Ecofogón Modelo Justa [Nicaragua]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Maria Rodriguez
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Johanna Jacobi, Alexandra Gavilano
Fogón Mejorado
technologies_4578 - Nicaragua
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Flores Ayestas Asuncion
Protagonista del programa de Gestión Comunitaria de la Cuenca del Río Dipilto.
Nicaragua
SLM specialist:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Para el mandato de backstopping para le programa gestion comunitaria de la cuenca de Rio Dipilto en Nicaragua (Gestion comunitaria - Nicaragua)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SwitzerlandName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio del Ambiente y los Recursos Naturales - Nicaragua (MARENA) - Nicaragua1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Eco fogón Mejorado Modelo Justa, utilizado para reducir el consumo de Leña.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
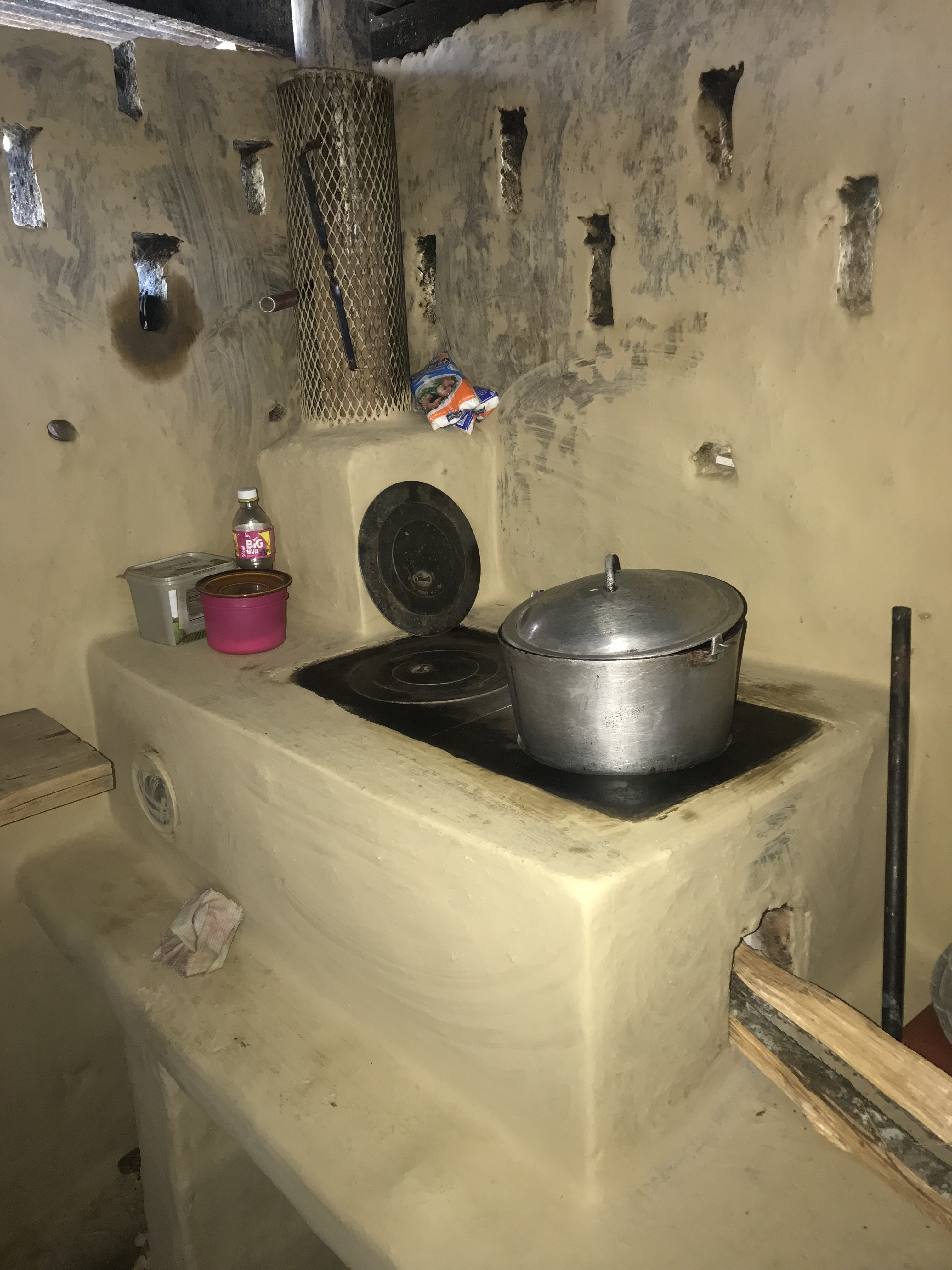
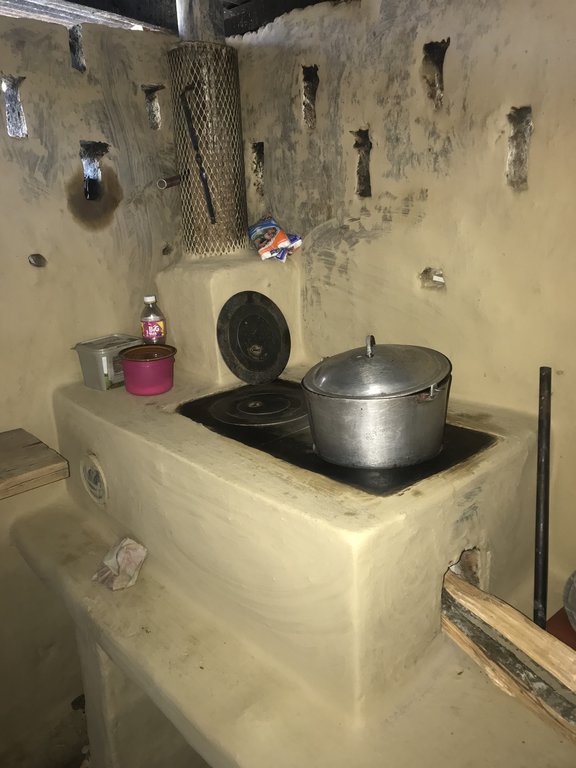
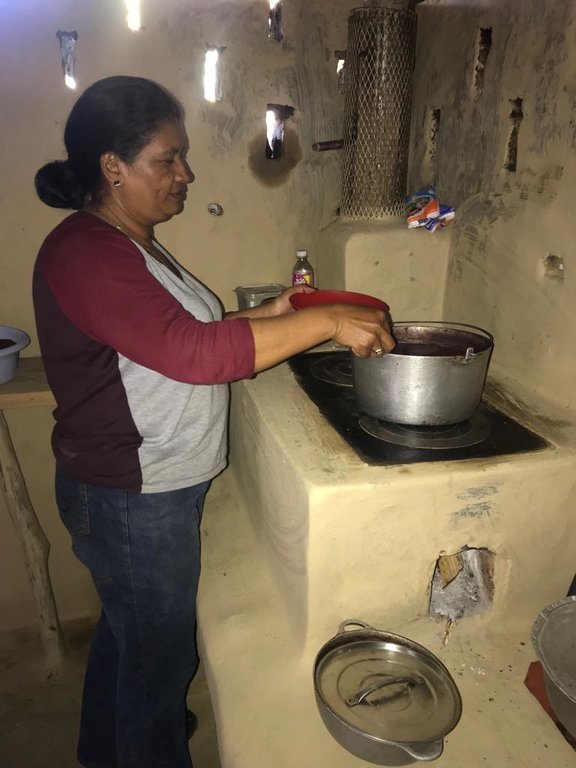
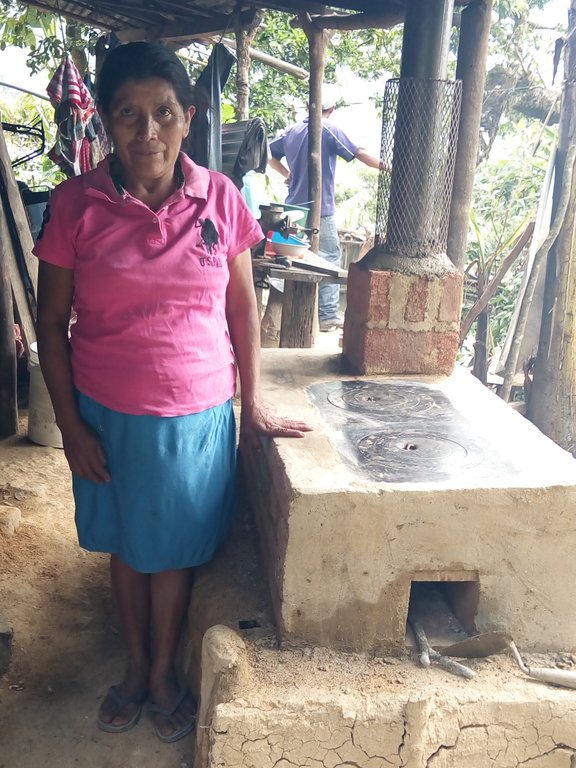
