Gabion check dam [突尼斯]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mongi Ben Zaied
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
Ouvrage en gabion
technologies_1400 - 突尼斯
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Mongi Sghaier
Institut des Régions Arides IRA
突尼斯
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Chniter Mongi
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole CRDA
突尼斯
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - 突尼斯有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole (CRDA) - 突尼斯1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
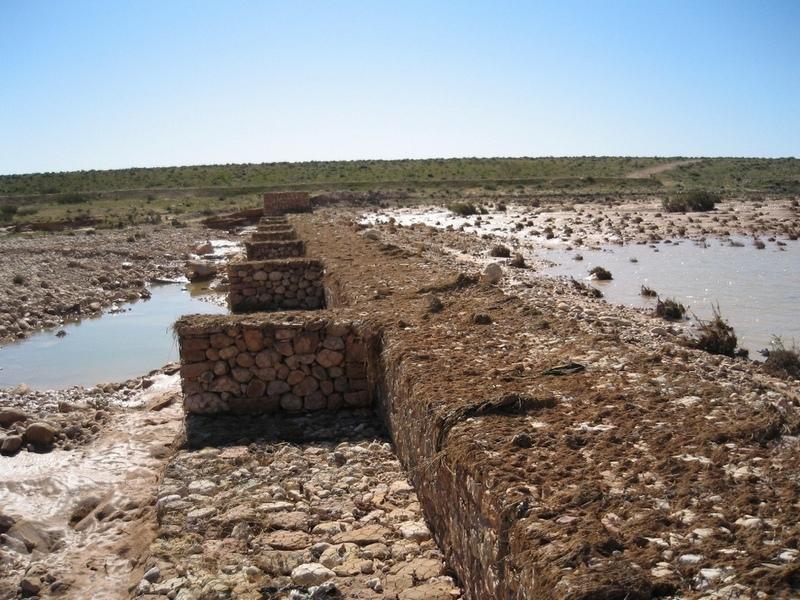
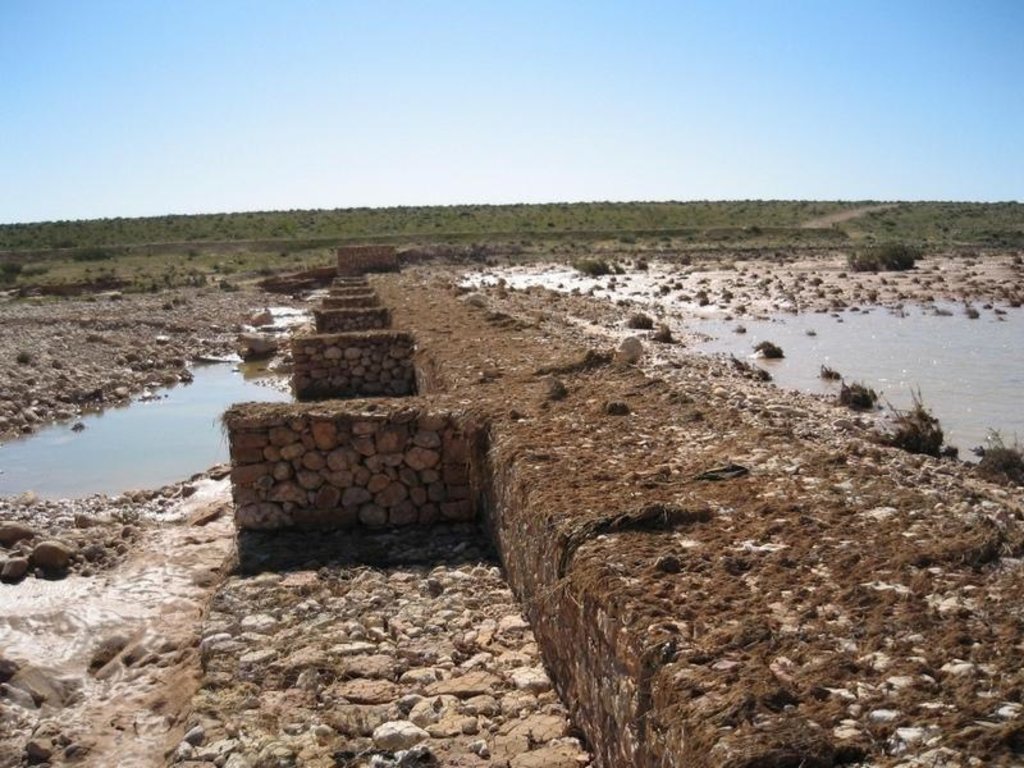
The technology of check dam is a technique consisting of binding different gabion cages filled with small stones together to form a complete flexible gabion unit.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
In order to slow down the water flow in the wadi courses and improve its infiltration into deeper soil layers and geologic formations, small check dams are installed on the wadi beds. They are usually positioned in series, with a spacing of 100-500m. These dams are made of gabion.
The gabion technique has been first introduced in the civil engineering domain. They are largely used since then and found many applications.
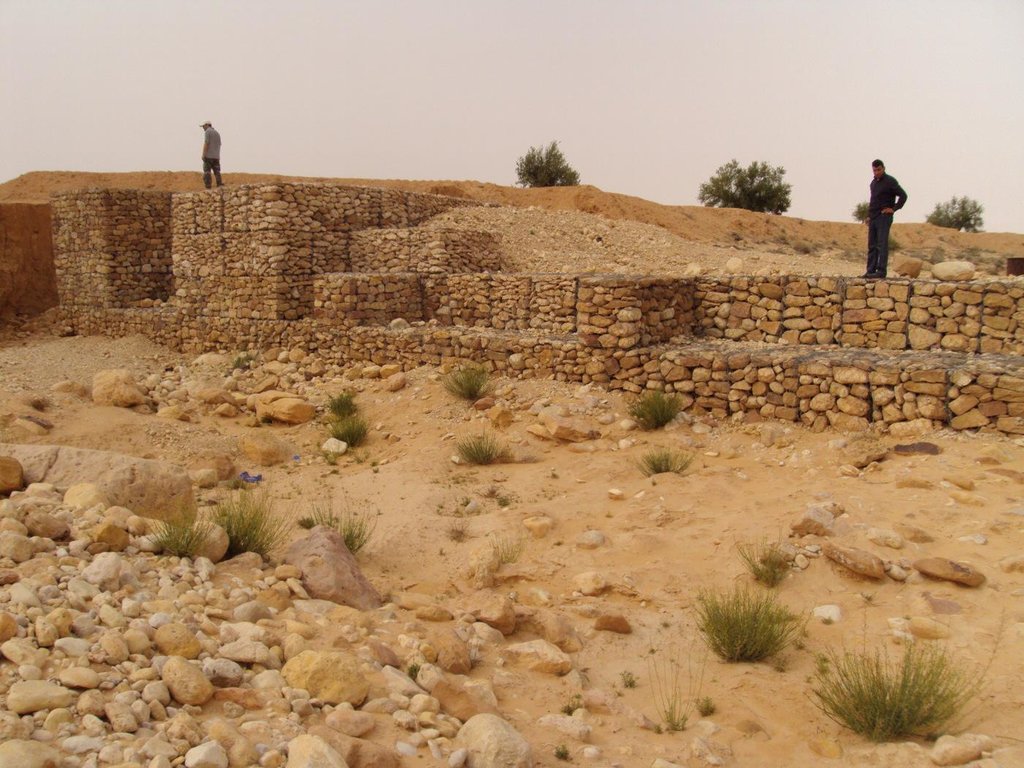
A gabion is a cage which has a cubic shape filled with stony material of suitable diameter enclosed in metal grating keeping the stones together and stops them from moving under the pressure of water. The gabion is normally the name of the cage only but it is also used frequently for the whole structure itself. The technique of gabion check dam consists in binding different cages together to form a complete gabion unit. The average height varies from 1 to 4 m and its length is a function of the width of the wadi bed (Royet, 1992).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
突尼斯
区域/州/省:
Medenine
有关地点的进一步说明:
Beni Kedhache - Bhayra
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
This technique is practiced in the Jeffara plain as well as in the mountain region.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
In the provinnce of Medenine, the first gabion check dams used for groudwater recharge and spreading have been constructed starting from 1985.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar

牧场
- Extensive grazing land
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): -Degradation of soil and land cover
-Loss of water and soil ressources
-Flooding
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of water resources by flow out from the watershed
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Constraints of wadi beds: floods
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植

牧场
注释:
Constraints of wadi beds: floods
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wr: riverbank erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (intensity)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (degradation of land cover), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
Third goal: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
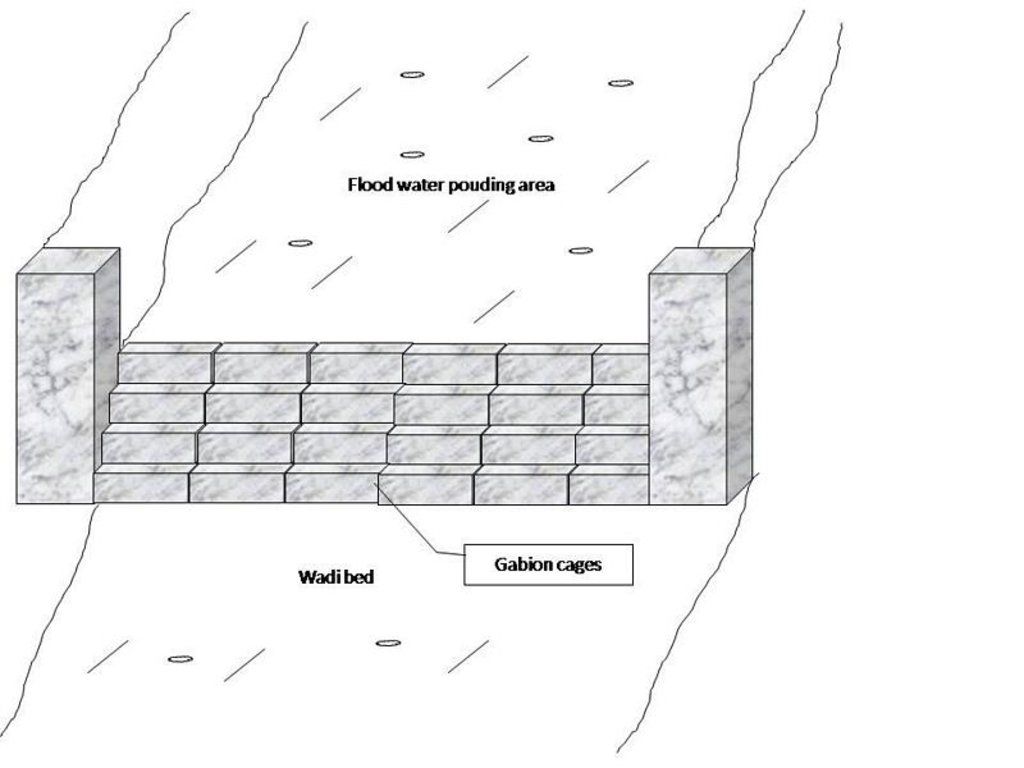
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Gabion check dam is made of galvanised blocks filled with stones.
Location: Jeffara plain. Medenine, Tunisia
Date: January 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Spacing between structures (m): 100-500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4-6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30-100
Construction material (stone): The average length varies between 15 and 30 cm
Construction material (other): Gabion: Galvanised cages of 1 to 3 m3.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: <1%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 5000-15000m3
Catchment area: 1-3 ham2
Beneficial area: 30-100ham2
Other specifications: The whole structure has the form of a spillway.
作者:
Ouessar M., Medenine, Tunisia
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tunisian Dinars
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.3
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topographic survey and selection of the site | |
| 2. | Digging of the basement | |
| 3. | Gabion installation |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Dam | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Construction material | dam | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Gabion cages | dam | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 20000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 15384.62 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1.5 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of breaks | each 1 to 2 years |
| 2. | Reconstruction | After heavy floods (once in 5-10 years) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | dam | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | construction material | dam | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Gabion cages | dam | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 2000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1538.46 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Generally, the work is manual but tractors can be used too.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
construction materials
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dry period from April to September
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: excess, medium, poor/ none (The wadi is almost always dry)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required) (from cisterns and wells) but good drinking water if pumped in the deep aquifer (100-300m)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Historically, the hard work is done by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are rich and own 50% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm incomes come from migration, construction works, commerce, tourism sector, administration or informal activities.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Generally, this technology is applied in the wadi beds which is considered as state owned but the local community can have access.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
社会文化影响
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Recharge of groundwater (water less salty and more available) and protection against the floods.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Gabion chech dams are financed by the State
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: This technology is supposed to be implemented solely by the government agencicies but in some cases the farmers can make use of it.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This technology is supposed to be implemented solely by the government agencicies but in some cases the farmers can make use of it.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Efficient structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular and good maintenance |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Robust and flexible structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular and good maintenance |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| They can not be fully exploited by the farmers | Change regulations. |
| Very expensive and cost not affordable by normal farmers | Continue subsidising by the government. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Accumulation of sediments | Desilting |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Yahyaoui, H., Chaieb, H., Ouessar, M. 2002. Impact des travaux de conservation des eaux et des sols sur la recharge de la nappe de Zeuss-Koutine (Sud-est tunisien). TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, pp: 71-86.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IRA - Medenine; DGRE - Tunis
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Boufelgha et al. 1998. Comportement des ouvrages CES dans le bassin versant d’oued Koutine lors de la crue d'Octobre 1998. Rapport interne, CRDA, Médenine
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
CRDA Médenine
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Chniter et al. 2007. Comportement des ouvrages CES dans le bassin versant d’oued Oum Zessar lors de la crue de 22 Février 2007. Rapport interne, CRDA, Médenine
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
CRDA Médenine
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sghaier, M., Mahdhi, N., De Graaff, J., Ouessar, M. 2002. Economic assessment of soil and water conservation works: case of the wadi Oum Zessar watershed in south-eastern Tunisia.TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, pp: 101-113.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IRA
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Mahdhi, N., Sghaier, M, Ouessar, M. 2000. Analyse d’impacts des aménagements de CES en zone aride: cas du bassin versant d’Oued Oum Zessar. Technical report, WAHIA project, IRA, Tunisia.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IRA
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Yahyaoui, H., Ouessar, M. 2000. Abstraction and recharge impacts on the ground water in the arid regions of Tunisia: Case of Zeuss-Koutine water table. UNU Desertification Series, 2: 72-78.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IRA
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ouessar M. 2007. Hydrological impacts of rainwater harvesting in wadi Oum Zessar watershed (Southern Tunisia). Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 154 pp.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IRA - Médenine;
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块