FFS/SLM Community Initiative [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Farmer Field School
approaches_2487 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/12/2013
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
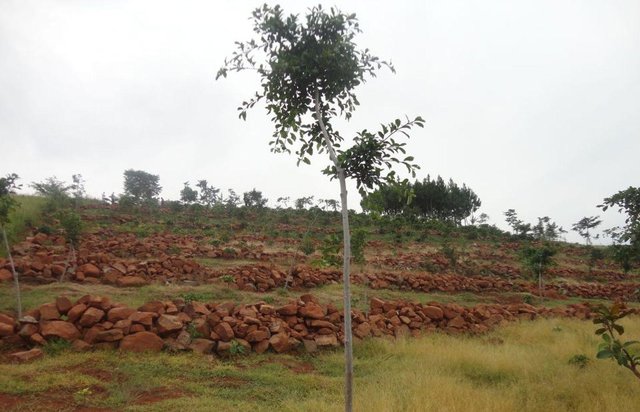

Stone lines [乌干达]
Stone lines are built along a contour to control soil erosion on a degraded steep slope.
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Farmers are organized to promote adoption of sustainable land management best practices within the community
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: To train farmers in land based technologies that improve productivity, land management and are resilient to climate changes
Methods: Planning meetings, agro-ecosystem analysis (AESA), farmer-to-farmer visits, monitoring and evaluation
Stages of implementation: Farmer Field School (FFS) formation to bring together 30 farmers from a catchment area; training in group dynamics; training in best practices to address land degradation problems; AESA; and action planning
Role of stakeholders: District facilitators: Facilitation of FFS formation, training of trainers for AESA, drawing village land use plans, prioritizing enterprises/challenges, making technical recommendations; Local leaders: Passing and implementing bye-laws.
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kijonjo, Katongero, Rakai District
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2011
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2015
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused on SLM only (Sustainable Land Management Farmer Cooperative)
To share knowledge, skills and information on establishment of local best practices to improve productivity and biodiversity and reduce soil erosion
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Low soil nutrient levels, vegetation loss and soil erosion on steep slopes
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Inadequate resources because farming is mainly subsistent
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers formed cooperatives to pool resources
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Little available information on addressing land management issues
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Trained facilitators were sourced to provide appropriate knowledge to address relevant constraints
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 阻碍
Increased workload required in the implementation caused expenses on hired labor to rise.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Sharing workload through working together to dig up stones and carry them on steep slopes, lay them along contours and plant Ficus natalensis to stabilize the soil
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Women constitute the majority of farmers in attendance because most agricultural production in the district is carried out by women, except in cattle-keeping areas where men are the majority
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 地方政府
District facilitators were provided by the district local government
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
Collaboration with the line Central Government Ministries through the Project Steering Committee at Permanent Secretary level
- 国际组织
Kagera TAMP (FAO-GEF) provided funding for specialist facilitators
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
Kagera TAMP international specialists with the help of national FFS specialists
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | FFS specialist facilitator with prospective FFS members to get farmers organized in FFS (30 members each) |
| 计划 | 互动 | Farmers in their farmer field schools sketched watershed maps and developed action plans with the help of district facilitators |
| 实施 | 互动 | Facilitators helped FFS members in the dynamics that sustained and strengthened the Approach |
| 监测/评估 | 被动 | A few members were co-opted to the monitoring team which comprised local government facilitators, Kagera TAMP Project specialists and the central government Project Steering Committee |
| Research | 互动 | FFS members carried out Agro-ecosystem Analysis (AESA) with training and field support from specialists |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
The FFS concept and methodology were introduced to the farmers by SLM specialists. The decisions on technology choice were the result of discussions bf the farmers with support from the specialists.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Farmers in the FFS decided how to overcome constraints posed by their hilly terrain and high cost of labor
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
- Politicians/Policy Makers
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
涵盖的主题:
Extension Training: use of demonstration plots and AESA to experiment and discover the appropriate methodology for implementation of SLM technologies. A formal session involves a facilitator and farmers. The facilitator guides the farmers on how to investigate a problem using marker-drawn sketches on flip chart. Observations, conclusions and recommendations are reached in a participatory manner.
Extension: FFS members adopt a resolution to carry out the recommended procedures/activities; community members are free to interact with FFS members on field days and copy recommendations. Farmer-to-farmer visits are encouraged and promoted to extend information.
Research: FFS members research together on a given problem/challenge such as soil fertility and arrive at recommendations together. They are guided by facilitators from government or government research institutions with collaborative support from Kagera TAMP/FAO project.
Importance of land use rights: Ownership of land affects land management practices. The attitude towards the recommendation by farmers is usually determined by the FFS members. In Kagera TAMP districts land ownership is customary but the right to use land is governed by national laws.
Incentives:
Labor: Farmer Field School members provide the labor to implement technologies. Hired labor may also be used.
Inputs: Farmers provide the basic tools such as hoes, pick axe etc. Seedlings and seeds may be provided by the project.
Credit: Small amounts may be acquired from the FFS cooperative savings.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
提供进一步细节:
Training workshops in Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Land Degradation Assessment (LADA) both national and international, seminars, and procurement and training in the use of computers, digital cameras and GPS units
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government, land users through observations; indicators: Measurement of crop yield, soil nutrients, biodiversity
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government, land users through measurements; indicators: Measurement of crop yield, soil nutrients, biodiversity
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by government, land users through observations; indicators: Measurement of crop yield, vigor
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: Measurement of crop yield, vigor
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government through observations; indicators: Measure by attendance, morale
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government through measurements; indicators: Measure by attendance, morale
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: None
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: FFS constantly refines and improves on what and how to achieve objectives, to discover and archive best practices in the most effective forms possible
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Height of stone lines, width between lines
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Agro-ecosystem Analysis (AESA) by FFS members
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- < 2,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (Kagera TAMP): 18.95%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (District and Sub-county facilitator time): 11.14%; local community / land user(s) (Land users as FFS members): 69.91%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
FFS members were facilitated with information and they carried out the approach without any financial or material support
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Formerly disused land was made productive
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Crop diversification, food security
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
FFS savings and credit cooperative helping members to access small unsecured agro-input financing
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 环境意识
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Stone lines [乌干达]
Stone lines are built along a contour to control soil erosion on a degraded steep slope.
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
模块
无模块