Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips [挪威]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Grasdekt buffersone
technologies_1656 - 挪威
- Grass buffer zones alongside waterways in cropland: Feb. 3, 2023 (public)
- Grass buffer zones alongside waterways in cropland: June 17, 2022 (inactive)
- Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips: Sept. 5, 2019 (inactive)
- Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips: March 16, 2017 (inactive)
- Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips: March 16, 2017 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Norwegian Institute for Agricultural and Environme (Norwegian Institute for Agricultural and Environme) - 挪威1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/08/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Establishment of grass covered vegetation strips along cropland waterways for reduced erosion and infiltration of surface runoff.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
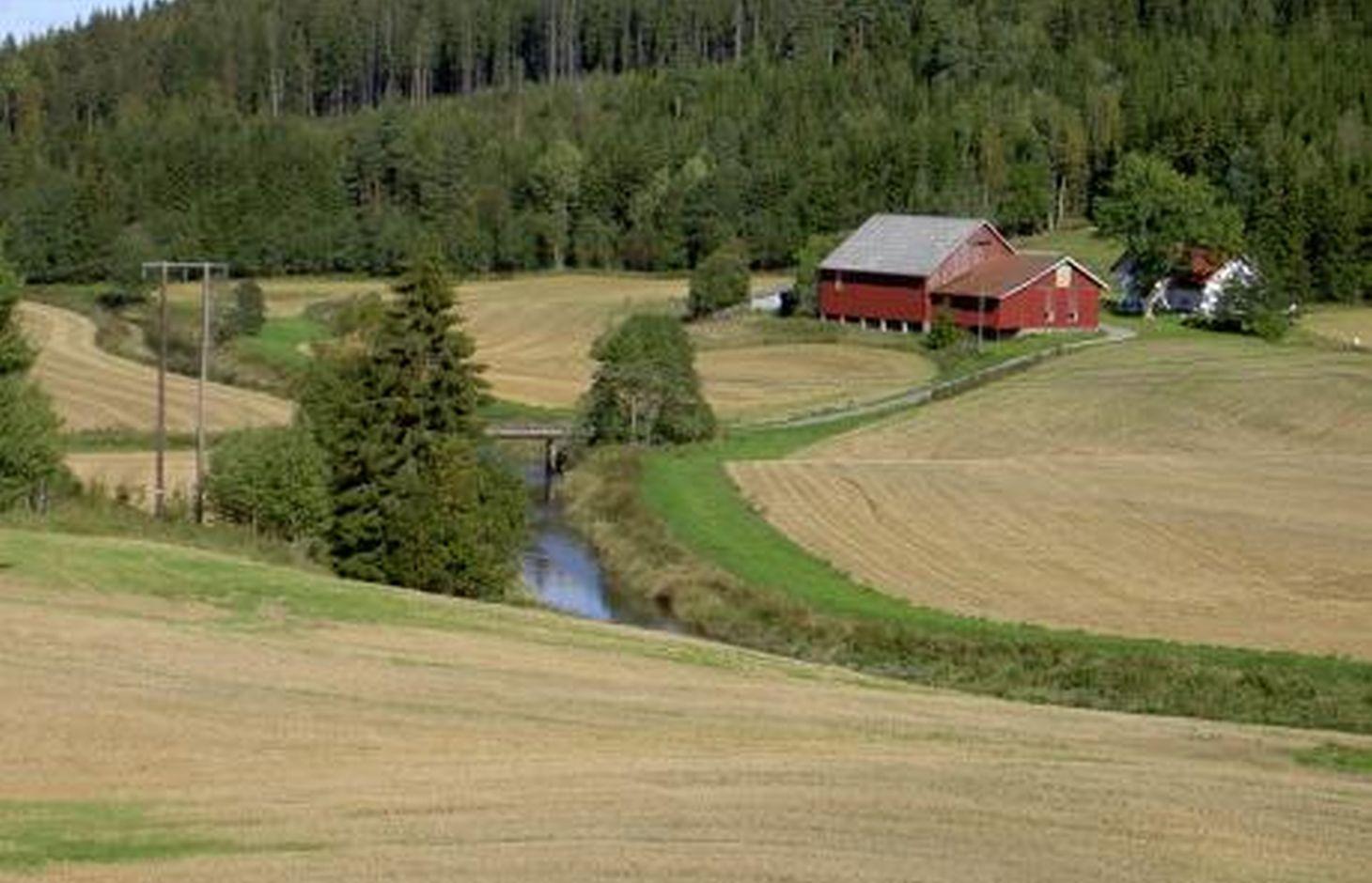
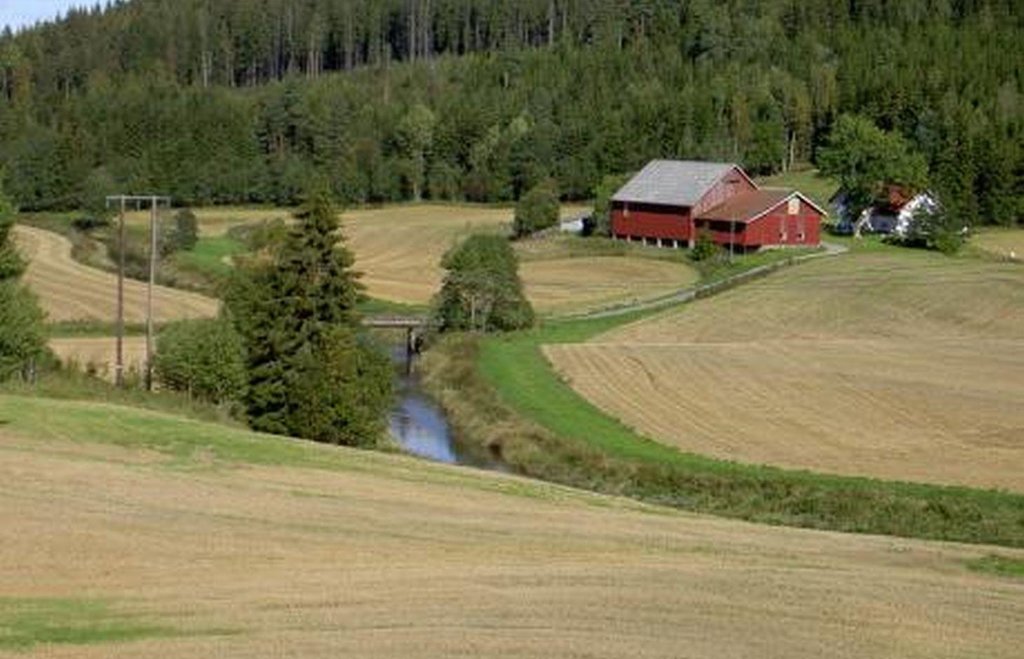
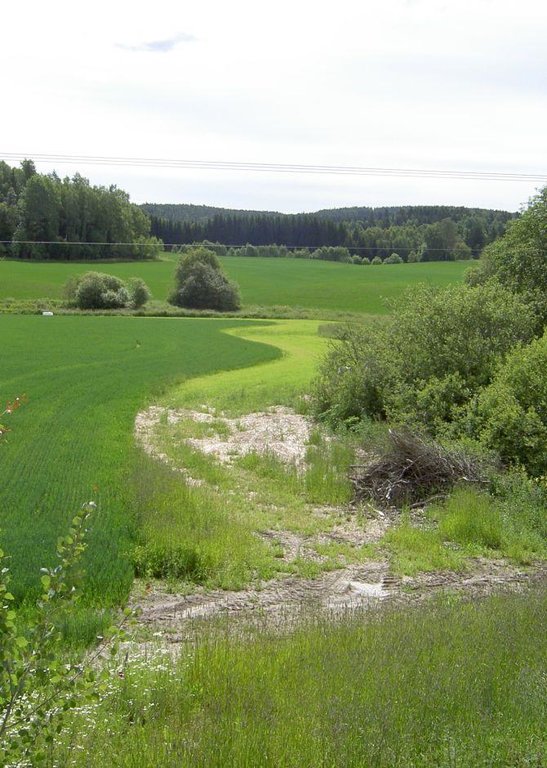
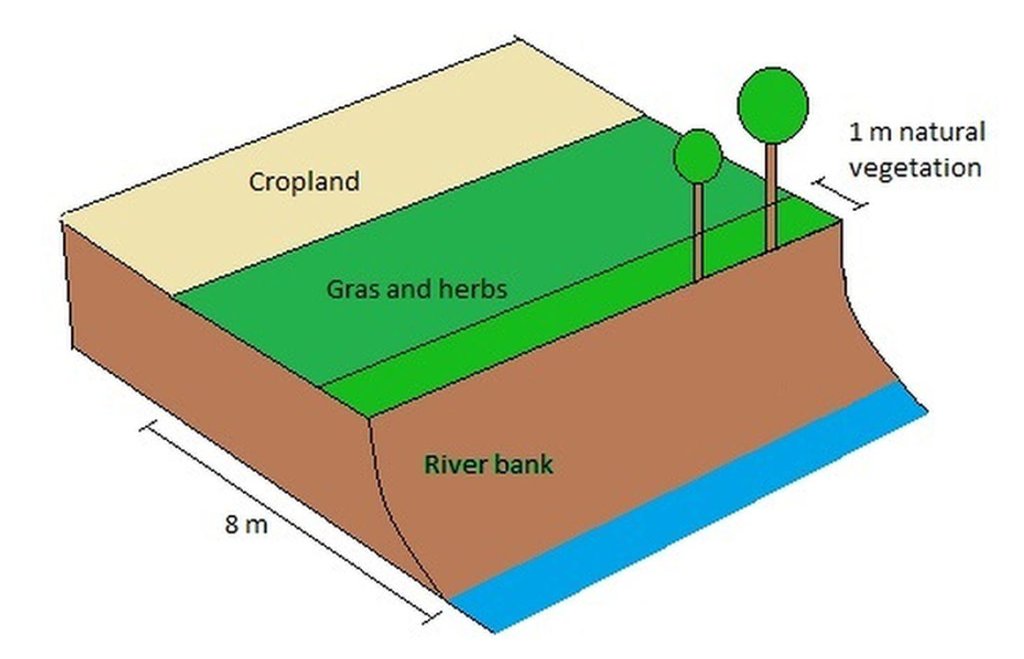
The farmers leave a strip of cropland for grass and herbs to grow along rivers, streams and lakes that intersect their cropland areas. Regulations that origins from the Morsa project (morsa.org) require vegetation zones with a width of approximately eight meters. The establishment of these buffer zones is of high importance in areas regularly exposed to flooding.
