Integrated Soil Management for Organic Vegetables on the Highland Watershed in the Northern Region [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Pitayakon Limtong
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Organic vegetables in the Royal Project
technologies_4283 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
co-compiler:
Wattanaprapat Kamalapa
Land Development Department
泰国
土地使用者:
Phojanabandit Watcharin
Headman of village
泰国
local extension officer:
Kerephuwadon Boontre
Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station, the Royal Project
泰国
local LDD officer:
Intha Charun
Royal Project Land Development Center, Land Development Office Region 6, Land Development Department.
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Organic vegetable production is a technology that prevents and restores land degradation due to soil management emphasized in using organic and natural materials to improve soil fertility and productivity, especially in terms of soil organic matter.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Organic vegetable cultivation on the highland area of the northern region of Thailand has been encouraged by local officers in order to produce safe food on degraded land through building up soil fertility and soil organic matter.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
This case study is of organic vegetable cultivation at Ban Muang Ang Village which is located in Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province, covering approx. 25,881 Rai (6.25 rai = 1 ha; 625 rai = 1 sq km). The topography is a complex mountainous area within the Doi Inthanon National Park, at an elevation of 600-800 m asl. The climate is quite cool and humid with average temperature throughout the year being 20⁰C. The average annual rainfall is 2,000-2,100 mm. Most of the population belong to the Pakhayo hilltribe, living in 219 households, with total population of 588 persons (308 males, 280 females). The main purpose of promoting growing organic vegetables in greenhouses is to change their way of life from forest encroachment/ shifting cultivation in the upper watershed, to improving the ecosystem services and environment with better health and higher incomes for villagers.
Since 2002, the government and the Royal Project Foundation have had a policy to change land use to organic farming. At the early stage, yields of organic vegetables were not good. In the year 2010, the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station brought a number of these land users to visit the Mae Tho Royal Project Development Center in Bo Sali Sub-district, Hot District, Chiang Mai Province. They obtained knowledge about organic cultivation in simple greenhouses made from bamboo poles, covered with plastic sheets and nylon nets. Local officers of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station supported with education, offered suggestions and recommended practices, as well as finding markets to sell the organic products; that became the model. It took only 25-30 days for a crop, and they could harvest about 200 kg of vegetables per greenhouse. They could produce 11 crops of vegetables in one year, which means that they could earn 10 times more income than before. At present, Muang Ang Village there are 153 members operating in 270 greenhouses which is the largest organic vegetable production area in the Inthanon Royal Project.
The production of organic vegetables in this area is outstanding. This network has received certification from the Department of Agriculture (DOA) and the Office of Organic Agriculture Certification Thailand (ACT Organic). Farmers or farming enterprises certified by this system are entitled to apply the logos and certification card of ACT Organic and IFOAM Accredited brand on their products. Moreover, the Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority of Singapore (AVA) has approved the production processes. Every production step has been approved through the standard regulation of each agency with tracking to the source of production inputs such as fertilizers, disease, weed and pest control measures, cultivation practices, etc. Now they have nine types of vegetables that constitute the main production: Choy, Baby Emperor, Cos Salad, Green Oak, Red Oak, Fille Iceberg, String Bean, Kale Hong Kong and Baby Carrot.
