Gabion check dam [ตูนิเซีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mongi Ben Zaied
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
Ouvrage en gabion
technologies_1400 - ตูนิเซีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mongi Sghaier
Institut des Régions Arides IRA
ตูนิเซีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Chniter Mongi
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole CRDA
ตูนิเซีย
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - ตูนิเซียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Commissariats Régionaux au Développement Agricole (CRDA) - ตูนิเซีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
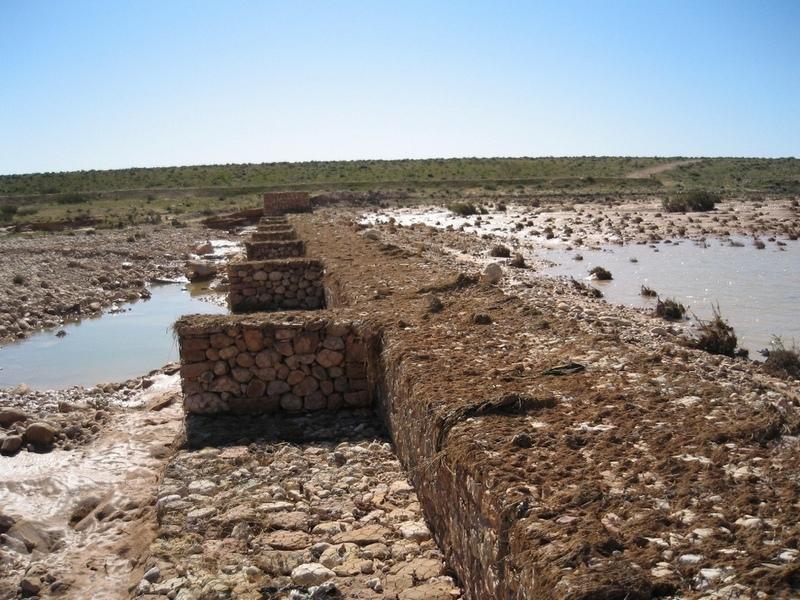
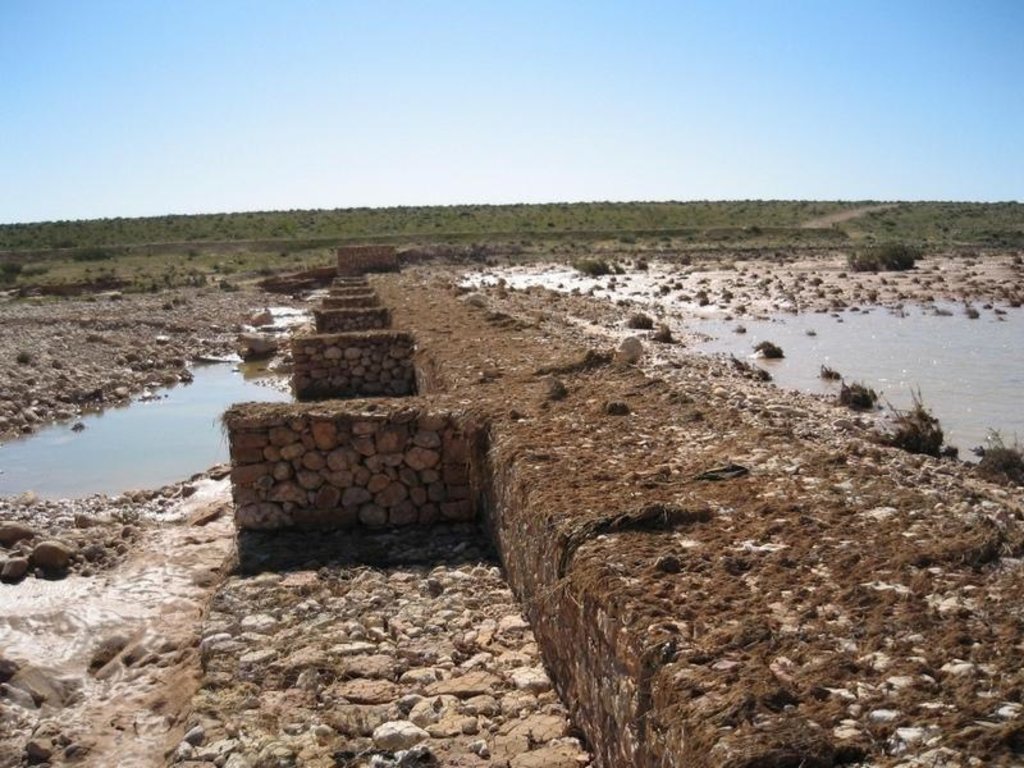
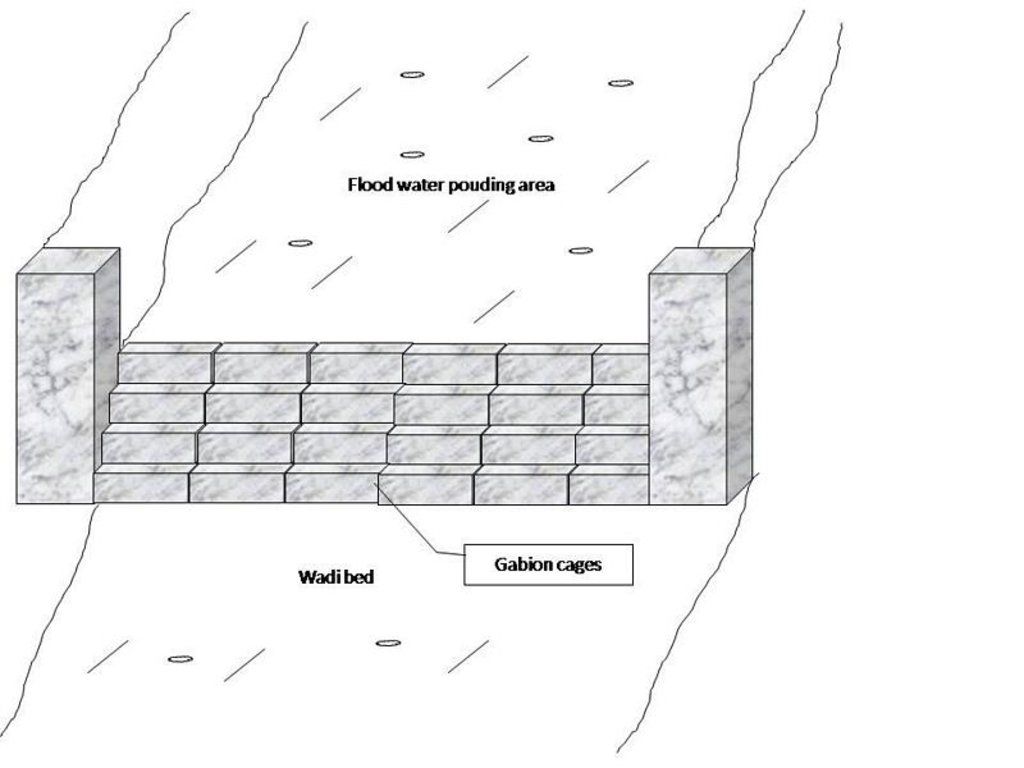
The technology of check dam is a technique consisting of binding different gabion cages filled with small stones together to form a complete flexible gabion unit.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
