Area closure and reforestation with Acacia [突尼斯]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Maarten De Boever
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1568 - 突尼斯
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Hamdi Lazar
Direction générale des fôrets
突尼斯
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Direction générale des fôrets - 突尼斯有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine (Institut des Régions Arides de Médenine) - 突尼斯有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ghent University (UGent) - 比利时1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Protection and reforestation of degraded arid lands in pre-Saharan Tunisia.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
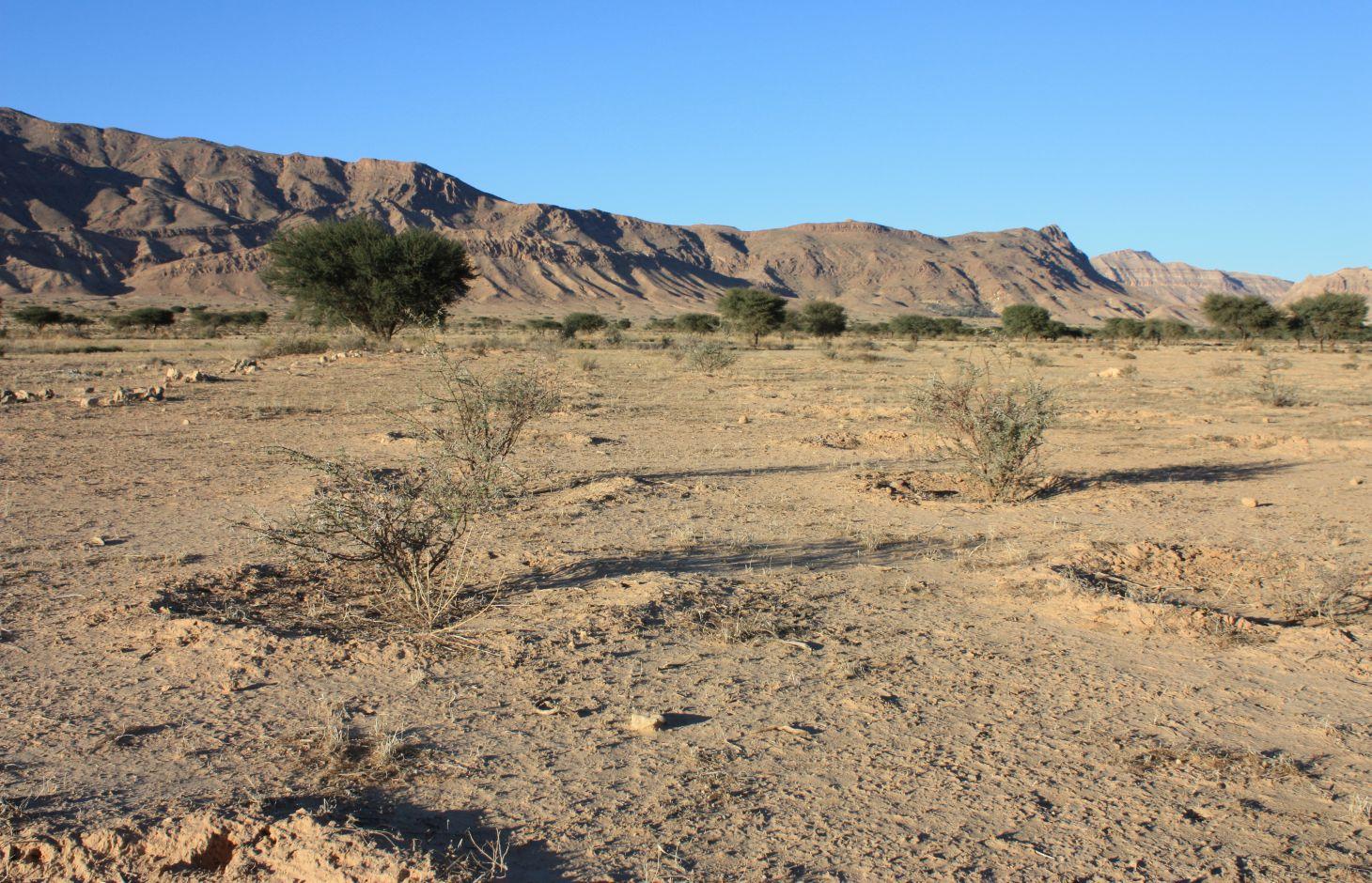
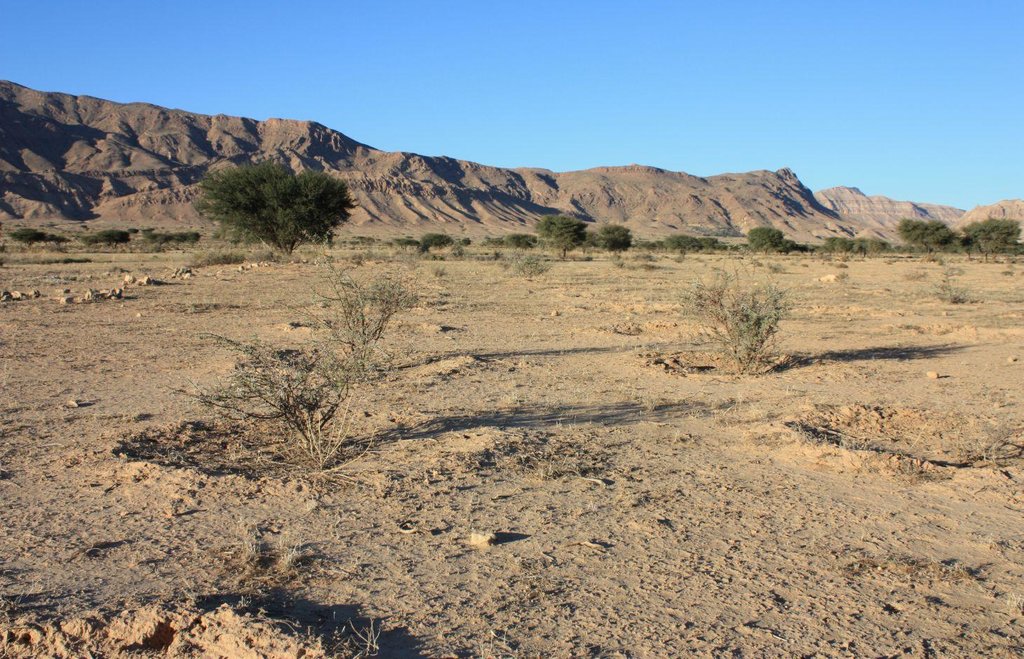
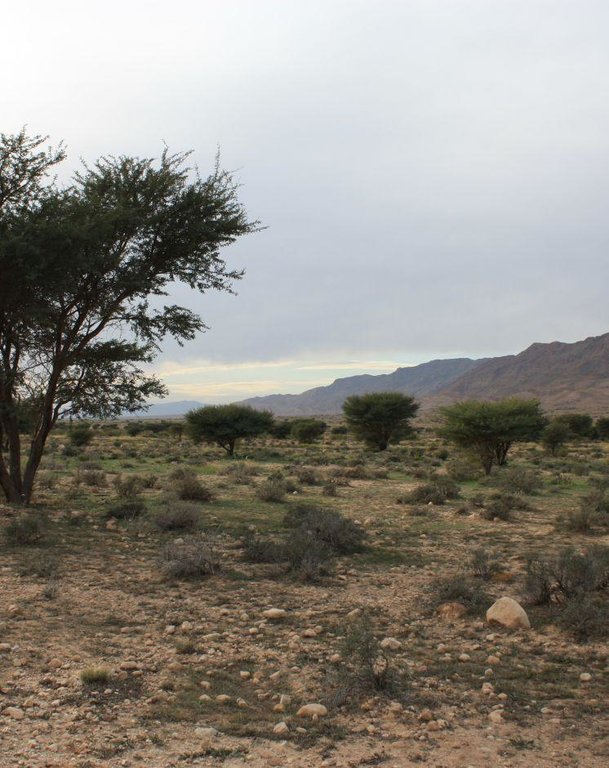
Protection and reforestation of degraded arid lands in central and southern Tunisia (Bled Talah region) with tree species Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana. A. raddiana is a native trees species which is able to tolerate extreme droughts and to persist on the edge of the Sahara desert. Acacia plantations are set up following a 3m x 3m grid using seedlings of A. raddiana. Seedlings are planted in the bottom of infiltration pits which are constructed for rainwater harvesting. Protection of the plantation area is established by means of a fence.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of afforestation is the rehabilitation of degraded drylands and restoration of the original forest-steppe ecosystem in the Bled Talah region, which suffered for over a century from overexploitation of natural resources and intensification of agricultural activities. Focus is put on the synergy between the protection of the natural resources with the involvement of local people and the improvement of their livelihoods.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The protection of the Bled Talah region was initiated in 1936 and from then on several actions were undertaken such as the construction of a tree nursery and the creation of Integral Protection Zones through complete fencing. The Bled Talah area was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1977. Bou Hedma National Park was officially created by the Ministry of Forests in 1980 covering an area of approximately 16.000 ha. The park consists of three Integral Protection Zones or core areas which are completely fenced, two agricultural zones and two buffer zones. Since the 1970s, several reforestation campaigns with A. raddiana are conducted in the Integral Protection Zones.
Natural / human environment: Arid Tunisia, i.e. the central and southern part of Tunisia, is characterized by an extremely irregular spatiotemporal rainfall pattern, a limited amount of rain (350 mm maximum per year), a limited number of days of rain (15 to 40 days a year) and a high average annual temperature (18 to 21 °C).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
突尼斯
区域/州/省:
Sidi Bouzid/Gafsa
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 165 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
- Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 放牧/啃牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overexploitation of natural resources such as tree cutting for fuelwood and intensification of agriculture such as intensive grazing of cattle lead to increased pressure on the environment causing severe degradation of the orginal ecosystem.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Less arable land and reduced fodder availability in the region.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

牧场

森林/林地
- 植树造林
注释:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pk: sealing and crusting, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (tree cutting for fuel), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fodder), overgrazing (intensive grazing), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure, poverty / wealth
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Third goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
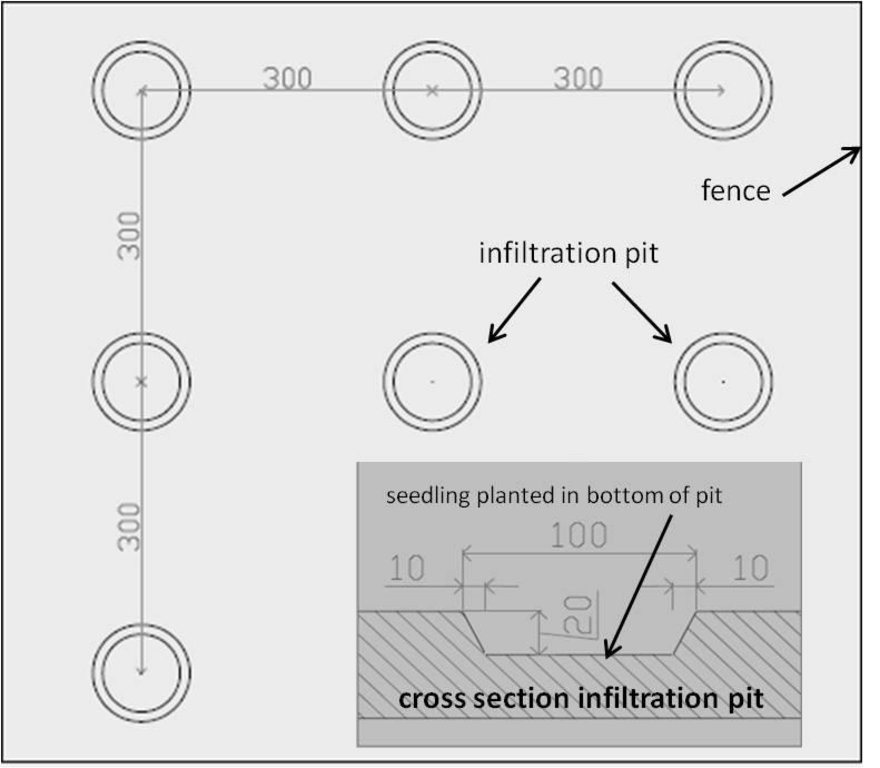
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Fenced plantation with Acacia trees on a 3m x 3m grid with cross section of infiltration pit (length given in cm)
Location: National Park Bou Hedma. Sidi Bouzid
Date: 2014-02-04
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia raddiana
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Construction material (other): wire fence
作者:
Maarten De Boever
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tunisian Dinar
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.65
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | seed collection | June/July/August |
| 2. | tree nursery | July/August |
| 3. | plantation | rainy season (sept-->dec) |
| 4. | installation fence | 1 day |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 330.0 | 330.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Iron wire fence | ha | 1.0 | 1600.0 | 1600.0 | |
| 施工材料 | iron poles | ha | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2730.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1654.55 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 8 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | follow up plantation (irrigation) | weekly 1 day by 2 workers for 1 year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 30.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 18.18 | |||||
注释:
The above costs were calculated for the establishment of a 1 ha fenced plantation with 1000 seedlings on a 3m x 3m grid. From collecting seeds to planting of the seedlings and fencing the plantation it takes about 8 months. Irrigation through the first year after planting is done to ensure survival of the seedlings.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factor affecting the costs is tree nursing. This factor is not only labour intersive but also high in water demand.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainy season September-December
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: coarse/medium (loamy sand/sandy loam)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium - poor
Soil water storage is low - medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Mainly men are involved because the establishment of a plantation is labour intensive.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology improves the livelihoods of local people directly through income generation from employment in the park and indirectly by the improvement of climatological conditions in the neighbourhood of the park.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Until now no land users have implemented the technology because the government does not provide any incentives/subsidies.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
protection (less soil degradation) and rehabilitation of the natural ecosystem How can they be sustained / enhanced? involvement of local people |
|
direct and indirect improvement of the livelihoods of local people How can they be sustained / enhanced? awareness raising |
|
improved soil carbon stocks How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of existing and establishment of new plantations |
|
increased biodiversity (trees act as fertility islands facilitating the growth of ground cover plants) How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of existing and establishment of new plantations |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| no tree planting initiatives undertaken by local people | incentives/subsidies from government |
| no public awareness of importance to conserve natural resources | set up of a large educational program with regular activities in the park and further elaboration of the small ecological museum |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块