Sweet Potato Relay Cropping [Philippines]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Lapat System
technologies_1301 - Philippines
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Raquid Jemar G.
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Garcia Pastor
Visayas State University,
Philippines
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - PhilippinesName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Visayas State University (VSU) - Philippines1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
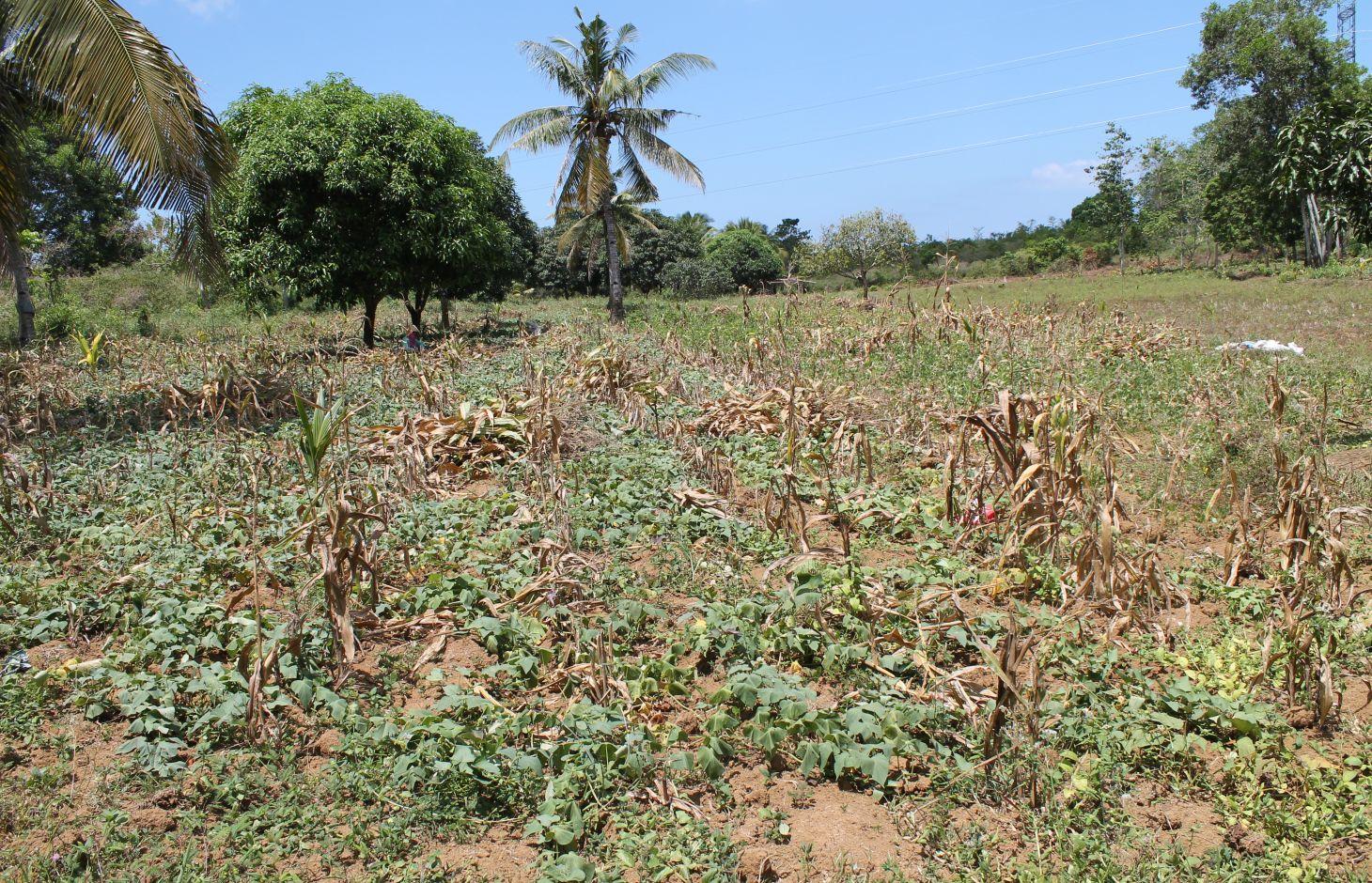
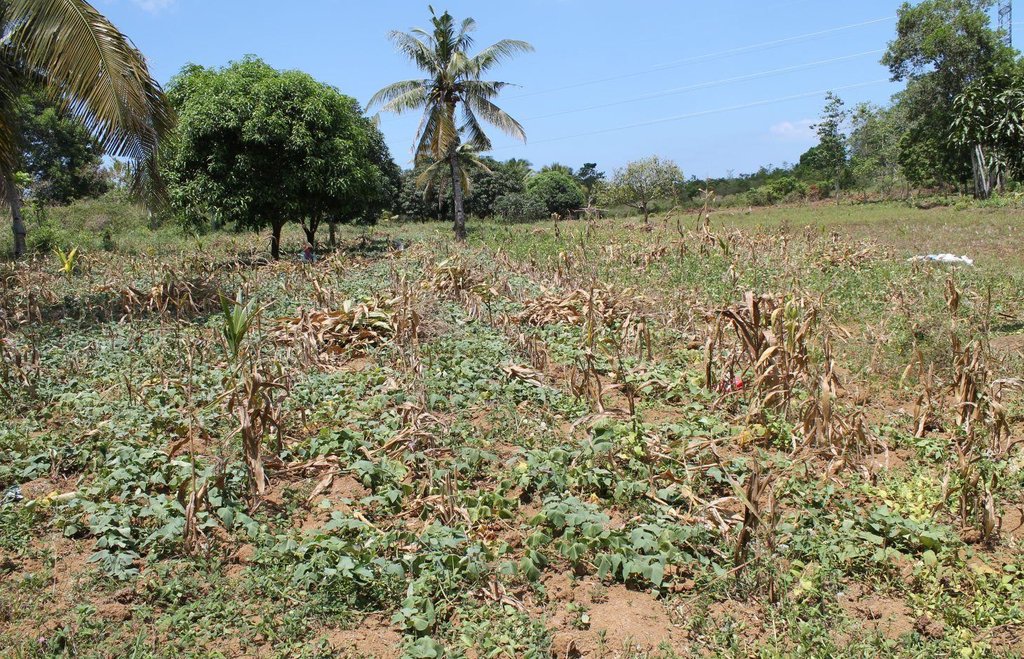
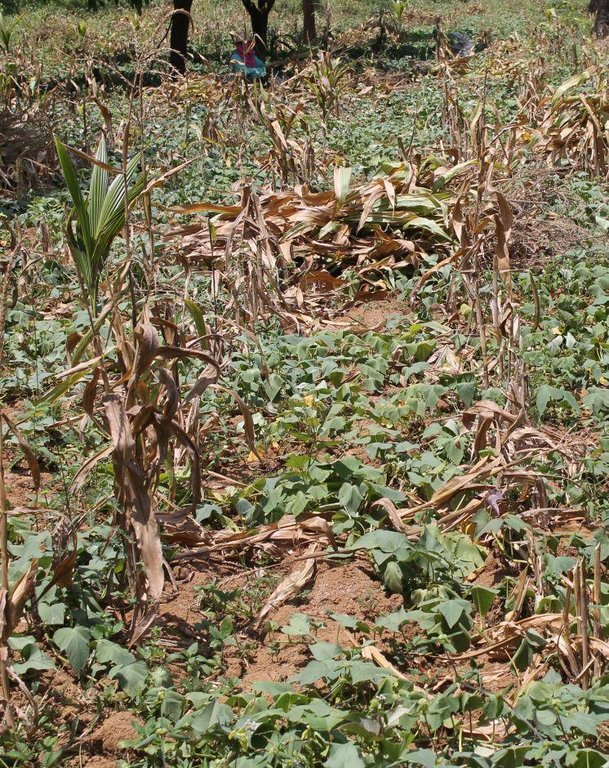
A farmer’s indigenous practice of growing sweet potato as a relay crop to its main crop of either rice or corn.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
It is the planting of sweet potato together with rice/corn on the same area, hence, maximizing the area for crop production. Specifically, a local sweet potato variety called “mayaman” is planted one to two months after planting rice/corn and is being cultivated in the field in between the rows of the above-mentioned main crop. The “mayaman” variety is selected by the farmers due to its excellent food quality and ability to produce more roots at its vine, enabling staggered harvesting and extending period of utilization. However, in some instances, rice and corn were planted at the same time.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of using creeping type of sweet potato is to provide cover to the soil which addresses soil moisture conservation primarily during growing period and after main crop harvesting time. It also protects the soil against erosion. Moreover, it provides additional and alternative food source for the farmers, in case the main crop fails due to some reasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main crop, either corn or rice, is planted first with a specified planting distance--75cm between rows and 75cm between hills with 2 to 3 seeds per hill (for corn) and 30cm between rows and 20cm between hills with 5 to 6 seeds per hill (for rice). After one month, the sweet potato cuttings are planted in between rows of the main crop at a distance of 1.5m between hills.
Natural / human environment: This relay cropping system is locally known as “lapat” in the areas of Matalom and Bato, Southern Leyte where it is commonly practiced.The soil in these areas is characterized as mostly acid soil. Whereas, its topography is generally comprises from rolling to steep hills. In terms of climate, rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year and typhoons usually occur during the months of October or November. In addition, most of local farmers cultivated 1 to 2 parcels with farm size from 0.12 to 5.95 hectares with farming as the principal source of livelihood and income. The fields ot the farms are basically rainfed because it is totally dependent on rainfall as water supply for irrigation.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Philippines
Region/ State/ Province:
Matalom, Southern Leyte
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
This is a traditional practice done by most of the farmers in the municipality of Matalom, Leyte.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
- rice
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Comments:
Major food crop: Rice, corn
Others: Sweet potato
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, soil moisture
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil erosion
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- rotational systems (crop rotation, fallows, shifting cultivation)
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- Intercropping
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A3: Soil surface treatment
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: soil management (contouring is not practice in sloping areas), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (topography)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (annual cropping), droughts
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Sweet potato and corn planted within an area
Location: Matalom. Leyte
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (proper planting distance and know how to mix crops)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Relay cropping
Material/ species: sweet potato
Remarks: 1.5m x 1.5m spacing in between the rows of main crop
Author:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water and Management
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
45.0
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant material | Corn seeds | kg | 2.0 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Rice seeds | kg | 43.2 | 0.7777777 | 33.6 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Sweet potato | cuttings | 13000.0 | 0.00555555 | 72.22 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 107.38 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2.39 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing | March |
| 2. | plowing | 10 days after clearing |
| 3. | harrowing | after plowing |
| 4. | furrowing | after harrowing |
| 5. | planting of rice | April |
| 6. | planting of corn | 2 weeks after planting rice |
| 7. | planting of sweet potato | 2 months after planting corn |
| 8. | weeding | every month |
| 9. | spraying | three times before harversting |
| 10. | harvesting of rice and corn |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 391.5 | 391.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 391.5 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 8.7 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage is medium
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Seasonality of water quality: Spring
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Level of mechanization is manual labour or animal traction (carabao)
Market orientation: subsistence (food consumption of the family)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
- mixed land ownership
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Income and costs
farm income
diversity of income sources
workload
Comments/ specify:
less weeding needed since sweet potato served also as cover crop
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Simplicity of the farming practice with minimal external input requirement How can they be sustained / enhanced? improvement in terms of planting distance or in the land preparation activity; look for other potential cover crop aside from sweet potato |
|
Enhance Soil moisture conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? conduct research study to have a more scientific basis |
|
Additional food source and farm income How can they be sustained / enhanced? integration of other suitable crops for diversification; consider possible value-adding activity; help in the marketing of the product |
|
Soil protection against erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Practice contouring and other soil conservation measures in the hilly land/sloping production areas to further minimize soil erosion |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Low market price for sweet potato | Value adding through post-harvest processing of sweet potato;Livelihood development related to sweet potato post-harvest processing |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules