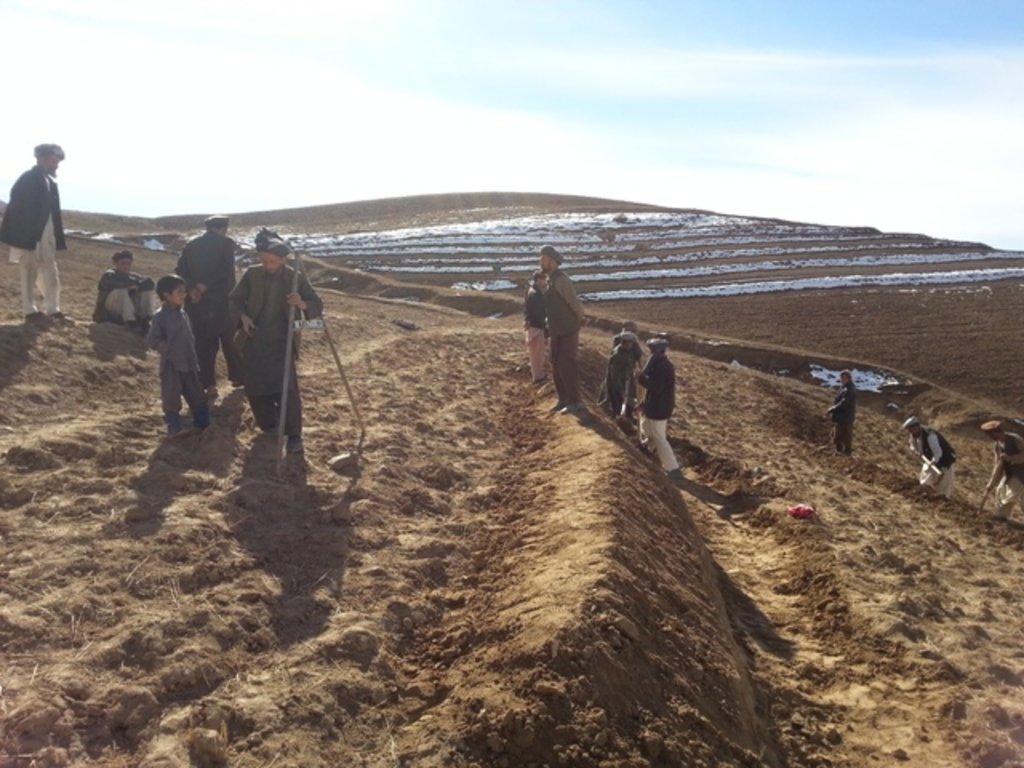
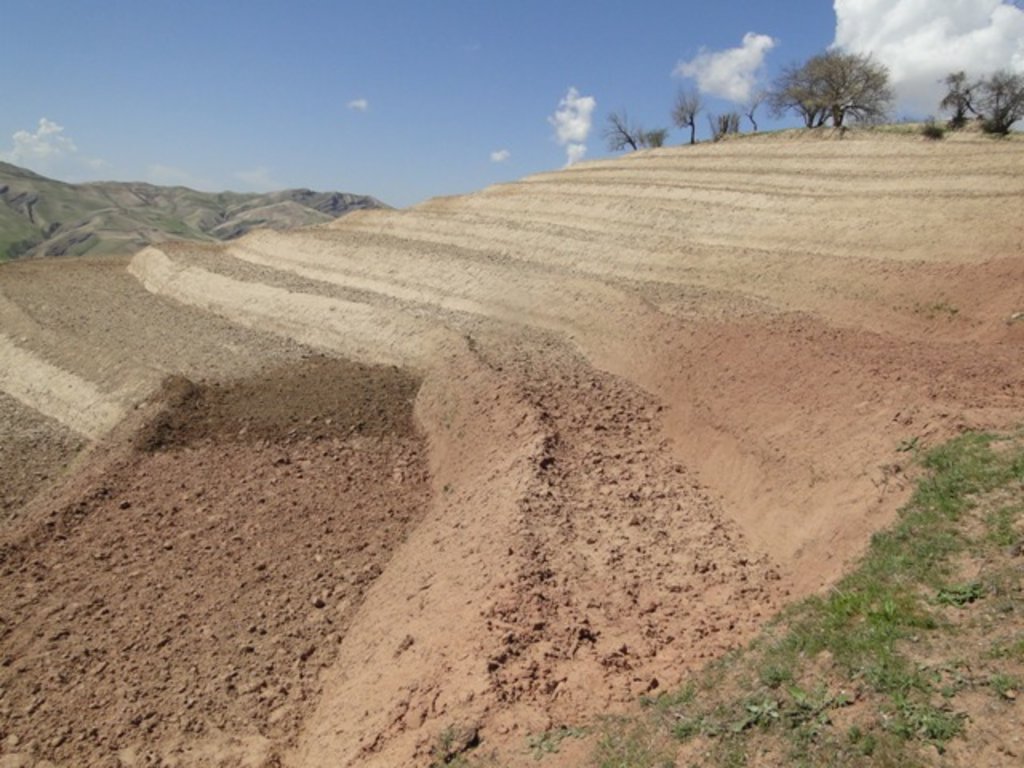
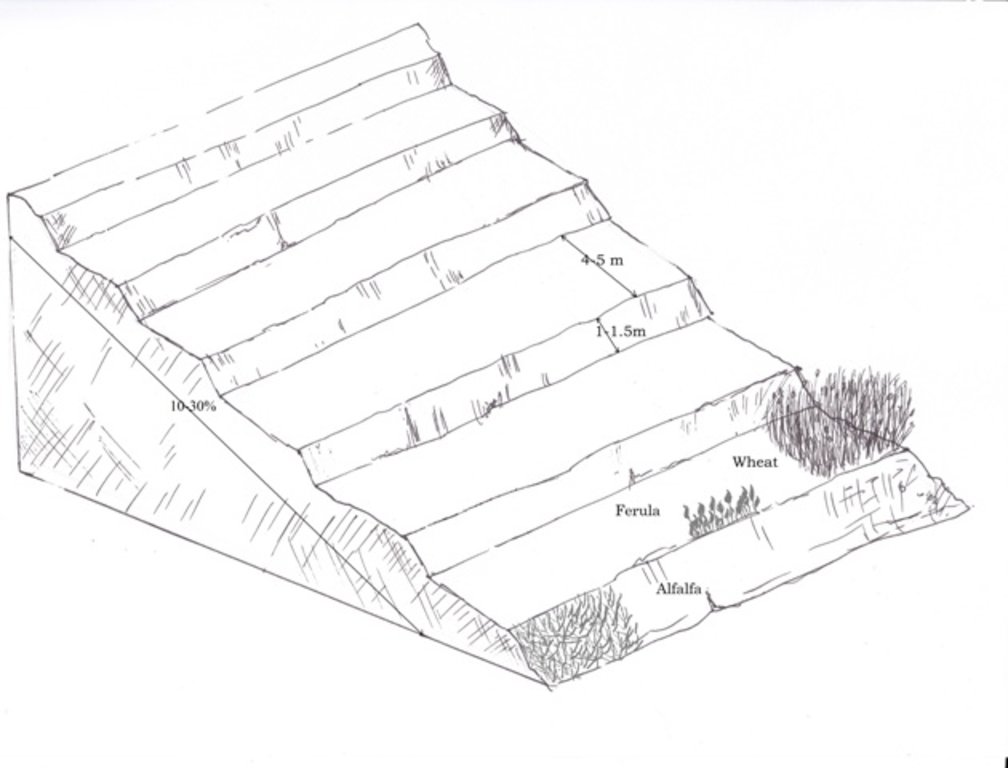
Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions. The project introduced terraces as sustainable land management practices on private plots, situated on rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes to protect the land from soil erosion and prevent the loss of water and fertile topsoil, seeds and fertilizers. The average plot size for terrace implementation is 2 Jerib (0.4 hectares) with contour strips of 40m x 4m. The height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. Terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil above the bench downwards. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, mostly alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs (ferula) are included they are cultivated along the bench contours .
Maintenance activities include small repair work on the riser by adding some amount of soil and re-sowing of alfalfa seeds on those spots.
The terraces allow application of improved seeds and fertilizers without them being washed off. The land-users report noticeable increase of wheat yield from the terraced plot with application of improved seeds and fertilizer compared to the non-terraced plot. An average plot of 0.2 ha on non-terraced hilly cropland used to give about 70 kg of wheat (350kg/ha). On terraces the yield has increased/ doubled to 140 kg on the same plot area (700kg/ha). The expectations regarding terraces remain high as over the time the land user hope their land will become more stable and improved soil moisture and fertility will have positive impact on the productivity as well. However, so far no cost-benefit assessment has been conducted allowing attribution of individual measure to the wheat increase.
Many land users are interested in the terrace technology due to a number of environmental and economic benefits expected, however the costs for building the terrace are considered high by an average local land user. They have to rely on external support in order to have sufficient resources for implementation. Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land (or other villagers land) when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อัฟกานิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Chokar Watershed: Sari Joy (upper watershed), Jawaz Khana (middle watershed), Dashti Mirzai (lower watershed)
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM impementers from Sari Joy (8 terraced plots), Jawaz Khana, (7 terraced plots), and Dashti Mirzai (11 terraced plots) as compiled during FGDs. The terraces located in Jawaz Khana have not been digitized yet. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in all three villages on farmers experiences and observations of terraced plots, with both SLM implementers (46) and observers (28).
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- Wheat, Alfalfa
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
May-July
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Before implementation of the Technology, only annual crops were cultivated, with wheat as the main crop. Plots were ploughed along the countours mostly by animal traction. In recent years land users are starting to use tractors for ploughing, , where villages and plots are accessible by machinery.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Agronomic measures: Terraces increase the economic viability of applying improved seeds and (chemical) fertilizer to badly nutrient depleted cropland.
Vegetative measures: Alfalfa is planted on the risers for stabilizing the terraces, and as an important contribution to fodder cropping.
Structural measures: The leveling of countour strips allows to harvest water and sediments.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Terraces are established predominantly on a privately owned land in a mountainous landscape with varying steepness of slopes.
The average size of a plot is 2 Jerib, which is equal to 0.4 ha. The design of the terrace depends on the steepness of the slope. Mostly rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes are used for building terraces.
Using an A-frame, the terrace is designed by dividing the slope into contour strips. Depending on the slope steepness, the terrace bench is around 4m wide and the the height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. The terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil of upper bench to the lower bench. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, such as alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs are included, such as ferula, they are cultivated along the bench contours.
ผู้เขียน:
Aslam Qadamov
วันที่:
14/02/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
67.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for establishing a terrace (Men) | Autumn |
| 2. | Designing of the terrace using A-frame, assisted by trained technician/project staff (Men) | End of autumn after rainy days |
| 3. | Leveling the soil with a shovel (Men) | Autumn/Winter |
| 4. | Sowing of alfalfa seeds on the risers (Men/women) | After 20 days of sowing wheat |
| 5. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Winter/Spring |
| 6. | Sowing of ferula along the contours (Men/women) | Winter/Spring |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Designing of the terrace using A-frame | person-day | 10.0 | 9.0 | 90.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Leveling the soil with a shovel | person-day | 150.0 | 5.3 | 795.0 | 51.0 |
| แรงงาน | Sowing of wheat and alfalfa seeds | person-day | 10.0 | 5.3 | 53.0 | 51.0 |
| แรงงาน | Sowing of ferula | person-day | 2.0 | 5.3 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Pick axe | Pcs | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Pitchfork | Pcs | 1.0 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Wheel barrow | Pcs | 1.0 | 38.0 | 38.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Shovel | Pcs | 1.0 | 3.8 | 3.8 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoe | Pcs | 1.0 | 7.5 | 7.5 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | A-Frame | Pcs | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140.0 | 0.42 | 58.8 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Alfalfa seeds | Kg | 17.5 | 0.42 | 7.35 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Ferula seeds | Kg | 2.5 | 6.35 | 15.88 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | DAP | Kg | 125.0 | 0.9 | 112.5 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Urea | Kg | 125.0 | 0.45 | 56.25 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicide | Liter | 50.0 | 0.25 | 12.5 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1275.48 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 19.04 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Equipment provided by the project was re-used for the implemenation of different SLM practices on different plots. For completness equipment costs are fully accounted for.
