Integrated Farming System [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Srikanta Kumar Parida
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1085 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Pradhan Gandhi
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Pradhan Damodar
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Mohanty B.B
Sarvodaya Samiti
Inde
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sarvodaya Samiti - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Inde]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilateur : Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Growing of crops for food, fodder trees and fibre forest in a compact patch.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
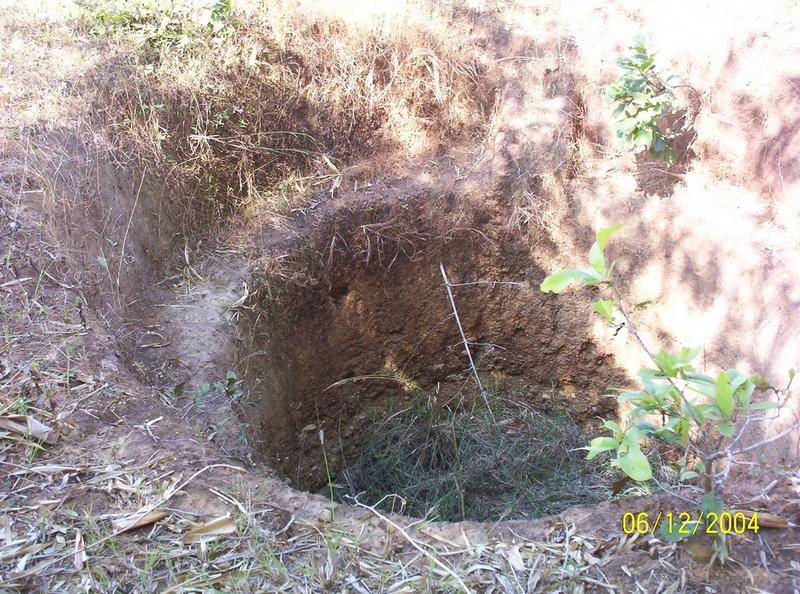
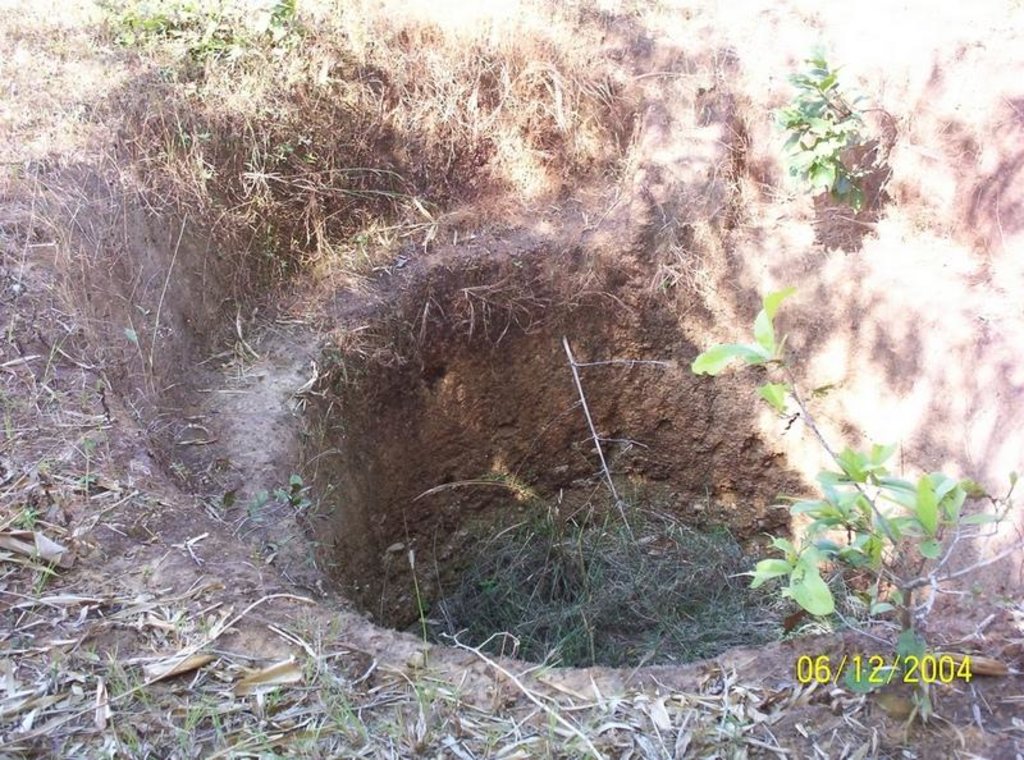
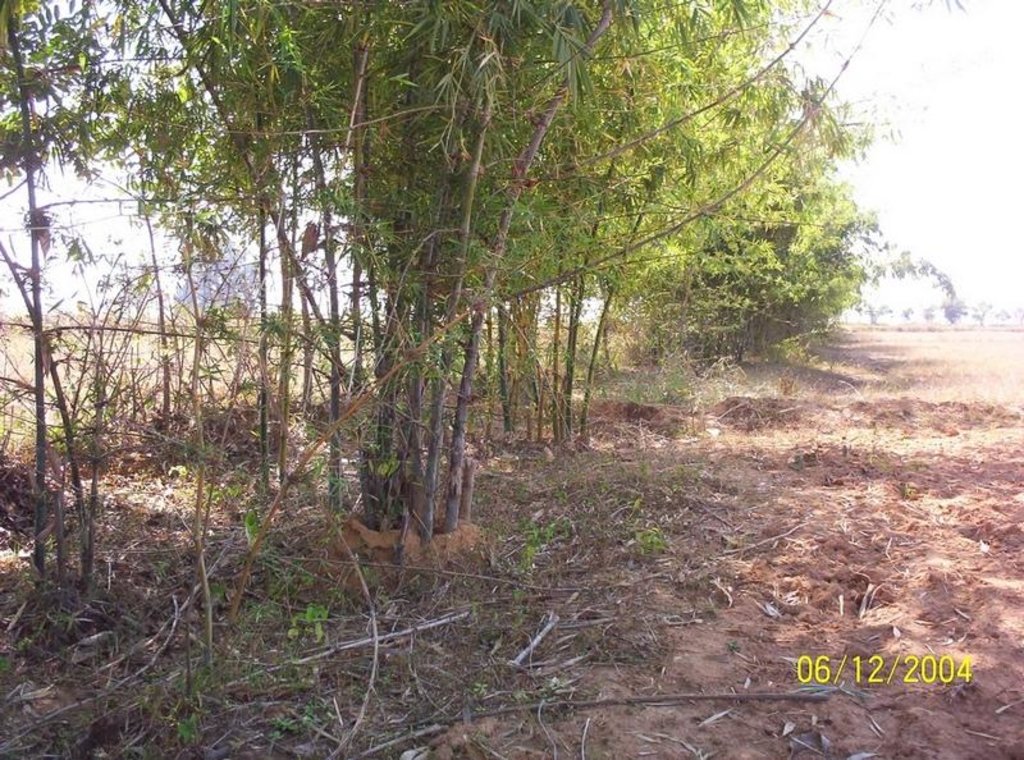
This technology has mainly to be applied on 5 Ha.of private waste land of poor farmers to increase production. This technology focuses on life fencing, planting of trees for both timber and food varieties, land development, water availability and green manuring. Three line bamboo plantation has been done by laying method at all along the boundary line. Agave also planted at boundary line to give additional protection. Then proper compartmentation has been done keeping intact the total area of individual land holders. Here 'V' ditches has been provided accross the slope of total land. Some fruit and fodder, forest trees were planted all along the bunds and inside the field. The density of tree plantation at crop field is less. So as to facilitate crop cultivation. Gullies has also been arrested by construction of gully control structures. One waterhole has been excavated for life saving irrigation. To manage field waste and to get green manure three compost pits also established.
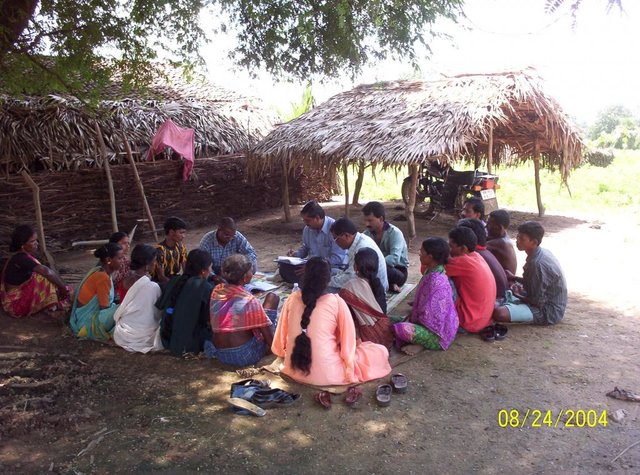
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After several meeting and interaction with village people, this technology has been established. All the land users where technology is applied were fully engaged for every construction work. So as to have a clear understaing of each small intervention. As this technology uses locally available materials, its maintenance by land users become easy.
Natural / human environment: Here Soil & Water Conservation has been given importance, hence more vegetative cover has been noticed in and around technology area. Increase of soil fertility has also been noticed. Complete barren land conveted in to crop land. So the technology has positive impact on the environment undoubtedly.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Orissa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Orissa
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,05
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Project SWC Specialist utilizing the earlier experience in the project and other area.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- agave/sisal

Forêts/ bois
- Plantations d'arbres, boisements
Plantation d'arbres, afforestation: Précisez l'origine et la composition des espèces. :
- Variété locale en monoculture
Type d’arbres:
- Bambou commun

Terres improductives
Précisez:
Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to slope and lack of vegetation cover, majority top soil were lost and many gullies also formed as a result there was no scope for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The soil was hard, no fertility, land is slopy. So there was no scope for any kind of cultivation in the same patch of land.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Slope, Soil loss
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -against wind
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Erosion problem, Common social practices
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
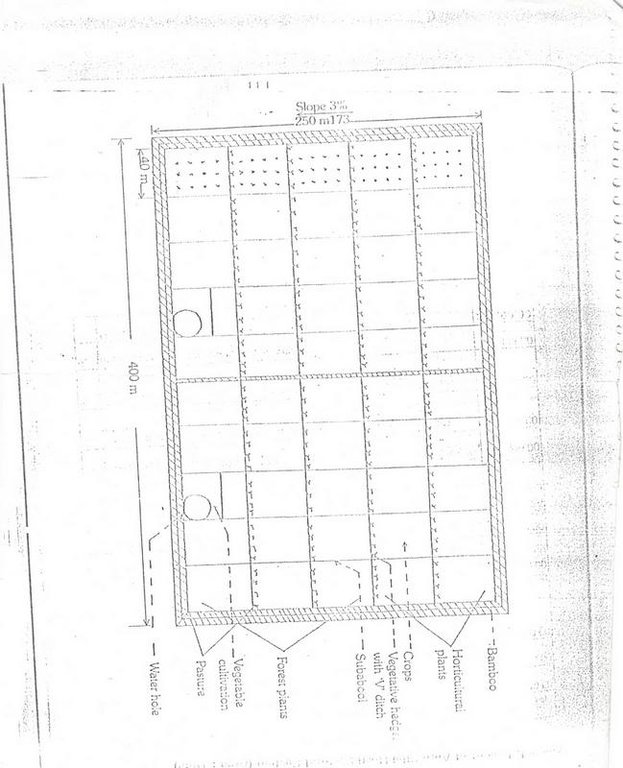
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Diagram showing different soil conservation measures
Location: Maliguda. Koraput/Orissa/India
Date: 15/3/2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measure: Green Fencing
Material/ species: Bamboo, Agave
Remarks: Two type of Bamboo and Agave provided all round the technology area
Manure / compost / residues
Remarks: 3 compost pits has been established.
Agronomic measure: Tillage with country plough
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 15000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 114
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.33
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo, Agave (Sisal)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango and Cashew
Other species: Teak, S.Glauca, Subabul
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Structural measure: Pits
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Structural measure: 'V'Ditch with bund
Vertical interval between structures (m): 20
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Construction material (earth): Bund constructed with earth
Construction material (other): Barries established with bamboo along the boundary for wind break as well as fence.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Auteur:
Parida S.K, Koraput,Orissa, In
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,45
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.88
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of matured bamboo and laying 9" below earth all along boundary in 3 rows | May |
| 2. | Collection of vertiver strips, trees from local nursery | July |
| 3. | Planting grasses, trees | July to Aug |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 313,0 | 313,0 | |
| Equipements | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 7,72 | 7,72 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 39,22 | 39,22 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 99,0 | 99,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 12,33 | 12,33 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Others | ha | 1,0 | 193,33 | 193,33 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 55,55 | 55,55 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Pitcher | ha | 1,0 | 13,55 | 13,55 | |
| Autre | Compost pit | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 783,7 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1741,56 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Jan to June / Twice |
| 2. | Line showing | July / Once |
| 3. | Weeding | Sept / Once |
| 4. | Fertilizer Application | Sept to Oct / Once |
| 5. | Harvesting | Nov / Once |
| 6. | Manuring, weeding and hoeing | September / |
| 7. | Catchpit, pitcher irrigation | November / |
| 8. | Spraying with plant protection materials | December / |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Convert of degraded fellow private land to a cultivable land on adopting new low cost technology in a 5 Ha. Compact patch. The following benefits -
(1) Slope of the land reduced.
(2) Land protected from severe soil erosion.
(3) Increase the moisture region of the soil.
(4) Soil fertility/ standy increased farmers achieved the minimum common needs (basic) common needy product from the technology i.e food, fuel and fodder etc.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
(1) High slope:- Slope reduced Nos. of structure adopted. Labour engagement are expose of sub-surface soil used Nos. of planting materials.
(2) Diference:- The planting materials are not locally available and transported from 20 K.Ms distance (Bamboo, Vertiver, Mango, Cashew)
(3) Comunication was not up to SWC spot during the establishment period.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Eastern Ghat High Land
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and valley floors (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Moderate (land Slope having undulated topography)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, sandy loam to silty clay loam) and coarse/light
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (loss of top soils due to heavy run off, ranked 1)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (soil varies from loam to silly clay loam, ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
24% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
45% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (30% of house hold comes in standard wealth.).
31% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land (70% of house hold comes below average).
Off-farm income specification: Through various training, interaction with specialist, they acquire more knowledge about other small business like Goatery, Poultry, Pisciculture, Beekeeping, Floriculture and also marketing facility and utilizing these knowledge their off-farm income increase.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production de bois
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Finding market and getting better price f or product
disparités économiques
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Formation of UG/ SHG
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Imparting teaching to nearby village people on erosion, loss of top soil and timely aprehension at field
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
50
Quantité après la GDT:
40
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Safe disposal of water.
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Adopting soil conservation activities
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Practising cropping
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
46
Quantité après la GDT:
20
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Planting of bamboo at boundary
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
On decomposition of straw
Biodiversity
Seed quality
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better procurement of good quality of seeds
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Stream flow remains up to February
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No flooding seen
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
26
Commentaires:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some land users adopted the technology partially. As the technology has different measures, some took field bunds with local grasses, some did tree plantation. Some are planning to plant bamboo in their plot boundary.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Low cost technology |
|
Early adoptbility by the farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Over all it is a best technology with proper management by the farmers |
| Combination of production gain from bamboo and crop, less use of chemical fertilizer as green manure is available localy. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Low cost and simple tech nology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper understanding by land user for technology |
| Materials are used for the technology available locally |
|
Due to increase of income migration is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper adoption of technology |
|
Reduction of runoff and soil loss and increase of soil fertility and soil moisture regime has been increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Adopting proper cropping pattern. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Ownerships of land and additional taxation there on after implementation of technology. | Clear understanding by competant authority ( By revenue people) |
| Fruit trees died | Beneficiaries planted Cashew instead of fruit trees. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Clear understanding of the technology. | Regular meeting with local representatives. |
| Availability of materials in the technology area. | Alternative available materials must be used in technology area. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
-do-
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Inde]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compilateur : Srikanta Kumar Parida
Modules
Aucun module trouvé