Intercropping Bananas and Pineapple for Optimal Land Utilisation [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jalia Namakula
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Drake Mubiru, Udo Höggel
Ori Onda le onda rii
technologies_2317 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Ecima Pascal
0779747476
Anzoa Mixed Farm
Adjumani District
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A banana (musa acuminata) and pineapple (ananas comosus) inter-cropping system focusses on optimal land utilization and efficient use of available resources for small holder farmers. This is a good practice for controlling long term soil loss in agro-ecosystems. It involves less crop- and soil management practices as compared to annual intercropping systems.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
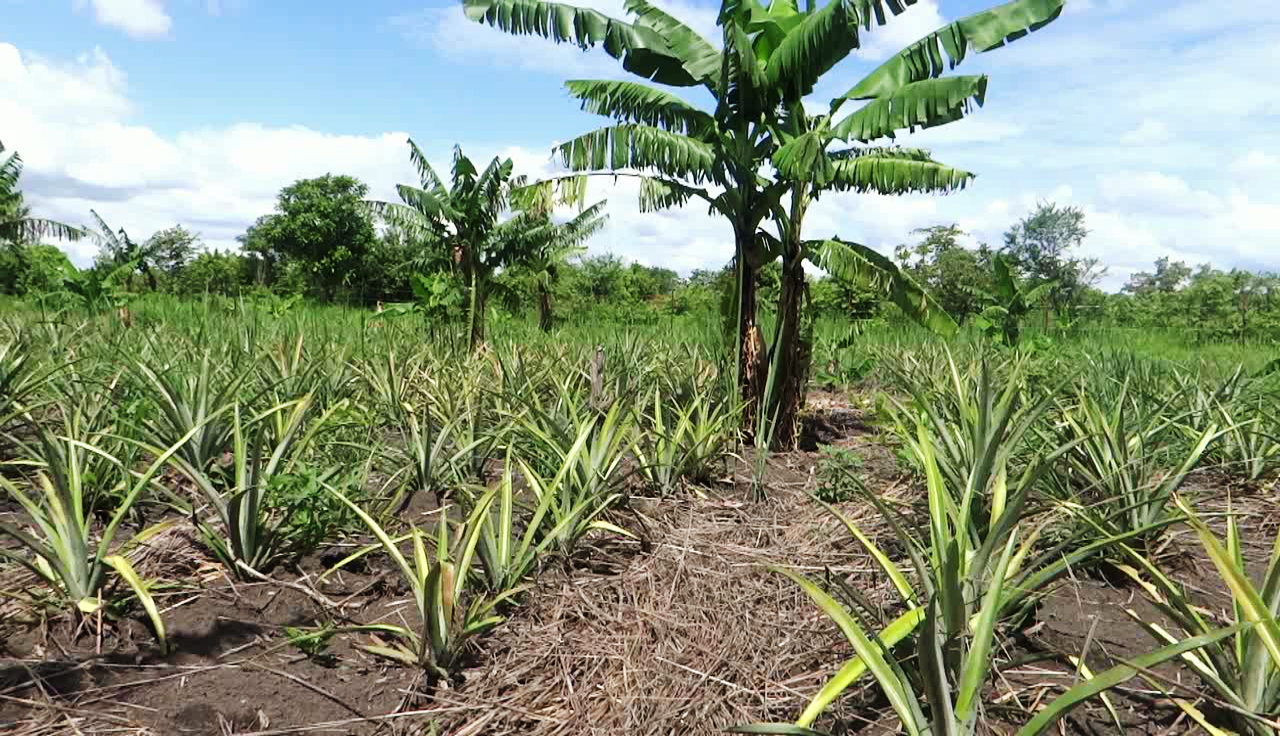
Intercropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in close proximity. Traditional growing of many annual crops like soybean, groundnut, beans and vegetables like tomatoes and onions as intercrop in banana plantations increased the risk of soil erosion in the agricultural land of Uganda. These crops require more cultural farming practices that enhance the removal of top soil layer. Therefore, the intercropping system of banana with pineapple is practiced for optimum land utilization and control of soil loss. As these crops are perennial, they require less soil and crop management practices as compared to annual crops.
