Biological Waste Water Treatment Plant [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Waste Water Treatment by the use of Reed Bed Technology
technologies_1179 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Thapa Kripa
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Mahat Sabnam
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Newa Manashree
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The technology adopted is a treatment plant that treats and purifies waste water being discharged from the hospital biologically.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
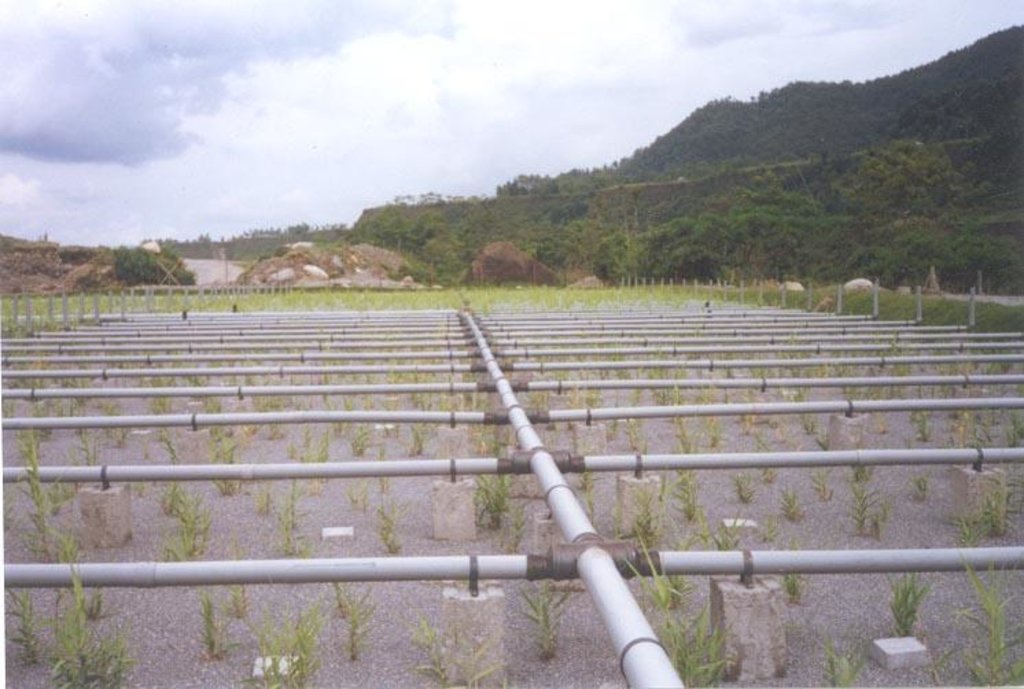
It is located in Dhulikhel Hospital premises, Kavre. This treatment plant purifies the waste water being discharged from the hospital biologically on a daily basis.
Biological action takes place in the horizontal and vertical reed bed with the help of bacteria present in the root nodules of Reed plant. The Reed plant helps in spreading the oxygen through its roots. Anaerobic decomposition takes place with the help of oxygen which is spread by the roots.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this plant is to make the water less toxic so that it does not pose any danger to the human health. It is a biological process in which the Reed plant treats the waste water coming from the hospital.
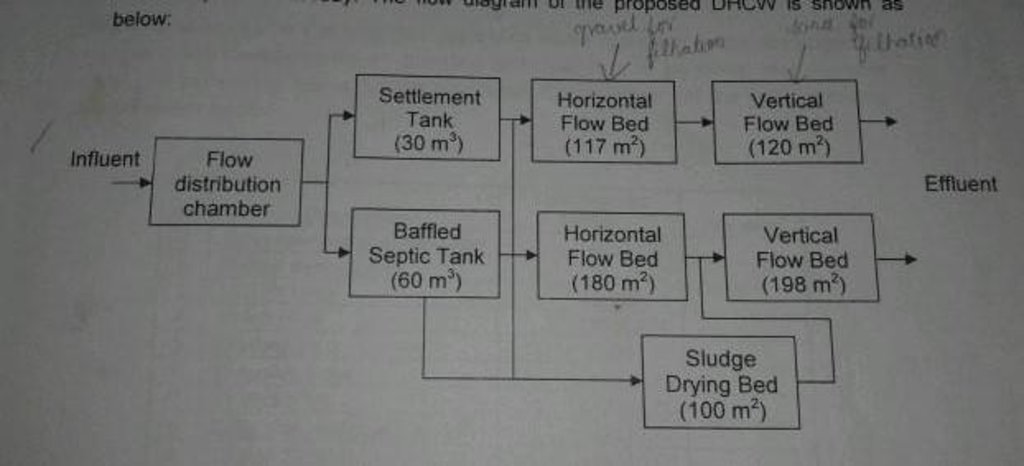
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Dhulikhel Hospital Constructed Wetland (DHCW) was commissioned in July 1997. The design of DHCW was designed for an average waste water volume of 10m3/ day. But at present, the waste water production is in the range of 75m3/day. Recently, it has been expanded and designed to treat the waste water volume up to 90m3/day.
The plant is maintained by the specialists themselves and the investors are the hospital owners. The task of planning, design, drawing and estimates for the expansion was undertaken by ENPHO (Environment and Public Health Organization ) in association with WATSAN (Water and Sanitation) solution.
Natural / human environment: The treatment plant needs gravel for filtration in horizontal flow bed where the reed bed plant is planted. In addition, sand is required for filtration in vertical flow bed. A slight slope is maintained for the water to flow in one direction.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Dhulikhel
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavre
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.002036
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002036 m2.
The total area covered by the SLM technology at Dhulikhel Hospital was found to be 4 ropanies that is 2036m2=0.002036km2
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- improve water quality
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Biological wastes from the hospital has a high chance in contaminating the area when disposed recklessly.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The water is safe to use for irrigation purpose.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 湿地保护/管理
- 废物管理/废水管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V5:其它

管理措施
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, contour planting / strip cropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

其它
具体说明:
Main causes of degradation: discharges (point contamination of water) (Sewage), other human induced causes (specify) (Infected Water), (Hospital Waste Water)
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Layout of the Biological Waste Water Treatment Plant is given below:
Location: Dhulikhel. Kavre
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Engineers)
Main technical functions: improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity)
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Norcot (Phragmites karka)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 6 p/m2
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4 p/m2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Trees/ shrubs species: Reed bed
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): S,C
Spacing between structures (m): 10 mm
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20-40 mm
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: From random to controlled
作者:
Kripa Thapa
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
103.0
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Earthwork in excavation in foundation, drain, pipe trench and lead | Dry Day |
| 2. | Earth work in refilling including watering and ramming | Dry day |
| 3. | Dry flat brick soiling for 10 m2 | Dry Day |
| 4. | Edge brick soiling in 1.6 cm and pointing in 1.2 cm for 10 m2 | |
| 5. | Dry edge brick soiling in 1:6 cm for 10 sq m |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Earthwork in excavation | unit | 1.0 | 122.21 | 122.21 | |
| 劳动力 | Earth work in refilling including watering and ramming | unit | 1.0 | 87.29 | 87.29 | |
| 劳动力 | Edge brick soiling (mason) | unit | 1.0 | 5293.83 | 5293.83 | |
| 施工材料 | Brick | unit | 1.0 | 253.92 | 253.92 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand | unit | 1.0 | 3412.38 | 3412.38 | |
| 施工材料 | Wood | unit | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| 其它 | Mason | unit | 1.0 | 1470.0 | 1470.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 11639.63 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 113.01 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is the labour cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture (topsoil): Filtration is vertical reed bed
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter is covered with gravel
Soil drainage / infiltration is good and filtration occurs through voids in sand and gravel
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不可用
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water is good during monsoon
Water quality (untreated) is unusable since it is biological and medical waste
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Only one species of plant is planted
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The treatment plant provided treated water which is mainly used for irrigation purpose. There is an equal involvement of men and women in the field.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
SLM technology is used by the hospital specialists. However, the water is openly accessible.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
Irrigation:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
the technology has increased the knowledge about irrigation and sanitation. This has indeed helped in better livelihoods and health.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地下水位/含水层
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
In 2007, expansion of the plant was proposed to treat the waste water volume up to 90m3/day.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This technology has provided positive results for irrigation purpose. |
| There has also been an increase in water availability. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The purification of water from the hospital has been used for various purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent cleaning of the chambers should be carried out. |
|
This technology has been proved to be very cost effective. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Periodic checking of the tanks and plants for any fault should be done. |
| This plant has been easily managed by the staff of Dhulikhel Hospital. |
| This technology provides opportunity to create/restore valuable wetland habitat. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The treatment plant may not be tested regularly. | Engineers and specialists should be concerned about the matter. |
| The water output may not be safe for drinking. | People should be made aware about boiling and filtering the water before drinking. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块