Hillside Terracing [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Hans Hurni
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Yegara irken (Amharic), Kenetawi metrebawi zala (Tigrigna)
technologies_1388 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
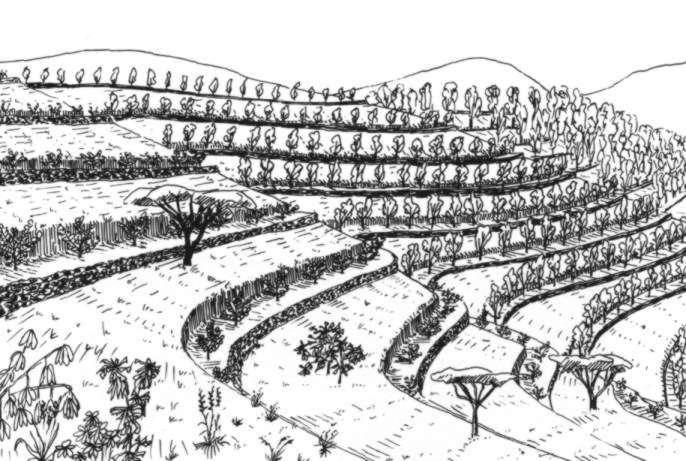
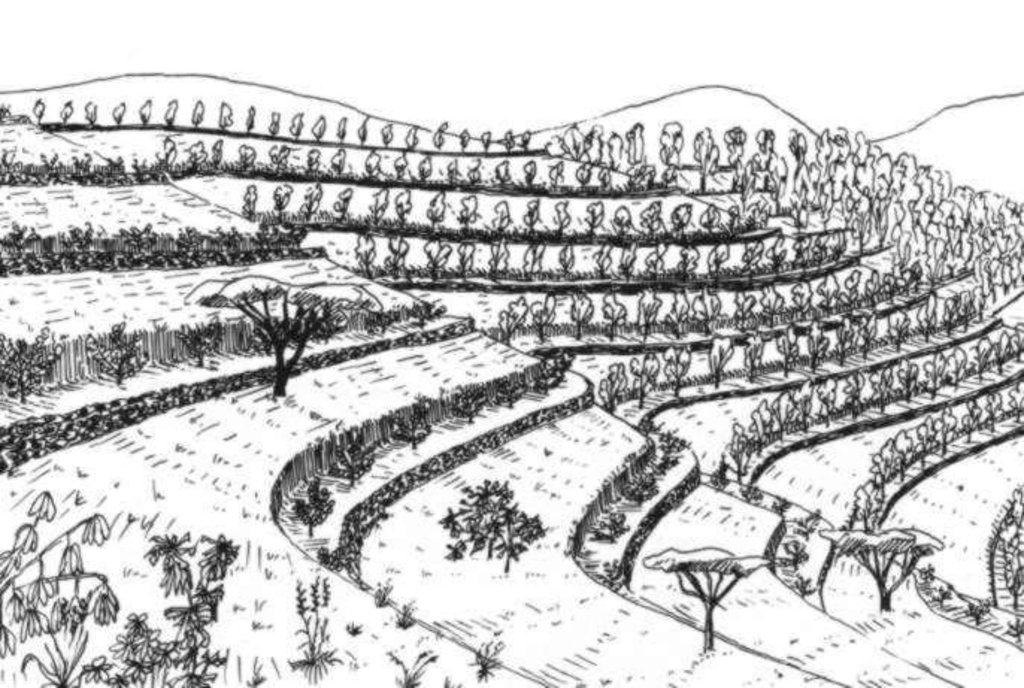
A hillside terrace is a structure along the contour, where a strip of land is levelled for tree planting.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
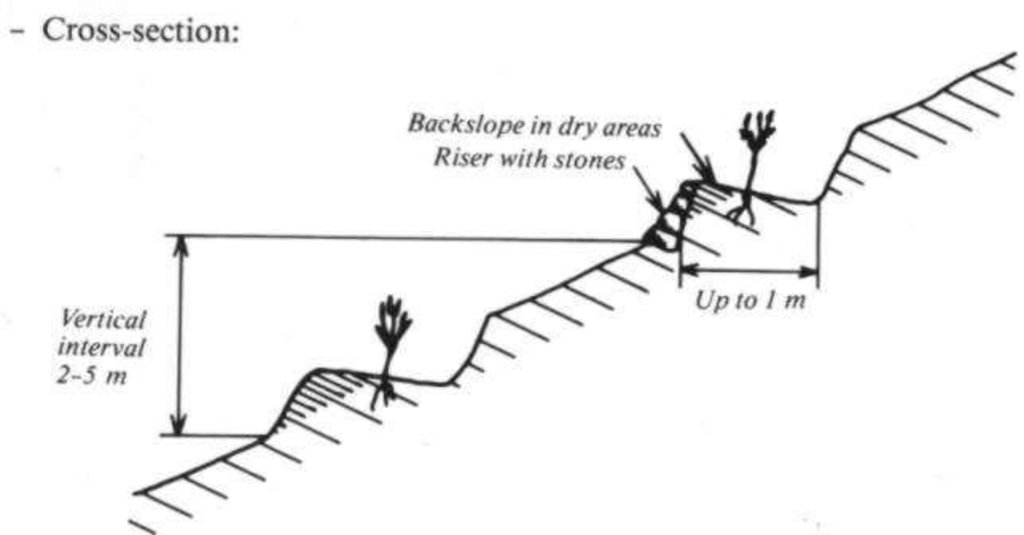
Hillside terraces are up to 1 metre wide and constructed at about 2-5 m vertical inteals. Hillside terraces should only be applied if there is a strong necessity of erosion control and/or water conservation justifying their construction. In Ethiopia and Eritrea, they have been mainly applied in the highlands, although the area of their applicability would be rather in the drier and lower lying agroclimatic zones. Slope range is 50-100%, soil range particularly on eavily degraded land. Hillside terraces are mainly used to prevent damage of flooding the area below steep slopes.
Hillside terraces help retain runoff and sediment on steep sloping land and to accommodate tree seedlings to be planted on them. They are also effective on badlands and in areas with low rainfall to conserve water. Hillside terraces are usually combined with area closure (against grazing). Little materials are needed for their construction: Line levels, digging instruments, stones, and other materials as needed for combined measures. Little management is needed for their maintenance, except for taking care of the tees planted, and for correcting damage that may be caused by livestock grazing.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Harerge, Shewa, Wello, Tigray, Gonder, Sidamo, and Hamasien (Eritrea)
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1,000-10,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1800 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Originated from engineering handbooks and Indian experience. Has been applied in Eritrea & Ethiopia since ~1978
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Eucalyptus, Cupressus, Juniperus

牧场

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High run-on from steep slopes onto cultivated land. Sheet and rill erosion from slopes, and subsequent gullying on cultivated land along footslopes. Lack of grass and woody biomass.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of grazing for livestock. Lack of cultivation land. General food deficiency.
Grazingland comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Almost the natural forest is not exist. Low growing condition.
Type of grazing system comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Constraints of wilderness: these are mainly badlands which are totally degraded
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also full irrigation
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
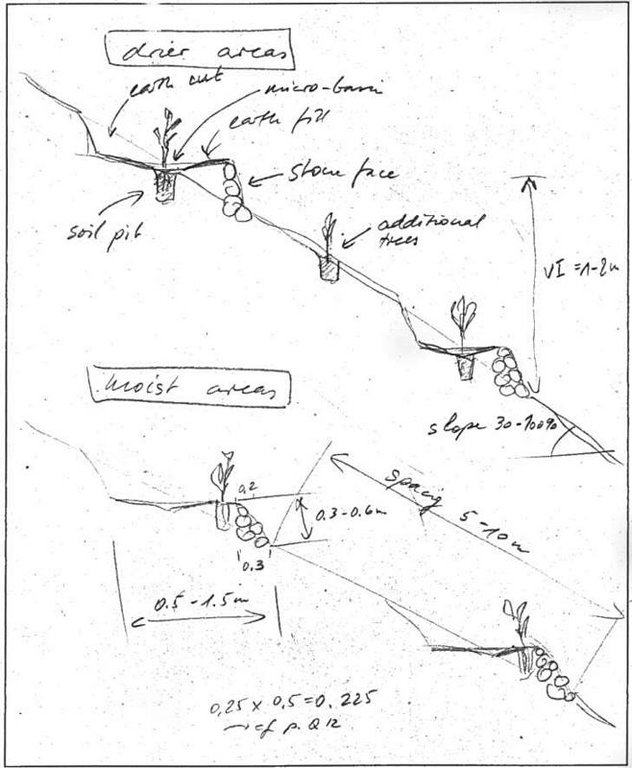
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Hillside terrace cross-section. Linied out along the contour, vertical interval between two terraces 2-5 m. (In: Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. CFSCDD, 1986)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Trees/ shrubs species: Eucalyptus, Cupressus, Juniperus
Construction material (stone): Cut and fill with stone wall in front
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Change of land use type: closed area
Other type of management: livestock management - prevention of grazing, cut and ary system
作者:
Joerg Wetzel, SCRP
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ethiopan Birr
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
7.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Seeding | nurseries |
| 3. | Construction | dry season |
| 4. | Planting | beginning of rainy season |
| 5. | Community guarding of closed areas | annual |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | rainy season /each cropping season |
| 2. | Control of grazing | always/annual |
| 3. | Care taking of seedlings | rainy season/each cropping season |
| 4. | communty guarding of closed areas | continuos / annual |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Length of structure on an average slope
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Slope, soil condition, length of terrace per hectare.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: Also 1000-1500 mm
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
- 干旱
Semi arid: Too little rainfall
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Everything below 16 % is to genly sloping to be useful
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Labour offered to projects.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
60
SLM之后的数量:
40
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
55
SLM之后的数量:
30
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
30600
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
600 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Very recently, some villages have begun to see the value of hillside terracing, afforestations and area closure if they are given full responsibility to manage the area by a group of land users.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Hurni H. : Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. Guidelines for Development Agents.. 1986.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SCRP Addis Abeba
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块