Conservation tillage in UK arable cropping: Loddington [สหราชอาณาจักร]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
minimum tillage (Eng), non-inversion tillage (Engl); no-tillage (Eng); direct drilling (Eng)
technologies_985 - สหราชอาณาจักร
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust - สหราชอาณาจักร1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Participatory on-farm resarch and demonstration in UK arable … [สหราชอาณาจักร]
To find and demonstrate ways of better managing the land.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
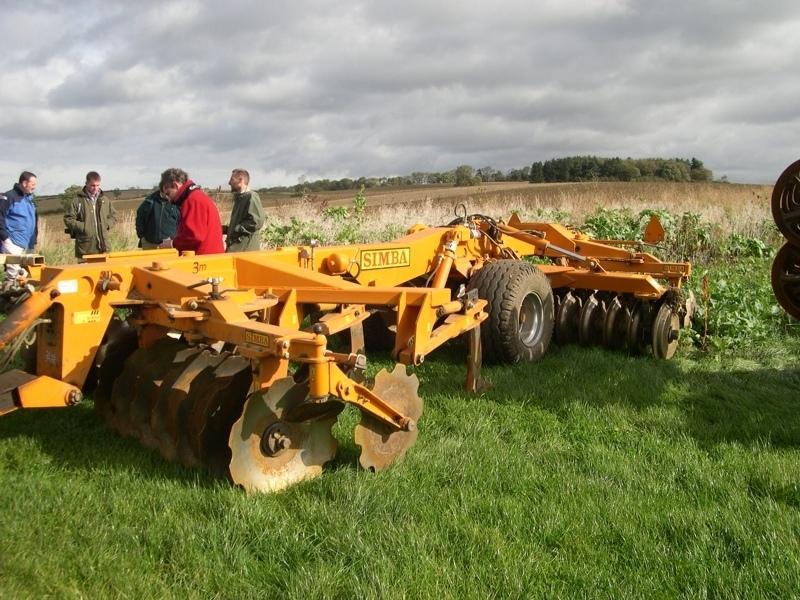
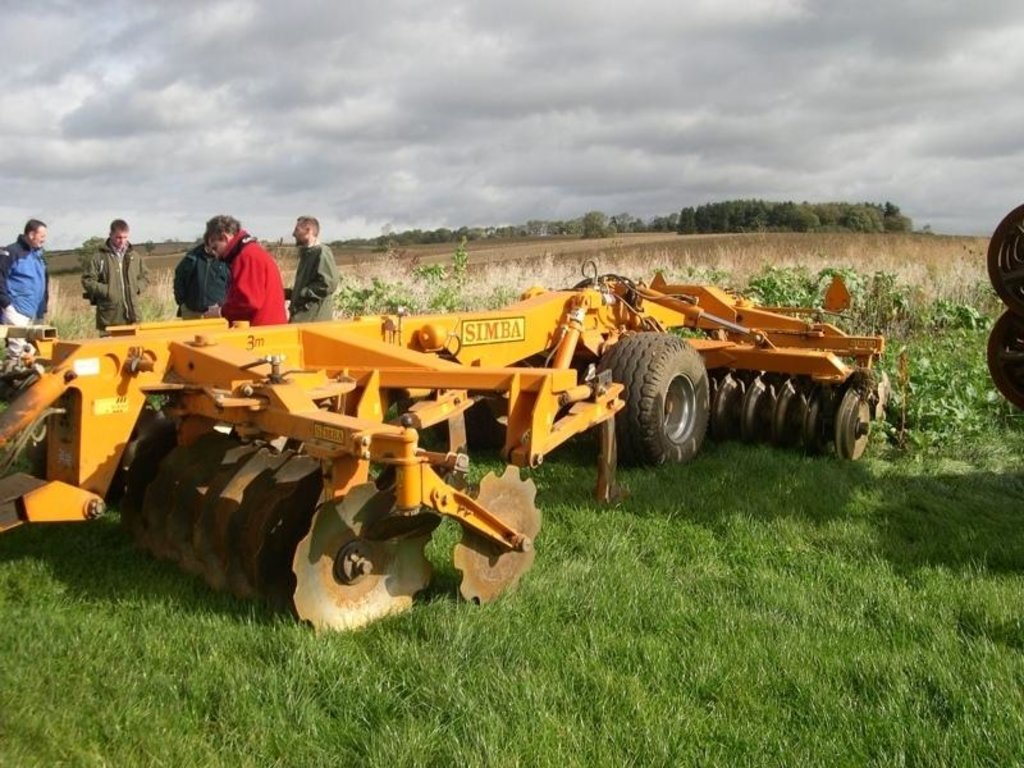
Surface cultivation of up to the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
machinery with discs or tines replace the plough for minimal cultivations of the soil. Equally crops may be established by no-tillage/ zero-tillage
Purpose of the Technology: (i) soil protection (ii) improved crop establishment particularly through the speeding up of of operations.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: appropriate machinery, soil condition and following crop all determine establishment. Maintenance: on an annual basis.
Natural / human environment: SOWAP (ww.sowap.org) project working with farmer to protect environment and maintain economic viability
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สหราชอาณาจักร
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Leicestershire
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Leicestershire
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.00063 Km2.
