Water retention/sediment capture pond [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
- 编辑者: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Víztározó/üledékfelfogó tó
technologies_6196 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute for Soil Sciences, Centre for Agricultural Research (ATK TAKI) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmer own initiated water harvesting pond in the … [孟加拉国]
This is an indigenous approach to store rain water for irrigating rice and other crops in the hillside earthen dam.
- 编制者: Tuku Talukder
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
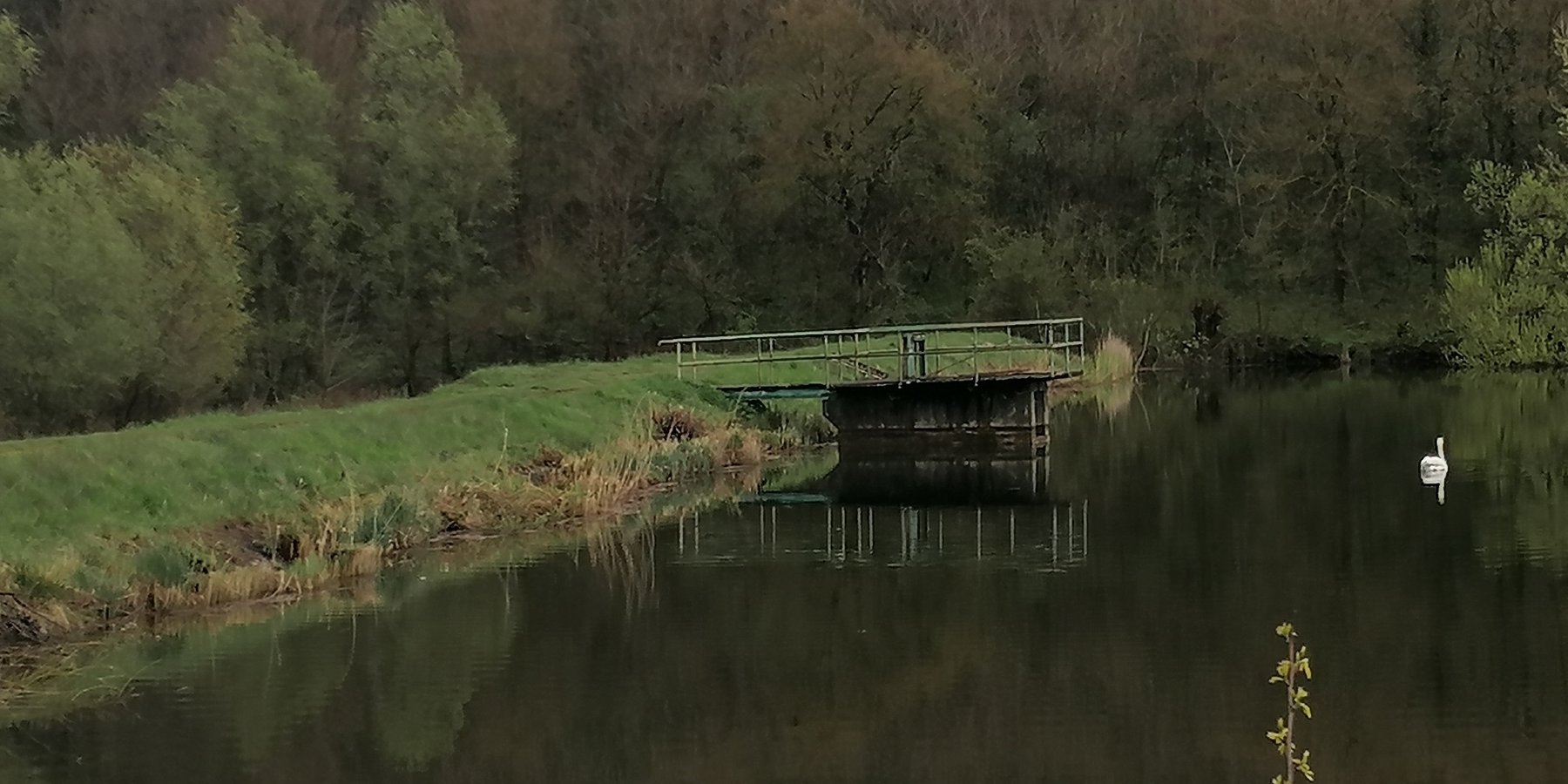
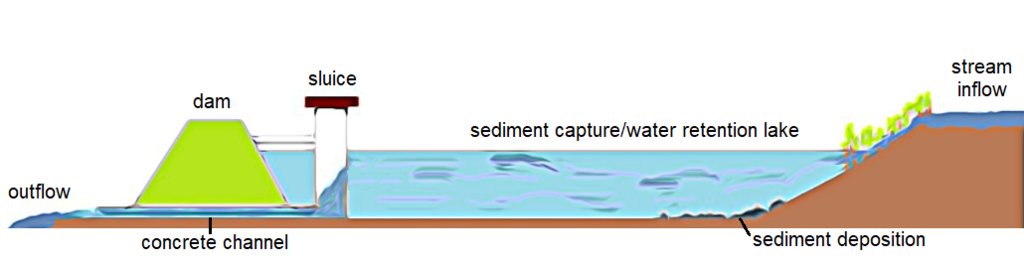
Sediment capture ponds are constructed and located along networks of ditches which drain watersheds. They slow the velocity of water and cause the deposition of suspended materials. These ponds help to avoid sediment accumulation in the ditches themselves, and can decrease sediment and nutrient pollution of surface water bodies downstream.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
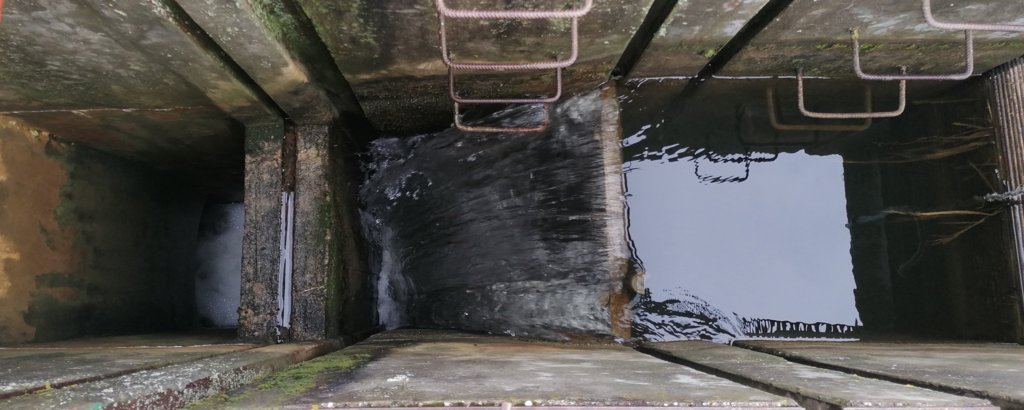
Sediment capture ponds are designed to be able to retain runoff water during rainy periods. They are located along networks of ditches which drain watersheds – and are constructed through mechanical excavation. The technology is usually applied in hilly areas, but sometimes downstream ponds are located in or near urban zones. The ponds slow the velocity of water and cause deposition of suspended materials. They help to avoid sediment accumulation in the ditches themselves, and can decrease sediment and nutrient pollution of surface water bodies downstream. Water retention in the upstream area results in better infiltration and provides a source of water for wildlife. As sediment is regularly deposited in the ponds, they need to be desilted to maintain effectiveness.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
video is not available
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Zala County
有关地点的进一步说明:
Esztergályhorváti
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
A project supported the management of the catchment area to improve municipal security and recreation.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
cover crops are grown between cash crops
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
oilseed rape - winter wheat - maize - spring barley
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 湿地保护/管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Larger sedimentation ponds can be several square kilometers in size, while others are only a few tens or hundreds of square meters. Generally, the size of sedimentation ponds depends on the characteristics of the surrounding area, the amount and frequency of rainfall, and the sources of water supply to the pond. The depth of a sedimentation pond can also vary depending on its purpose and location. In general, sedimentation ponds are designed to have a shallow depth, typically around 1 to 3 meters.
作者:
Piroska Kassai
日期:
17/04/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Pond
指定单位面积(如相关):
108,000 m3
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | excavation of pond | not relevant |
| 2. | building dam | |
| 3. | building flood gate | |
| 4. | excavation of ditch system |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 其它 | building the wole system by contractor | whole pond and belongings | 1.0 | 1420000.0 | 1420000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1420000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1420000.0 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
1420000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
costs were covered by public and municipal funds
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | periodic excavation of deposited sediments | not relevant |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 其它 | periodic excavation of deposited sediments is carried out by contractor | whole work | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 40000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 40000.0 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
40000.0
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
amount of sediments, topographical conditions
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
653.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
distribution is uneven
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Keszthely meteorological station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
distribution of rainfall is uneven, heat waves often occur during summertime
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
landscape is hilly and different land use patterns (arable land, ward and forest) are mixed in the area
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil type is Luvisol
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
source of pollution is agriculture (manure, fertilisers, pesticides)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The pond was built by communal and local water authority collaboration.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
- 大规模的
注释:
large cooperatives and small farms are mixed in the area
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Water of sediment capture/retention ponds can be used for irrigation purposes, depending on the quality of the water and the intended use of the irrigation.
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Some retention ponds allow for some recreational activities too such as fishing, bird-watching, or walking trails around the pond.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
The water flowing out of the stormwater retention pond may be clearer than the water flowing into it because the sedimentation process in the pond removes suspended solids from the water.
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Water retention ponds are an effective way to collect and manage stormwater runoff.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Water retention ponds can help to reduce surface runoff during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, which can help to mitigate the risk of flooding and erosion.
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
By reducing the volume and peak flow rate of stormwater runoff, retention ponds can help to reduce the velocity and erosive power of water
生物多样性:植被、动物
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Water retention ponds can have both positive and negative effects on biodiversity. Besides fish and waterfowl, mosquitoes may also proliferate, which can be disturbing for nearby settlements.
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Stormwater retention ponds are the most effective solutions to prevent floods and their impacts
滑坡/泥石流
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Ponds can increase humidity levels and the presence of vegetation around the water body can also have a cooling effect
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Lakes are capable of capturing large amounts of sediment.
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
The stream water flowing out of lakes is generally much cleaner and less polluted due to the settling of suspended sediment.
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Stormwater retention ponds and other similar water bodies can act as natural filters.
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
By providing a place for the excess water to go, these ponds reduce the amount of water that flows onto streets and buildings, which can help prevent flash flooding and water damage.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
These ponds are not generally constructed by land users, but by municipalities using grants/subsidies. Therefore, it is a very cost-effective solution from land users perspective in both the short and long term.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
zero
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| water reservoir for irrigation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| possible fish pond management |
| recreation |
| increasing habitat and bio diversity |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| habitats for mosquitoes |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
5
- 与土地使用者的访谈
5
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/10/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ponds - Planning, Design, Construction (Agriculture Handbook 590), USDA, ISBN 9781365086069
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
enbook.hu, 25 USD
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
European NWRM Platform
URL:
http://nwrm.eu/measures-catalogue
7.4 一般注释
Questionnaire is very detailed
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmer own initiated water harvesting pond in the … [孟加拉国]
This is an indigenous approach to store rain water for irrigating rice and other crops in the hillside earthen dam.
- 编制者: Tuku Talukder
模块
无模块