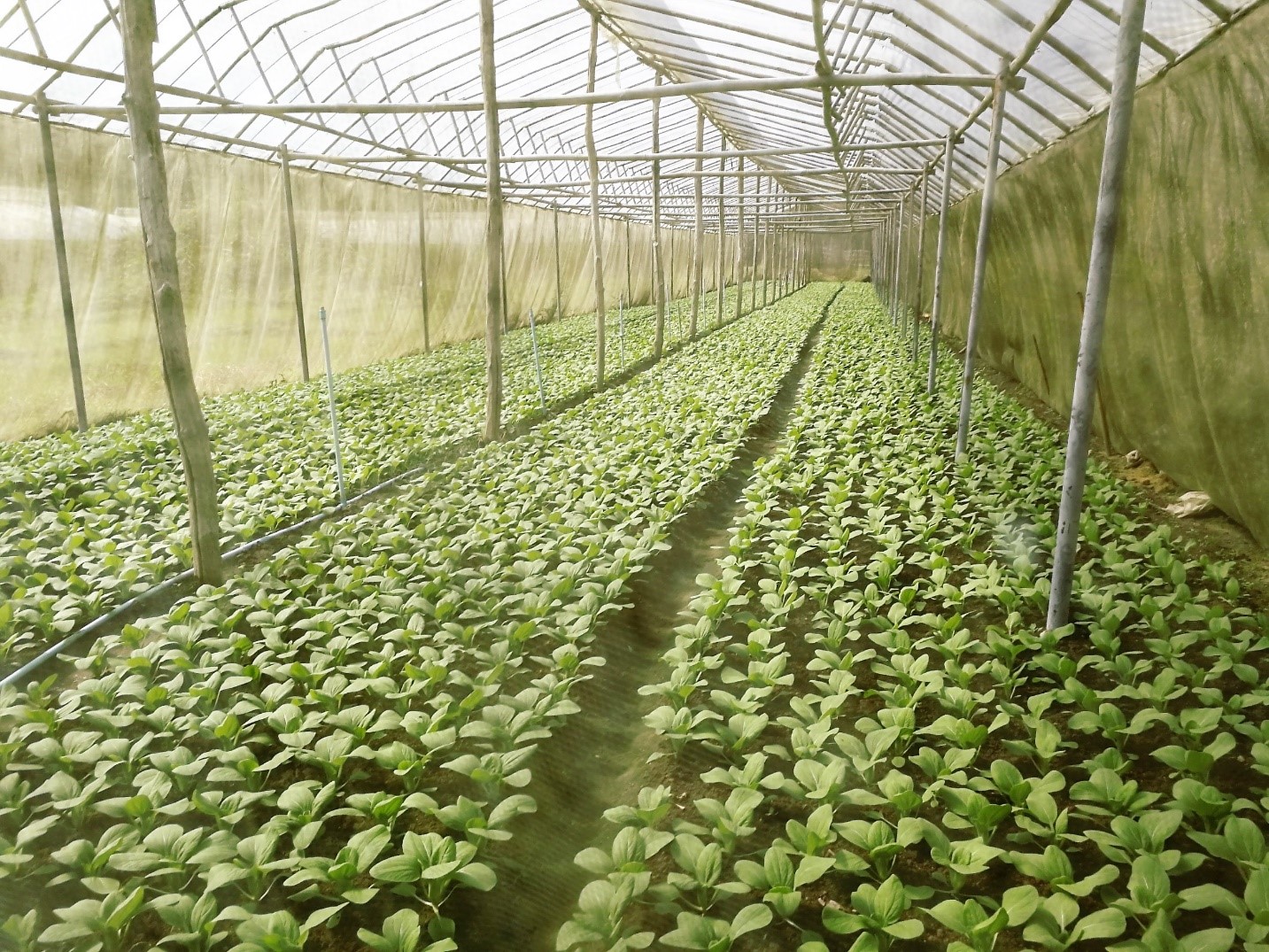
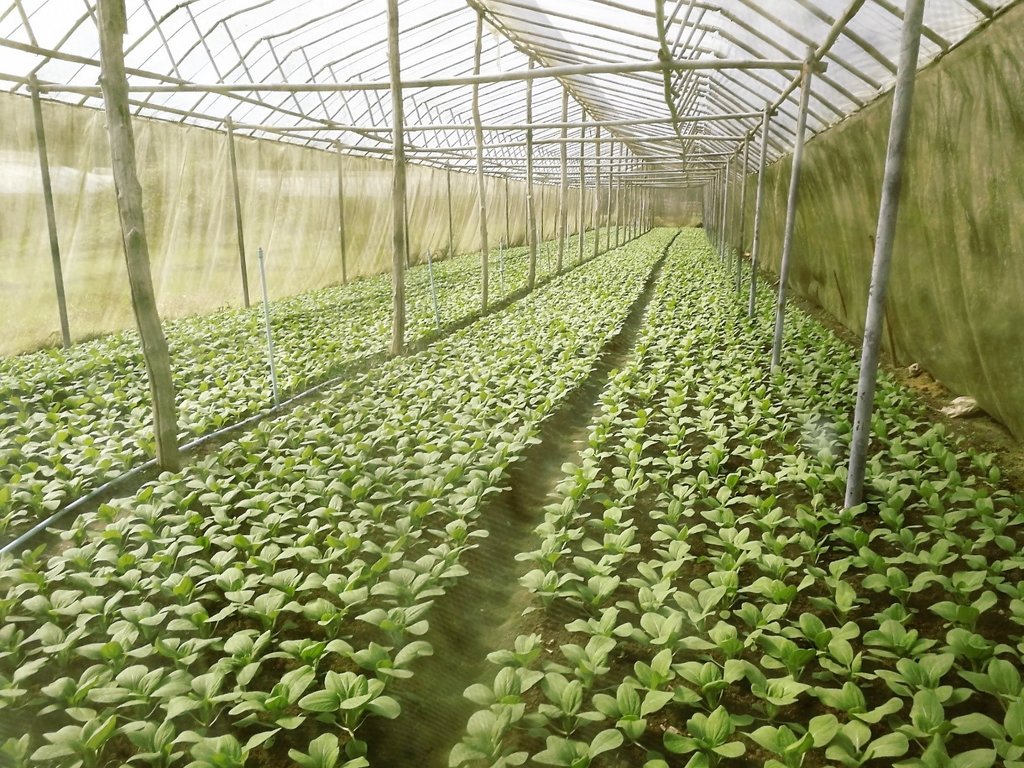
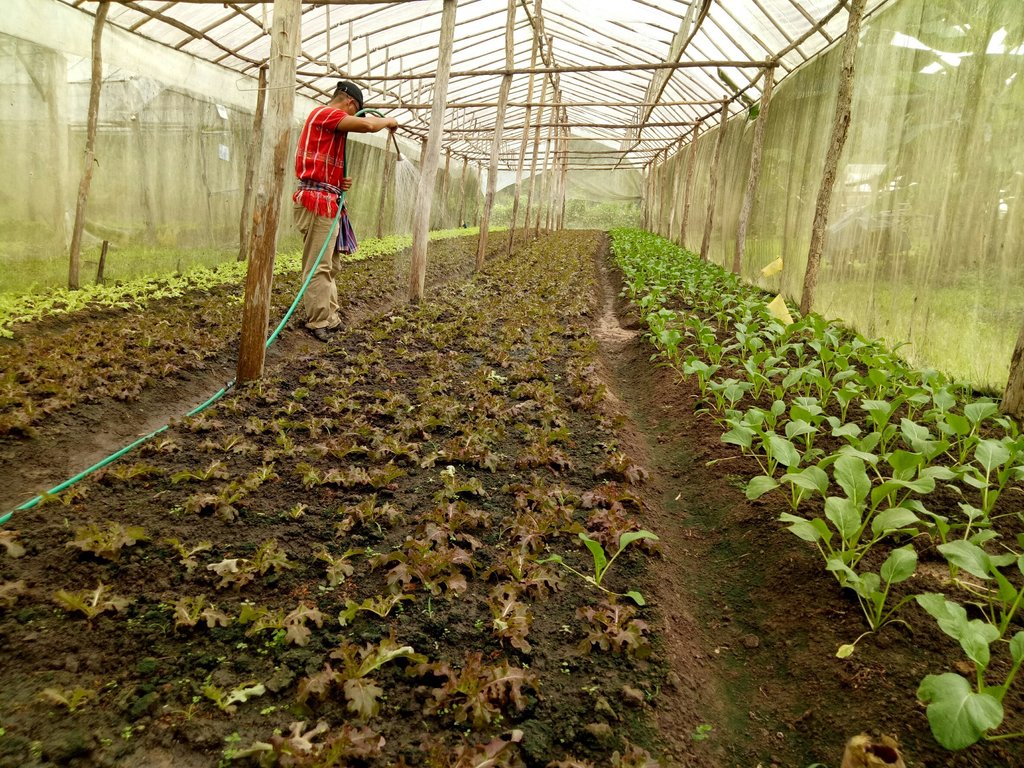