The banana pineapple intercrop pattern was established with the aim of making effective use of available resources, optimum land utilisation, and sustainable production. The technology was established in 2016. The area experiences a bimodal rainfall pattern with annual rainfall ranging between 700mm-1200mm. The farm lies on 0.32 ha of land located in the valley and from observations the soils on this farm could be classified as clay loams. The bananas grown are a local Musa spp. Bananas are planted at a spacing of 4 m×4 m from row to row and plant to plant and are taken as the major crop in this technology. The pineapples are an improved variety (smooth cayenne) which is yellow cylindrical and juicy, planted at a spacing of 60 cm × 60 cm inter and intra row and planted at a distance of 75cm from a banana plant.
Establishment activities for the banana plantation were bush clearing, ploughing, excavation of 60cm×60cm planting holes, animal manure application (obtained from the owner’s farm) mixed with top soil and used to fill half the planting holes and, lastly planting the banana suckers. After a year the farmer introduced pineapples which, involved digging planting holes, the application of animal manure and the planting of pineapple suckers. Planting of bananas took 2 man days whereas planting of pineapples took 4 man days. Maintenance activities included regular spraying of pineapples with pesticide and fungicides, pruning, desuckering and thinning of bananas, weeding and watering.
According to the farmer, inter-cropping bananas with high value crops such as pineapples increases his income while ensuring food security. It reduces his vulnerability to climate change since the pineapples act as soil cover and therefore increase soil moisture retention. “With this technology we reduce management costs since we do not need to weed, spray, apply manure on 2 separate gardens” he says. In addition inter-cropping minimizes risks associated with growing a single crop and ensures stable subsistence food availability and possible income. It also promotes the effective use of available resources, increased crop productivity and soil erosion control.
The disadvantages of the technology include:
- Increased competition for water and nutrients
- Weeding in banana pineapple inter crops becomes challenging since pineapples have a prickly leaf
