Drip irrigation for kitchen gardens in dry areas [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Daler Domullodzhanov
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Обёрии қатрагӣ дар заминҳои наздиҳавлигии минтақаҳои хушк
technologies_6164 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Promotion of low-pressure drip irrigation kits among vulnerable women-led households in dry agrolandscapes of Southern Tajikistan has helped to fight desertification, improve food security and enhance economic opportunities.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
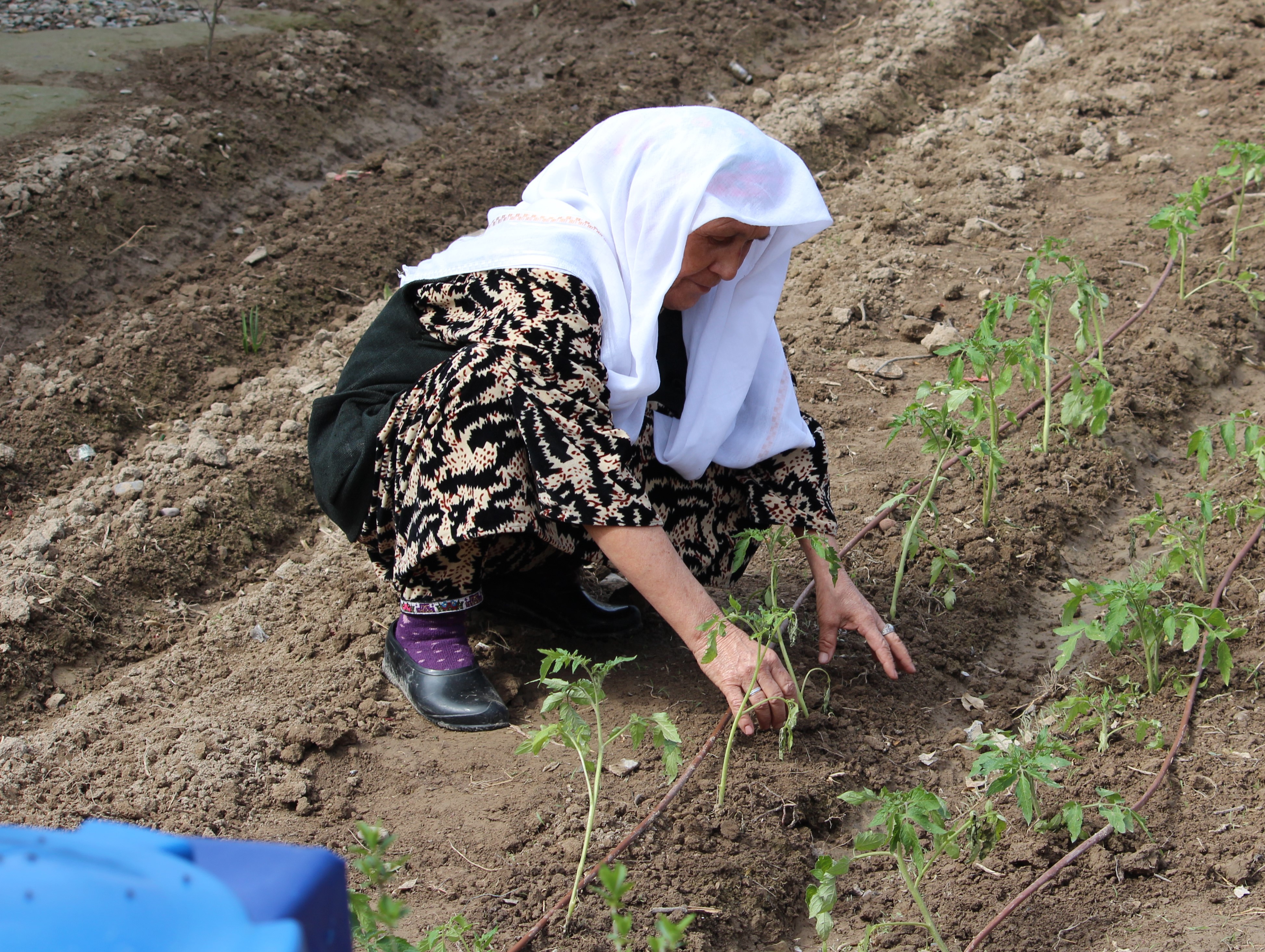
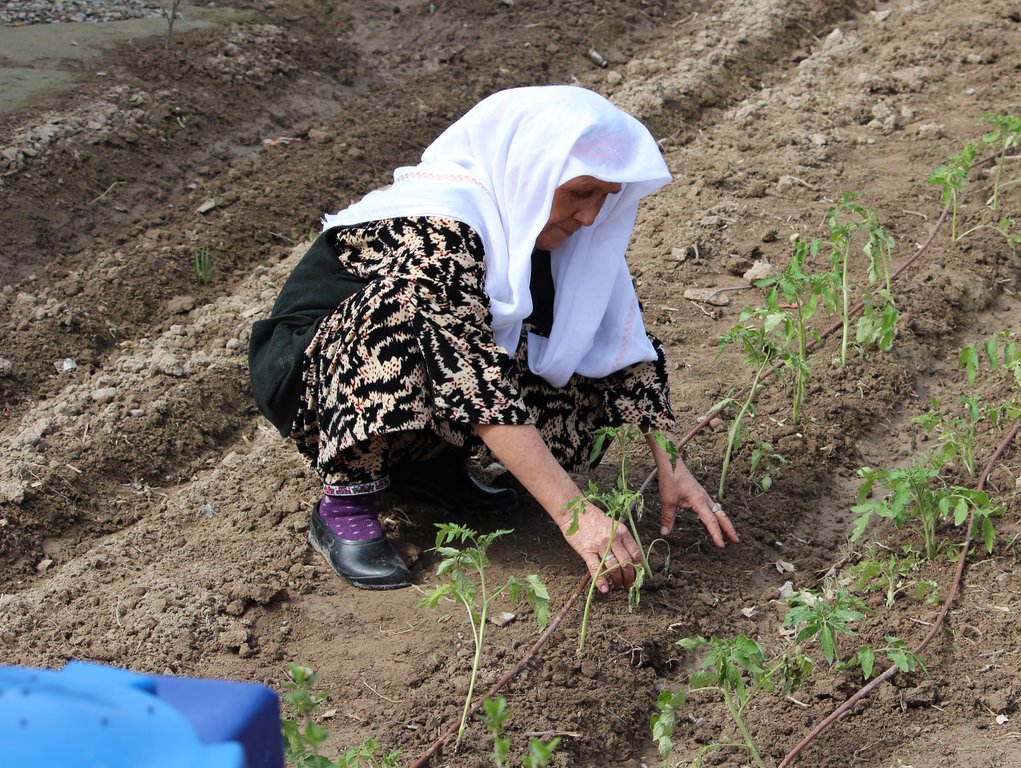
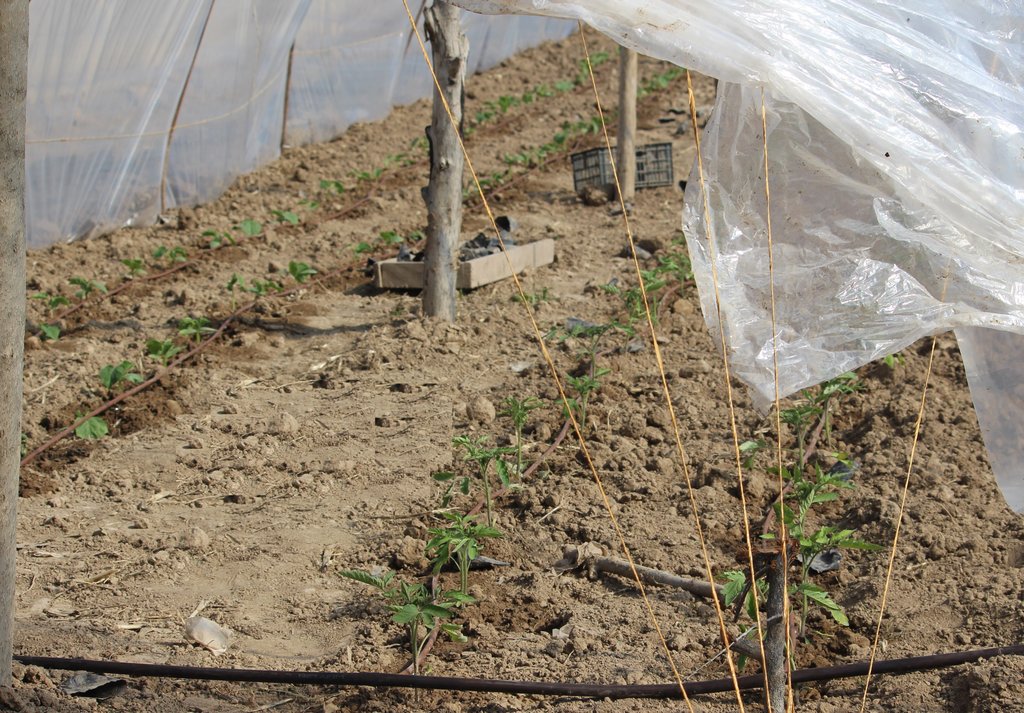
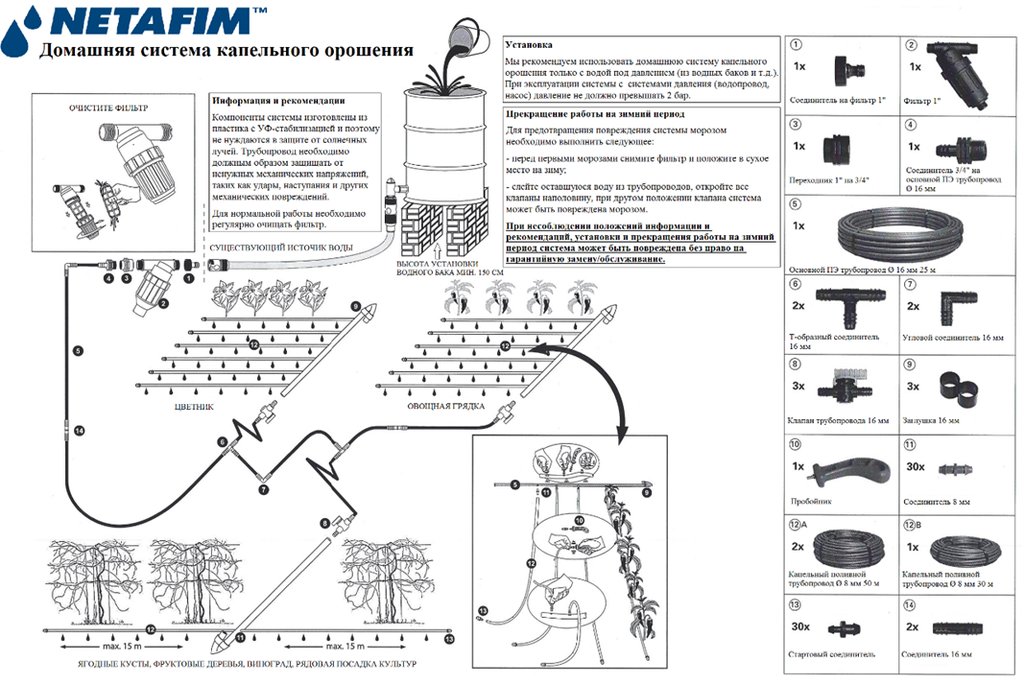
Low-pressure drip irrigation systems or Family Farm Drip Irrigation (FFDI) kits including water tanks and high-quality planting materials were distributed in the framework of an FAO project. The project aimed at enhancing food production by providing affordable irrigation solutions in dry and saline agrolandscapes of the Central Asian region. The FFDI systems were distributed to 60 women-led households in Khatlon province of Tajikistan. Additionally FFDI systems were installed in eight demonstration plots of organizations and state institutes. The beneficiaries were identified according to selection criteria to best contribute to food security and livelihood improvement through these affordable irrigation solutions. They were trained in irrigation and crop husbandry through a workshop, and their irrigation and plant production activities were monitored. Despite problems with pest management, vulnerable women-headed farms in the climate change affected areas increased crop productivity by 50% and harvested 2 crops a year. Vegetables were the crops of focus, and the average area irrigated was 300m2. Moreover, the application of the mulching helped to preserve more moisture and