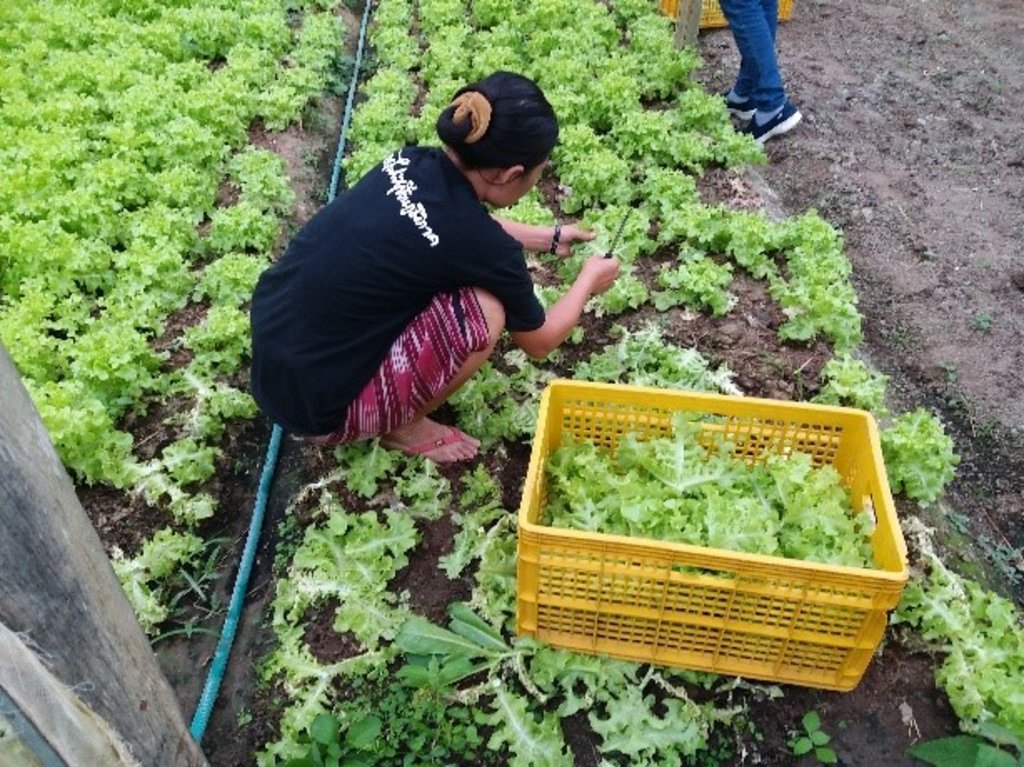
2.3 技术照片
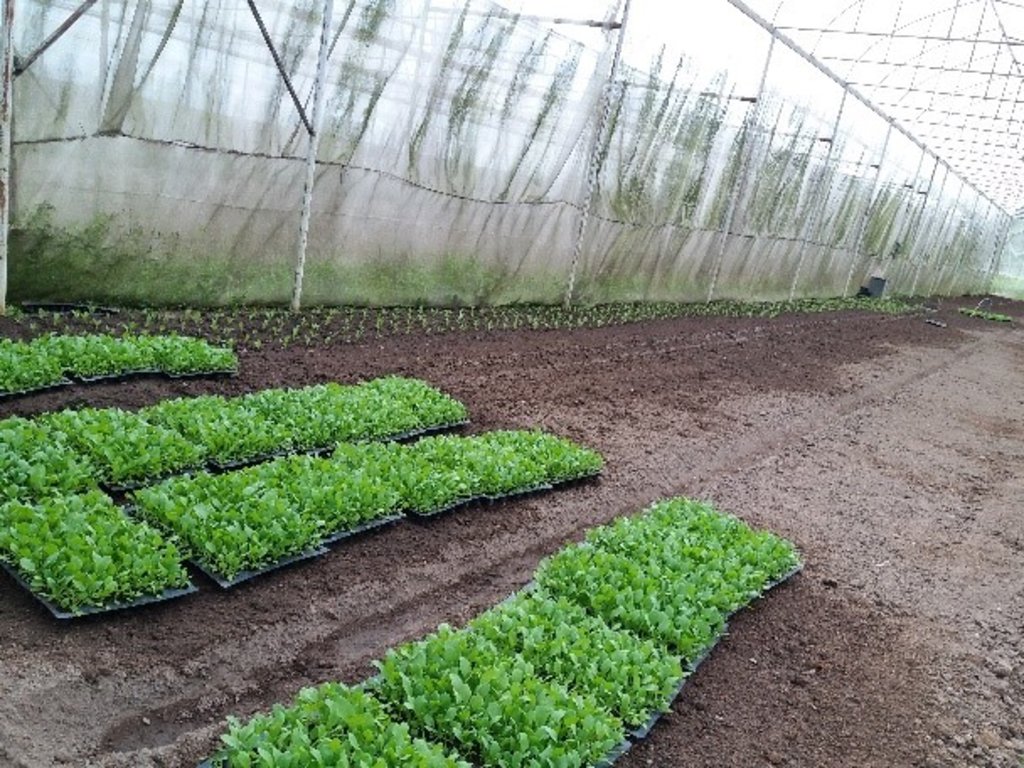