- During establishment of the bananas and pineapples plantations trees are cut down to create space for the crops and this leads to deforestation
- Pineapples habour pests and diseases that may cause damage to bananas
- This intercrop requires a high level of skills from the farmer
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video showing the banana pineapple intercrop captured in Anzoa village, Adjumani District, Northern Uganda
日期:
10/05/2017
位置:
Anzoa village, Adjumani District
摄影师的名字:
Jalia Namakula
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Anzoa Adjumani District
注释:
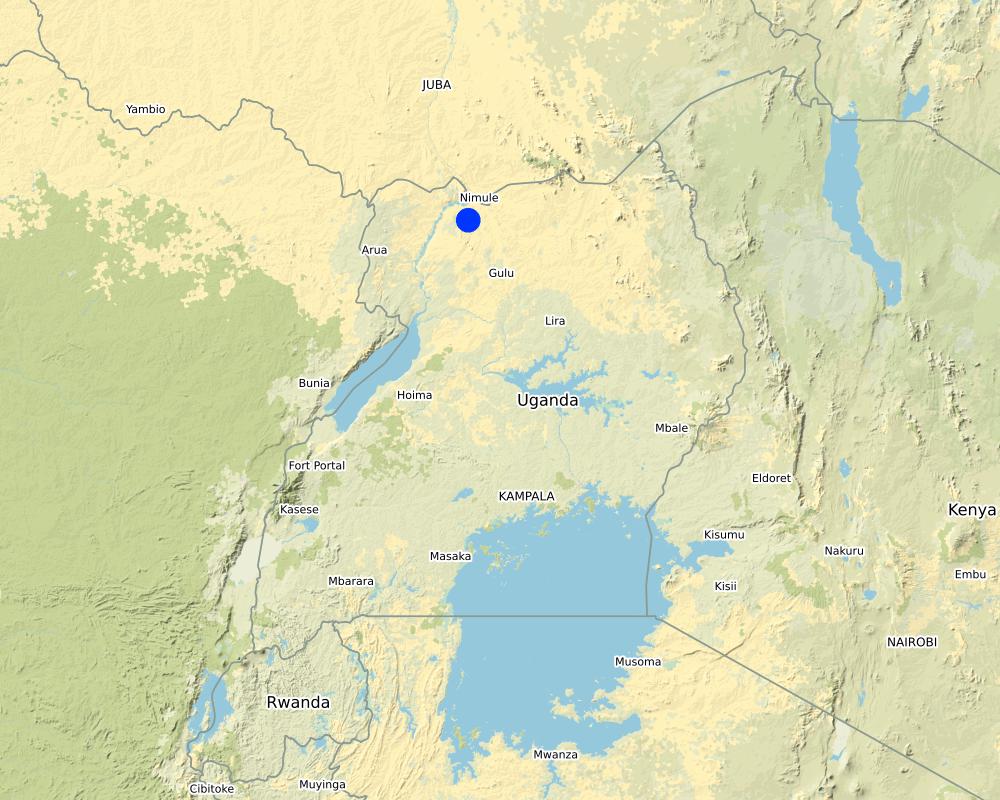
Geo reference 3.34850 and 31.93278. Captured in Adjumani District Northern Uganda
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
- Farmer to Farmer adoption
注释(项目类型等):
The land user got knowledge on establishment and management of the inter-cropping system from a fellow farmer in Luwero District Central Uganda
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Banana, pineapple
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The area was originally a private woodlot which was cut to establish this enterprise
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
During the dry season the farm depends on pumped water from a stream (River Adiidi) which flows through it
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Pineapples and bananas are a perenial crops. However the banana is harvested once annually whereas the pineaple is harvested twice annually
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Pineapples act as a soil cover because it spreads out
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
The pineapples once well established act as a soil cover enhancing moisture retention, reduction of soil erosion and increase of soil fertility in the field when the leaves decompose
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
The pineapples cover the soils hence prevent soil erosion
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
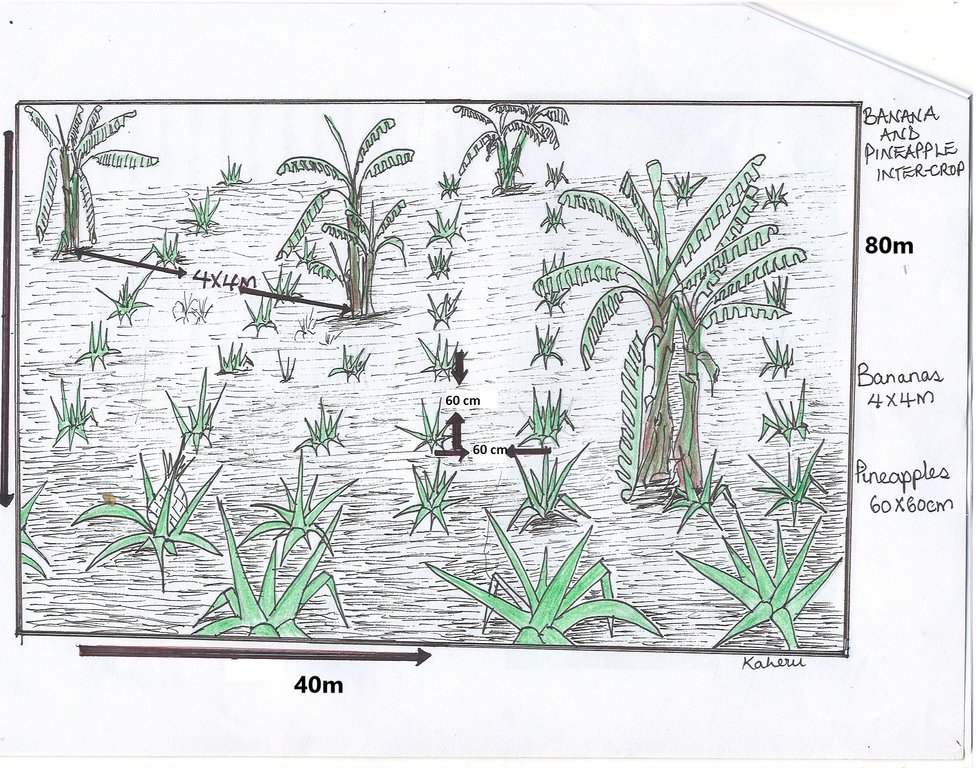
The banana-pineapple inter-crop lies on a 0.32ha land size with 300 suckers of local banana variety bought from Kasese District Western Uganda and planted at a spacing of 4m×4m . The size of the banana planting hole was 60× 60 cm.
Some of the pineapple planting material (500 suckers) was sourced from the Operation Wealth Creation (OWC) a government programme and the other planting material (7500) was bought from Luweero District and planted at a spacing of 60× 60 cm within the banana plantation. The pineapple variety grown is 'Smooth Cayenne'.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
3200 square meter
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3650.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6600
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bush Clearing | 管理 | August 2016 |
| 2. | Excavating planting holes for bananas | 管理 | August 2016 |
| 3. | Application of manure | 农业学的 | September 2016 |
| 4. | Acquisition of planting material | 管理 | September 2016 |
| 5. | Planting | 农业学的 | November 2016 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果可能,按下表分列技术建立费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出建立该技术的总成本估算。:
-1.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Bush clearing | people | 14.0 | 6600.0 | 92400.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Excavating planting holes | hole | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Application of manure | basket | 100.0 | 500.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting | plant | 100.0 | 200.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Water pump | piece | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pangas | piece | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | piece | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hose pipes | Roll | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Jerricans | pc | 4.0 | 7000.0 | 28000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Banana suckers | piece | 300.0 | 1500.0 | 450000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Pineapple suckers | piece | 8000.0 | |||
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Animal manure | bgs | 20.0 | 15000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1250400.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
500 pineapple suckers were given to the farmer by the OWC. The remaining 7500 suckers were received from Luweero District, Central Uganda.
注释:
The farmer bought the banana suckers from Kasese District
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 农业学的 | twice a week in dry season |
| 2. | Watering | 农业学的 | thrice a year |
| 3. | Spraying with pesticides | 农业学的 | once a fortnight |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | weeding | pp | 3.0 | 6600.0 | 19800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | watering | pp | 3.0 | 6600.0 | 19800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | spraying | knapsack | 3.0 | 3000.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pesticides | liters | 6.0 | 20000.0 | 120000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 168600.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Peoples attitudes (people fear weeding in pineapples because they are prickly and pineapples habour snakes), labour scarcity
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1200.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The rainfall onset for the first season came late (early April instead of March)
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Biodiversity is medium on farm but the surrounding area is a woodlot with a diversity of organisms
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The owner of the farm is a medical doctor
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Average land holding here is 5 acres
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
For this land, the farmer owns a land title. However because it is close to a river, other members are allowed to use the river water resources
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Application of manure on pineapples benefits the bananas. Since the intercrop was establish more bigger bunches of bananas are harvested, though records were not available
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Pineapples act as a soil cover for the bananas hence reducing their vulnerability to droughts, thereby reducing on risk of crop failure
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
is yet to harvest
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Workload reduces since weeding pineapples means weeding bananas too
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
The pineapple intercrop acts as a soil cover therefore increasing soil moisture retention
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
pineapples act as soil cover
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
The land user, at this point in time, has not yet started harvesting the pineapples. He, however has started harvesting the bananas and their yield has slightly increased.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
注释:
The land user adopted the technology from another region. Adjumani is an area with relatively longer drought periods, so far he is the only farmer practicing this technology.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Income diversity |
| Weeds are suppressed |
| Optimal utilisation of land |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Moisture retention |
| Reduction of total crop failure risk |
| Maximisation of resource utilisation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Weeding is challenging | Hire labour |
| The pineapples have prickly leaves | Put on overalls while weeding |
| As pineapples grow they close the spacing in between making field maintenance difficult | Use chemical control for weeds |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Competition for water and nutrients is enhanced | Apply animal manure |
| Inter-crops habour pests that are harmful | Spraying using herbicides and regular crop checks for effective mangement |
| The bananas may provide a lot of shade for the pineapples thereby reducing their productivity | Make the banana spacing a little wider |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1 person
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1 person
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Intercropping and its application to banana production in East Africa, Ouma, 2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228488472_Intercropping_and_its_application_to_banana_production_in_East_Africa_A_review
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块