Integrated Farming System [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Srikanta Kumar Parida
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1085 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Pradhan Gandhi
印度
SLM专业人员:
Pradhan Damodar
印度
SLM专业人员:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
印度
SLM专业人员:
Mohanty B.B
Sarvodaya Samiti
印度
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Sarvodaya Samiti - 印度1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
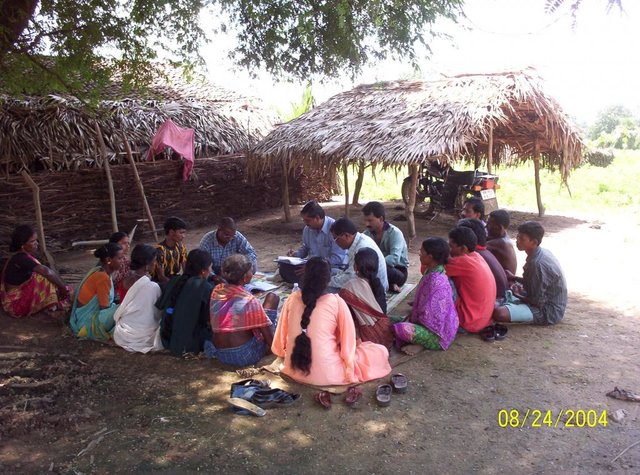

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [印度]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- 编制者: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Growing of crops for food, fodder trees and fibre forest in a compact patch.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
This technology has mainly to be applied on 5 Ha.of private waste land of poor farmers to increase production. This technology focuses on life fencing, planting of trees for both timber and food varieties, land development, water availability and green manuring. Three line bamboo plantation has been done by laying method at all along the boundary line. Agave also planted at boundary line to give additional protection. Then proper compartmentation has been done keeping intact the total area of individual land holders. Here 'V' ditches has been provided accross the slope of total land. Some fruit and fodder, forest trees were planted all along the bunds and inside the field. The density of tree plantation at crop field is less. So as to facilitate crop cultivation. Gullies has also been arrested by construction of gully control structures. One waterhole has been excavated for life saving irrigation. To manage field waste and to get green manure three compost pits also established.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After several meeting and interaction with village people, this technology has been established. All the land users where technology is applied were fully engaged for every construction work. So as to have a clear understaing of each small intervention. As this technology uses locally available materials, its maintenance by land users become easy.
Natural / human environment: Here Soil & Water Conservation has been given importance, hence more vegetative cover has been noticed in and around technology area. Increase of soil fertility has also been noticed. Complete barren land conveted in to crop land. So the technology has positive impact on the environment undoubtedly.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Orissa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Orissa
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.05
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Project SWC Specialist utilizing the earlier experience in the project and other area.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 龙舌兰/剑麻

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 单一栽培的本地品种
树木类型:
- 竹子

不毛之地
具体说明:
Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to slope and lack of vegetation cover, majority top soil were lost and many gullies also formed as a result there was no scope for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The soil was hard, no fertility, land is slopy. So there was no scope for any kind of cultivation in the same patch of land.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Slope, Soil loss
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -against wind
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Erosion problem, Common social practices
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
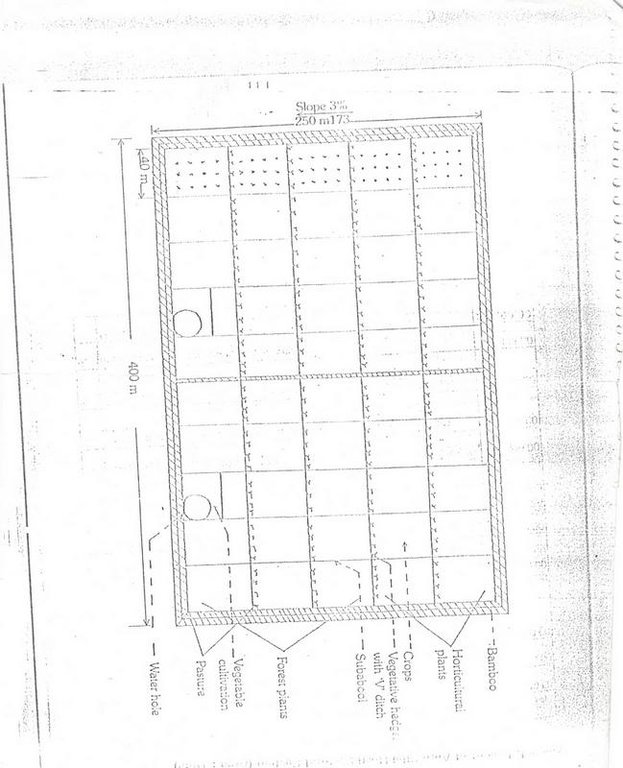
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Diagram showing different soil conservation measures
Location: Maliguda. Koraput/Orissa/India
Date: 15/3/2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measure: Green Fencing
Material/ species: Bamboo, Agave
Remarks: Two type of Bamboo and Agave provided all round the technology area
Manure / compost / residues
Remarks: 3 compost pits has been established.
Agronomic measure: Tillage with country plough
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 15000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 114
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.33
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo, Agave (Sisal)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango and Cashew
Other species: Teak, S.Glauca, Subabul
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Structural measure: Pits
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Structural measure: 'V'Ditch with bund
Vertical interval between structures (m): 20
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Construction material (earth): Bund constructed with earth
Construction material (other): Barries established with bamboo along the boundary for wind break as well as fence.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
Parida S.K, Koraput,Orissa, In
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.45
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.88
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of matured bamboo and laying 9" below earth all along boundary in 3 rows | May |
| 2. | Collection of vertiver strips, trees from local nursery | July |
| 3. | Planting grasses, trees | July to Aug |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 313.0 | 313.0 | |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 7.72 | 7.72 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 39.22 | 39.22 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 12.33 | 12.33 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Others | ha | 1.0 | 193.33 | 193.33 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 55.55 | 55.55 | |
| 施工材料 | Pitcher | ha | 1.0 | 13.55 | 13.55 | |
| 其它 | Compost pit | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 783.7 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1741.56 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Jan to June / Twice |
| 2. | Line showing | July / Once |
| 3. | Weeding | Sept / Once |
| 4. | Fertilizer Application | Sept to Oct / Once |
| 5. | Harvesting | Nov / Once |
| 6. | Manuring, weeding and hoeing | September / |
| 7. | Catchpit, pitcher irrigation | November / |
| 8. | Spraying with plant protection materials | December / |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Convert of degraded fellow private land to a cultivable land on adopting new low cost technology in a 5 Ha. Compact patch. The following benefits -
(1) Slope of the land reduced.
(2) Land protected from severe soil erosion.
(3) Increase the moisture region of the soil.
(4) Soil fertility/ standy increased farmers achieved the minimum common needs (basic) common needy product from the technology i.e food, fuel and fodder etc.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
(1) High slope:- Slope reduced Nos. of structure adopted. Labour engagement are expose of sub-surface soil used Nos. of planting materials.
(2) Diference:- The planting materials are not locally available and transported from 20 K.Ms distance (Bamboo, Vertiver, Mango, Cashew)
(3) Comunication was not up to SWC spot during the establishment period.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Eastern Ghat High Land
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and valley floors (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Moderate (land Slope having undulated topography)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, sandy loam to silty clay loam) and coarse/light
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (loss of top soils due to heavy run off, ranked 1)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (soil varies from loam to silly clay loam, ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
24% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
45% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (30% of house hold comes in standard wealth.).
31% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land (70% of house hold comes below average).
Off-farm income specification: Through various training, interaction with specialist, they acquire more knowledge about other small business like Goatery, Poultry, Pisciculture, Beekeeping, Floriculture and also marketing facility and utilizing these knowledge their off-farm income increase.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Finding market and getting better price f or product
经济差异
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Formation of UG/ SHG
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Imparting teaching to nearby village people on erosion, loss of top soil and timely aprehension at field
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
40
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Safe disposal of water.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Adopting soil conservation activities
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Practising cropping
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
46
SLM之后的数量:
20
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
注释/具体说明:
Planting of bamboo at boundary
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
On decomposition of straw
Biodiversity
Seed quality
注释/具体说明:
Better procurement of good quality of seeds
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
Stream flow remains up to February
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
No flooding seen
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
26
注释:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some land users adopted the technology partially. As the technology has different measures, some took field bunds with local grasses, some did tree plantation. Some are planning to plant bamboo in their plot boundary.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Low cost technology |
|
Early adoptbility by the farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Over all it is a best technology with proper management by the farmers |
| Combination of production gain from bamboo and crop, less use of chemical fertilizer as green manure is available localy. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Low cost and simple tech nology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper understanding by land user for technology |
| Materials are used for the technology available locally |
|
Due to increase of income migration is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper adoption of technology |
|
Reduction of runoff and soil loss and increase of soil fertility and soil moisture regime has been increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Adopting proper cropping pattern. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Ownerships of land and additional taxation there on after implementation of technology. | Clear understanding by competant authority ( By revenue people) |
| Fruit trees died | Beneficiaries planted Cashew instead of fruit trees. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Clear understanding of the technology. | Regular meeting with local representatives. |
| Availability of materials in the technology area. | Alternative available materials must be used in technology area. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
-do-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [印度]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- 编制者: Srikanta Kumar Parida
模块
无模块