Chemical bush control [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Chemical bush control with special reference to thinning and clearing
technologies_1375 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Richter Chris
Department of Agriculture, South Africa
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture of Zambia (Department of Agriculture) - 赞比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
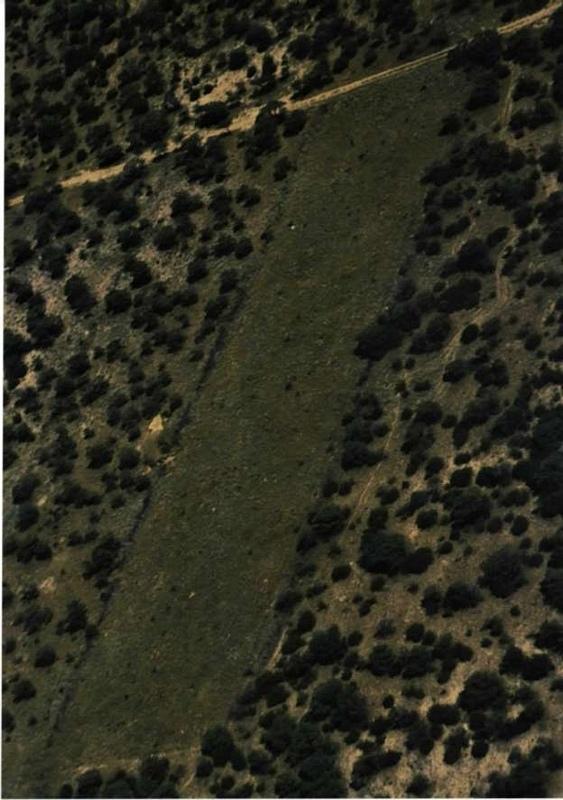
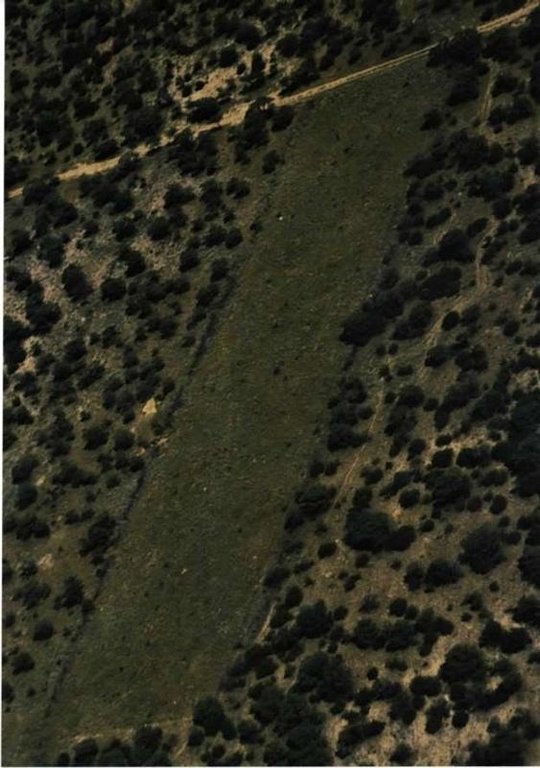
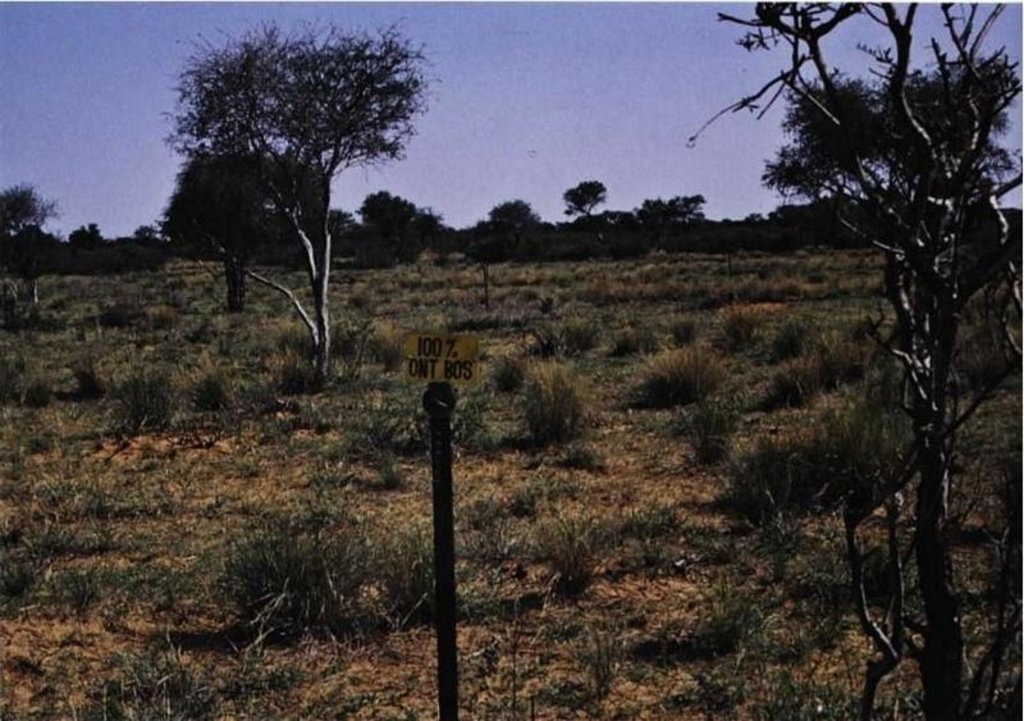
To either clear or thin bush (trees) in encroached areas by chemical means.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
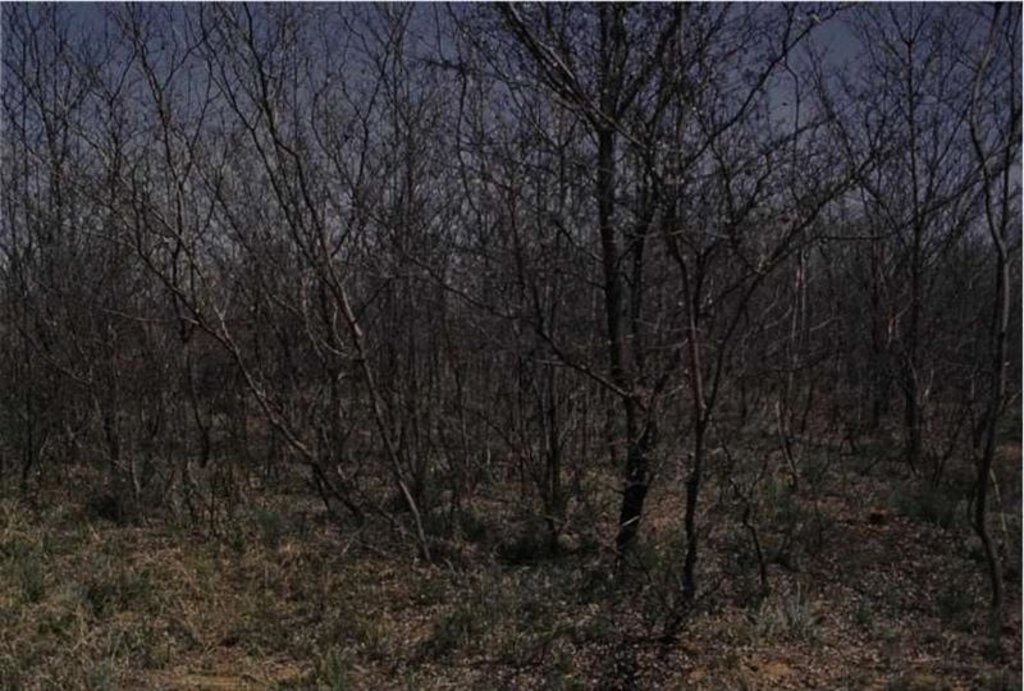
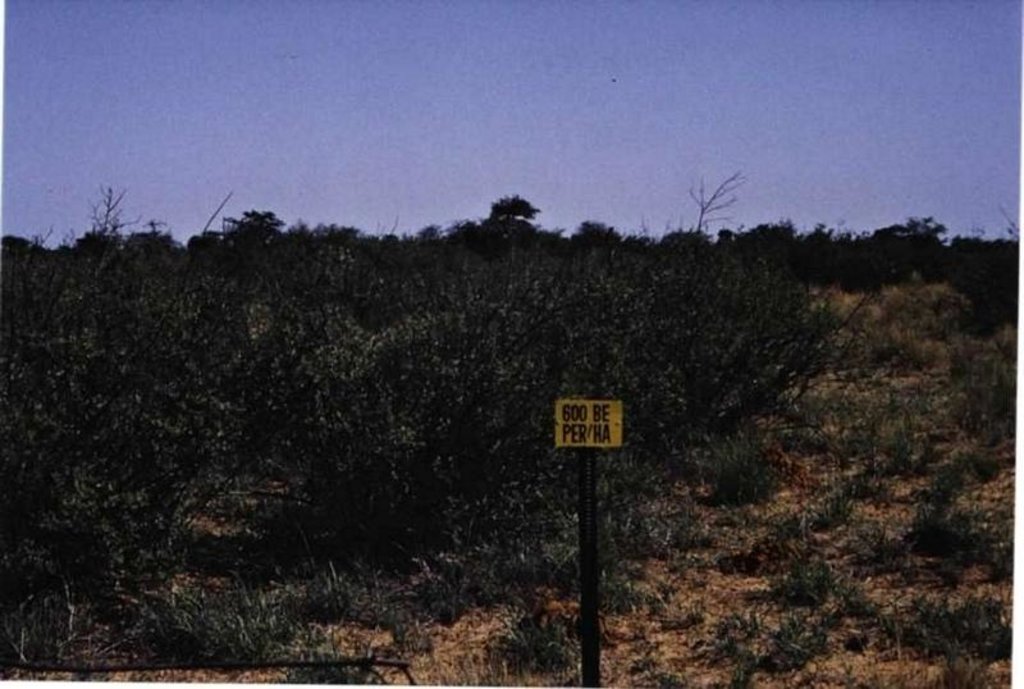
In some areas, the bushes are so dense (more than 2000 plants/ha) that access to the area is not possible and therefore the aerial application of chemicals is the only solution. All the plants in this area get treated this way, but no selective treatment is possible (this is still a problem to overcome). This aerial application can be selective to some extent because some bushes survive the treatment. If that is the case, selected thinning with chemical bush control can be done on bushes (but not on palatable/usable species).
The purpose was to characterise and control bush encroachment; to define and quantify grass-bush interactions in mixed savannahs, by chemical bush control; to be able to make recommendations for larger application chemical bush control like by aerial application. There was a lack of a technique for economic comparison between the potential loss of income due to bush encroachment and the cost of controlling bush.
Aftercare is very important and is an on-going process. After the first application of the chemicals, it is possible to let in goats. Browsers are better than game, because they browse the small bushes and prevent the area from further bush encroachment. The application of fire is also possible. In this area it should only be done every 7th -10th year (depending on the rainfall and grass production). There is very little communal land in this large area (5 million ha).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province & Northern Cape
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vryburg, Griekwastad, Mafekeng
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.4 km2.
The developed technology, bush cleaning & control, will be applied on +- 5 million ha. * The technologies assist of thinning, cleaning & eradication
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Started as a research project by the Department of Agriculture in the middle - late sixties and have been updated since the eighties.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Improve access to land
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
动物类型:
- 绵羊
- cattle
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The negative impact that bush encroachment has on the production and botanical composition of the grass layer in these areas - thus making economical farming impossible.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The negative impact that bush encroachment has on the production and botanical composition of the grass layer in these areas - thus making economical farming impossible.
In the small communal areas camps are not used, the area is overstocked.
Ranching: Cattle, sheep
Grazingland comments: A definite shift to game farming and production. Grazing capacity is 10 ha/LSU. Economic farm unit perceived as to be not smaller than 3000 ha.
Type of grazing system comments: A definite shift to game farming and production. Grazing capacity is 10 ha/LSU. Economic farm unit perceived as to be not smaller than 3000 ha.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Apr
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- Tap/deploy land
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V3:植被的清理
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Decrease in game led to over utilising of grass and under utilisation of woody species.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - Farmers didn't realise that they were causing the problem by not management correctly the veld)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Especially new & around water), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Limiting of natural fires)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase / maintain water stored in soil
作者:
Chris Richter
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
7.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil applied chemicals (tebuthiuron) | Not important, better close to rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Apply chemicals | ha | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 6000.0 | 6000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | chemicals, subsistence allowan | ha | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 66000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 11000.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Burning the veld | / 7-10 years |
| 2. | Browsing the veld by goats |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Burning and browsing the veld | ha | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chemicals, subsistence allowan | ha | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 16500.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 2750.0 | |||||
注释:
High salary of researcher and technician are included in the costs.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
For all 4 plots. They were working on each plot for 3 months. Travel and subsistence costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The average is +-340mm
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: All sites in the North West Province are flat and only the one site in the Northern Cape is hilly
Altitudinal zone: Duncan, 1057m, Karlsruehe 1200-1500m, Slabbertshof 1130m
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: The site in the Northern Cape is very shallow North West Province the soils are very deep
Soil texture: Coarse in the North West and medium in the Northern Cape
Soil fertility is medium- low in both areas concerned. Very sandy soils, however, and have a poor fertility
Soil drainage / infiltration is good in the North West and poor in the Northern Cape
Soil water storage capacity is low: Plexut 71 mm at a depth 2.1m
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (Commercial).
85% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (Compared with other commercial farmers).
Off-farm income specification: up to 25% farmers get involved in ecotourism (trend is to more game for ecotourism and hunting)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Primary production grasses, all seasons, composition changes
饲料质量
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
With regard to woody component (game farming)
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Higher grazing capacity
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Creating an open Savannah
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
Initial cost
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Decrease in encroachers
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Grass density, all seasons
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Change of habitat
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
90 percent of the area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: See it is working, improvement of the veld return on the inputs
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement in grazing capacity |
| Improvement of veld condition and production |
| Accessibility |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement of veld condition and production |
| Accessibility (because it was to dense) |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Very expensive |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Under aero-application utilisable plants can be irradiated, if not adhered to directive | Hand application |
| Very expensive |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Msc of C. Richter, Gras-bosinteraksie in die bosveldgebiede van Noord-Kaap. 1991.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
C. Richter
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块