WINDBREAKS [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1421 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
retired governement official:
Mananghaya Florencio
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Rondal Jose
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
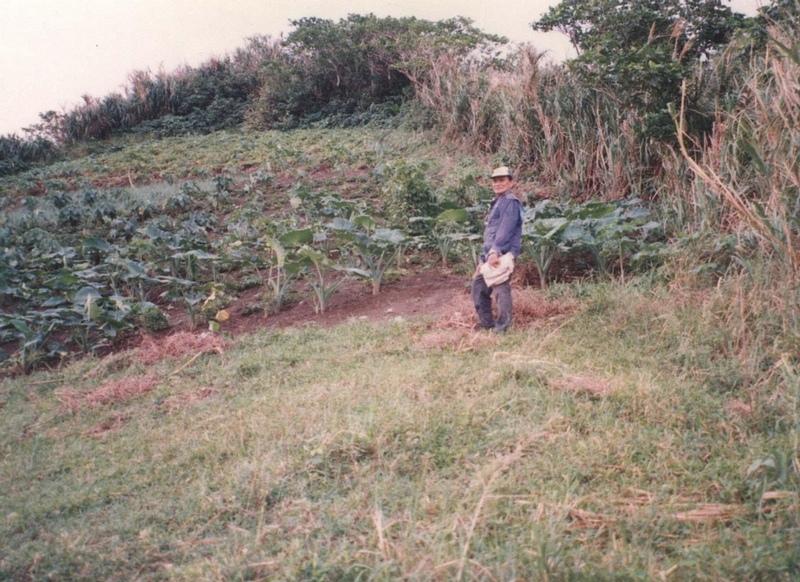
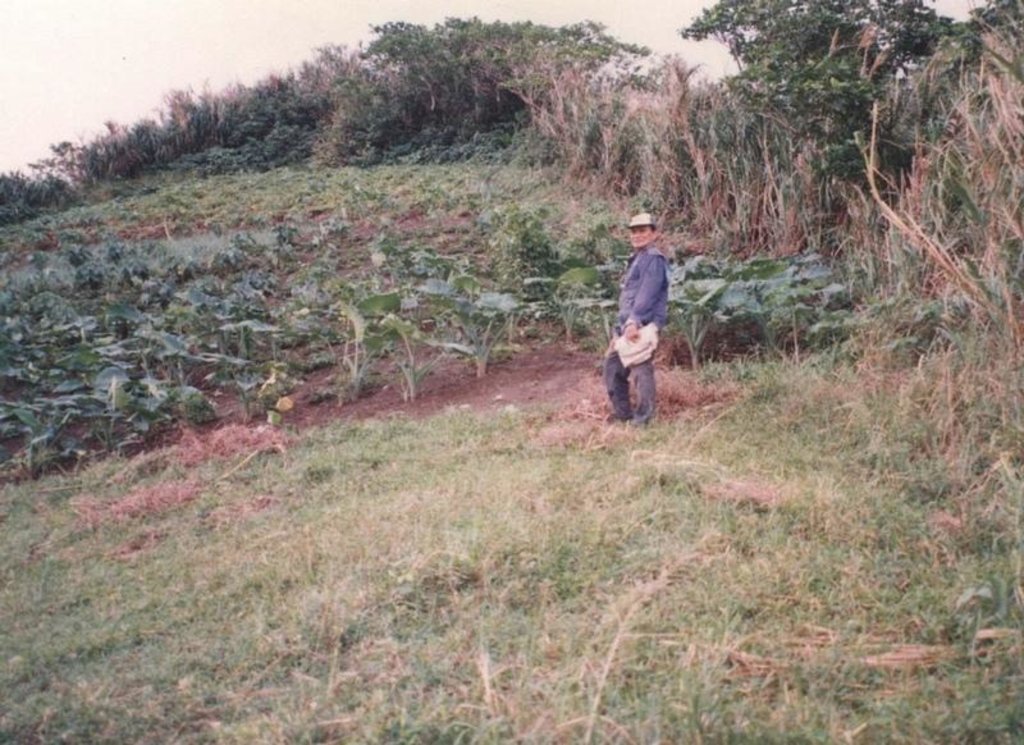
The main characteristic of the technology is the planting of herbaceous crops, grasses or trees along property boundaries. The grasses and herbs are occassionally cut and served as fodder or fuel. The trees are allowed to grow up to maturity which will then be felled for timber (construction) or for boat making. With time, especially when trees are used for boudary planting, individual fields look like boxes from the air. The choice of plants between two adjacent farms is agreed upon by the two landowner.
Purpose of the Technology: The boundary planting serves as windbreak to protect agricultural crops from wind damage. Other uses are fodder and fuelwood. The planting especially when done along the contours also trapped eroded soil from the upper portions of the field.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Planting is done once. The herbs and grasses are regularly cut to serve as animal feed. Trees are allowed to grow to maturity. Dead branches are gathered to be used as fuel.
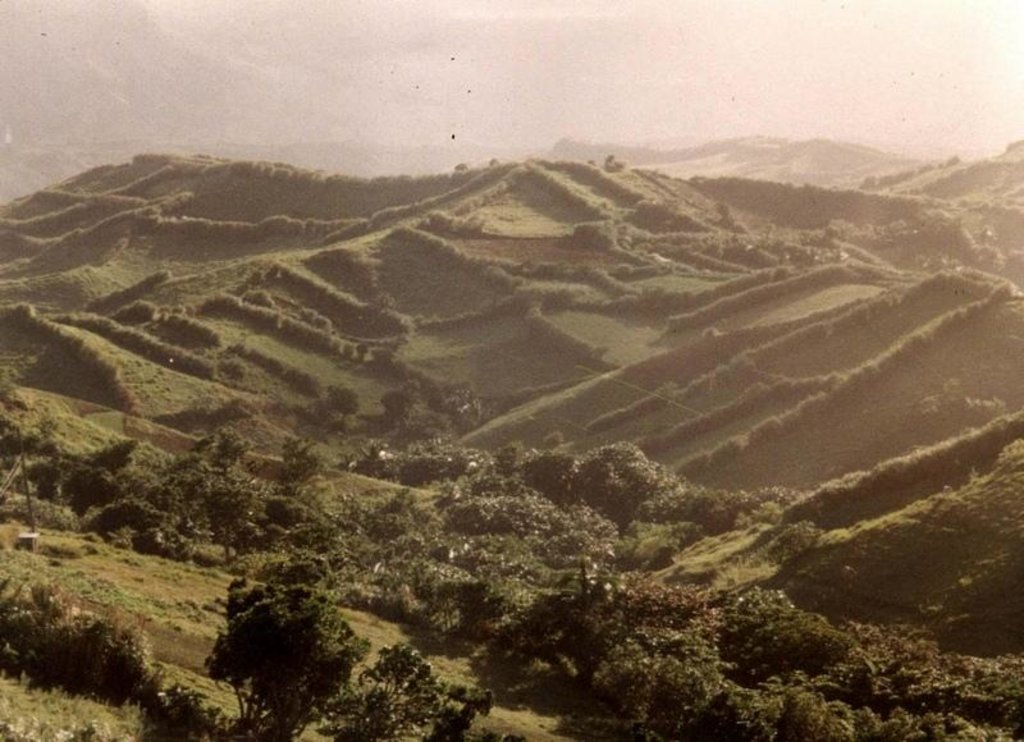
Natural / human environment: The area where the technology is applied is frequently visited by typhoons. The climate is maritime and even at times when there are no typhoons, wind speed is still strong enough to cause damage to crops. Susceptibility to wind damage is further agravated by the nature of the terrain which is mostly hilly.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Batanes, Philippines
有关地点的进一步说明:
Batanes
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec
注释:
Major cash crop: None indicated; major food crop: corn, garlic; other crops; rootcrops
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop damage due to frequent typhoons and strong winds.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low crop yield due to wind damage, poor crop quality and lack of market.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Corn, garlic or root crops are grown in separate fields. Corn is planted in December; garlic in September and rootcrops in July.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 防风林/防护林带
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3, 5, 0.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Mahogany, native shrubs
Perennial crops species: Coconut
Grass species: Napier
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedling/planting | beginning of rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of dead branches (trees) | /twice a year |
| 2. | Cutting (grass) | /every two months |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Perimeter length (m) of area to be treated/planted.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
rainy season lasts for 5 to 6 months
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zones: 0-100m a.s.l. (hills range from 70 to 270 meters altitude)
Landforms: hill slopes (slopes are gentle and gradual )
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium: (1 to 2 years fallow period improves soil fertility)
Topsoil organic matter: 1-3% (Average O.M. content is 2 .0 percent)
Soil drainage is good to medium: (Medium only in depressions)
Soil water sotrage is medium: (soil is deep)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
10% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
5% of the land users are average wealthy and own 8% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Fishing
Level of mechanization: animal traction: Plowing, harrowing, furrowing
Market orientation: Market is practically non-existent
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average farm size is 1,200 sq.m.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
fodder source --> medium 20-50%
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
conservation / erosion knowledge medium (20-50%)
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
socio cultural conflicts - little (5-20%) - conflicts between two adjacent farms possible
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
40
SLM之后的数量:
20
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
10
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
increase in soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
medium 20-50%
biodiversity enhancement
注释/具体说明:
medium 20-50%
Fuelwood source
注释/具体说明:
high 50-100% - dead branches, twigs
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Almost all the agricultural areas have adopted the technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Low maintenance cost How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent removal of unnecessary foliage |
|
Protect crops from wind damage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of canopy and foliage |
|
Improves soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use vegetative parts as mulch. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption for other land users |
|
Provides other benefits such as fodder and fuelwood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent cutting in the case of reeds/grasses to stimulate new growth. |
|
Provides residue for organic matter build-up How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent cutting and spreading of vegetative parts |
|
Trap for eroded soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? Close-spacing of trees and grass |
|
Good for eco-tourism How can they be sustained / enhanced? Aggressive promotion and marketing |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Competition with crops for space | Use narrower strips for hedgerows |
| Shading effect of trees | Planting of "taro" in shaded area. Frequent cutting of branches |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of space for crops | Use narrower strips for windbreaks |
| Possible sanctuary for pests | Practice integrated pest management |
| Shading effect in the case of tree windbreaks | Use of shade tolerant crops. Trees should be pruned regularly. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块