Bio-gas [Nepal]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Joana Eichenberger
Gobar gas
approaches_2521 - Nepal
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
Singh Abhishek
Kathmandu University
Nepal
SLM specialist:
Bajracharya Luniva
Kathmandu University
Nepal
SLM specialist:
Kayastha Priya
Kathmandu university
Nepal
SLM specialist:
Rajhuram Baidhaya
VDC Sarada Database
Nepal
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Kathmandu University (KU) - NepalName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Sarada Batase Village Development Committee (Sarada Batase VDC) - Nepal1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
10/04/2013
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
Bio Gas [Nepal]
Production of fuel and manure from animal waste
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
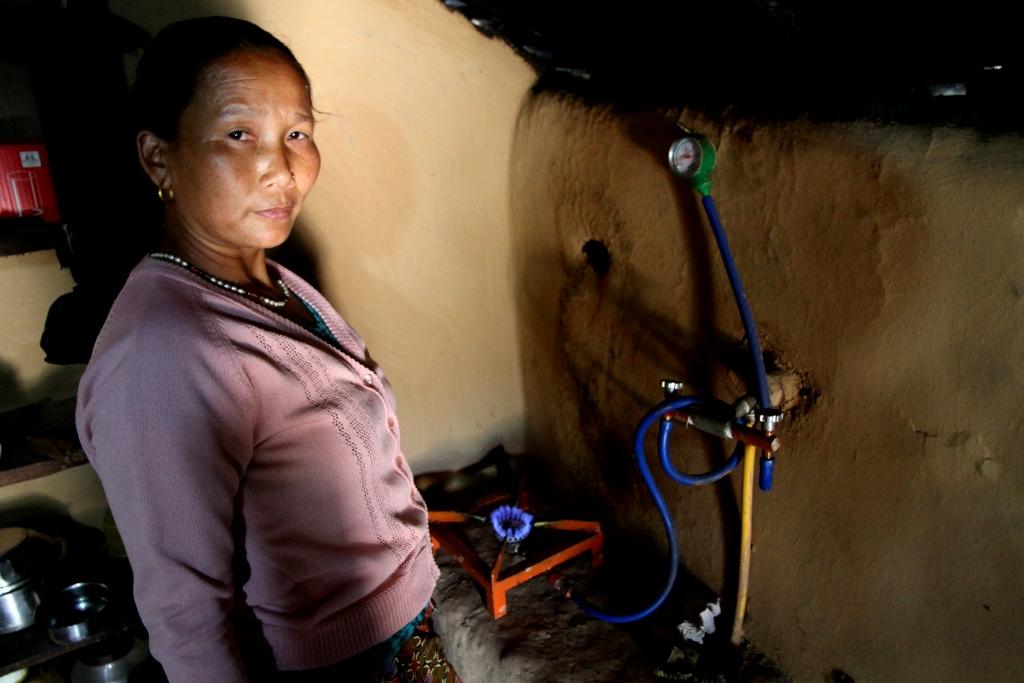
Production of fuel from the animal waste.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Aims / objectives: It is used for cooking. It can be also used as compost manure which helps to save money to purchase fertilizer and even for electricity purpose.
Methods: By collecting as much as animal waste.
Stages of implementation: The project was first introduced by the Nether land government and handle to local people and was funded by Dutch Co-operation.
Role of stakeholders: They provide training to the local people
Other important information: It improved the economic status of people by obtaining the cheap fuel.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Nepal
Region/ State/ Province:
Nepal
Further specification of location:
Kavre
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2055
Year of termination (if Approach is no longer applied):
2015
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (cooking,natural waste management ,economic support)
1.To provide economic support.
2.For cooking food.
3.For the management of animal waste.
4.For natural waste treatment.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Deforestation,low agricultural production,health sanitation and indoor pollution
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
social/ cultural/ religious norms and values
- hindering
No any social problems
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Economically backward group were allowed to pay less as per income as renewal fund.
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
Financial problems as the people could not afford the materials.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: But the organization provided the fund for the project.
institutional setting
- hindering
farmers did not know where to go when they needed advice regarding the procedure and funding required for the biogas production.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: programs were conducted to solve the problems and various institutions were assigned to help farmer if they had to go through any problem
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: community ownership meant no hindrance to development.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
lack of technical knowledge
Treatment through the SLM Approach: training was provided to the people.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
They spread the approach to all the farmers. Since the people were financially aided by the Government as well as other international organisations it helped a bit fot the socially and economically disadvantaged group
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
They provide technical education and advices to farmers on the benefits of bio-gas plants.
- local government
Village Development Commitee
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
Agricultural Development bank of Nepal
The Ministry Of Finance help in the funding for the establishment of biogas plants through their agreement with the Agricultural Development Bank.
- international organization
SNV Netherlands Development Organisation
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
The Netherlands Development Organization helped to develop lower cost bio-gas and the agreement between the Ministry of Finance and SNV Nepal ,Agricultural Development Bank helped to promote and install this bio gas as indigenous and sustainable source of energy and also provided financial aid.
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | they interacted with the farmers discussing about the benefits of the bio-gas and how it could reduce their workload of firewood cutting and motivated them to use bio-gas . |
| planning | external support | They conducted various programs to develop curiosity and anxiousness about the bio-gas production and provided financial aid. |
| implementation | external support | Implementation was done by helping the farmers to get loan and subsidy from the Government and banks. |
| monitoring/ evaluation | self-mobilization | Monitoring and evaluation was done on the basis of how the new approach has affected the people's livelihood. |
| Research | none | no research were done |
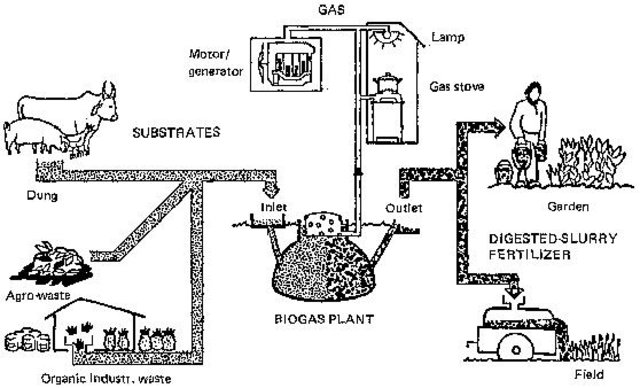
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
The Netherlands Development organisation helped to develop lower cost bio-gas plants .The Ministry of Finance ,the Agricultural Bank of Nepal, Gobar Gas company ,Bio-gas Support Program ,(AEPC) Alternative Energy Promotion Center has really helped in financial help and to promote the bio-gas as the indigenous and sustainable source of energy.
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
Explain:
if the farmers had any problem or questionnaires they can contact the near by village development community ,municipality and they can conduct various programs for providing information and promotion work.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. for financial aid they can go to Agricultural Development Bank which will provided them funding and they can contact the nearby Village Development Commitee (VDC )or municipality.
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Specify who was trained:
- land users
Form of training:
- farmer-to-farmer
- public meetings
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
Describe/ comments:
Name of method used for advisory service: conducting programs and supplying financial services; Key elements: books were provided , pamplets to promote the service, materials use and procedure methods were taught; financial help was also provided regarding loan subsidies and many others serviec for the farmers to make the service easy to reach.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; yes they are adequate because they are the main source of help and their help can make it easy for the promotion throughout the nation.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, a little
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- financial
Give further details:
the local institution were given financial services to provide it to the the local people and farmers
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by other through observations
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by land users through measurements
management of Approach aspects were monitored by None through observations
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: no,the approach was just to introduce new better ideas .
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: advancement and improvement in technology was there as a result of monitoring and evaluation.
5. Financing and external material support
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
the contributions per area was provided by the private sectors as they provided financial help and other services.
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| machinery | fully financed | Jar and tank |
- construction
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| bricks, cement, pipes | partly financed | |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- paid in cash
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Since the approach was bio-gas production from animal waste this help in increasing the soil quality very much which led to sustainable land management.It used the resources of the environment which helped a lot in sustainable land management,
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
This approach also helped for job opportunity as the agricultural products get better they can sell it and earn money.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
There was no hindrance. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. The approach creates a framework to use in the future.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
neighboring village adopt technology. Since it helped to flourish the economic and financial status with very less investment.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
better water resource for irrigation. It also helped in improving the agricultural products and also saved the money of farmers which they spend on fertlizers.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
increase crop yield and also decreases the investment of money on fertilizers as they could get compost from the animal waste which was far much better.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- reduced workload
it will decrease the work load of cutting trees for firewood and other purposes.
- environmental consciousness
reduces indoor air pollution,cleaner environment and natural waste management
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
compost increases the crop yield and productivity and the farmers can sell it in good amount .
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- no
If no or uncertain, specify and comment:
No, the active involvement of NGO's in the promotion,organisation ,financing and construction of bio-gas plant has made it much more efficient for the continuation of approach.
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| it will lead to sustainable land management with less deforestation, and a cleaner environment. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: the approach should be made accessible to all the individuals.) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| it will help to conserve the energy with the promotion of better environment. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Bio-gas production should be adopted by all the communities.) |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Size of safety tank is too big. They cannot fulfill the requirement of the tank. | Small tank should be constructed. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
|
Methane released cause global warming. Cannot use chemical in toilet,because it cause environmental hazards. |
Approach should be well-constructed. Avoid the toilet paper. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Bio Gas [Nepal]
Production of fuel and manure from animal waste
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
Modules
No modules