Use of sediment retention fibre rolls (SRFR) and erosion blankets to stabilise slopes after fire [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dirk Pretorius
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Wood wool rolls/fibre rolls
technologies_6000 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Buckle Jacob
Hive Carbon
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Working for Water Programme, South Africa (WfW)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Environmental Affairs South Africa (DEA) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Working for Water [南非]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
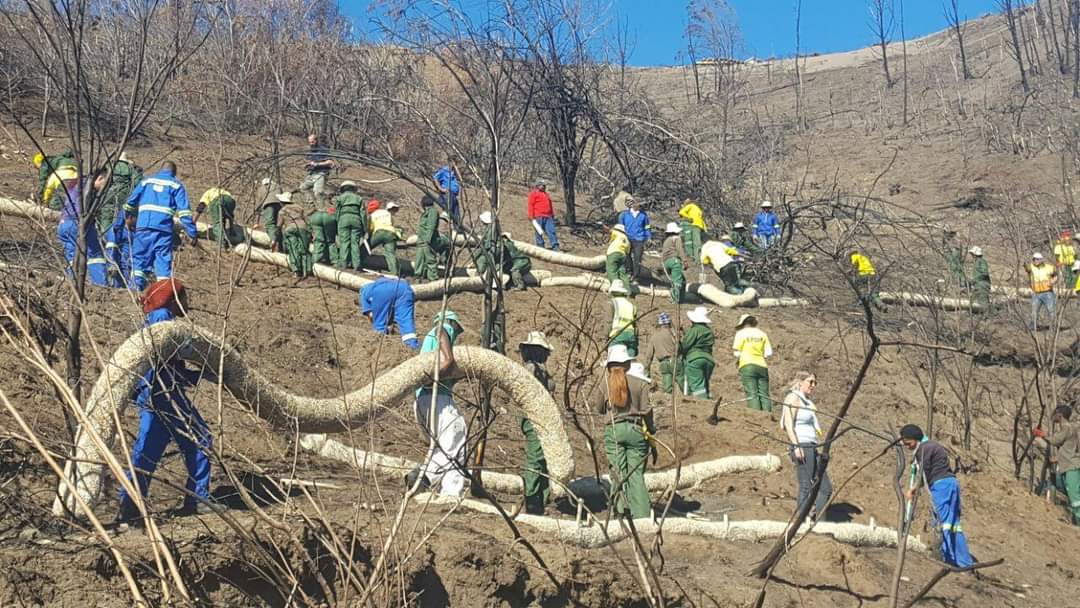
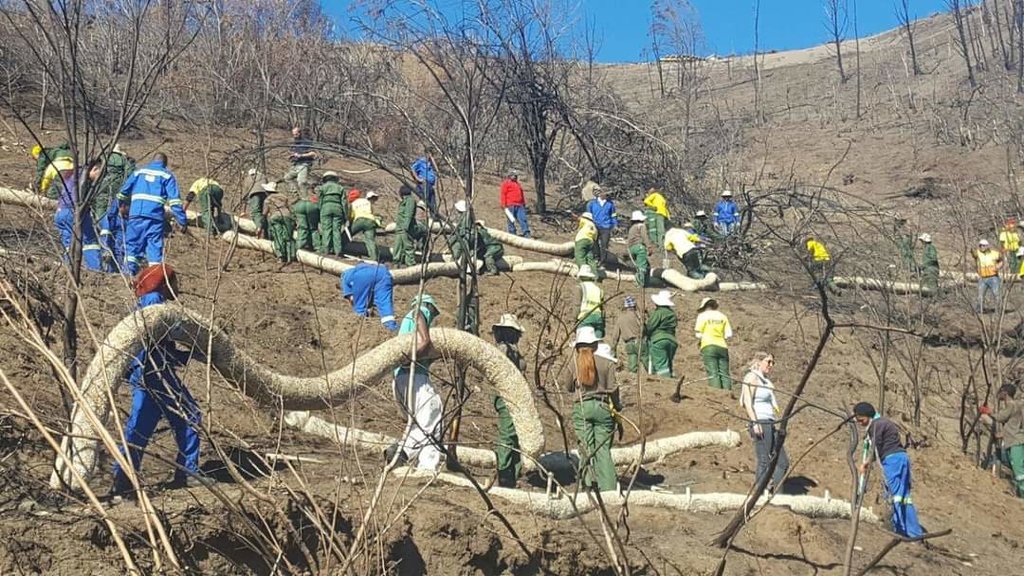
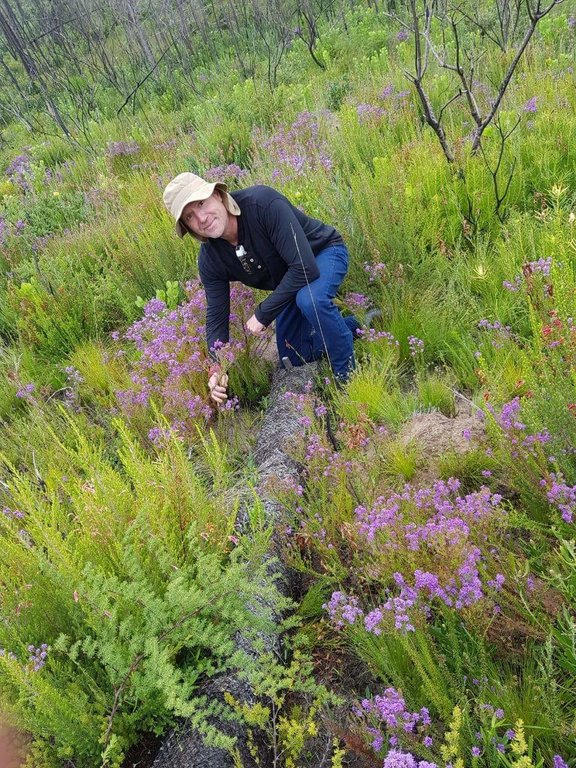
Sediment retention fibre rolls (SRFR) and erosion blankets were deployed to stabilise steep slopes after vegetation cover was destroyed by fire, near the town of Knysna in the Western Cape Province, South Africa
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
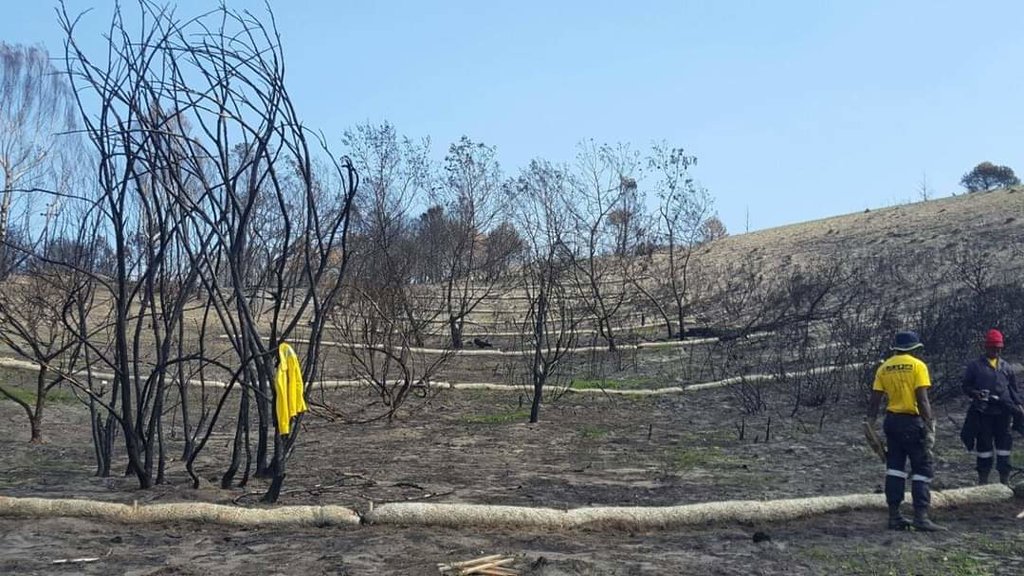
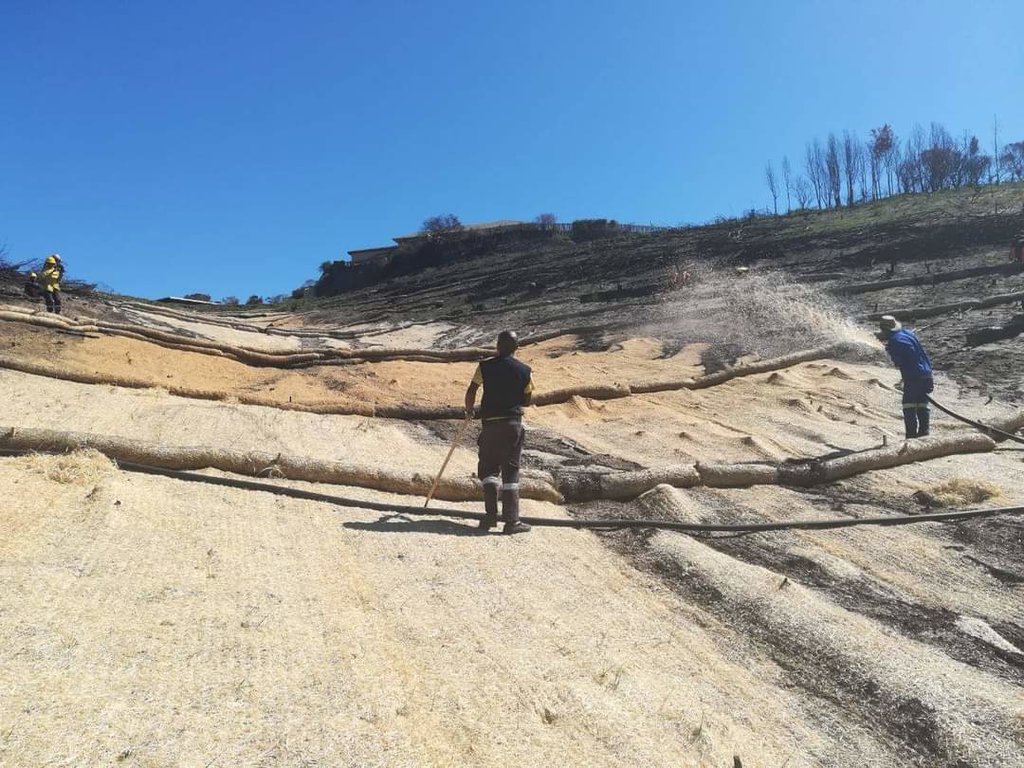
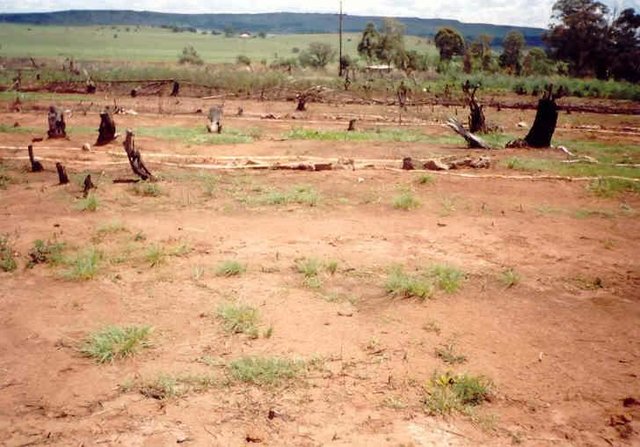
Sediment retention fibre rolls (SRFR) and erosion blankets were deployed near the town of Knysna in the Western Cape Province of South Africa to stabilise slopes after vegetation was destroyed by wildfires in 2017. The predominant geology is quartzite, shale, schist, conglomerate and dune sand. The soils of this area are generally acidic and nutrient-poor occurring, on moderate to steep slopes, ranging from 5 m to 1,220 m above sea level. The area receives summer and winter rainfall with an annual average of around 650 to 700 mm. The Knysna fires were the worst wildfire disaster in South African history (more than 21 000 ha were affected – destroying more than 800 buildings, 5000 ha of forest plantations and claiming the lives of seven people). Investigations reported that its severity was caused by a cocktail of factors, including drought, low atmospheric humidity, strong warm Bergwind conditions and abundant biomass. After the fires, the lack of vegetation cover on steep sandy slopes in the affected areas posed an immediate danger of erosion and landslides to downstream catchments, ravines and man-made infrastructure. Areas with high infestations of invasive alien plants required active re-establishment of indigenous plants and the removal of alien seedlings (popular and aspen) after germination. It is estimated that 53 km of wood fibre rolls (or "sausages") and 54 000 m² of erosion blankets (Woodwool fibre filled) have been installed on post-fire erosion mitigation projects. Furthermore hydroseeding was carried out with the annual grass "teff" (Eragrostis tef) to serve as an interim (annual grass) soil stabiliser. This will be replaced by indigenous plant growth in time. The project was implemented in the following stages:
1.Identification of priority areas where infrastructure was threatened (using GIS modelling)
2.Acquisition of restoration materials – SRFR and erosion blankets produced through secondary industries created through the removal of invasive alien plants (popular and aspen)
3.Training of local community members on implementation of restoration measures
4.Removal of all burnt woody material
5.Introduction of indigenous seed
6.Installation of erosion control blankets or hydroseeding (seeding using a slurry of seed and mulch)
7.Installation of SRFR
8.As part of maintenance, removal of invasive alien vegetation seedlings
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Western Cape
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 非木材森林的利用
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 自然灾害防护

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

土壤风蚀
- Eo:场外劣化效应

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
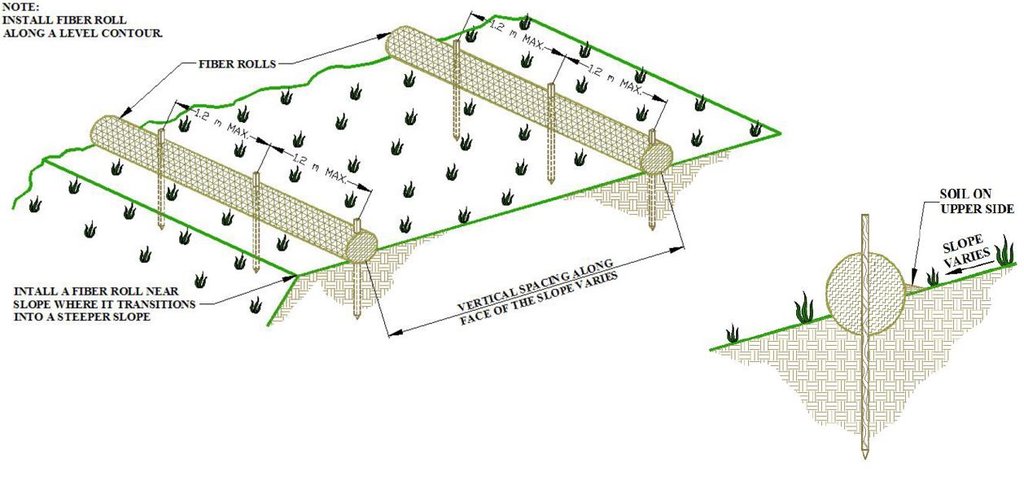
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
1.Prepare the area to be restored
2.Determine the spacing of the rolls as a function of soil type and slope
3.Installation of erosion rolls (6 m long) and blankets (2.5m x 50 m) must overlap
4.Use wooden stakes to secure the rolls and blankets – rolls (50cm) – 1.2 meter apart, blankets (30cm) – 1meter appart
作者:
Erosion Control Technology Council
日期:
09/11/2021
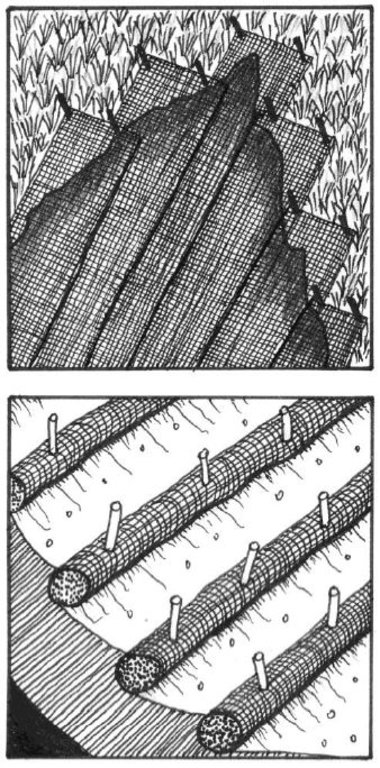
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
1. The first step in the installation of the erosion blankets on slopes is site preparation. Be sure the site is properly prepared before installing any blankets. The site should be fine graded to a smooth profile and relatively free from all weeds, clods, stones, roots, sticks, rivulets, gullies, crusting and caking. Fill any voids and make sure that the slope is compacted properly.
2. At the top of the slope dig an anchor trench 20 cm deep by 20 cm wide. The blankets will be anchored in this trench with staples.
3. Starting at the crest of the slope, roll the blankets down the slope in a controlled manner.
4. Seed the area to be vegetated (hydroseeding).
作者:
Erosion Control Technology Council
日期:
09/11/2021
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
ha
指定单位面积(如相关):
1
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
15.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
R180
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare area to be restored | After fires before onset of rainfall period |
| 2. | Installation of erosion rolls (6m Long) and erosion blankets (2.5 m by 50 m) - must overlap | After fires before onset of rainfall period |
| 3. | Hydroseeding | After installation of erosion rolls and blankets |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled labour (including transport) | per day | 84.0 | 260.0 | 21840.0 | |
| 设备 | Spades, hammer, scissors, rakes, hand saw | per day | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Grass seed mix | kg | 50.0 | 100.0 | 5000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | SRFB 10m interval including stakes | per meter | 1000.0 | 50.0 | 50000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Erosion blankets | per square meter | 10000.0 | 13.0 | 130000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | 1.0 | |||||
| 其它 | Hydro seeding (including fiber, binding medium, seed and organic fertilizer) | per ha | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 218940.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 14596.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | After floods the site must be inspected and restored if necessary | After floods |
| 2. | Remove invasive alien vegetation seedlings | After germination (during first 6 months) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Restoration of site after flooding events | per day | 24.0 | 260.0 | 6240.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools to do restoration (same as installation) | per day | 3.0 | 30.0 | 90.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Removal of invasive alien vegetation | per day | 24.0 | 60.0 | 1440.0 | |
| 施工材料 | SRFR | per meter | 50.0 | 50.0 | 2500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Erosion blankets (only pegs) | per square meter | 300.0 | 3.0 | 900.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 11170.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 744.67 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour availability, availability of material, transport cost
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- municipality owned
- municipality
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Restoration resulted in job creation for local communities
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Improved ecotourism - land restored to natural state - hiking and cycling
Value of land for development
注释/具体说明:
Land without degradation more valuable for development
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
The introduction of structures and increased vegetation cover resulted in reduced runoff
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
The introduced technologies also improved excess water drainage and less flooding
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation cover improved with the introduction of hydroseeding and retention of topsoil containing indigenous seed
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Soil loss was reduced due to the introduction of the SRFR and improved vegetation cover
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation cover improved due to the soil stabilisation and introduction of hydroseeding (annual grass protected soil until natural vegetation established)
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Improved biomass due to the improved vegetation cover and reduction of soil loss (topsoil with high C content)
外来入侵物种
注释/具体说明:
Maintenance of the applied technology included the removal of alien species
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
The technology resulted in the reestablishment of the natural vegetation and improved biodiversity
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
One of the main reasons for the introduction of this innovative technology is the reduction in flood impacts due to the inclusion of structures as well as improved vegetation cover
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
The added benefit of the technology is the reduction in the risk of landslides due to the inclusion of soil stabilising structures and improved vegetation cover
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
The introduction of the technology resulted in improved drainage and therefore less downstream flooding
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
The introduction of sediment trapping structures as well as improved vegetation cover resulted in less downstream siltation
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
The risk of damage to infrastructure was reduced due to the decrease in risk of flooding and landslides
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 森林火灾 | 非常不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Very important technology to stabilise degraded landscapes |
| Technology helps to improve the habitat - biodiversity in the protected area |
| Technology helps to prevent landslides and down-stream siltation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Although fairly expensive to implement the technology helped to restore high value land in the Knysna area |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sensitive to fire | Construct fire breaks around areas of intervention |
| Sensitive to flooding | Better timing of intervention (avoid high rainfall periods) |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/09/2021
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Title, author, year, ISBN Caring for Natural Rangelands, Ken Coetzee, 978-1-86914-071-7
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.loot.co.za/product/ken-coetzee-caring-for-natural-rangelands/stkr-450-g690
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
KNYSNA FIRES: HOW SOON WE FORGET
URL:
https://www.scli.org.za/knysna-fires-soon-forget
标题/说明:
Sediment retention fiber rolls – general usage and installation guidelines April 2011
URL:
https://www.ectc.org
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Working for Water [南非]
Government funded restoration/rehabilitation initiative as part of Working for Water project. Aim was to eradicate alien invasive.
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
模块
无模块