Purpose of the Technology: The buffer strips are a measure to slow down surface runoff for more water to infiltrate and for particles carried by the water to settle in the vegetation. It is also meant to contribute to reduce erosion and increase the binding of phosphorous to soil particles, as well as the uptake by the vegetation. A decreased input of particles and nutrients to the cropland waterways is desirable both in order to limit soil loss and to prevent eutrophication of downstream waterbodies.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: To sow grass is recommended when establishing grass covered riparian buffer strips. Robust and dense grass types with a high demand of nutrients are often the most suited for the purpose. The grass strips should generally not be plowed, fertilized or treated by herbicides, but some exceptions may be made. The degree of which it is harvested varies with the grass type and if it is used for animal fodder.
Natural / human environment: The Kråkstad River is mainly situated in Ski commune in Akershus County in South-Eastern parts of Norway. The river catchment is a western tributary of the Vannsjø-Hobøl watercourse, also known as the Morsa watercourse. The Kråkstad River catchment constitutes of a total area of about 22 km², consisting mainly of cropland and forest/woodland. The recipient Vannsjø is a eutrophic lake with a history of algal blooms of e.g. toxic cyanobacterias. The lake is both used as a drinking water source and for recreational purposes, and the Morsa project was established in order to find measures to improve the water quality of Vannsjø.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
挪威
区域/州/省:
Akershus
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ski
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: (59.595, 10.896), (59.611, 10.866), (59.670, 10.869), (59.676, 10.849), (59.717, 10.844), (59.723, 10.893), (59.694, 10.969), (59.655, 10.952), (59.668, 10.904), (59.629, 10.915)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The Morsa Project (morsa.org)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Small grain
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Fire wood

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 薪材
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Erosion, flooding and landslides, eutrophication of rivers and lakes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cropland is occupied by the buffer strips, which may lead to decreased production and loss of income.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 135Longest growing period from month to month: May to mid September
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 4.3 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Wr: riverbank erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Use of fertilizer and heavy machinery (compression of the soil and low infiltration rate)), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More flooding and erosion), floods
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (The runoff has a lower retention time in the forest. Leads to higher velocity and more flooding of downstream cropland areas), change of seasonal rainfall (Heavier rainfall events due to climate change), land tenure, governance / institutional
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
A technical drawing of a grass covered riperian buffer strip with grass cover and riperian vegetation
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Along waterways
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Naturally
Grass species: Seeded
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kroner (NOK)
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
7.73
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
827.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing | 植物性的 | 1 time/yr |
| 2. | Harrowing | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
| 3. | Sawing grass | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
| 4. | Harvesting grass | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Plowing | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | 7.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harrowing | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | 7.0 |
| 劳动力 | Sawing grass | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | 7.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting grass | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | 7.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1284.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing | 植物性的 | Once every 6th year |
| 2. | Harrowing | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
| 3. | Sawing grass | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
| 4. | Harvesting grass | 植物性的 | 2-3 times/yr |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Plowing | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 53.0 | 53.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harrowing | zone/farmer/day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Sawing grass | Day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting grass | Day | 1.0 | 321.0 | 321.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1016.0 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium-high
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low-low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Because of the drinking water quality
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
轻度消极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local regulations determine that farmers only receive subsidies per production area along with financial grants if they implement the technology.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The grass catches sediments from the cropland How can they be sustained / enhanced? May be more efficient with a change in grass type (but this is not tested) |
|
Reduced fertilizer usage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue in the same way |
|
Corporation between farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Joint company for utilizing the buffer strips for grass production |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of productive cropland | Narrower buffer strips |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Low infiltration rates | Less heavy machinery on the buffer strips and a wider zone of natural vegetation along the banks |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块