it helped to reduce irrigation norms by 25-30 per cent. For mulching, wheat straw and/or flax straw with a thickness of 7-10 cm was used. The FFDI system is affordable, does not require pumping, is easy to install and move, is easily adjustable and is supported by an installation kit. However, it does require relatively clean irrigation water. It is recommended to test expanded FFDI systems to continue the promotion of SLM and produce more food.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
vegetables, potato
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 家庭花园
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

结构措施
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
The marginalized kitchen gardens plots were rehabilitated through the application of drip irrigation, intercropping, crop rotation, composting, mulching and better management of the plots.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
300 m2
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
TJS
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
9.2
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
100
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layouting of plot for drip irrigation system | |
| 2. | Levelling the ploughing, Harrowing | |
| 3. | Inter row cultivation | |
| 4. | Sowing | |
| 5. | Application of mulching | |
| 6. | Application of fertilizers | |
| 7. | Weeding, 3 times | |
| 8. | Harvesting (1 crop - 4 times tomato, 15-20 times cucumber) | |
| 9. | Instalment and dismantling of poles and cord for tomato, drip irrigation system | |
| 10. | Instalment and dismantling of, drip irrigation system |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Operation and maintainence on kitchen garden | days | 20.0 | 100.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 设备 | Drip irrigation system including installation | set | 1.0 | 736.0 | 736.0 | |
| 设备 | Water tanks with transportation cost | set | 1.0 | 384.0 | 384.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Hybrid varieties of cucumber seeds or saplings | package | 1.0 | 230.0 | 230.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic fertilizer | kg | 90.0 | 1.0 | 90.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Mineral fertilizer (N, P) | kg | 12.0 | 7.0 | 84.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 3524.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 383.04 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assembling and unmounting | twice per season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Assembling and unmounting | times | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 100.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 10.87 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The 51% of the initial cost was covered by FAO
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
355.00
农业气候带
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
60 t/ha
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
nothing
SLM之后的数量:
well managed kitchen garden
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
60 t/ha
注释/具体说明:
The kitchen gardens were not productive at all, because of limited access to the water resources.
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
very limited
SLM之后的数量:
improved
注释/具体说明:
if before rural women had limited knowledge of SLM and CSA techniques, now they started experimenting with different options of the techniques.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
very limited, based on rain fall events
SLM之后的数量:
regulated
注释/具体说明:
The soil moisture was regulated to ensure the best condition to produce vegetables on the plots. The moisture storing capacity of the soil was improved, by enhancing the organic matter.
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
bared
SLM之后的数量:
covered
注释/具体说明:
The soil was coved during the dry period of the year by biomass and the area between irrigation lines was covered by mulch to preserve soil moisture.
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
encreased
注释/具体说明:
The application of organic matter has increased soil fertility and crops yield.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The ToT training for promotors and best farmers on the topics of proper operation and maintenance of the drip irrigation systems were delivered to enable the active farmers from the different districts for continuing the promotion of the techniques. |
| The provided support of the project for most vulnerable families helped to increase family income and benefit from the crops yield increases and water is used with maximum efficiency, weeds cannot absorb water as it is not available for them. there are fewer weeds, soil infiltration capacity is increased, there is no soil erosion, applying water locally, leaching is reduced; fertilizer/nutrient loss is minimized. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Provision of the agriculture inputs for free can negatively affect the promotion of the best SLM techniques after the project life span. High investment costs can be one of the reasons for blocking upscaling. | To find a co-financing source and/or to increase co-financing ratio by the farmers. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Data was provided by FAO specialist and beneficiaries.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/10/2019
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Manual for farmers. Using Low-Pressure Drip Irrigation Systems to Irrigate Vegetables and Potatoes, Daler Domullodzhanov, 2012, ISBN 978-99947-913-2-3
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
article "Drip irrigation boosts water efficiency for Tajik farmers"
URL:
https://www.fao.org/europe/news/detail-news/en/c/1189380/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块