Home Garden Drip Irrigation [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: betty adoch
- 编辑者: Charles Malingu, JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: John Stephen Tenywa, Nicole Harari, Luigi Piemontese, Udo Höggel
Lino pii poto (Luo-Uganda)
technologies_2801 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/04/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology enables landusers to harvest vegetables from the home garden throughout the year.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
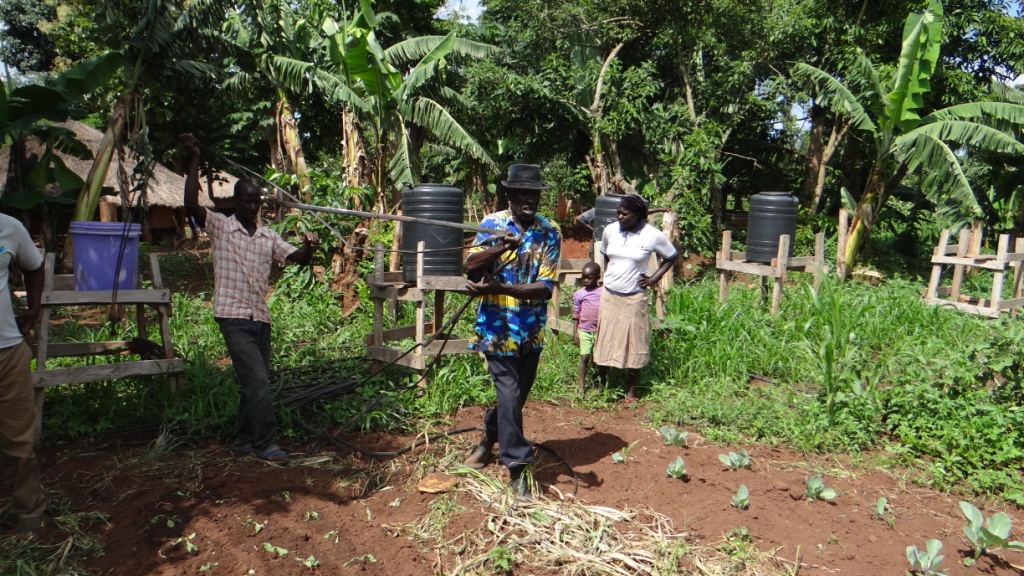
Plastic tanks of 50 to 100 liters of water with taps are placed on high platforms. Perforated plastic tubes allow water to flow and drip irrigate vegetable patches. Home gardening, once established can be carried out throughout the year.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Home garden irrigation is a commonly used practice promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda. It allows involving watering of home gardens during periods of unreliable rainfall. To implement this technology, the land user was first trained by the International Institute for Rural Reconstruction ( IIRR ) which provided the initial training to farmers as part of a campaign to promote adaptation to climate change.
50 to 100 liters tanks with taps were placed on a raised platforms. Perforated plastic tubes allow water to flow and drip irrigate vegetable patches.
A water source is needed in order for the irrigation processes to take place. Hence water is pumped by a tredle pump into the plastic tanks. Perforated plastic tubes help to direct water to the gardens grown within the land users plots. In terms of maintenance, the water tank should be cleaned every month so that only uncontaminated water is used for irrigation purposes. Home gardening can be carried out throughout the year if there is enough water available.
With this technology, the most significant costs occur during the establishment phase for the procurement of water tanks. Important to note with this technology as testified by the land user, is that the high cost of water is the most important factor during the hot and dry season while maintenance costs are low once established in the medium and long term thus making the technology good for scaling.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Vegetable garden being irrigated by the land user.
日期:
28/4/2017
位置:
Pader Town Council
摄影师的名字:
Betty Adoch
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda.
有关地点的进一步说明:
Town council
注释:
The GPS point shows the technology site.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2009
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Pineapples, bananas
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Throughout the year water can be harvested.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
The small area is usually home gardens that are irrigated via drip irrigation.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Soil erosion can be prevented through a good soil cover facilitated by and an irrigated stand of crops in the home gardens.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 不适用
注释:
Drip irrigation system is used to irrigate home gardens at smaller scales only.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
日期:
28/4/2017
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
50 to 100 liters tanks with taps were placed on a raised platforms. Perforated plastic tubes, connected to the tanks, allow the irrigation of home gardens.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
4 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3900.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3,000shs
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchasing a plastic tank | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
| 2. | Construction of the tank stand | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
| 3. | Filling the tank with water | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
| 4. | Purchasing the plastic tubes | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Man days | days | 14.0 | 5000.0 | 70000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Water tanks | pieces | 1.0 | 350000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Taps | pieces | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Plastic tube depending on size | pieces | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 580000.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Refilling the tank | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
| 2. | Cleaning the tank | 管理 | dry and wet seasons |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labourforce | Man day | 30.0 | 5000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Repairs of taps | Repairs | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 210000.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most important cost at establishment phase is the procurement of water tanks followed by labour costs and maintenance in terms repairs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1000.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Two rainy season and two dry seasons
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Savanna climate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Due to constant irrigation
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Due to constant irrigation and monitoring
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Water retained in the soil for crop production, thus making land management easier.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Stored in the water tank
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Due to increased production in the home gardens resulting from irrigation.
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
From harvested quality crops.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Watering of home gardens using irrigation technology, no manual carrying water for irrigation required.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Due to increased harvests resulting from irrigation.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Water stored in tanks as described.
水质
注释/具体说明:
due to constant maintenance
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Water stored in tanks as decribed.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Water is collected and retained in the tank and used as required.
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Soil is irrigated by dripping causing no run-off.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
water harvested and used as required; no excess water run-off to cause floods.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is good at conserving water for irrigation during dry spell. |
| The technology is good at providing soil moisture through constant water infiltration. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Home gardening once established can be carried out throughout the year. |
| Home irrigation maintains cool breeze and is environmentally friendly. |
| Maintenance costs are low, making the technology good for scaling. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It's a slow, thorough watering process. | The land user can have other options along side such as routine running water. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Tank Purchase is very expensive. | The land user can join group saving associations for loans to purchase tanks on credit. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
01
- 与土地使用者的访谈
01
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Improving livelihoods through water for production Ministry of Water and Environment, Episode 2, September 2019
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Online, free of cost
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Tips for Installing drip Irrigation at home
URL:
https://www.savingwater.org/wp-content/uploads/tips-for-installing-drip-irrigation-at-home.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块