关于照片的一般说明:
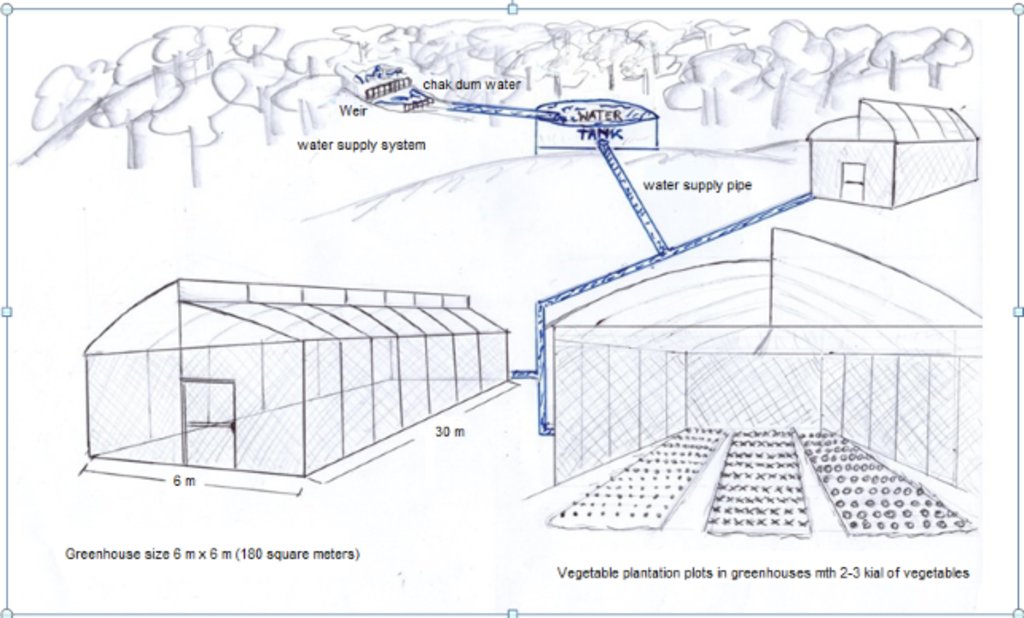
The simple nursery is 6 meters wide, 30 meters long, and 5 meters high. Organic vegetable seed is supported from the Royal Project with ready to planting into the plot.
2.4 技术视频
日期:
13/09/2018
位置:
Moo 9, Ban Mung Aung Village, Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province
摄影师的名字:
Ms. Kamalapa Wattanaprapat
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Ban Luang Sub-district, Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
This activity is the integrated implementation project of the Royal Project in collaboration with other government agencies.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2002
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
All knowledge and technology is supported by the Royal Project collaboration with Land Development Department and other government and private agencies.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
具体说明:
Vegetables: Cantonese, Baby Emperor, CosSalad, Oak leaf Green, Oak leaf Red, Guest Bean, Filler Iceberg, Kale Hong Kong and Baby Carrot.

水道、水体、湿地
主要产品/服务:
Irrigation water from a storage tank at the upper part, through PVC pipes to the area cultivated to the organic vegetables.
注释:
In the past, villagers had encroached on forest areas and deforestation in highland for shifting cultivation, and also expand cultivation area into steep slope. Resulting in the destruction of forest areas and accelerated soil degradation. Villagers have low incomes: not enough to survive. But due to the grace of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej, King Rama 9 set up the Royal Project to distribute knowledge and education to all farmers in this area, and assist them to have better occupation and living standards.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
注释:
The Royal Project has promoted the production of organic vegetables. Farmers therefore have changed from shifting cultivation to organic agriculture with sustainable soil management. As well as returning from forest areas and conserving soil, water and forest resources, maintaining ecological balance, this all makes villagers lives better. According to the cultivation schedule provided by the Royal Project, this area can cultivated throughout the year due to the development of irrigation systems from the storage tank in the upper part and supply to each plot of this targeted area.
3.4 供水
其它(比如洪水后):
- water from watershed area
注释:
Water resources are obtained from watercourses in the watershed, with a small dam which collects water in a reservoir. A PVC pipe is connected from the reservoir to individual plots and this irrigation system allows allocation to every farmer by the water management group.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
-
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cp:土壤污染

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
Organic vegetable production in greenhouses can solve the problem of soil erosion with utilization of compost, animal and green manure to increase fertility and organic matter.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
This organic vegetable production on very steep land can prevent and reduce soil erosion. Moreover, organic material and fertilizers can restore and improve soil fertility and productivity.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Operating procedures
1. Establishment of networks: All land users set up networks of organic vegetable producers and register the members properly; all members must act strictly according to the regulations.
2. Integrated cooperation: The Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station and the Inthanon Highland Agricultural Extension Center organize training on organic farming at least once a year, including study trip/s to visit other successful organic farmers.
3. Selection of the area: Leaders and members select the area for members, each member occupying not more than three greenhouses, 6m wide, 30m long and 3-5m high (180 sq m).
4. Production planning: land users discuss with the staff of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station, and plan the production schedule and types of vegetables to meet the market demand.
5. Procurement of production inputs: Both of local officers with inspectors and farmers can buy production inputs by themselves. All materials must be organic and are from reliable sources. Farmers must be very careful in this matter.
6. Organic vegetables cultivation: All land users must strictly comply with the schedule of cultivation, practices in soil improvement, control of pests and diseases, plus recording every step of their activities.
7. Production monitoring: Staffs of the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station and Department of Agricultural Extension (DOAE) monitor and observe land users’ practices in using soil improvement methods and using bioproducts for controlling insects, predators, parasites and diseases. Department of Agriculture (DOA) and the Organic Agriculture Certification Thailand (ACT Organic) monitor the production process.
