Stone bund of Tigray [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Emni Zala (Tigrigna)
technologies_1397 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Woldu Kebede
Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources (MoA) - 埃塞俄比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Mass mobilization [埃塞俄比亚]
Mass Mobilization is an approach pursued to implement SLM technologies by organizing land users to undertake SLM activities without incentives being involved.
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
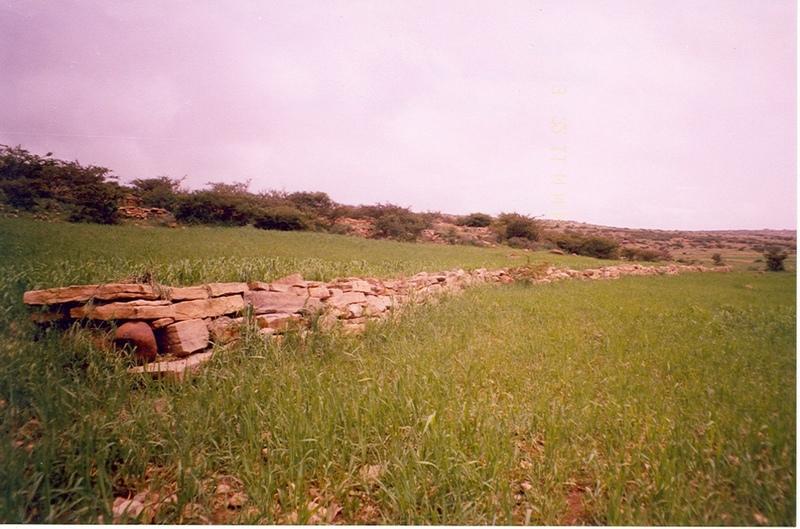
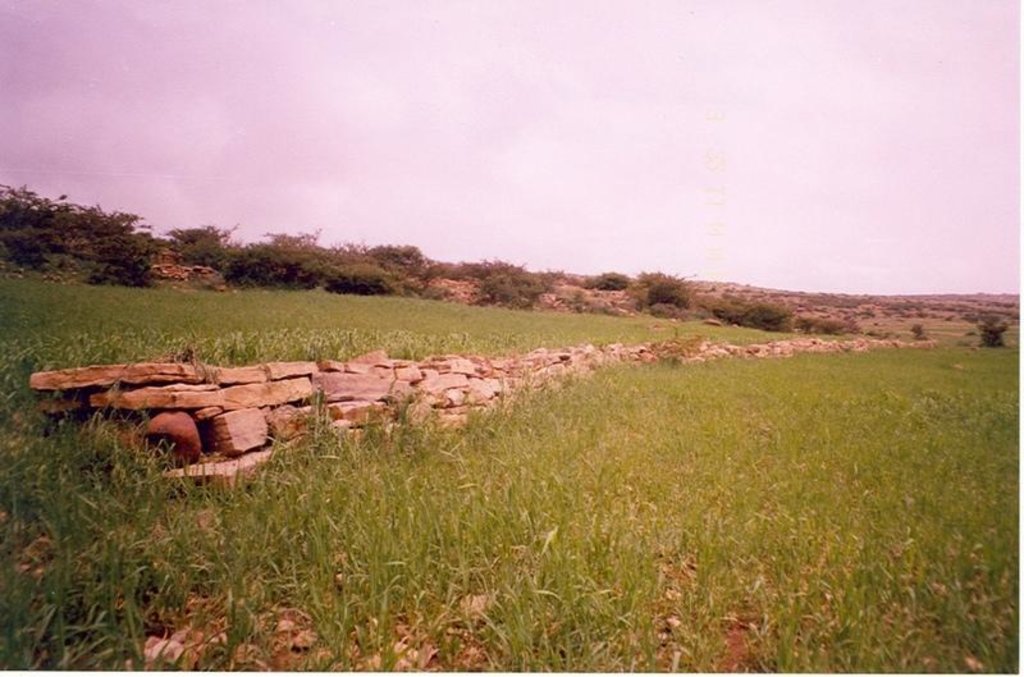
an allignment of stone along the contour line which stabilzes with grass species
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Description: construction of stone bunds along the contour to reduce soil erosion, conserve moisture, decrease slope length, and to decrease down stream siltation. It is integrated with biological SWC measures and maintenance is made where ever necessary. The technique enhances the growth of natural grasses and improves the micro climate.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Tigray
有关地点的进一步说明:
Enderta Woreda/District
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.15 km2.
The spacing is wider. Unproper foundation and excavation is observed in some places
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
the introduced methods come from other areas
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
- chickpeas, wheat, teff
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Oct

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, overgrazing and trampling, deforestation, decline of fertility and productivity, aridity, low soil moisture, free grazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): shortage of drinking water, shortage of forage and fuel wood, drought
Grazingland comments: cut and carry is allowed
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8-1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.8-1.5m
Spacing between structures (m): 15-20m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.70m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-60m
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Birr
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.88
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | area closure (leave for natural regeneration) | June-October |
| 2. | survey and layout | December |
| 3. | stone collection | January |
| 4. | foundation excavation | Jan.-March |
| 5. | construction | Jan.-March |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 83.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 83.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 125.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 15.63 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contour cultivation | January-June / 3-4 times |
| 2. | repairing broken bund by placing more stones | Dec-Jan/annual |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 11.25 | 11.25 | 83.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 11.25 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1.41 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: crowbar, hammer, hoe, spade, shovel, sprit level
length of structure (600m long soil bund is constructed per hectar)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
construction materials (stone availabilty) and excavation of foundation could be difficult
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
550.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Hilly and moderate. Also: Gentle
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep. Also: Shallow and deep
Soil texture is medium. Also: Fine/heavy and coarse/light
Soil fertility is medium-low
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium. Also: poor and good
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Also: high and low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
55% of the land users are poor and own 55% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: daily labourer
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased cropland: 0.5-1 ha
Average area of land owned or leased grazing land: 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
社会文化影响
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Can lead to waterlogging
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
Input constraints
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
消极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
消极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
25000
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
83% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20750 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
4250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: they need some incentive
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance, stablize with biological SWC measures |
| enhancing spring development |
| increase animal feed |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
erosion control, moisture harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance, stablize with biological SWC measures |
|
yield and forage production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance, stablize with biological SWC measures, area closure and introduction of cut and carry system |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| reduce cultivated land | widen the spacing between bunds |
| harbour rodants | integrate with biological SWC measures and take rodent control measures |
| labour intensive | incentives |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| labour intensive | provision of incentives |
| shortage of construction materials and hand tools | provision of hand tools |
| shortage of skilled man power | capacity building through training and field visit |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Mass mobilization [埃塞俄比亚]
Mass Mobilization is an approach pursued to implement SLM technologies by organizing land users to undertake SLM activities without incentives being involved.
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块