Eco fogón mejorado modelo justa, se utiliza en los hogares de las familias que habitan en la cuenca del río Dipilto. Esta construido de ladillo cuarterón, con dos planchas metálicas movibles que forman las hornillas una Chimenea metálica cubierta con malla , en la parte interna lleva una cámara de combustión de ladrillo a una fundición de 1000 °C, también tiene otro compartimento pequeño,para la extracción de residuos producto de la salida de humo. El propósito de esta tecnología es reducir el consumo de leña y disminuir la presión sobre el recurso bosque. Las principales actividades de mantenimiento consisten en: limpieza general del eco fogón, introducir pequeños trozos de leña para lograr el funcionamiento adecuado, en caso de las planchas se limpian cada vez que se finaliza de cocinar, una vez que el nivel de ceniza haya bajado se vuelve a rellenar para mantener el calor. Entre los beneficios e impacto adquiridos por la tecnología se determinan el ahorro del consumo de leña hasta en un 75%, Mayor higiene en la cocina, no hay inhalación de humo por las personas que hacen uso de el, menor cantidad de corte de arboles para ser utilizados de leña. Lo mejor de la tecnología que los usuarios expresan satisfacción por la complementación de la tecnología y no se exponen a enfermedades respiratoria, es fácil de mantenerlo.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Nicaragua
Region/ State/ Province:
Comunidad El Volcán, Municipio de Dipilto Nueva Segovia
Further specification of location:
Municipio Dipilto, Comunidad El Volcán, Finca Santa Rosa
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
Yes
If yes, specify:
97 km superficie que cubre la cuenca del Rio Dipilto.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Algunos cultivos como las Musaceas se cosechan todo el año
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Agroforesteria de café diversificada
Is crop rotation practiced?
No

Settlements, infrastructure
- Settlements, buildings
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- energy efficiency technologies
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S10: Energy saving measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- not applicable
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
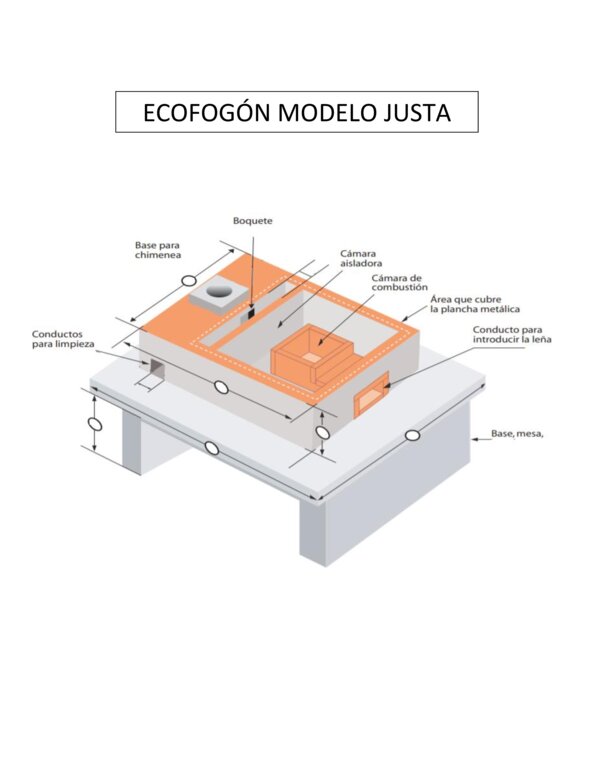
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Altura de l a mesa del Ecofogón 22", Ancho de la mesa del Ecofogón 23", Largo de la mesa del Ecofogon 61". Alto de la parte superior del Ecofogon 11". El Material de construcción utilizado : Ladrillo cuarterón y/o bloque, plancha metálica, arena, tubo de hierro de 4", malla metálica, protector de chimenea, pinza para remover tapaderas de las hornillas, sellador para evitar entrada de agua de la lluvia, la mesa puede ser construida de Adobe, Ladrillo o bloque.
Author:
Maria Teresa Rodríguez Pérez
Date:
21/03/2019
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Ecofogón
other/ national currency (specify):
Cordoba
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
33.0
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ubicación del lugar de construcción | Al inicio |
| 2. | Preparación y traslado de materiales | Después de haber preparado el sitio de construcción del eco fogon. |
| 3. | Construcción de eco fogón | Después haber preparado y traslado de materiales. |
| 4. | Prueba de funcionamiento | Dos días después de construido el eco fogón. |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Construcción del Ecofogón | D/H | 2.0 | 700.0 | 1400.0 | |
| Labour | Contrapartida del protagonista | D/H | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | 5.0 |
| Construction material | Adobe para Mesa | Und | 30.0 | 10.0 | 300.0 | |
| Construction material | Ladrillo Cuarterón | Unid | 55.0 | 6.0 | 330.0 | |
| Construction material | Ladrillo Para Cámara de combustión | Unid | 4.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 | |
| Construction material | Cemento | lbr | 75.0 | 3.5 | 262.5 | |
| Construction material | Tubo Para Chimenea de 4"Pulgadas | mts | 3.0 | 120.0 | 360.0 | |
| Construction material | Arena | baldes | 5.0 | 40.0 | 200.0 | |
| Construction material | Plancha metálica de 0.70 mt, largo * 0.35 mts de ancho , * 32 ml de grosor | und | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Construction material | Malla expandida aislante de calor | mts | 2.0 | 220.0 | 440.0 | |
| Other | Protector para chimenea de Zinc Liso y Remaches | und | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | |
| Other | Pinza para retirar hornillas | und | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6462.5 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 195.83 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
El Programa Gestión Comunitaria de la cuenca del rió Dipílto
Comments:
El total general para establecer la tecnología equivale a 6462.5 córdobas, incluyendo mano de obra y aporte del protagonista (195.83 dolares americanos). estos costos se refieren a la construcción de una unidad de Ecofogón.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza de las planchas diario | Después que termina de cocinar |
| 2. | Limpieza de chimenea | de 8 a 15 días |
| 3. | Limpieza en el área externa del eco fogón con tierra o cal | diario |
| 4. | Extracción de ceniza al momento de encenderlo | diario |
| 5. | Rellenar con ceniza cuando baja el nivel optimo | al mes |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Limpieza y mantenimiento del Ecofogon | D/H | 12.0 | 120.0 | 1440.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1440.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 43.64 | |||||
Comments:
En la parte del mantenimiento, referente a la limpieza general del Ecofogón y relleno con ceniza es asumida el 100% por el usuario de la tierra.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Yes
Specify:
Titulo de Propiedad /Escritura publica
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
forest/ woodland quality
Comments/ specify:
Disminuye la presión al bosque, aumentando cobertura vegetal, retención de agua y productividad de los suelos dentro del área de influencia del proyecto.
Income and costs
workload
Comments/ specify:
Al disminuir la cantidad de leña quese usa, disminuye el tiempo para la recolección de la misma y costos al comprar la leña para preparar alimentos.
Socio-cultural impacts
health situation
Comments/ specify:
Es aceptado por la mayoría de los usuarios de la tierra, dado que reduce el consumo de leña e inhalación de humo que disminuye enfermedades respiratorias.
Ecological impacts
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
Al aumentar la cobertura vegetal no se altera los nichos ecológicos.
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
Diversidad de ecosistemas conservados para las diferentes especies .
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
Al reducir el consumo de leña , los usuarios de la tierra ya no entran a extraerla donde los vecinos o asear ajenas.
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Evitamos la contaminación ambiental |
| Reducción de gastos por consumo de leña |
| Mejora las condiciones de salud ( enfermedades respiratorias) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Es asimilada por usuarios ( protagonistas) |
| Fácil construcción y manejo |
| Comprobada la reducción del consumo de leña y no requiere de mucha inversión para el mantenimiento. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| No todos los usuarios han adoptado la tecnología | Capacitar y sensibilizar a los usuarios |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
3
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
21/03/2019
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links