In order to slow down the water flow in the wadi courses and improve its infiltration into deeper soil layers and geologic formations, small check dams are installed on the wadi beds. They are usually positioned in series, with a spacing of 100-500m. These dams are made of gabion.
The gabion technique has been first introduced in the civil engineering domain. They are largely used since then and found many applications.
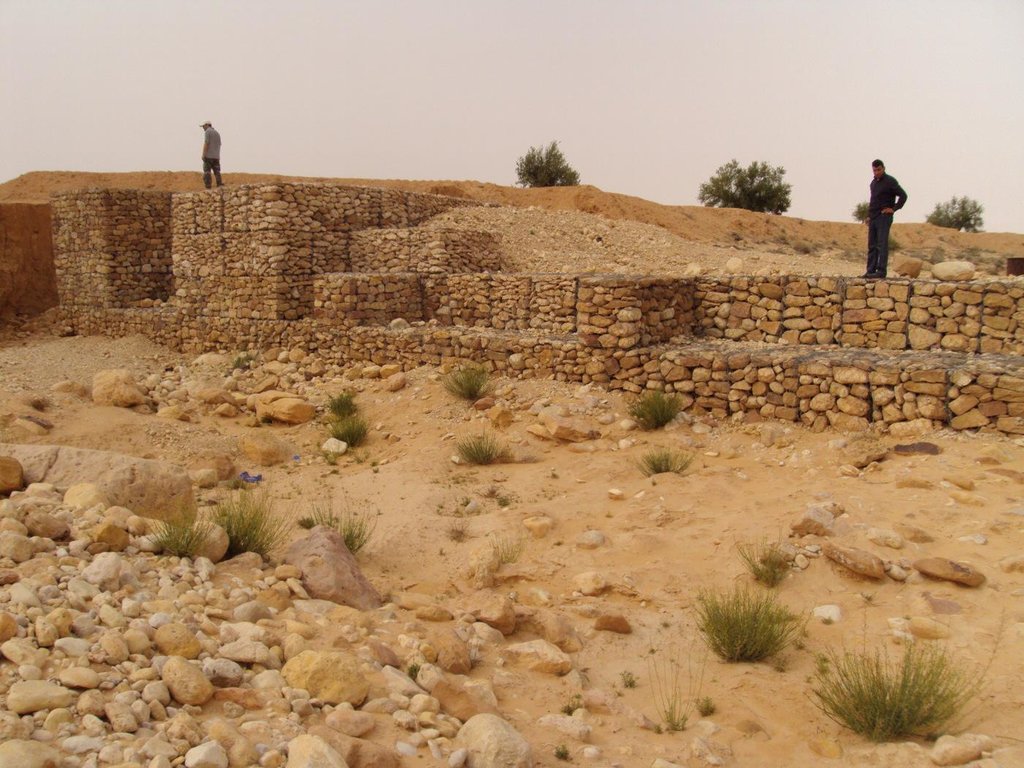
A gabion is a cage which has a cubic shape filled with stony material of suitable diameter enclosed in metal grating keeping the stones together and stops them from moving under the pressure of water. The gabion is normally the name of the cage only but it is also used frequently for the whole structure itself. The technique of gabion check dam consists in binding different cages together to form a complete gabion unit. The average height varies from 1 to 4 m and its length is a function of the width of the wadi bed (Royet, 1992).
