Water run-off control plan on cultivated land [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Carin Pretorius
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Watercourses and contours
technologies_956 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/06/1999
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Artificially built watercourses with contour banks with a specific gradient
2.2 技术的详细说明
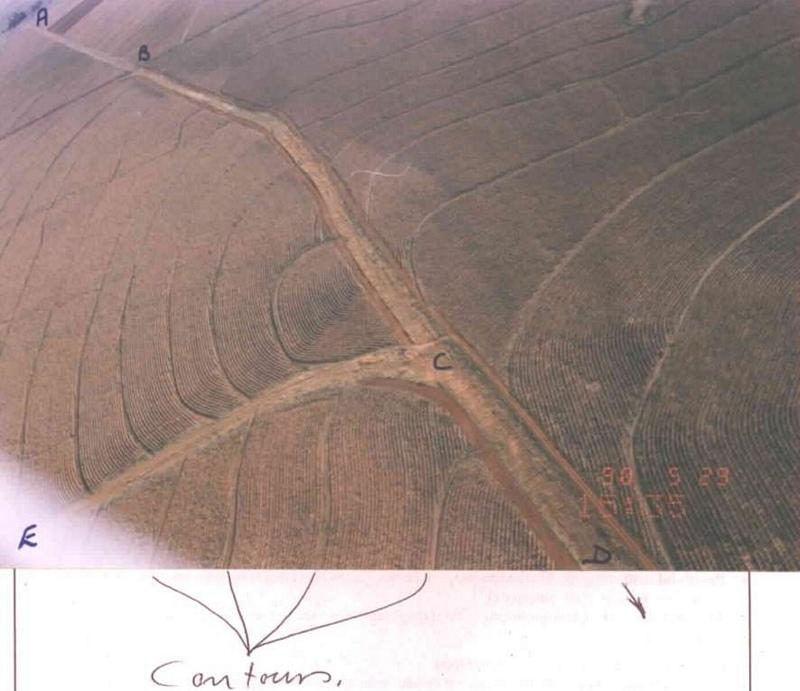
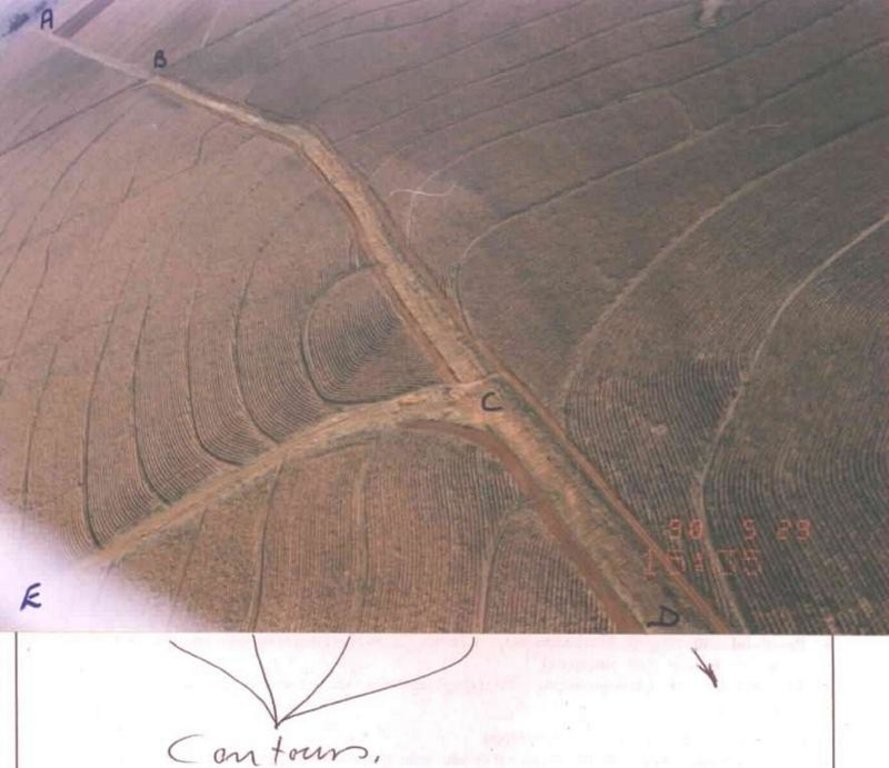
说明:
Watercourse: According to the topography, one or two watercourses are needed to drain any excess run-off water during high rainfall intensities. A watercourse is built directly downhill. A perennial grass adapted to the specific environment is established in the watercourses. Maintenance requires that the grass must be fertilised according to the climate of the area. Regular (once or twice a year) cutting of the grass is very important to maintain a good grass cover, through which soil erosion in the watercourse can be prevented.
Contour banks: These are built with a gradient to spill the excess water into the watercourse. The purpose of contour banks is to shorten the slope so as to reduce the speed of the water and prevent soil erosion. The maintenance requires keeping the canal in good shape and maintaining the height of the banks.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lichtenburg
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The contour part came mainly form the USA.
The watercourse part was developed in South Africa.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cultivating lands without the necessary soil conservation works to prevent soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cultivating the lands preventing soil erosion through plant directions
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 m2.
Although the total extent of the farm is 584 ha, only 250 ha plus 50 ha adjacent land was addressed through this technology.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Cultivating land on a step slope without proper conservation practices.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - How to solve the problem)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topography; concentrating water in valleys causing soil erosion (steep slopes).), Poor conservation ethic
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
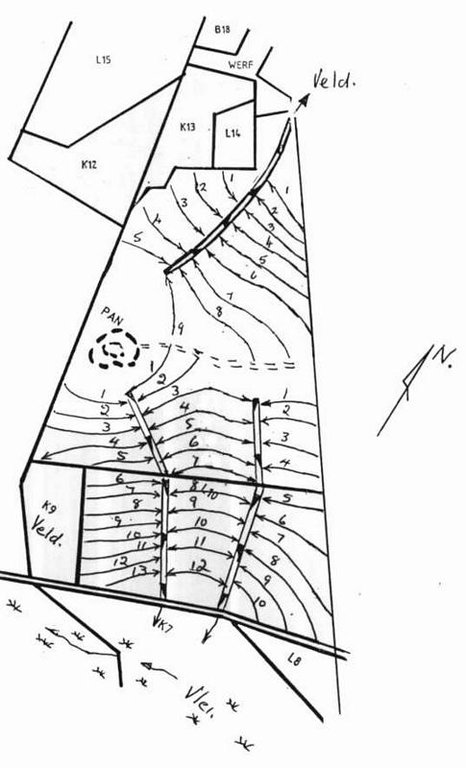
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Water run-off control plan
Location: Lichtenburg. North West
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, Maintain soil fertility as less fertilizer are lost by water run-off
Vegetative measure: watercourses
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): seeds 6-8kg/ha
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Grass species: Digitaria Smuts, Eragrostis curvula, Cynodom dactylon
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3-1.75
Spacing between structures (m): 72-33
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Construction material (earth): Construction contour banks with soil form the ditches
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.3%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
rand
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
6.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Established grass in the watercourses | 植物性的 | After construction according to design specifications |
| 2. | Surveying | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 3. | Construction of contours | 结构性的 | Any time depending on soil moisture |
| 4. | Construction of watercourse | 结构性的 | Before growing season |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building contours and watercourses | 农业学的 | Any time / Before planting of crops |
| 2. | Building contours and watercourses | 农业学的 | Depending on soil moisture / |
| 3. | Maintenance | 农业学的 | Before planting of crops / Annually |
| 4. | Cultivation between contours | 农业学的 | Depending on the crop / Annually |
| 5. | Maintaining a good grass cover | 植物性的 | Rainy season /Once or more times a year depending on the grass |
| 6. | Fertilisation of the grass in the watercourse | 植物性的 | Rainy season /Once or twice in the rainy season |
| 7. | Watercourse, cutting the grass | 结构性的 | Beginning of rainy season/Annual |
| 8. | Contours repairing flood damage | 结构性的 | Dry season/After heavy rains |
| 9. | Contour opening ditches | 结构性的 | Before planting of cops/Annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & plough or a grader
Contours per kilometre. NB currant tariff for subsidy. Watercourse construction per volume soil moved and grass establishing per ha above the current tariff for subsidy from April 1998
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Soil moisture and clay contents
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 100% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (If management is good).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers are dedicated to make a living out of farming, although there are some farmers with an off-farm income such as transport.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
土地管理
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
60
SLM之后的数量:
20
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
25
SLM之后的数量:
4
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
注释:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: So little, almost none. The lack in technicians from government promoting this technology and to deliver technical services are the main reasons expect for the poor conservation ethic of the farmers.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good regular maintenance |
| Building up a good layer of topsoil |
| Effective run-off control of excess rainwater |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Effective erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Improve water infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Increase crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Prevent off-site siltation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Hampers cultivation | Adapt change in cultivation practises |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Cannot think of any |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块