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing the land with animal traction (Men) | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 2. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 3. | Application of fertilizer (Men/Women) | Fall |
| 4. | Weeding (Women) | Summer |
| 5. | Harvesting wheat (Men and women together) | Summer/Fall |
| 6. | Harvesting alfalfa (Men and women together) | Summer/Fall |
| 7. | Collecting and delivering harvested wheat (Men and women) | Fall |
| 8. | Collecting and delivering harvested alfalfa (Men and women) | Fall |
| 9. | Repairing terrace risers with a shovel (Men) | Winter/Spring/After heavy rain or snow |
| 10. | Sowing alfalfa seeds on the repaired area (Men/Women) | Winter/Spring/When required |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Ploughing the land with animal traction | person day | 2.5 | 5.3 | 13.25 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weeding and Fertilizer application | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Harvesting and delivering wheat and alfalfa | person day | 70.0 | 5.3 | 371.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sickle | Pcs | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140.0 | 0.42 | 58.8 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | DAP | Kg | 125.0 | 0.9 | 112.5 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Urea | Kg | 125.0 | 0.45 | 56.25 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicide | Liter | 50.0 | 0.25 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 677.3 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 10.11 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
580.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimums in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximums in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Specifications: Derived from the publically available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The information was derived from two different sources:
-SLM implementers information provided in the Land User Protocol (LUP) during an FGD
-Elevation and slope statistics derived for terraced plots from ASTGTM. ASTGTM is the ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V002 with a 30 m spatial resolution. More information on ASTGTM is available here: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/node/1079. The data can be downloaded here: https://gdex.cr.usgs.gov/gdex/
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where terraces are implemented:
-Light soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); low topsoil organic matter
-Dark soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); medium topsoil organic matter
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower laying stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob, the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
350 kg / ha
หลังจาก SLM:
700 kg / ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The integration of measures including agronomic (improved seed and fertilizer) and structural (terraces to control water flow and loss of top soil, including nutrients and seeds) results in an increase of crop yield already in the first year. The effects cannot be attributed to one or the other measure specifically.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Alfalfa is planted on the risers.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No change in total area for production, as the riser of the terraces are used for fodder production. However, there is some reduction of area available for annual crop production.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The yield of the main staple crop (wheat)has been reported to be double on terraced plots with application of improved seed and fertilizer. In addition, fodder crops, such as alfalfa grown on the risers, can be harvested.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Technicians in the villages were trained in the use of A-frames. Implementers of terraces voiced that they themselves would not be able to replicated the designing of terraces.
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have the opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
in situ water harvesting
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Both an increase in vegetation cover during the growing season when most erosive rains are observed as well as permenant vegetation cover from perennial alfalfa plants can been observed.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits for their Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all SLM implementers are reflected here.
- Ecological impacts and off-site impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly , well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrices compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs: As larger parts of the establishment of the technology were covered by the project, farmers consideration of the total costs are likely underestimated.
Benefits: Two plots were terraced in 2012, and 5 plots in 2013. However, most terraces were implemented in 2014 (11 plots ) and 2015 (8 plots). The Rustaq NRM study was conducted in autumn 2016. 1-2 years of cultivating the terrace system is too short a period for providing evidence on short- and long-term returns.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
10.7 ha has been terraced within the 3 study villages with LIPT project support.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%". 3 implementers claimed full project support, 22 claimed some support, and 1 implementer claimed no project support.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
Ferula is planted on the terrace in addition to wheat and alfalfa. The resin-like gum from the dried sap extracted from the stem and roots of Ferula is in high demand as a basic product for pharmaceuticals. Ferula can be sold to local merchants, who resell it to India, and is thus intercropped by some farmers on the terraces.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Notable higher crop yields on the plots where improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on newly established terraces. Farmers have high expectations for the years to come and for yields of annual crops (such as wheat) to remain high. |
| Diversity of crops planted on terraces is valued by the land users. For example, cultivating wheat and alfalfa on the terraced plot provides household with the key crop and also fodder for the livestock and thereby contributes to securing food for the family and maintaining better health of their cattle. Additionally, some farmers have started intercropping Ferula, a medical herb and cash crop. |
| Farmers percieve soil quality on terraced plots with fertilizer application to improve. An improvement in soil fertility (which may relate first of all to the effects of fertilizer application) and increased soil moisture have been reported. Single statements also related to effectiveness of applying fertilizer on terraced plots, as here fertilizer is not washed away during rains. |
| Terraced plots are considered less vulnerable to the effects of rainstorms and dry spells, than non-terraced plots on slopes where annual crops are cultivated. |
| Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home. At the same time the terracing of the land is seen as an opportunity to improve the land resources on their families plots. An increase in women's workload related to bringing food to the field during establishment was considered to be acceptable, especially compared to the expected increase in yields. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The application of fertilizer on terraces is expected to show multiple effects: yields from these fertility depleted croplands can be increased. This includes an increase in biomass production, which may be used as green manure on the field or as animal feed or as straw. Further, vegetation cover during the growing period can be increased, which helps to protect the soil from erosive rains. |
| The project paid establishment of terraces on farmers' plots provided 20 days of employment per 2 jerib (0.4 ha) plot for farmers in their home villages. At the same time the terracing is a long-term investment into the land resources. Terracing provides an opportunity to decrease soil degradation and even to rehabilitate degraded lands. Application of improved seeds and fertilizer contribute in the establishment year to increased crop and fodder yields. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The implementation costs are high and land users state that it is impossible for them to cover establishment costs on their own. | |
| Farmers expectations partly exceeded the actual yield harvested from the terraces in the first years after the implementation. | |
| Both men and women from households that have implemened terraces state that during the establishment year the household experiences an increased workload, that is not well compatible with other on-going household / farm activities. | |
| The production area for annual crops only is slighty reduced. | So far not all farmers seem to use the production area fully. Intercropping with perennial plants is recommended in order to use the risers of the terraces for fodder production. Some farmers have started intercropping of Ferula as cash crop. |
| Sufficient own land is required. | How does the amount of cropland affect the innovation readiness of a farmer? A better understanding is required on farmers willingness to take a risk for investing in a new SLM technology, and especially terracing, and influencing factors. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technology requires technical knowledge for implementation and maintenance, which is key for successful adoption, replication and upscaling. The project trained technicians to support land users with the design of terraces. While the project aided implementation of terraces has improved the general knowledge and awareness of the land users on the benefits of SLM practices, most farmers will not be able to design terraces on their own. | |
| Technically correct design of the terrace presents a challenge and might not be always achieved. Forward sloping terrace benches may lead to channeled runoff and have the risk of rills and gully formation. | |
| There is an attribution gap regarding the increased wheat yields, especially with regard to individual contribution of the terraces, the application of improved seeds and the fertilizer, and the combined effects (role of terraces in making improved seed and fertilizer application effective). | A cost benefit analysis (CBA) needs to be conducted to determine short- and long-term returns of the SLM technology. On farm trials are necessary for assessing impacts of the different measures (agricultural, vegetative and structural measures) before-and-after, as well as with-without the SLM technology. |
| Terrace maintenance is crucial. If not maintained properly for a longer period of time, the damaged terrace can lead to further land degradation through channeled runoff, sever erosion and possible risks of disaster for the surrounding settlements on the slopes. | |
| The technology is established mainly by better-off households, which own more land than the average SLM implementer. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 26 land users who have implemented terraces participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 74 persons interested in terrace implementation, of which 46 persons are from households that already have implemented terraces.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
The technical staff of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq, responsible for the implementation of the technology were consulted on a number of occasions during the compilation of this material.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
17/10/2016
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Watershed Associations (WSA) and Natural Resource Management Committees … [อัฟกานิสถาน]
Two Watershed Associations (WSA), in Chaker and Nahristan watershed areas respectively, are registered at the national level with the Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (MAIL) and at the regional level with the Department of Agriculture. Both associations are strong, active, dynamic, and have the capacity to coordinate and support …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Bettina Wolfgramm
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล