Biofiltro para tratamiento de aguas grises [Nicaragua]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Luis Picado
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Johanna Jacobi, Alexandra Gavilano
Filtro para aguas grises
technologies_4585 - Nicaragua
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Para el mandato de backstopping para le programa gestion comunitaria de la cuenca de Rio Dipilto en Nicaragua (Gestion comunitaria - Nicaragua)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SwitzerlandName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio del Ambiente y los Recursos Naturales - Nicaragua (MARENA) - Nicaragua1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
recursos disponibles, son locales
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
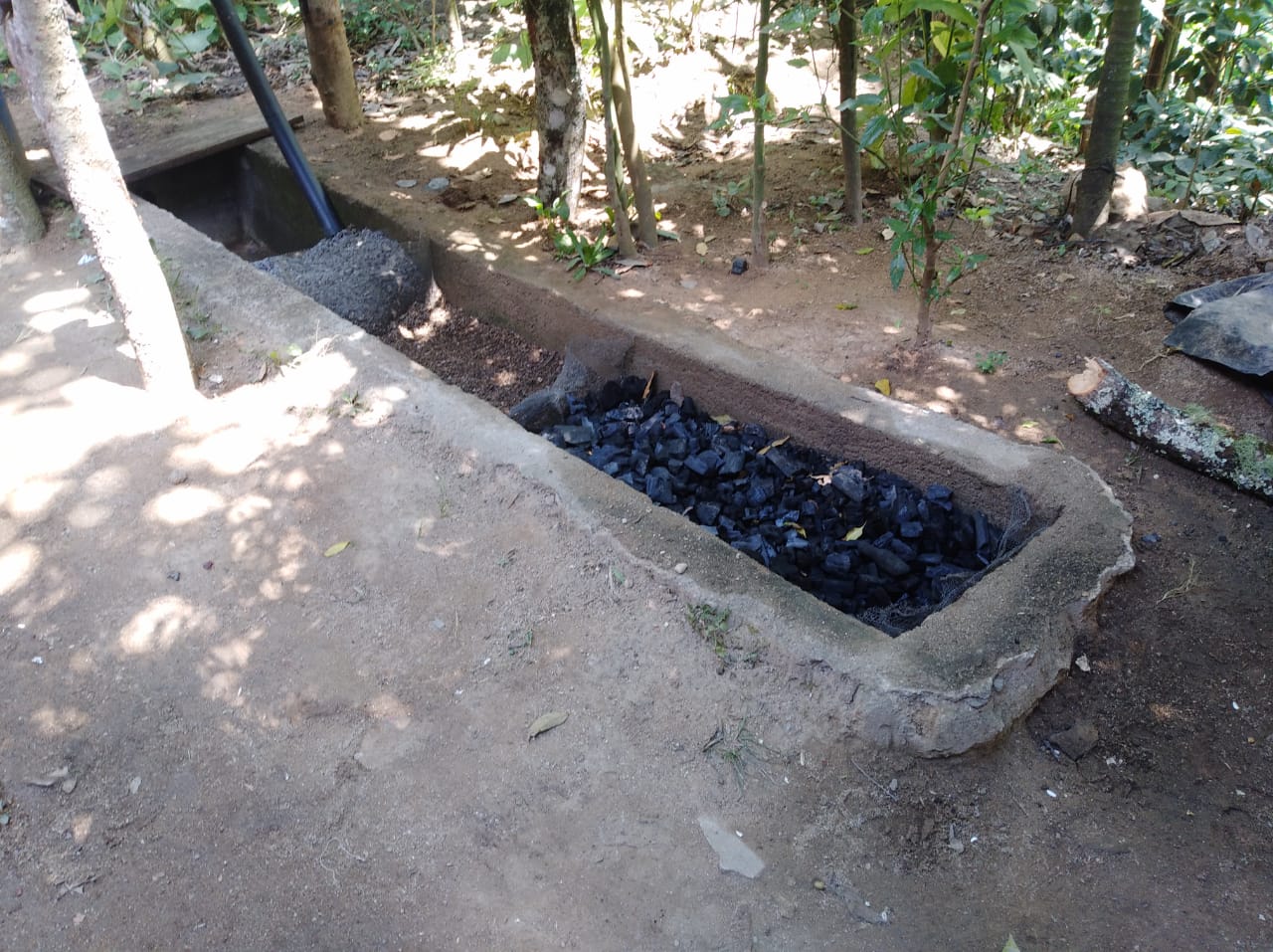
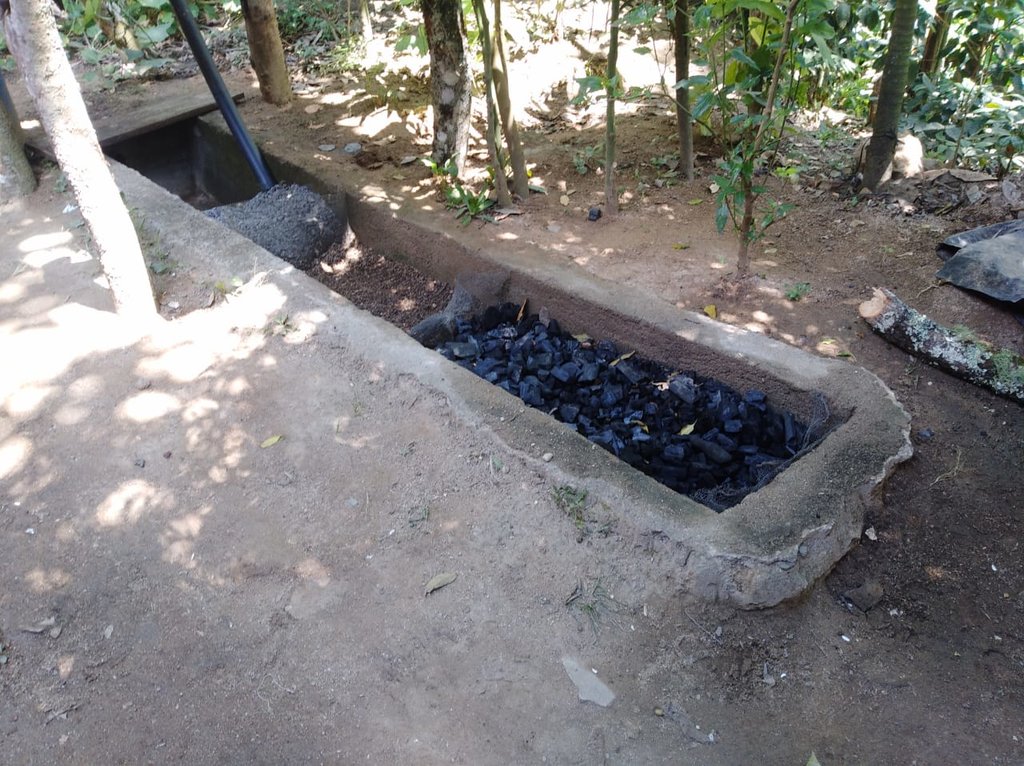
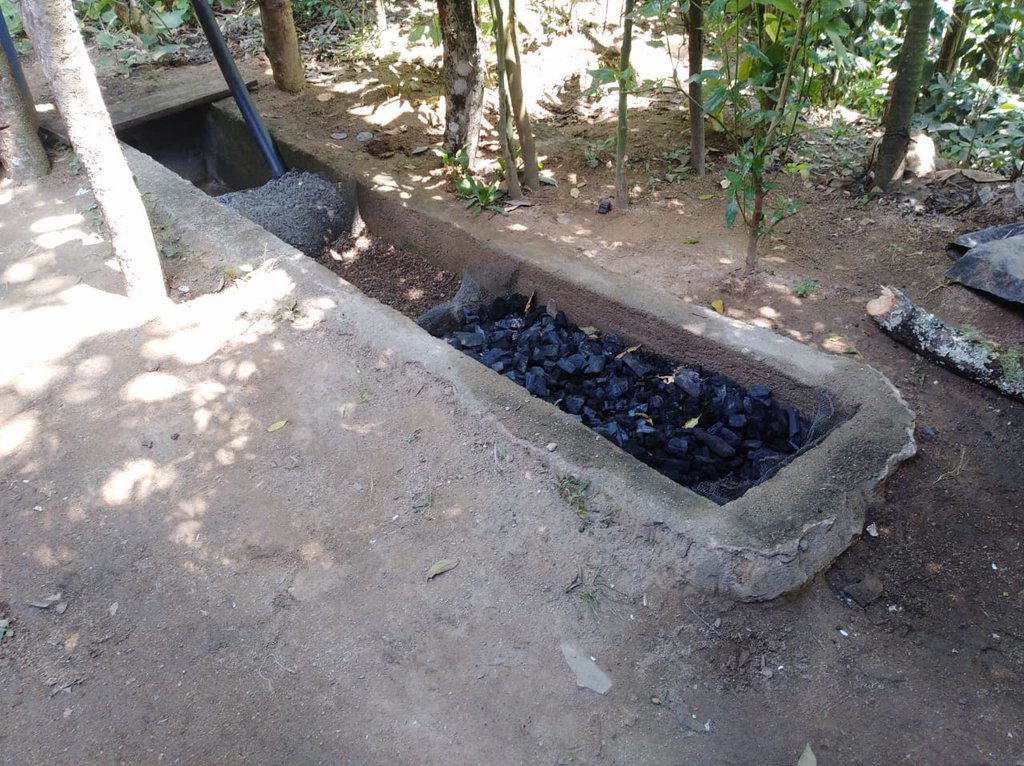
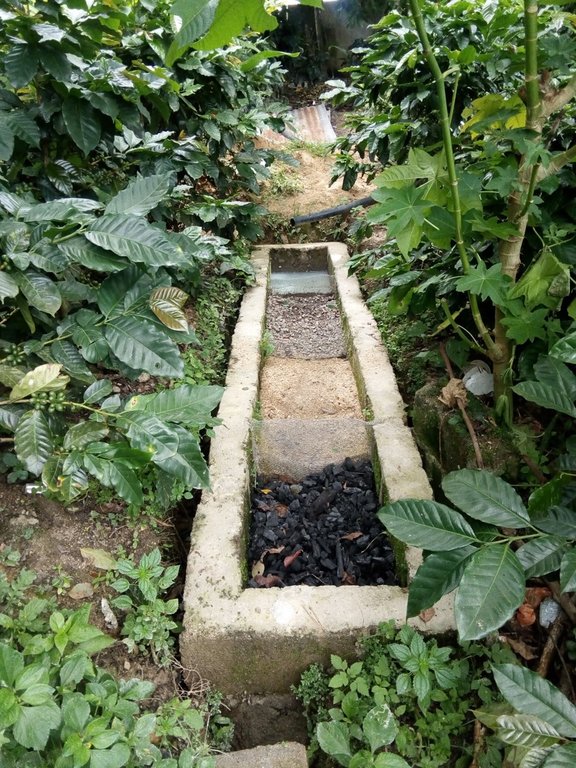
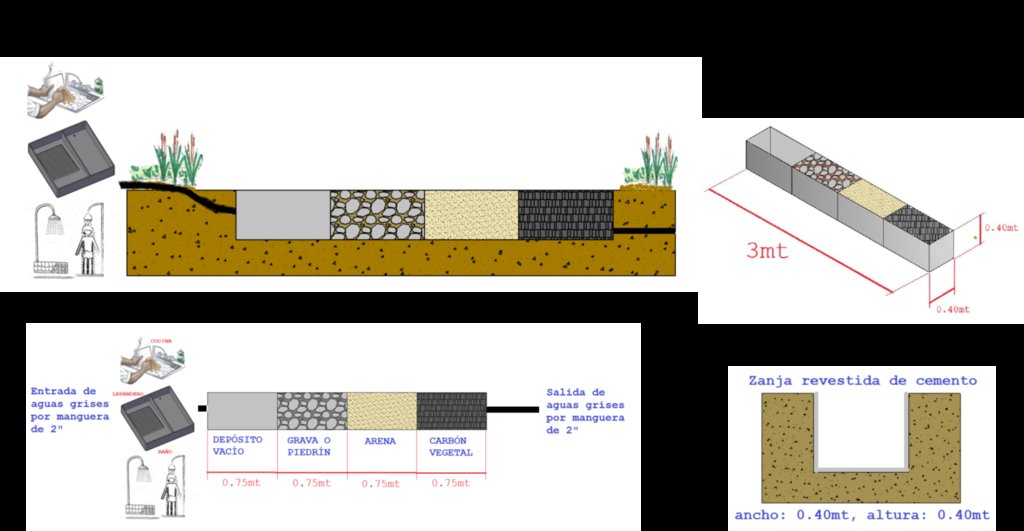
El biofiltro para tratamiento de aguas grises es una zanja de cemento llenada con piedrín, arena, y con carbón activado. El agua filtrada puede servir para riego de jardinería y plantas frutales.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
La tecnología del Biofiltro para tratamiento de aguas grises es implementada en la cuenca del Rio Dipilto, en el departamento de Nueva Segovia, en Nicaragua. Se aplica a fincas y hogares de las comunidades y hogares ubicados en zonas peri-urbanas de los municipios de Dipilto y Ocotal. Consiste en una zanja o un foso de 3 metros de largo, revestido de cemento o ladrillo de barro cocido. El ancho es de 0.4 metros y su profundidad es también 0.4 metros. El foso o zanja esta dividido en 4 espacios o divisiones de 0.75 metros cada uno, el primero es para recibir las aguas grises provenientes de las actividades domesticas, el segundo esta lleno de piedrín, el tercero con arena y el ultimo con carbón activado, la pendiente de 2-3% permite la circulación de las aguas grises a través de los materiales filtrantes, el agua sale filtrada por una manguera de 2 pulgadas, la que al final del filtrado es usada para riego en jardineria o frutales. El propósito es el tratamiento de las aguas grises para reducir la contaminación de las aguas superficiales. Para su instalación se necesita piedrín, arena, carbon activado y mangueras de 2 pulgadas. El mantenimiento se realiza mensualmente lavando el piedrín y ocasionalmente la arena si esta muy sucia. El carbón se reemplaza cada año, dependiendo del uso. La tecnología reduce la contaminación del agua y el agua se puede reusar para riego. Los usuarios de la tierra dicen que es excelente porque quita del agua el Jabón, grasas, etc.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Nicaragua
Region/ State/ Province:
Nueva Segovia
Further specification of location:
Municipios de Ocotal y Dipilto
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
97.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 km2
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
Yes
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
En un programa de gestion comunitaria para el manejo de la cuenca del Río Dipilto.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- coffee, shade grown
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Hay cultivos que se cosechan todo el año (cultivo de enramadas, frutas, musaceas)
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Cultivos de enramadas (Chayotes, maraculla, granadilla), musaceas (Platano, bananos) Café, Cacao, Firjol.
Is crop rotation practiced?
No
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)

Settlements, infrastructure
- Settlements, buildings
Remarks:
El poposito de la tecnologia es el tratamiento de las aguas servidas domiciliares
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water diversion and drainage
- surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
- waste management/ waste water management
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation

other
Specify:
La tecnología esta destinada a enfrentar la reduccion de la calidad de las aguas superficiales originadas por las aguas grises o servidas que llevan consigo contaminantes como jabón, grasas, detergentes y aceite, que son vertidas directamente a las masas de agua fresca en la cuenca del Río Dipilto.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- not applicable
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
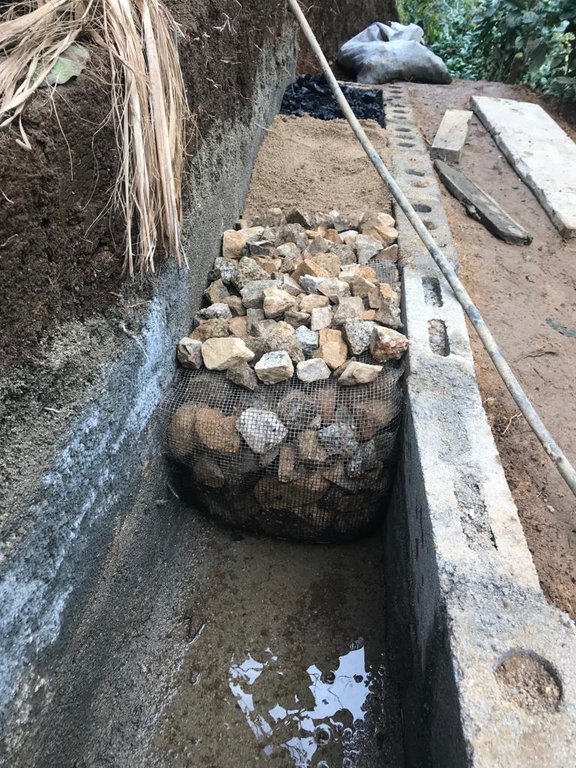
Es una zanja o foso de 3 mts de largo, revestido de cemento o ladrillo de barro cocido, el ancho es de 0.4 mts y su profundidad es tambien 0.4 mts . El foso o zanja esta dividido en 4 compartimentos o divisiones de 0.75 mts cada uno, el primero es para recepcionar las aguas grises provenientes de las actividades domesticas, el segundo esta lleno de piedrin, el tercero con arena y el ultimo con carbón activado, la pendiente de 2-3% permite la circulación de las aguas grises a través de los materiales filtrantes, el agua sale filtrada por una manguera de 2 pulgadas, la que al final del filtrado es usada para riego en jardineria o frutales.
Author:
Carlos Marín
Date:
20/03/2019
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
3 mt de largo por 0.4 mts de ancho por 0.4 mt de alto, dividido en 4 compartimentos de 0.75 mts cada uno.
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
33.3
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
C$ 150.00 (ciento cincuenta cordobas netos)
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seleccion del lugar y diseño del biofiltro | en cualquier momento del año |
| 2. | Niveles, excavacion | en cualquier momento del año |
| 3. | poner revestimiento de concreto o ladrillos | en cualquier momento del año |
| 4. | Excavacion, instalar tubos de entrada y salida | en cualquier momento del año |
| 5. | activar carbón (lavado del carbón y secado al sol por tres días) | en cualquier momento del año |
| 6. | lavar piedrin | en cualquier momento del año |
| 7. | Hacer divisones con malla (opcional) | en cualquier momento del año |
| 8. | Relleno con materiales filtrantes | en cualquier momento del año |
| 9. | coneccion al sistema de drenaje de cocina y/o baño. | en cualquier momento del año |
Comments:
Es una tecnología que puede construirse en cualquier época del año.
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Mano de obra para construccion de biofiltro | D/H | 2.0 | 400.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Pala | unid | 1.0 | 260.0 | 260.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Barra | Unid | 1.0 | 605.0 | 605.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Piocha | Unid | 1.0 | 378.0 | 378.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Carretilla | Unid | 1.0 | 1435.0 | 1435.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | madera | PT | 29.0 | 25.0 | 725.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Cemento | bolsa 46 Kg | 2.0 | 340.0 | 680.0 | |
| Construction material | Arena | mt3 | 0.5 | 800.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Carbon | Sacos | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | |
| Construction material | Piedrin | balde/lata | 3.0 | 50.0 | 150.0 | |
| Construction material | Manguera de 2 pulg | Rollo | 0.5 | 4000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Construction material | Piedra | m3 | 0.25 | 1000.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 8583.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 257.75 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
257.75
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Programa de gestión comunitaria de la cuenca del rió Dipilto
Comments:
La tecnologia es barata porque el protagonista asume mucho del costo de mano de obra y materiales.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza (Lavar los materiales) | mensual |
| 2. | Cambiar el carbon | anual |
| 3. | cambio de arena | anual |
| 4. | Mantener limpio el biofiltro | permanente |
Comments:
Los materiales filtrantes son locales.
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | mano de obra para limpieza | D/H | 6.0 | 150.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Carbon | Sacos | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Arena | Blades/Latas | 3.0 | 50.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1950.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 58.56 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
58.56
Comments:
El mantenimiento es barato por que lo asume el protagonista
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Solamente el costo de transporte de los materiales desde el mercado hasta la finca/hogar
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1300.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
La cuenca tiene un rango de precipitacion pluvial entre 800-1800 mm anuales
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Comunidad Las manos (Erick Almendares) , Comunidad El Volcan (Guiillermo Montenegro)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Water quality refers to:
surface water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Yes
Specify:
Dueño de la propiedad segun titulo y/o escritura publica
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Water availability and quality
irrigation water availability
irrigation water quality
Socio-cultural impacts
health situation
Comments/ specify:
No hay mosquitos, no moscas se reducen en poblaciones porque no hay ambiente donde reproducirse.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
Soil
soil moisture
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
groundwater/ river pollution
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 11-50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
426
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Todos lo han hecho con el programa.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Yes
other (specify):
De acuerdo a materiales disponibles
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
La estructura se ha revestido de concreto, ladrillos de barro cosidos y bloques de cemento, si hay poco espacio se hace vertical sin perder las dimensiones y la posicion de los materiales filtrantes.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Costos minimos en comparacion con los beneficios |
| Evitamos contaminacion |
| Mejor aprovechamiento del agua |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Facil de construir |
| Es una tecnica sencilla, construida con materiales locales |
| Es una tecnologia orientada a enfrentar problema fuerte en las comunidades |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| El Carbon es un material que debe llevarse desde fjuera de la comunidad. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Hay que hacer fuerte enfasis en el mantenimiento del biofiltro | Se propone elaborar un manual de construccion y mantenimiento del Biofiltro |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
7
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
3
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
20/03/2019
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
No aplica
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules