Current agroforestry: orchard with wheat intercropping [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Malgorzata Conder
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1134 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Current agroforestry of a degraded mulberry and apple orchard with wheat intercropping
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
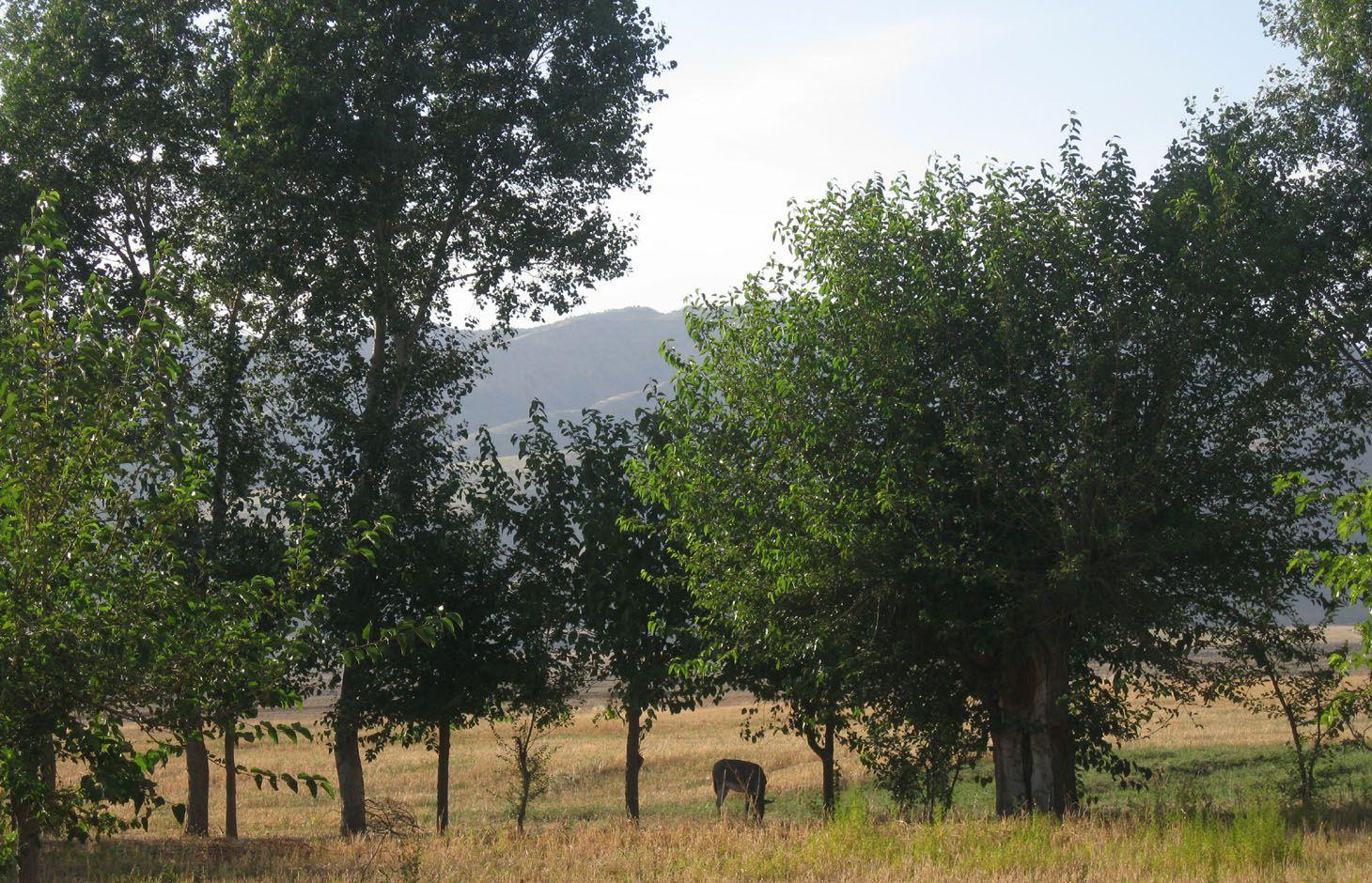
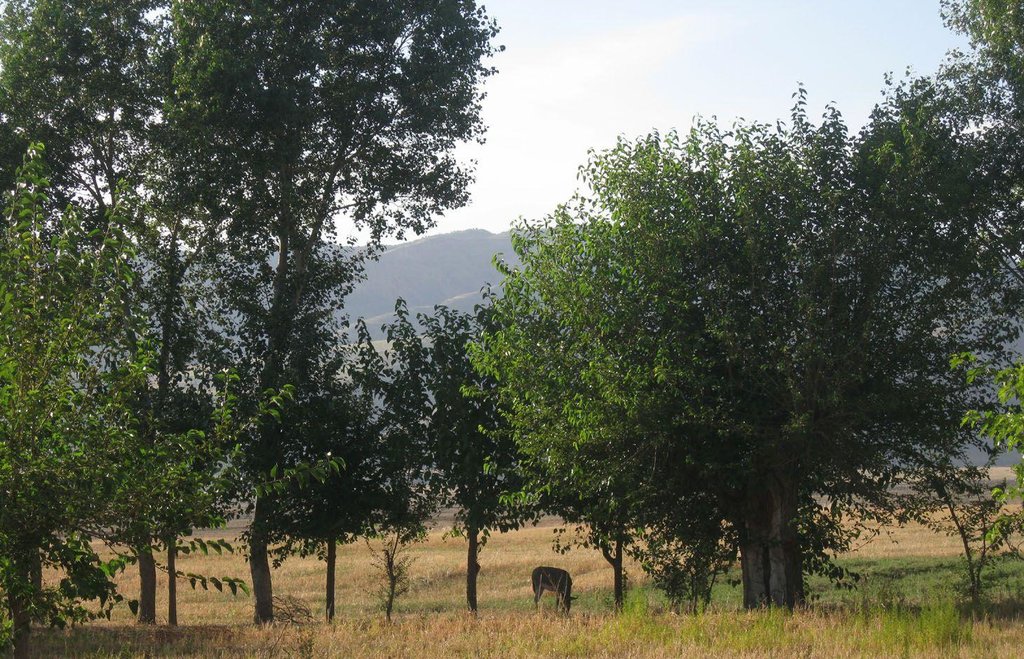
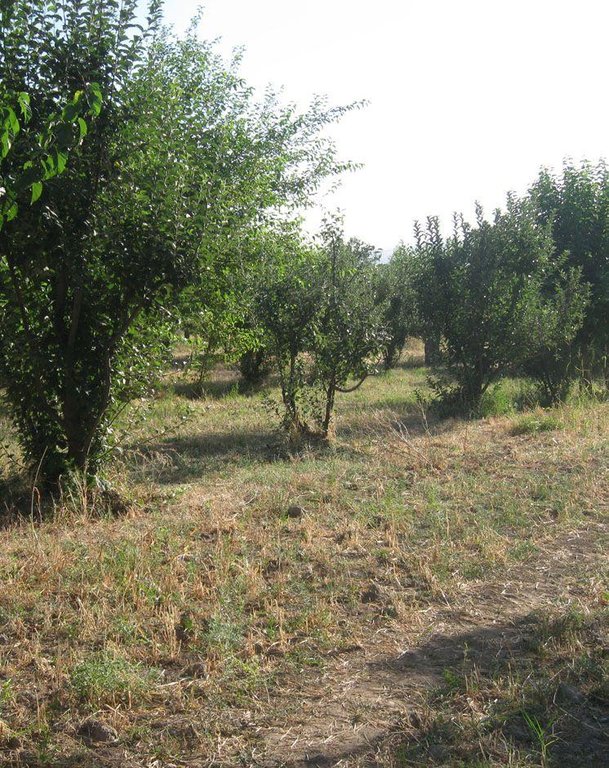
Since 1992 an area of around one ha has been owned by the farmer. He planted mulberry trees the same year. At that time, orchards were established in the whole surrounding area because the government decreed that a territory should have plenty of mulberry trees. Despite the government plan, all the land users of that area began to switch their orchards into wheat crops. Five years later the farmer planted apple trees within the mulberry orchard. The orchard had 200 mulberry and 100 apple trees. The motivation was to feed the working farmers of the fields around. Five years later the apple trees gave fruits. But only the first two years gave a good yield and income from selling them. Later on the fruits were just eaten by the farmer’s family. After another seven or eight years the farmer grew a wheat crop in between the tree lines. Nowadays it's the only remaining orchard in that area. Due to the lack of proper maintenance and water availability the orchard is degraded and the output is very low.
Purpose of the Technology: The government established a large territory of mulberry orchards, for three reasons: First to reduce the impact of natural hazards, second to increase silk production and last to improve fire wood availability. The planting of apple trees should be beneficial for farmers working in the surrounding crops and well as for the family, who sell the fruits and the mulberry leaves. As the yield started to decrease the wheat crop was established to have a bigger output for that crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Due to the government’s order to establish orchards, the local authorities provided the mulberry trees. Hence, it was in the responsibility of the farmer to plant the trees and to look after them by soil loosening and pruning. The latter activity must be done once in the first five years after planting. The farmer bought the apple trees himself as they were cheap at that time. To establish the wheat crop, ploughing, seeding, fertilizing and finally harvesting must be done. One person is supposed to guard the orchard and wheat crop every day. Yearly maintenance consists of soil loosening around the fruit trees and the above mentioned task for cropping. The maintenance of the orchard seems to be abandoned more and more, probably because the output decreases year by year.
Natural / human environment: The orchard is situated below Momandion village, on the very last foot slope before the valley plain begins and, hence, it has a slight slope,. In the past, orchards were numerous, but nowadays wheat crops have mostly replaced the orchard. As there is no fence and no one to control it regularly, livestock invades the property. During its first two years there was a water source, which had dried up by the time. The orchard is a relic being the only and last one in that area. Broken branches, unpruned trees and a trampled crop, show signs of insufficient control and maintenance and therefore of a gradual abandonment of the orchard.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Muminabad
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
According to farmer it's 1 ha, according to GoogleEarth around 1.6 ha
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
- government
注释(项目类型等):
Since 1992 it's property of the farmer
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 浆果类
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
wheat crop

牧场

森林/林地
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Trampled and degraded soil as a consequence of no fences or control. Soil crusting and compaction because of lack in organic matter resulting in a low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water scarcity and low soil moisture, small yield of the fruit trees
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: In the past the wheat and apple yield was much higher thereby they were cash crops. As the yield decreased by then and he gets low yield the use them as food crops.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (monocropping, lack of maintenance)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Because if no fence), education, access to knowledge and support services (More agronomic/ technical advice needed)
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Location: Muminobod, South of Momandion, Obishur Watershed. Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (How to regenerate the poor soil and water conditions, which species are useful to plant etc)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat intercropping within orchard
Agronomic measure: vertical plowing
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, apple
Change of land use type: Mulberry and apple orchard combined additionally with wheat crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More pressure on natural resources because of additional wheat crop in the orchard
作者:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.83
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
12.40
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying, transport and planting of mulberry trees, 10 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1992 |
| 2. | Buying, transport and planting of apple trees, 5 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1997 |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 497.4 | 497.4 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 311.0 | 311.0 | 33.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 808.4 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 167.37 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing vertically, 4 hours of labour, tractor and petrol | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 2. | Buying (200 kg) and sowing wheat, 2 hours, 3 persons | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer, 2 hours, 1 person, 2 bucks à 50 kg | once a year, september |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 4-5 days (6 hours/ day), 4 people | September, once a year |
| 5. | Guardening | every day |
| 6. | loosening around trees (ca. on 1/3 of the trees), 4-5 trees a day | every year, spring |
| 7. | pruning (ca. 1/2 of mulberry trees), 7-8 days (2-3 hours/ day), 3 persons | every year, autumn |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 572.2 | 572.2 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 24.8 | 24.8 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Petrol | l | 25.0 | 28.5 | 712.5 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 82.8 | 82.8 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 76.6 | 76.6 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1468.9 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 304.12 | |||||
注释:
The cost were calculated for 1 ha, but one have to consider that an orchard and wheat crop is on the same plot. This means that there's not fully a wheat crop of 1 ha.
Mulberry seedling were paid by the government, apple trees by the farmer.
Machine use and petrol, are all included in the labour input in the establishment phase, as it was not separately mentioned by the farmer.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour is the most important input, but as it is done mostly by the farmer or the family itself it's mainly agricultural material as seedlings, seeds and fertilizer. Latter particularly as recurrent costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked1, mostly) and rolling (ranked 2)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, no rainfall from July to August) and medium (ranked 2, winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm))
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and mechanised (ranked 2, only for plowing)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, mainly subsistent, depending on yield more or less commercial) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
注释:
Based on land user's Certificates
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
less apple and wheat production
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
灌溉用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
More fertilizer and pesticides needed than in the past
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Reduced crop production and fruit yield
工作量
注释/具体说明:
less maintenance work
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Mulberries were shared with other people working next to the field (no fence)
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
negligible thanks to a little slope
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
注释:
Higher vegetation cover, which would make the land use more resistant to drought, more stable in case of floods and heavy rainfalls.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The orchard gave by-product as leaves for silk production and branches. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is the only orchard in the neighbourhood, which is why it would be worthy to maintain it. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Put more effort and labour into the orchard, currently only the wheat crops seems to be of interest for the farmer. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Currently the orchard is too old to get a good yield and maintenance activities are comparatively high. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of maintenance and guarding or fencing. | More focus on the orchard as it has also ecological benefits. Enhance the farmer to put more labour into the orchard. |
| Show good examples of orchards and their resulting benefits. Round tables by and for farmers to share experiences. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块