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ตูนิเซีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Medenine
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Beni Kedhache - Bhayra
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technique is practiced in the Jeffara plain as well as in the mountain region.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
In the provinnce of Medenine, the first gabion check dams used for groudwater recharge and spreading have been constructed starting from 1985.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- Extensive grazing land
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): -Degradation of soil and land cover
-Loss of water and soil ressources
-Flooding
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of water resources by flow out from the watershed
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Constraints of wadi beds: floods
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Constraints of wadi beds: floods
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wr: riverbank erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (intensity)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (degradation of land cover), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
Third goal: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Gabion check dam is made of galvanised blocks filled with stones.
Location: Jeffara plain. Medenine, Tunisia
Date: January 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Spacing between structures (m): 100-500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4-6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30-100
Construction material (stone): The average length varies between 15 and 30 cm
Construction material (other): Gabion: Galvanised cages of 1 to 3 m3.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: <1%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 5000-15000m3
Catchment area: 1-3 ham2
Beneficial area: 30-100ham2
Other specifications: The whole structure has the form of a spillway.
ผู้เขียน:
Ouessar M., Medenine, Tunisia
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tunisian Dinars
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1.3
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
10.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topographic survey and selection of the site | |
| 2. | Digging of the basement | |
| 3. | Gabion installation |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | Dam | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Construction material | dam | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gabion cages | dam | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 20000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 15384.62 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 1.5 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of breaks | each 1 to 2 years |
| 2. | Reconstruction | After heavy floods (once in 5-10 years) |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | dam | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | construction material | dam | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Gabion cages | dam | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1538.46 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Generally, the work is manual but tractors can be used too.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
construction materials
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Dry period from April to September
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: excess, medium, poor/ none (The wadi is almost always dry)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required) (from cisterns and wells) but good drinking water if pumped in the deep aquifer (100-300m)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Historically, the hard work is done by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are rich and own 50% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm incomes come from migration, construction works, commerce, tourism sector, administration or informal activities.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Generally, this technology is applied in the wadi beds which is considered as state owned but the local community can have access.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Recharge of groundwater (water less salty and more available) and protection against the floods.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Gabion chech dams are financed by the State
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: This technology is supposed to be implemented solely by the government agencicies but in some cases the farmers can make use of it.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This technology is supposed to be implemented solely by the government agencicies but in some cases the farmers can make use of it.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Efficient structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular and good maintenance |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Robust and flexible structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular and good maintenance |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| They can not be fully exploited by the farmers | Change regulations. |
| Very expensive and cost not affordable by normal farmers | Continue subsidising by the government. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Accumulation of sediments | Desilting |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Yahyaoui, H., Chaieb, H., Ouessar, M. 2002. Impact des travaux de conservation des eaux et des sols sur la recharge de la nappe de Zeuss-Koutine (Sud-est tunisien). TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, pp: 71-86.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA - Medenine; DGRE - Tunis
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Boufelgha et al. 1998. Comportement des ouvrages CES dans le bassin versant d’oued Koutine lors de la crue d'Octobre 1998. Rapport interne, CRDA, Médenine
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
CRDA Médenine
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Chniter et al. 2007. Comportement des ouvrages CES dans le bassin versant d’oued Oum Zessar lors de la crue de 22 Février 2007. Rapport interne, CRDA, Médenine
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
CRDA Médenine
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Sghaier, M., Mahdhi, N., De Graaff, J., Ouessar, M. 2002. Economic assessment of soil and water conservation works: case of the wadi Oum Zessar watershed in south-eastern Tunisia.TRMP paper n° 40, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, pp: 101-113.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mahdhi, N., Sghaier, M, Ouessar, M. 2000. Analyse d’impacts des aménagements de CES en zone aride: cas du bassin versant d’Oued Oum Zessar. Technical report, WAHIA project, IRA, Tunisia.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Yahyaoui, H., Ouessar, M. 2000. Abstraction and recharge impacts on the ground water in the arid regions of Tunisia: Case of Zeuss-Koutine water table. UNU Desertification Series, 2: 72-78.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ouessar M. 2007. Hydrological impacts of rainwater harvesting in wadi Oum Zessar watershed (Southern Tunisia). Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 154 pp.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IRA - Médenine;
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล