Small Irrigation System for Highland Rice Terraces [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Pitayakon Limtong
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
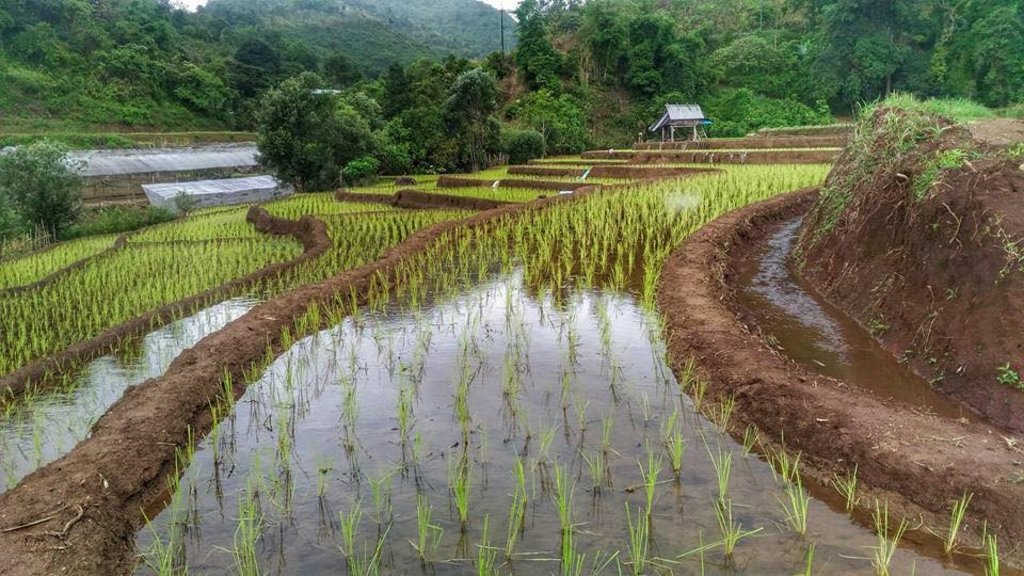
Checkdam for highland rice terrace
technologies_4114 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Srisomkhew Sasirin
662 579 1409 / 669 8269 6410
sasirin0928@gmail.com / sasirin0928@gmail.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
泰国
SLM Consultant:
Limtong Pitayakon
66 89 444 6599
pitaya@ldd.go.th / pitaya49@msn.com
Land Development Department
Paholyothin Road, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10999, Thailand
泰国
土地使用者:
Kayanyaiyie Mr.Vitoon
668 7188 0798
Soil Doctor Volunteer
Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
泰国
土地使用者:
Kongvili Mr.Boonpan
668 4740 1550
47 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
泰国
土地使用者:
khangJing Mr.Suchat
668 3660 0272
1/2 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
泰国
土地使用者:
KangJing Mr.Somnuek
668 8764 1683
Village Headman
1 Moo 5, Ban Don Village, Mae La Noi Sub-district, Huay Hom District, Mae Hong Son Province 58120
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/09/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Water supply systems in the high landscape rice terraces can prevent land degradation and also land users can utilize this area for producing rice in limited agricultural land. Because this system slows down the water flow, it reduces soil erosion into water courses and controls the amount of water that flows from the forest upstream to the rice terraces. This system increases water available to the rice terraces and improves the utilization of water, thus maximizing benefits for growth and yield of rice.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds upstream to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
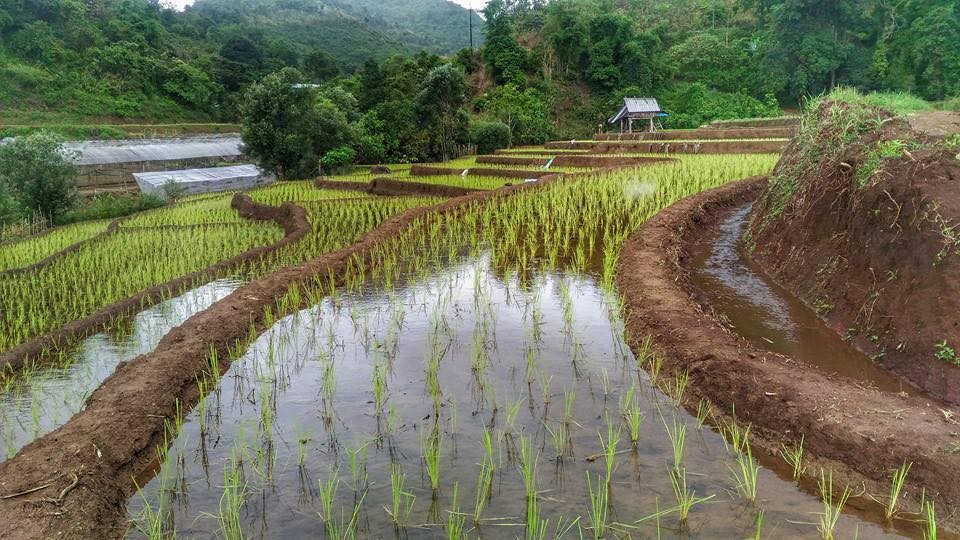
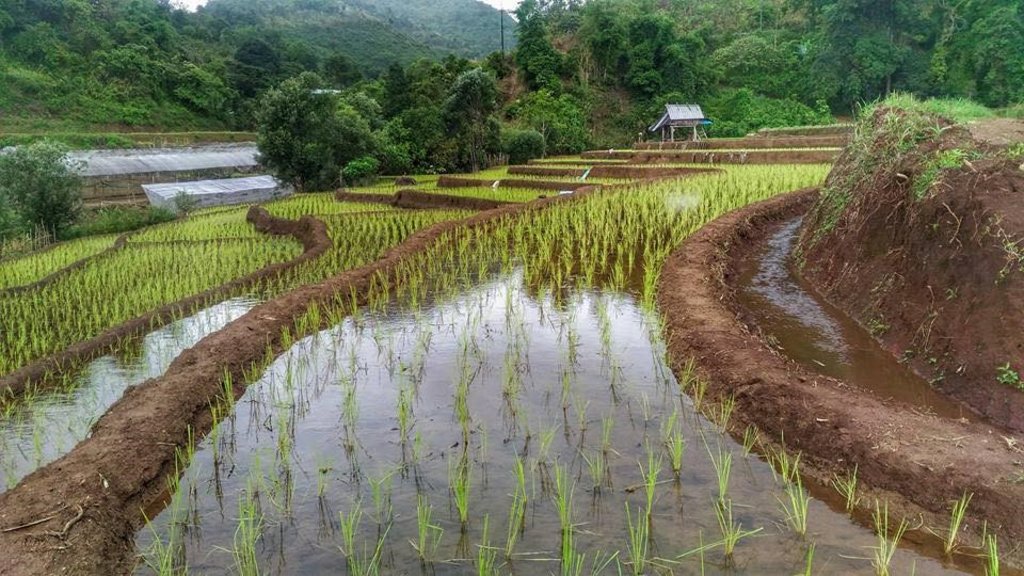
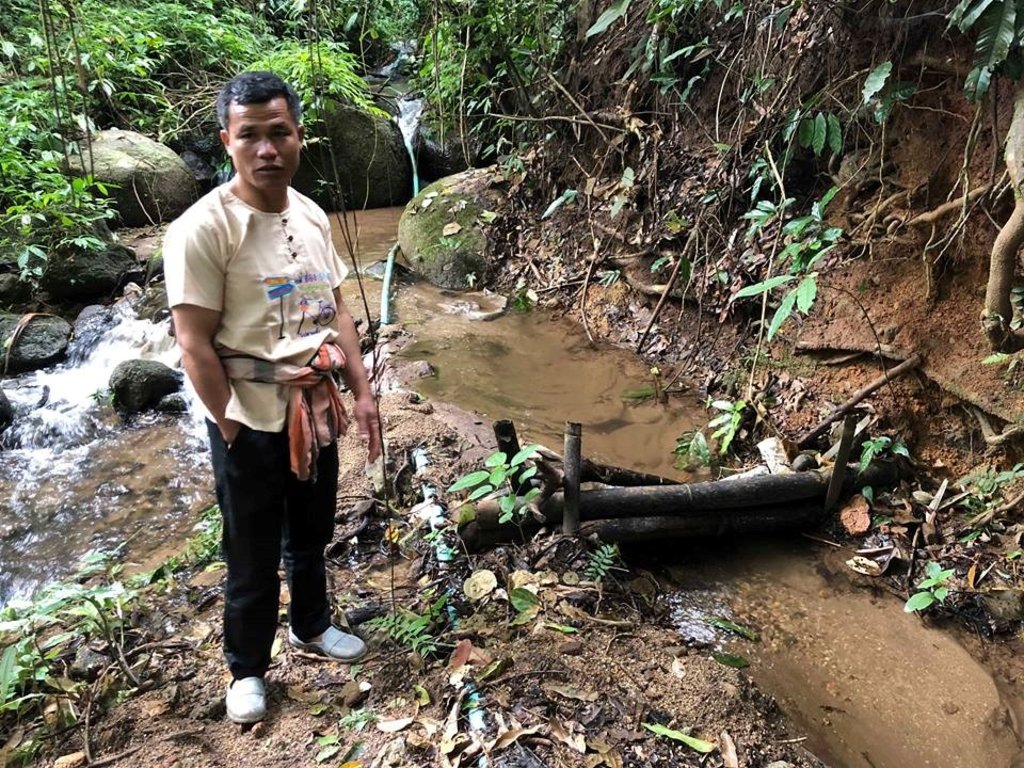
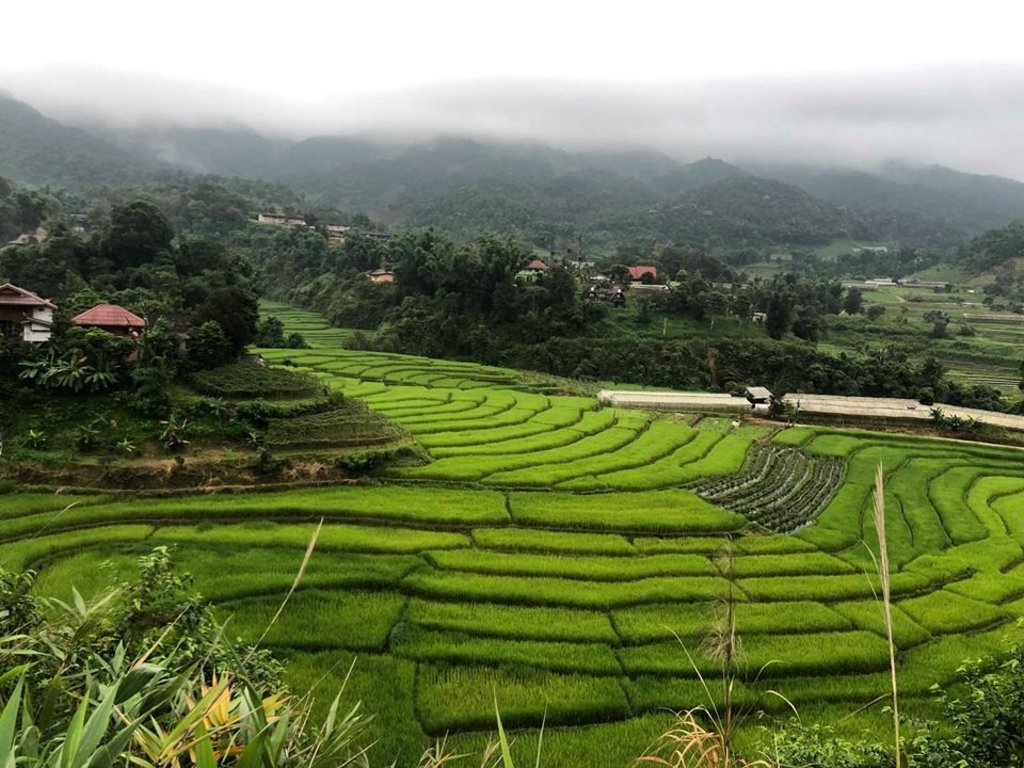
The topography of this mountainous area, Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, is complex. The height ranges from 994 -1,100 m above sea level (m asl). The main river is Mae La Noi. The climate is cool all year round. The annual average temperature is 25 degrees Celsius (⁰C), maximum temperature is 37⁰C in April, and minimum temperature is 8⁰C during December. The annual average rainfall is 1,500 mm and lasts from June to October. The number of households is 147, with total population of approx 763, 400 (Mae La Noi Royal Project Development Center, 2561). An irrigation distribution system to highland rice terraces is required for agriculture on these highland slopes. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream areas to the agricultural land - with regulation by village community consensus. The steps of preparation are as follows. 1. Site selection: Rice terraces should be on suitable slopes, not more than 60 degrees, otherwise it will be difficult to excavate the slope and rice fields become very narrow. 2. Reshaping and leveling the slope: The sloping land for rice terrace should be reshaped and levelled by either manpower or mechanical means. The terraces can extend up to 50 m long, be as little as 1 m wide and 0.5 m deep, depending on the slope. The leveling of soil surface in the plot is done by releasing water into that plot and adjust the soil surface until a good level is attained. 3. Soil improvement: Generally, soil structure and fertility in the plots is very low because of reshaping and leveling. It is therefore necessary to restore and improve by application of organic matter, compost, animal manure, legumes, etc. Soil pH must be adjusted, and nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium should be added based on soil analytical results. 4. Rice cultivation: In the first years of cultivation, the terraces may not store water at the desired level, so rice is planted in small holes. Normally, farmers plant rice seedlings (3-5 seedlings per hole) at a spacing of 20 x 20 cm. 5. Fertilizer application: In this highland area focus should be on organic fertilizers to reduce costs, because people can find materials locally such as animal manure and plant residues. 6. Water supply system: Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weirs to release suitable amount of water through a small water channel to rice terraces. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year. 7. Disease and insect control: Most rice varieties are native, so they have high resistance. But there could be some disease/insect outbreaks; they have to be protected according to instructions. The submerged condition in the paddy field can help control weeds, but some labour is still needed. 8. Maintenance: For small dams or weirs, small water channels and terraces, it is necessary to restore and maintain twice a year, i.e. before and after harvest.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
11/09/2018
位置:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
摄影师的名字:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
日期:
21/03/2018
位置:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
日期:
11/09/2018
位置:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
摄影师的名字:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Mae La Noi District, Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Paddy rice and vegetables such as chili, cabbage

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
主要产品/服务:
Small dams or weirs with small water channels to supply/distribute water to rice terraces.
注释:
Farmers in the area will grow rice in the rainy season for household consumption. The duration of cultivation until harvesting is about 6 months. In the dry season, the farms are converted to several kind of vegetables under support by the Royal Project Foundation.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The system of water supply of this technology distributes water resources from forest upstream to the rice terrace.
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Paddy rice once a year and vegetables 1-2 crops a year
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 引水和排水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
This water system covered around 200 households, each household covers an area of 0.5 hectare.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地

管理措施
- M7:其它
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Ms.Sasirin Srisomkhew
日期:
25/09/2018
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The irrigation water distribution system for highland rice terraces by farmers in the village is suitable for highland, sloping agriculture, with slopes ranging from 5-60 degrees. It is based on the principles of water management in the area by diversion of water from natural watersheds in the upstream zone to the agricultural land through the consensus of community members. Distribution of water to the rice terraces is managed by small dams or weir which are used to divert and release suitable amount of water through small water channels to rice terraces. The terraces can extend up to 50m long, 1m (or more) wide and 0.5m deep, depending on the degree of the slope. This water distribution system will spread water to all land users in this area, and there is sufficient water for farming throughout the year.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.48 hectare for each farmer
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht (THB)
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
32.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | prepare small dam and water canal | 结构性的 | in the first year |
| 2. | prepare terraces and land leveling | 结构性的 | in the first year |
| 3. | cultivation | 结构性的 | before rainny season |
| 4. | soil improvement | 管理 | after preparing and cultivating the soil |
| 5. | rice planting | 植物性的 | rainy season |
| 6. | fertilizer application | 管理 | after planting |
| 7. | irrigation | 管理 | after planting |
| 8. | disease, pest and weed control | 管理 | after planting |
| 9. | havesting | 农业学的 | when rice grains are mature |
| 10. | None | None |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果可能,按下表分列技术建立费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出建立该技术的总成本估算。:
98100.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | prepare dam and canal | 7x10 | 70.0 | 300.0 | 21000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | planting | 7x1 | 7.0 | 300.0 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | maintainance | 20x2 | 40.0 | 300.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | harvesting | 20x7 | 140.0 | 300.0 | 42000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tractor | set | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | fuel | liter | 20.0 | 30.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | rice seed | bag | 3.0 | 100.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | chili seed | plant | 5000.0 | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer 21-0-0 | bag | 3.0 | 400.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer 15-15-15 | bag | 3.0 | 700.0 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer 16-20-0 | bag | 3.0 | 600.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | animal manure | bag | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 98100.0 | |||||
注释:
Labour of small and canal preparation was paid in the first year, after that paid for maintain all of these structuer.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | restoration and maintain dam, canal and terrace | 结构性的 | 2 times a year |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果可能,按下表分解技术维护费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出维护该技术的总成本估算。:
1800.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | restoring and maintaining the dam, water canal and terraces | 2dx3m | 6.0 | 300.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1800.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Land user spend their money for 100% of costs
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most important factors that affect the costs is the labour factor, where farmers need to hire labourers for rice cultivation such as planting, fertilizer application, maintaining the system and harvesting, including, the excavation and restoration of the small dam, water channels and terraces.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1500.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
收入和成本
农业投入费用
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
干旱影响
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 适度 | ||
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 不好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 适度 |
| 局地雹灾 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 森林火灾 | 适度 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 非常不好 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 非常不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The villagers are self-reliant by living in balance between demand and supply to meet their own needs. So every household will grow rice for their consumption and solve some problems in water management of these rice terraces by their community. |
| Villagers have knowledge and technology of water management and systematically and continuously transfer to other land users from generation to generation, causing a connection between kinship and community. There are groups to solve the main problems of the community. |
| Villagers have a stable and strong mental state with the hard thinking to fight the obstacle in the way of living, to achieve a more prosperous life. Individual communities have strength in self-reliance, and also have strong mind in learning, having virtue and rationality in thinking and decision-making. |
| They have the ability to promote agriculture with natural resources and ecological tourism and develop the communication system for visitors to access the local information and facilities. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The selection of appropriate technology can solve the problem of soil degradation, reduce soil erosion and manage adequate water supply to agricultural area for the whole year. |
| The villagers have to rely and trust on each other with high willingness to share their knowledge and experience. |
| Communities have the ability to use existing natural resources in maximizing benefits, and at the same time they try to conserve and prevent soil degradation in this area. |
| Community networking allows them to conduct activities to achieve self-reliance. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land users’ lack of ownership of the land that cannot be legally owned by individuals, as the area is located in a preserved forest. The villagers therefore might be afraid to move out of the area in the future. | The community leaders and villagers need to solve this problem, one thing being that they should ask the government to help. |
| Lack of opportunities for children to have education caused by the poverty of their parents. | Schools in the area have increased educational opportunities for poor children by sponsoring underprivileged children. |
| Lack of social and health welfare because this area is far from the city. Villagers will not be able to reach the hospital in time in the case of emergency. | Villagers take the right treatment from the gold card or project 30 baht free treatment of all diseases for emergency situations. |
| Lack the coverage of energy and communication system in this area. Some areas still lack electricity, telephone and internet facilities. | Some villagers purchased and installed solar panels for their own use. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The villagers lack the ownership of the land, which located in the conserved forest. That means they do not have right to hold the land. | The government has a policy to solve these problems, and at the same time serve and arrange this preserved forest as natural resource. |
| Lack of educational opportunities, The study site is located in a remote area. Children living there lack opportunities in education. | The government has a policy to give underprivileged children equal education to children. |
| Villagers lack social and health welfare because of the remoteness of the place that they live. It is difficult to access medical treatment and hospital. | The government has set up and supported the budget to develop district health promotion hospitals in the sub-district level. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Ecological tourism of Mae La Noi Development Center, Royal Project
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=818zn7JMKsU
标题/说明:
Mae La Noi Royal Project Foundation
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M8pFfl18fC8
标题/说明:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/interest510.htm
标题/说明:
History of Mae La Noi Development Center
URL:
http://www.mhsdc.org/rypmaenoi.htm
标题/说明:
Mae La Noi Project for tourism of beautiful paddy rice terrace
URL:
https://mgronline.com/travel/detail/9590000106920
标题/说明:
Mae La Noi Development Center of Royal Project Foundation
URL:
http://royalprojectthailand.com/maelanoi
标题/说明:
Rice terrace in highland
URL:
http://www.ricethailand.go.th/rkb/management/index.php
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块