8. Harvesting of Products: All land users must harvest according to the harvesting schedule and the preservation methods. DOA and ACT Organic serve as certification agencies by analyzing the contamination of substances in the products.
9. Screening and packing: All land users must clean their products with non-contaminated equipment, and also screen the quality and specified size/s of products for delivery to the Inthanon Royal Agricultural Station.
作者:
Ms.Kamalapa Watanaprapat
日期:
25/10/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
70 rai
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 6.25 rai
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht (THB)
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
32.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establish organic vegetables group | The first year of cultivation |
| 2. | Site selection | Before cultivation |
| 3. | Construct greenhouse or nursery | Before cultivation |
| 4. | Production work plan | Before cultivation |
| 5. | Procurement of production factors | Before cultivation |
| 6. | Soil preparation and improvement | During soil preparation |
| 7. | Vegetables seedling preparation | During soil preparation |
| 8. | Plantation | During vegetables planting |
| 9. | Disease and pest control | During vegetables planting |
| 10. | Vegetable harvesting | During harvesting |
| 11. | Screening and packing | After harvesting |
| 12. | Technology maintenance | After harvesting |
注释:
-
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construct greenhouse | man | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | During cultivation | man | 6.0 | 300.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | During maintenance | man | 45.0 | 300.0 | 13500.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | During harvesting | man | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Rubber pipe | piece | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tractor for soil preparation | Rai | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Vegetables seed | site | 1.0 | 700.0 | 700.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Animal manure (cow manure) | bag | 20.0 | 30.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | BT bio-product | litre | 100.0 | |||
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Predators and parasites | - | ||||
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Insect glue trap | liter | 0.5 | 290.0 | 145.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Yellow plastic plate | piece | 60.0 | 5.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Yellow plastic bag | litre | 0.5 | 120.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wood frame / mesh net / plastic cloth | site | 1.0 | 14700.0 | 14700.0 | 40.0 |
| 施工材料 | PVC pipe | piece | 40.0 | 40.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 40705.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1272.03 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Construction greenhouse cost, land users support 40%, and Organic Vegetable Production Fund support 60% of this cost.
注释:
Labor cost in greenhouse construction, greenhouse materials, which land users would only pay for the first year, but they do not pay for the second year and do not much towards repair cost.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Changing the plastic sheet of the roof of greenhouse | 3,000 baht per greenhouse every 3 years |
| 2. | Washing the plastic sheet of the greenhouse roof | Once a year |
注释:
-
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Changing plastic sheets | man | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Wash plastic sheets | man | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Plastic sheet (change every 3 years) | roll | 1.0 | 3700.0 | 3700.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 5500.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 171.88 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Land users purchase 100%
注释:
Land users purchase 100%
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most important factor that affects other costs is seed. Manure must be purchased from standard organic source. The Royal Project provides standard seed, and animal manure must be purchased from other provinces that require natural cultivation farming. The source of the materials used can be traced back to the original provider. Labor factors are not impacted because they can help each other, and land users work together in each greenhouse.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1500.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainy season is from June - October
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Inthanon Royal Project Meteorological Station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
-
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Most of the area is mountainous slope complex, with a steep slope and attitude is 1,200-1,400 meters above sea level. The forest condition is good, and some areas of the Doi Inthanon is national park and some is in national forest reserve.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil pH is 5.5-6.0
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water flows from the watershed area of the upper forest, and not flow through the conventional agricultural area.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Biodiversity in this area has a variety of insects. There are both pests and predators.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users can cultivate organic vegetables and earning more income, where young generation in the village become interested and help their families to cultivate organic vegetables. Moreover these young generation who have graduated from university like to become farmers and do not leave to other occupations.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Most land users have an average land of 20 rai, consisting of 3-5 rai for rice fields, and 10-15 rai of rotation cultivation. They do not have right in landownership because all of these land are in the reserved forest area and national park. But they have right in utilize their land under the Royal Project.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
具体说明:
-
注释:
Land users in this area are Lawa hill tribe who migrated from different places to settle here. The main occupation is agriculture under crop rotation, some harvesting of forest products, and some animals. They have not right in landownership but they have right to utilize their land and water for agricultural activities under the Royal Project.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
Average debt 20,000 baht per person:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
-
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Land users can cultivate 11 times per year.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
GAP and organic products
森林/林地质量
注释/具体说明:
Reforestation in this area, around 1,700 rai
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Land users can cultivate continuously and local officers visit and advise them for good practices under GAP and organic agriculture.
产品多样性
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Area for agriculture decreased and forest area increased. That corresponds to the policy of the Royal Project to produce strictly organic vegetables.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Membership in this network increased by 3-4 persons a year.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Cost of fertilizers, bioproduct and pesticides
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
GAP and organic vegetable products
工作量
注释/具体说明:
They usually work in their land almost everyday because organic vegetables need more intensive practices.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
That is the main concept of the organic vegetable activities.
健康状况
娱乐机会
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
The Royal Project officers supported knowledge and suggestion to community network.
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Local officers and training in implementation
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Rainwater from the upstream of this watershed
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
They usually use organic fertilizers.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Several kinds of vegetables are used in this organic farming.
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
They used bioproducts for disease and pest control.
减少气候和灾害风险
飓风、暴雨的影响
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The main objective of organic vegetables cultivation is to increase their income and produce green vegetable products, they can work throughout the year with higher income with the less of area.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
地下水/河流污染
对邻近农田的破坏
温室气体的影响
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Moreover, land users in the upstream area would cultivate in organic vegetables with bioproducts of disease and pest control, where it would safe to the downstream area.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 适度 | ||
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 不好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 局地雷暴 | 适度 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 非常不好 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 非常不好 |
注释:
-
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Land users are 153 members, with 270 greenhouses
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
In the first stage some of land user cultivated organic vegetables without greenhouses, then they lost their grain. After they had train and study trip, they improve their implement and construct greenhouse.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Promoting occupation and income earning of land users in this area. |
| All land users have been well trained; they receive consistent knowledge and suggestions from local officers and several agencies. |
| All land users produce certified organic vegetables that are green and are sold as organic food in the market. |
| They established the community enterprises of organic vegetables producer group. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Encouraging organic vegetable production is the activity of the government and the Royal Project in order to conserve this highland area with the intensive management. |
| Members of the land users community trust and assist each other with willingness to share the knowledge and experience in organic farming practices. |
| As a model of self-sufficient agriculture, they should have more income from the sustainable use of their land. |
| Establish and strengthen the community network to carry out and extend to others in this area. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| They are allowed to use the land for cultivating organic vegetables. | The government policy needs to have stability and consistency in using this land for a long time. |
| They need educational opportunity for their children. | The government needs to set up more schools in this area, and also to provide more chance to study in the higher level. |
| They need to have opportunity to access energy resources, especially in electricity. | Provincial Electricity Authority (PEA) has allocated budget for installing small electrical systems. |
| Transportation and road conditions are not convenient to access this area. | Local administrative organizations should be allocated more budget to develop such infrastructure. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| They do not have land ownership but they are allowed to use their land. | The government has a policy to "Issue a community land title deed" to solve this problem. |
| Almost of them cannot produce such as manure, compost, insect repellents by themselves. | Local officers have supported the knowledge and financial advice. |
| Almost of them cannot find organic product market by themselves. | establishment their cooperatives or network to promote in marketing. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
2
注释:
-
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
-
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
-
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
The North attitude: Ang village cultivate vegetables to the forest
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKLG2ImGwDE
标题/说明:
Organic vegetables at Ang village, Joam Tong Sub-district
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ALL9jJYzVyI
标题/说明:
Regional 4.0: ภูมิภาค 3.0: Ang village cultivate vegetables to the forest
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6u02SB_53IM
7.4 一般注释
-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块