This represents a 630m2 on-farm research and demonstration plot
Map
×2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
From the USA where in te 1930's the 'dust-bowls' necessitated the development of soil conservation in intensive agriculture.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - wheat (winter)
- legumes and pulses - beans
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 330 Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Aug
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water turbidity, compaction, erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Compaction
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: wheat - oilseed rape - wheat - beans. Typically these will be winter-sown (Sept) crops rather than spring sown (March)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.1: No tillage
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, zero tillage / no-till, minimum tillage, deep tillage / double digging
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes: focus on yields), labour availability (too much labour: attempting to maintain rural employment)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), insufficient time for farmers to consider the issu
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility
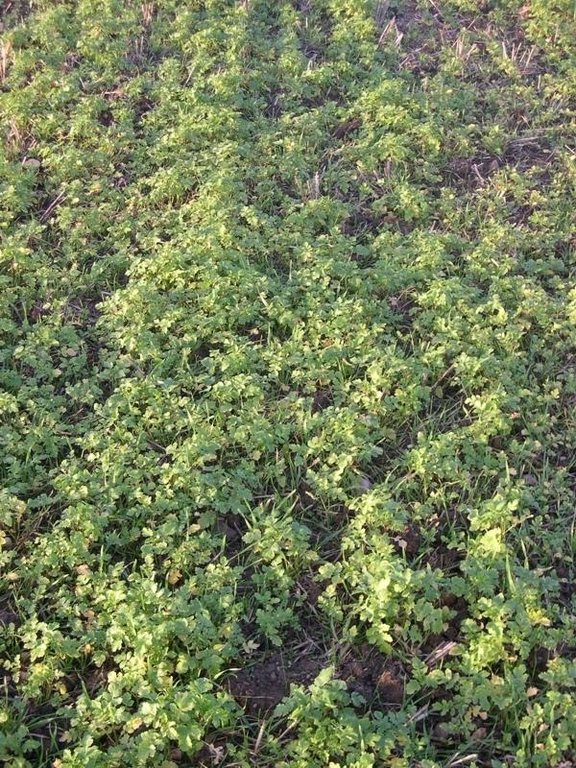
Cover cropping
Material/ species: mustard or mustard-rye mixture
Remarks: drilled
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residue
Quantity/ density: up to 5 t/
Remarks: quantity dependent on crop; dispersed over soil surface
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: NPK
Quantity/ density: 0.14 t/ha
Remarks: broadcast
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: cereals/ broad-leaved crops
Remarks: alternate years
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: as appropriate
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: as appropriate
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
UK pounds (£)
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.56
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
155.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Additional info: - Year 1: consolidation: October / per crop - Year2: chop straw close to soil surface: harvest / annual - Year2: incorporate straw and prepare seed bed: September / annual - Year2: drill mustard-rye cover crop: September / annual - Year2: drill crop (2.5-4cm depth): March / once per crop - Year 3: chop straw close to soil surface: harvest / annual - Year3: incorporate straw and overcome compaction: October / per crop - Year3: additional cultivation: October / per crop - Year3: drill crop (2.5-4cm depth): October / once per crop - Year3: consolidation: October / per crop
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Year1: chop straw close to soil surface | harvest / annual |
| 2. | Year1: drill mustard cover crop | after harvest / annual |
| 3. | Year1: incorporate straw and cover crop | September / per crop |
| 4. | Year1: additional cultivation | October / per crop |
| 5. | Year 1: drill crop (4cm depth) (More in Annex 3) | October / once per crop |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | drill cover crop (year 1) | ha | 1.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | drill cover crop (year 2) | ha | 1.0 | 128.0 | 128.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 204.0 | 204.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine hours (year 2) | ha | 1.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine hours (year 3) | ha | 1.0 | 236.0 | 236.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds (kg) cover crop (year 2) | ha | 1.0 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 838.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1496.43 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Simba Solo, Cambridge rollers, Vaderstad drill
Per hectare of land where technology applied. The costs listed are for crop establishment costs only as all other costs (seed, fertiliser, pesticide) are identical to those incurred by other technologies (UNK1a, UNK1c) undertaken on this farm.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Equipment costs, slope (higher horse power required for steeper slopes), time taken for operation
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
660.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Hill slopes (some slopes < 8%)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
50% of the land users are rich and own 60% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
250 ha of cultivated arable land
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
- Trust
- Trust
- Trust
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Uncertain after only 3 years
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
Impression of the technology
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Land manager enthusiastic about the technology
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Residue and/or cover crop
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0.01
หลังจาก SLM:
0
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Higher earthworm populations, improved soil microbiology
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Soil fertility
Input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Better range of herbicide options
Cost of cover crop seed
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Can negate the cost savings achieved through the lower crop establishment costs
Soil erosion locally
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Immediately after drilling cover crop
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced nutrient loss
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Currently about 40% of the UK practices conservation tillage
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
timeliness How can they be sustained / enhanced? good planning |
| improved biodiversity |
| improved soil organic matter |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
cost effectiveness How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase are under cultivation (economy of scale) |
|
improved soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? continuing practice; retention of straw |
| increased soil biodiversity |
| improved water quality |
| increased work rate |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| as above |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| potential for increased weed populations | improved rotations, greater use of cover crops to compete with weeds |
| cost of cover crop seed and lack of appropriate species | greater use will encourage lower cost and more speciesw research |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Participatory on-farm resarch and demonstration in UK arable … [สหราชอาณาจักร]
To find and demonstrate ways of better managing the land.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ceris A. Jones
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล