Wetland rehabilitation [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1377 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Bronkhorst Frik
Mpumalanga Parks Board
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Mpumalanga Tourism and Parks Authority Board (MTPA) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Working for Water Wetland rehabilitation [南非]
To improve the quality & quantity of water production and biodiversity in the Blyde River catchment area.
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
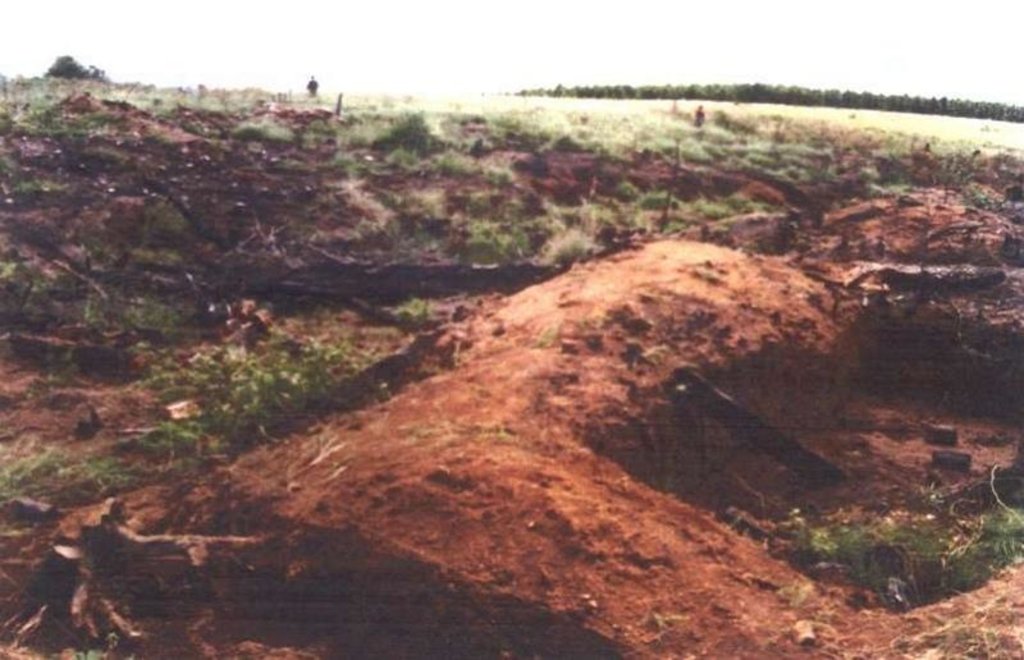
To rehabilitate/stabilise distorted wetlands as close as possible to its original state/function.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
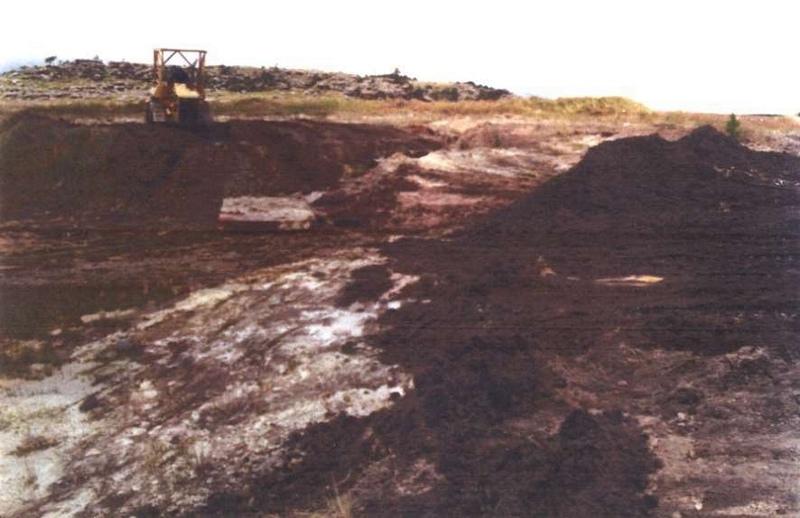
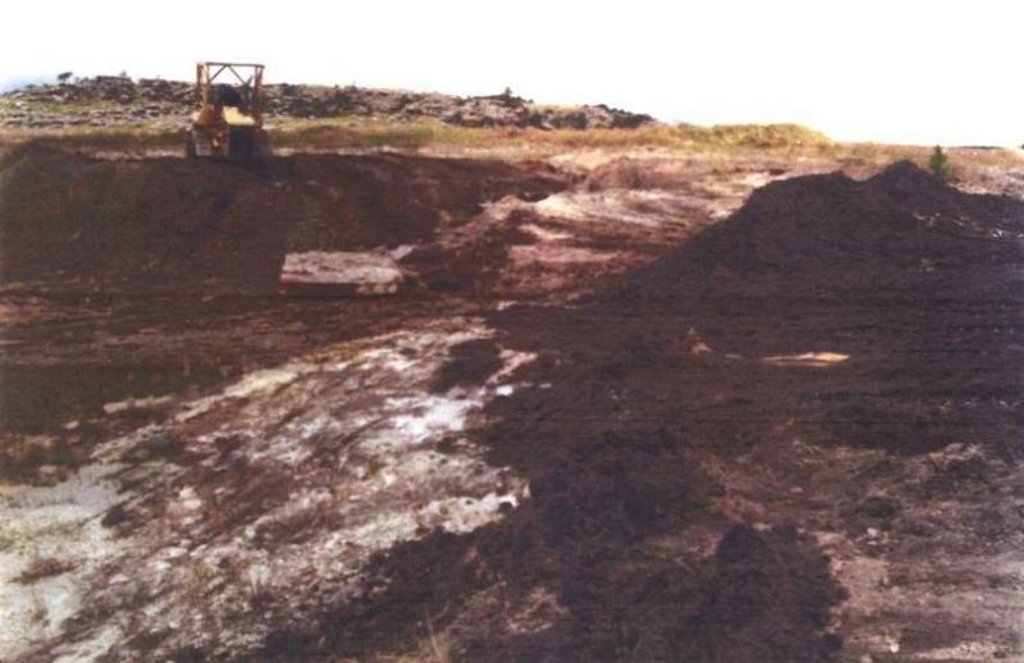
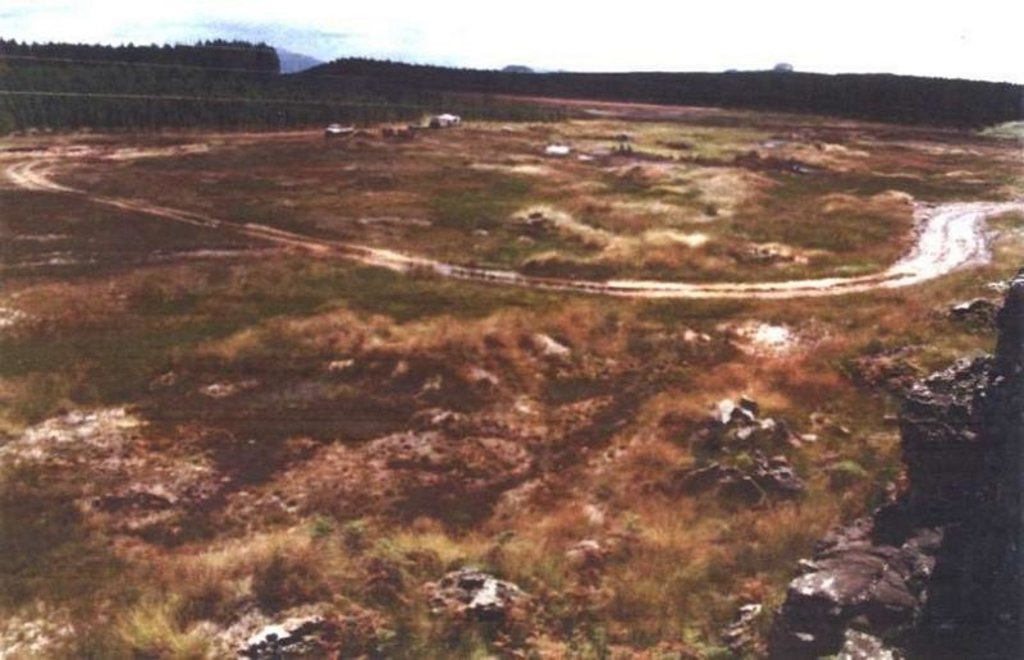
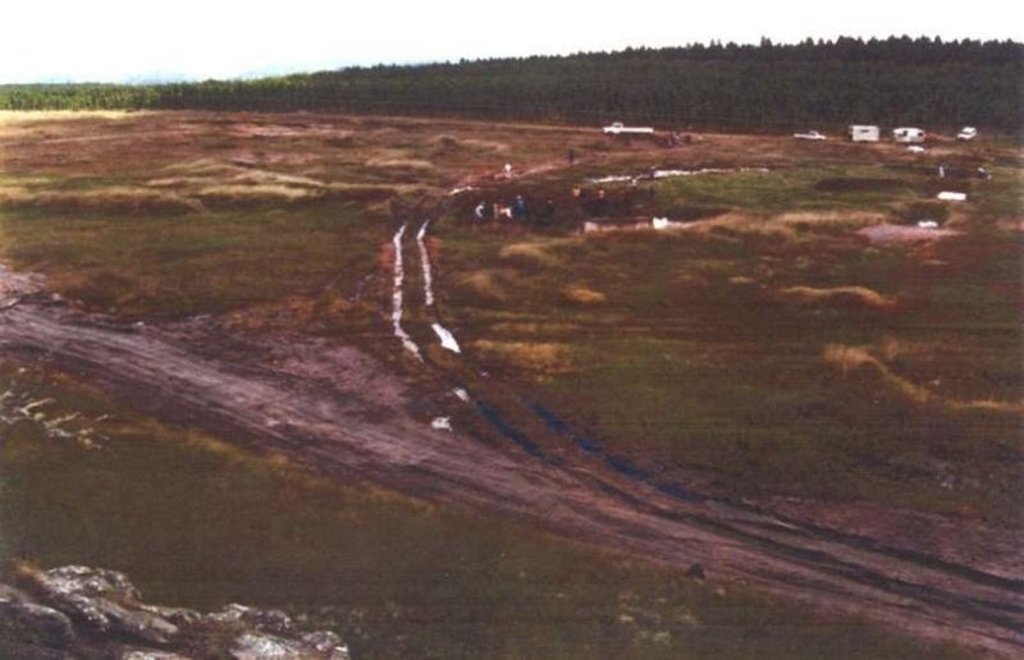
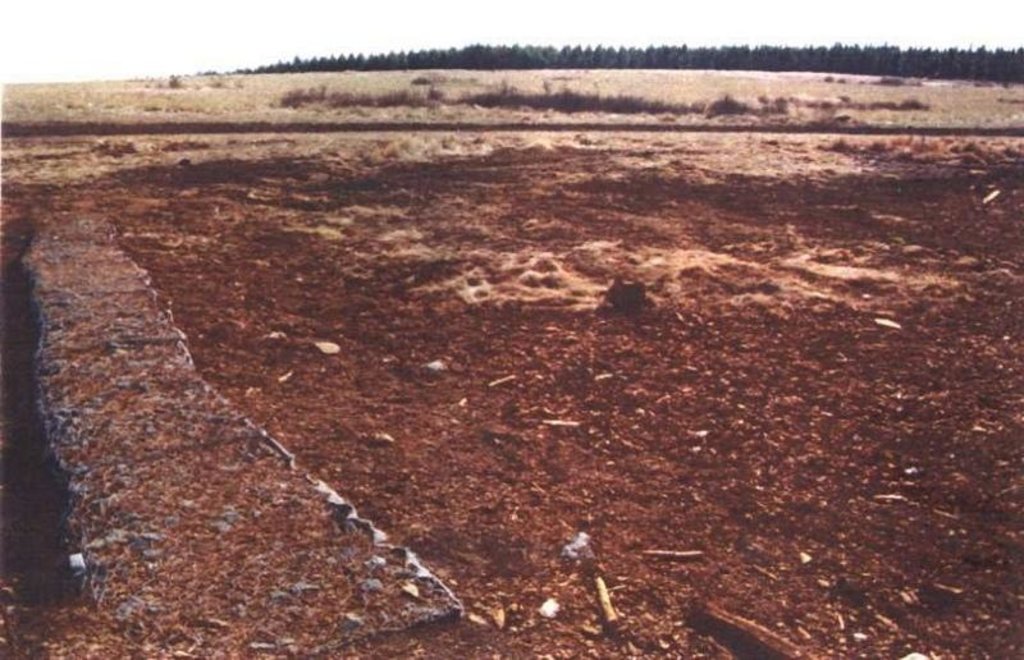
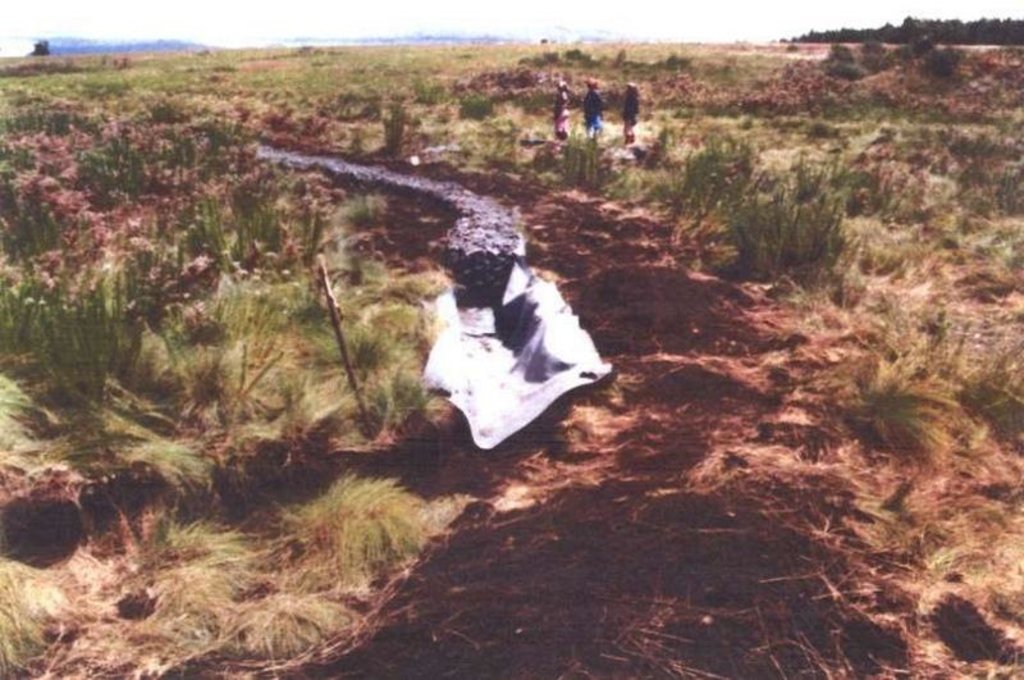
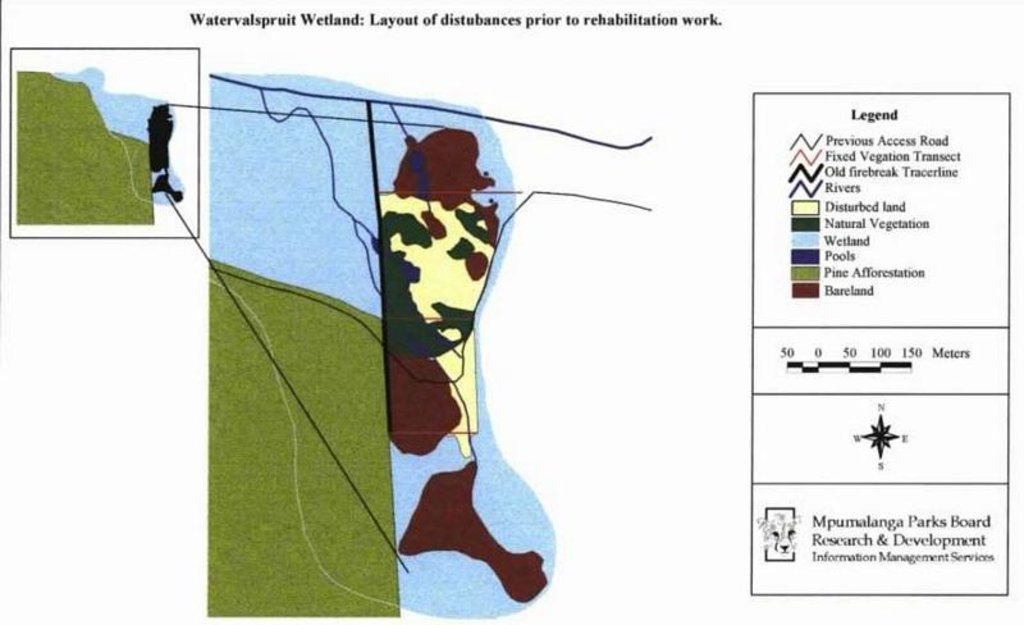
Two wetland rehabilitation sites that are part of a large wetland area (15 and 10ha).
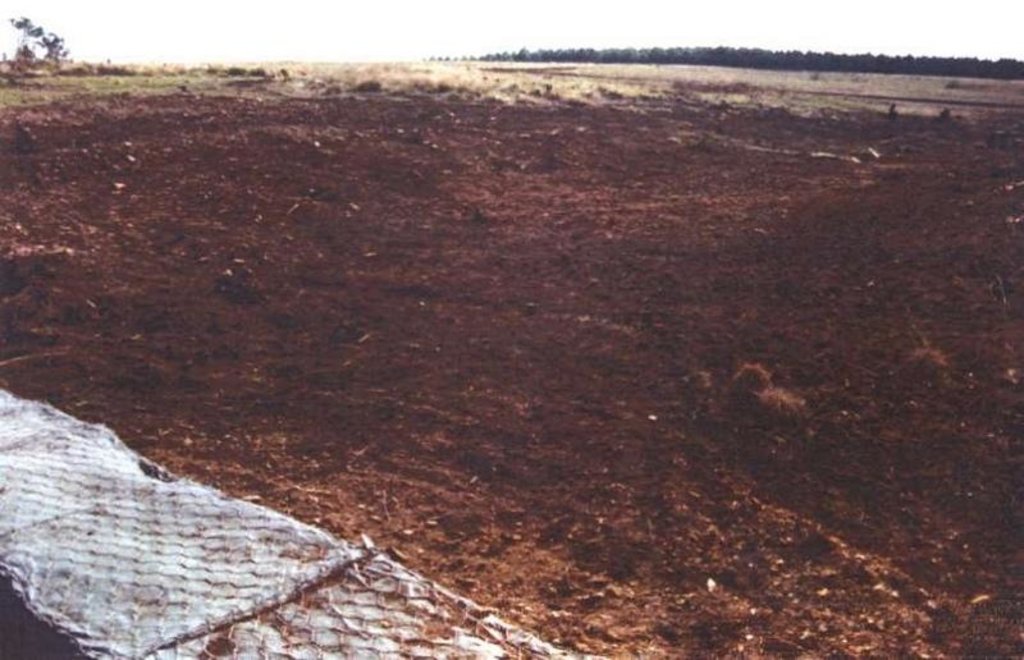
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the rehabilitation work was to stabilise, landscape and re-vegetate distorted areas to again fulfil their original function in the catchment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Maintenance included follow-up on re-seeding distorted areas and alien plant control (cut down plants and treads strips with roundup). Structure maintenance (such as gabions, roads) is also done.
Fire management to protect and manage the area of rehabilitation until such time as it has proved to be stabilised. Leave for ± 3 years before considering burning.
2.3 技术照片
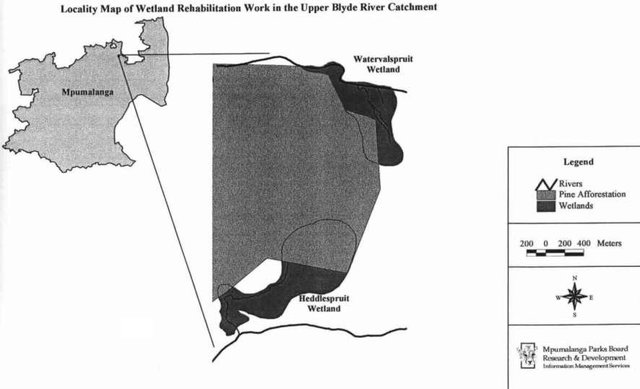
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
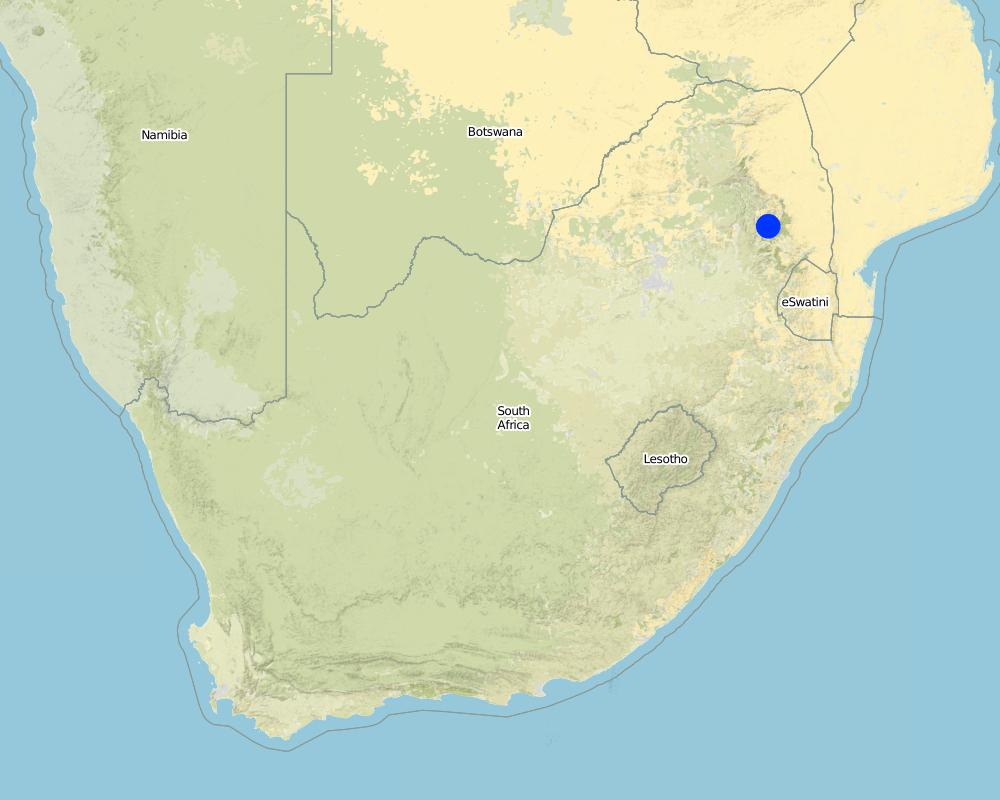
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Mpumalanga
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mpumalanga
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.3
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.3 km2.
Wetland rehabilitation work has been executed on two wetlands in the upper catchment of the Blyde River in Mpumalanga.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Subjective inputs/discussions with specialists in variety of disciplines (scientist, botanists, hydrologists, managers, ecologists)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
- game
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Afforestation: Pine plantations destroys diversity, also has a major effect on quality & quantity of water run-off, mining opencast activities
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Production of wood/timber, job creation
Ranching: Game occur natural in this area/nature reserve
Grazingland comments: Area in which these two wetlands are situated is proclaimed conservation land. The aim is to manage the area in an as natural as possible condition as it was historically.
Type of grazing system comments: Area in which these two wetlands are situated is proclaimed conservation land. The aim is to manage the area in an as natural as possible condition as it was historically.
Constraints of nature reserve: Fire management/adjacent to pine plantations
Longest growing period in days: 240; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - May
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
- 湿地保护/管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施

植物措施

结构措施
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining, education, access to knowledge and support services (Mineral affairs don’t inspect and allows anything.), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (2.1.3.2 Government has not enough authority), Mining
Secondary causes of degradation: Forestry
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
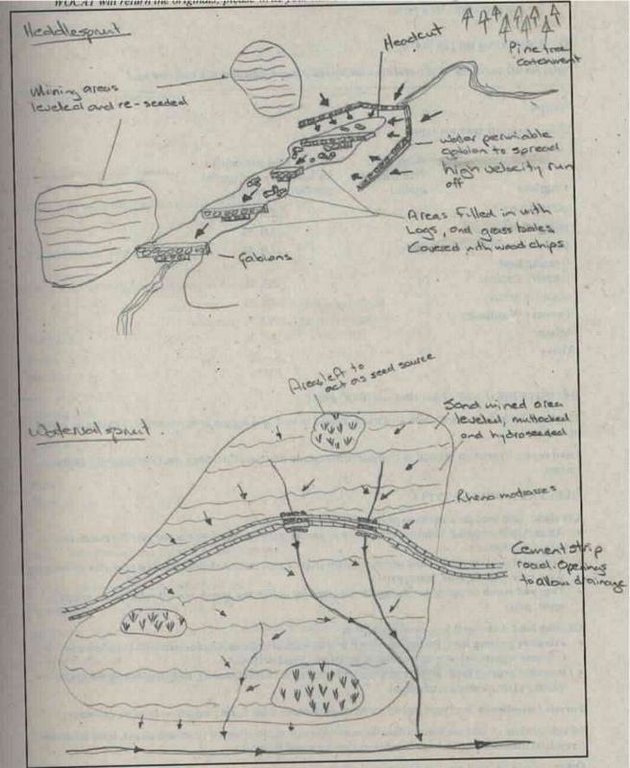
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
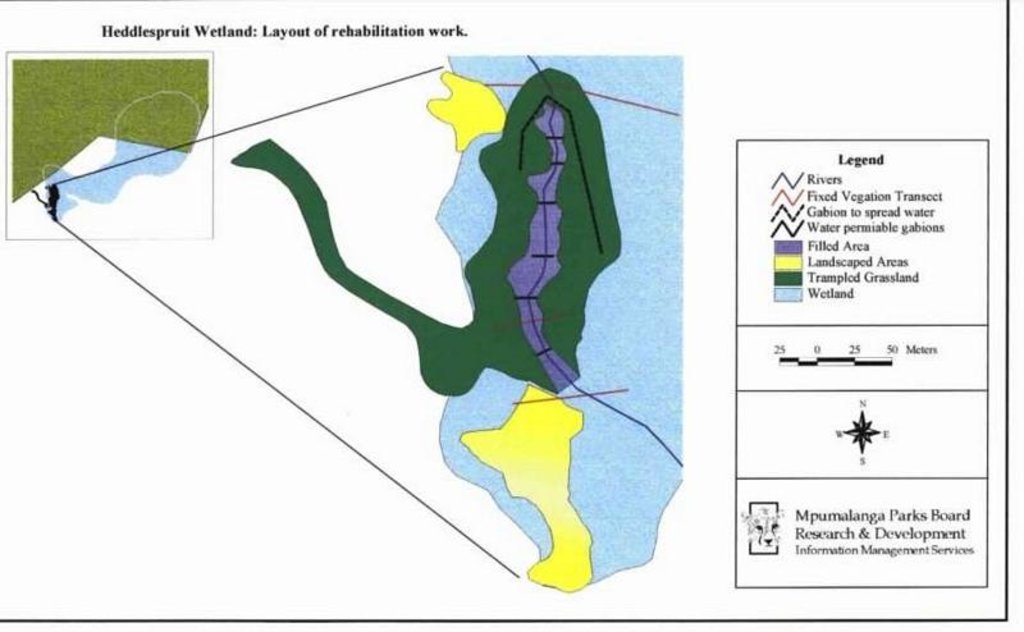
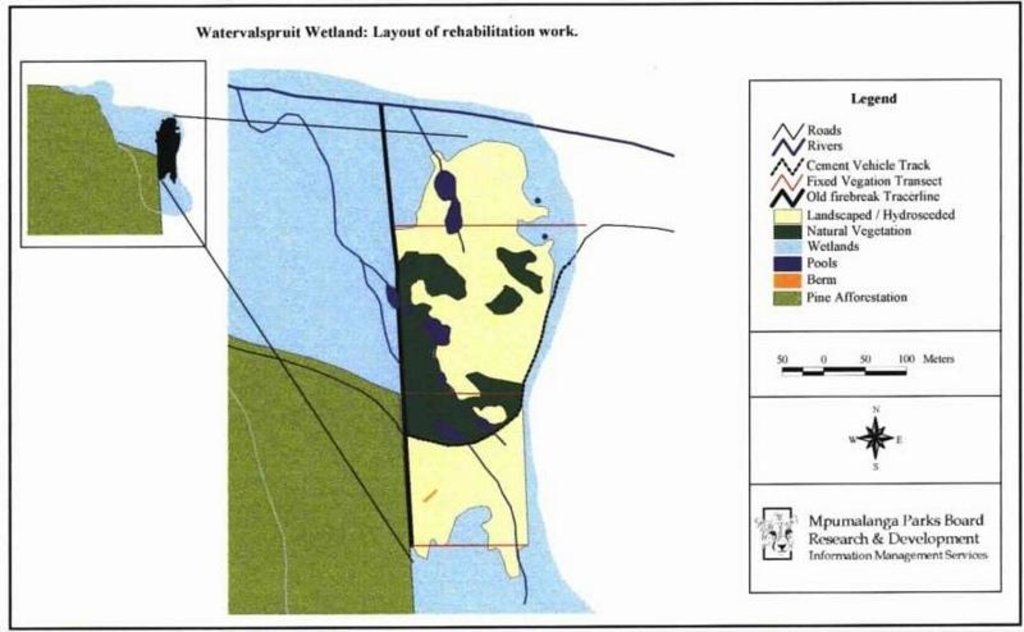
Wetland rehabilitation
Location: Blyde canyon. Mpumalanga
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, control of fires, fire management
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, water spreading, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vegetative measure: graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Eragrostis, Stiburus, Cynodon
Gradient along the rows / strips: 3.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60
Structural measure: road
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 120
Structural measure: filling heddle
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.15
Spacing between structures (m): 0.15
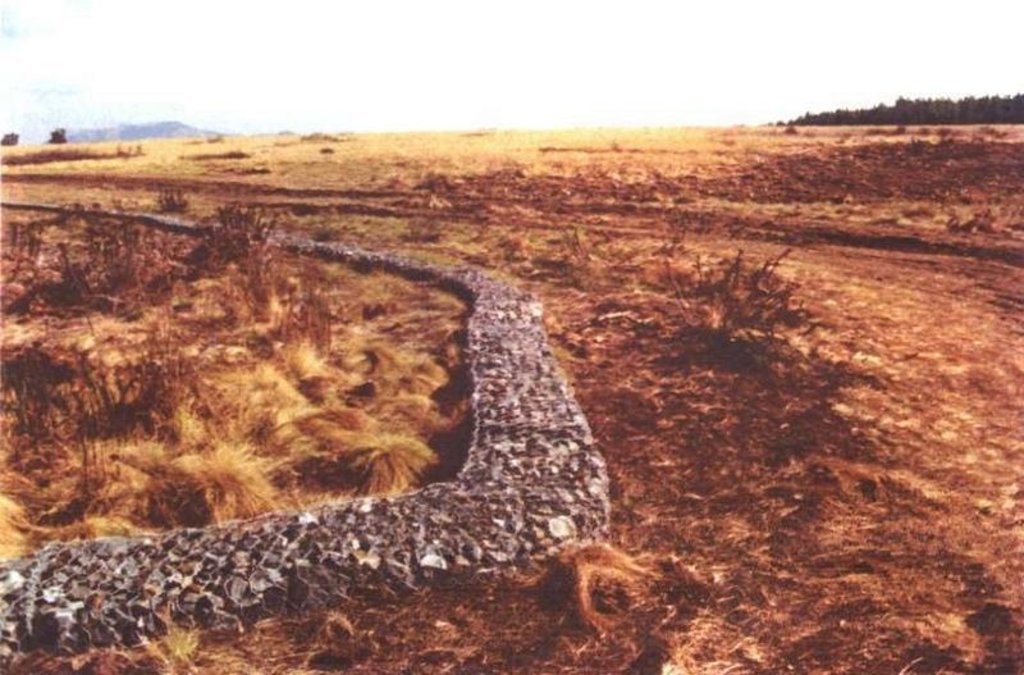
Construction material (earth): Contour muttrocking
Construction material (stone): At Heddlespruit: gabions & stonewall to spread high velocity runoff
Construction material (concrete): Strip road with 1m interval openings to allow for draining
Construction material (other): Heddle filling: pine logs, hay bales, wood chips
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: Fire management
作者:
Frik Bronkhorst
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hydro-seeding | Directly after landscaping/levelling |
| 2. | Hand seeding | Directly after landscaping/levelling |
| 3. | Harvesting & replanting of vlei grass | Directly after landscaping/levelling |
| 4. | Scarifying forming | Directly after landscaping/levelling |
| 5. | Horizontal chills | Directly after landscaping/levelling |
| 6. | Gabion building | March |
| 7. | Landscaping | March |
| 8. | Muttrocking | April |
| 9. | Replanting grasses | April |
| 10. | Hydroseeding | April/May |
| 11. | Tracers and firebreaks (to secure rehabilitation work) | Autumn/winter |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Rehabilitate wetland | ha | 1.0 | 56000.0 | 56000.0 | 80.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 56000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 7000.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fire protection | June /Once a year |
| 2. | Gabion maintenance | /Ad hoc |
| 3. | Hydroseeding | September/Once |
| 4. | Gabion maintenance | Ad hoc/Ad hoc |
| 5. | Road maintenance | Ad hoc/Ad hoc |
| 6. | Tracers & firebreaks | Autumn / Annual |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour: By using machinery where applicable, work can be done less expensive.
Weather conditions: High rainfall areas, delays work, can destroy half done/partially done processes.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2500.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow for Watervalspruit wetland and moderatly deep for Heddlespruit wetland
Soil texture: Coarse for Watervalspruit wetland and fine for Heddlespruit wetland
Topsoil organic matter: Medium for Heddlespruit wetland and low for Watervalspruit wetland
Soil fertility is high for Watervalspruit wetland and very low for Heddlespruit wetland
Soil drainage / infiltration is good for Watervalspruit wetland and medium for Heddlespruit wetland
Soil water storage capacity is very high for Heddlespruit wetland and medium for Watervalspruit wetland
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
(State budget limitations (Parks board)).
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 公司
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
其它社会经济效应
Employment
注释/具体说明:
Approx. 100 people for 4 month employed
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Only during rainy seasons, prevent water
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
soil fertility
biodiversity
Conservation
注释/具体说明:
Distracted wetland areas on reserve rehabilitated
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: 3.4.2.4 Mpumalanga is the first. A proposal for the Lowveld has been submitted and also D. Lindley.
Moderate increase; next year there will be another wetland in the project.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Hydroseeding How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provides quick basal cover to limit erosion |
|
Cement strip-road How can they be sustained / enhanced? Almost no maintenance necessary |
|
Stabilization of erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Gabions well build, minimal maintenance |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Landscaping of stabilized areas | Must be done to re-shape area - no solution |
| Access roads | Correct choice of season for construction phase |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Business plan: Wetland rehabilitation, Blyde River Catchment
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mpumalanga Parks Board, P.O. Box 511, Graskop 1270,Lydenburg,South Africa
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Working for Water Wetland rehabilitation [南非]
To improve the quality & quantity of water production and biodiversity in the Blyde River catchment area.
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块