Crop-livestock integration to enhance soil productivity [斯里兰卡]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Head Soil Science
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley
technologies_6236 - 斯里兰卡
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Kallora Shantha
斯里兰卡
SLM专业人员:
Gunasena Nimal
斯里兰卡
co-compiler:
Rajapaksha Chandi
斯里兰卡
co-compiler:
Beddegama Nilanthika
斯里兰卡
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Lands in Kandy, Badulla and Nuwara Eliya Districts in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - 斯里兰卡1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity, and soil productivity technology improves nutrient recycling and soil productivity in the land and SLM practices are reducing land degradation
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [斯里兰卡]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- 编制者: Bandara Rotawewa
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
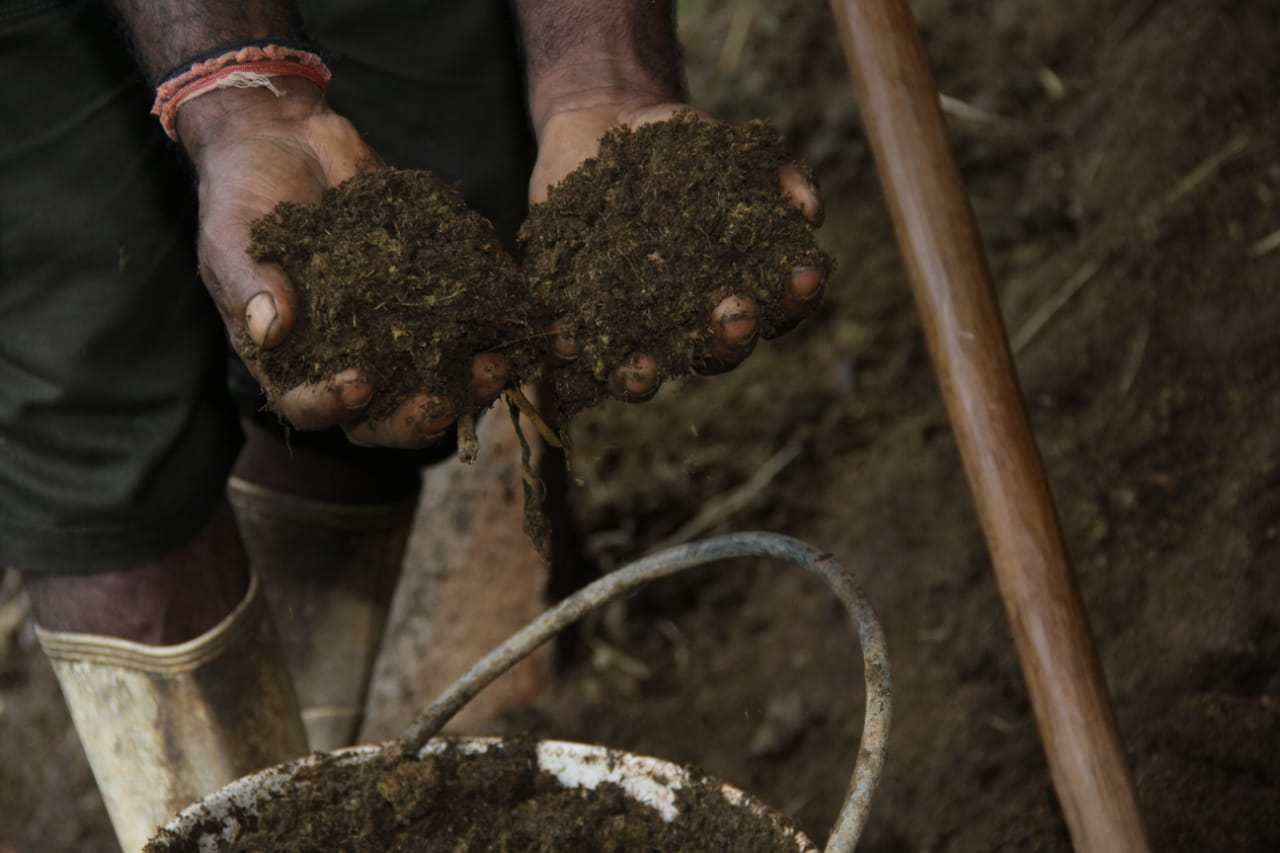
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity and soil productivity: solid and liquid organic fertilizers prepared from cow manure are incorporated to soil or sprayed on leaves of vegetables and tea.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
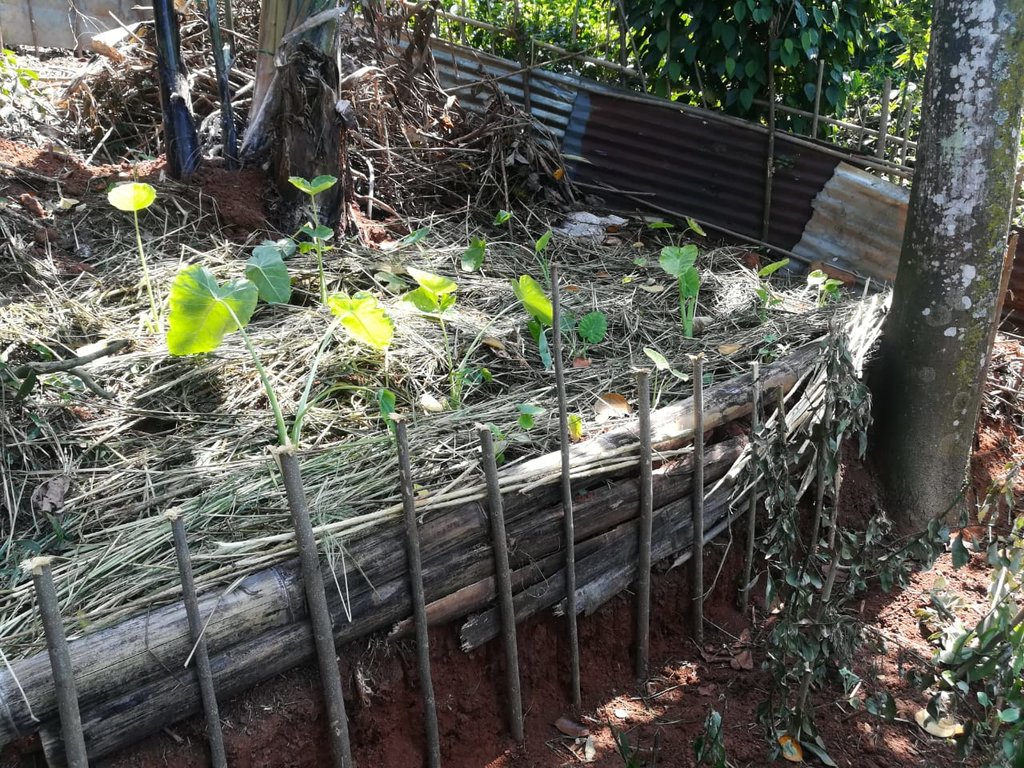
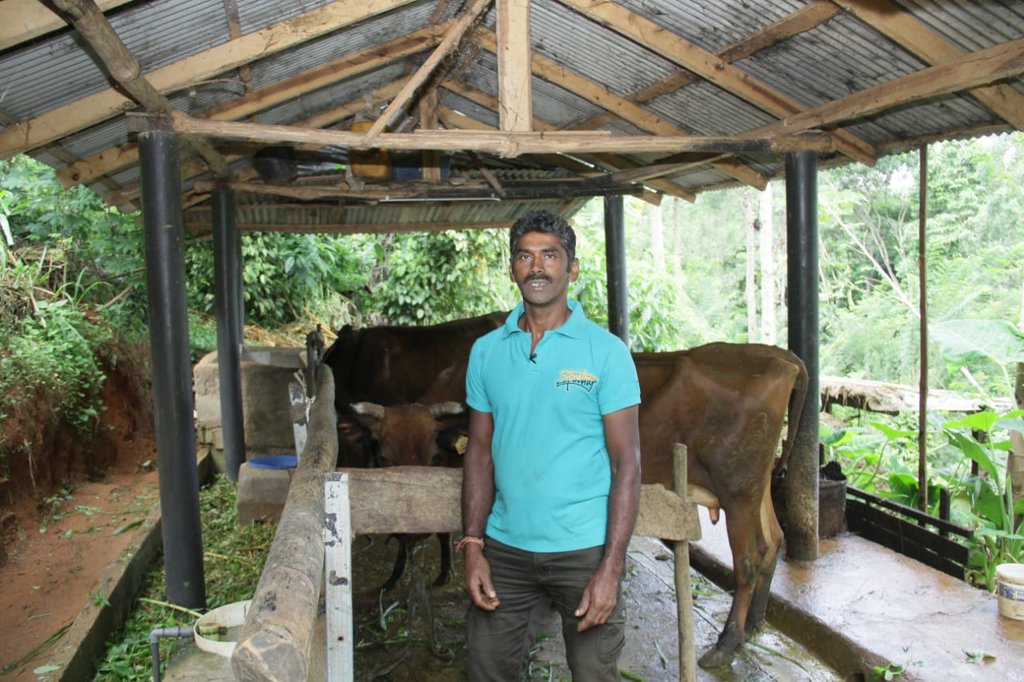
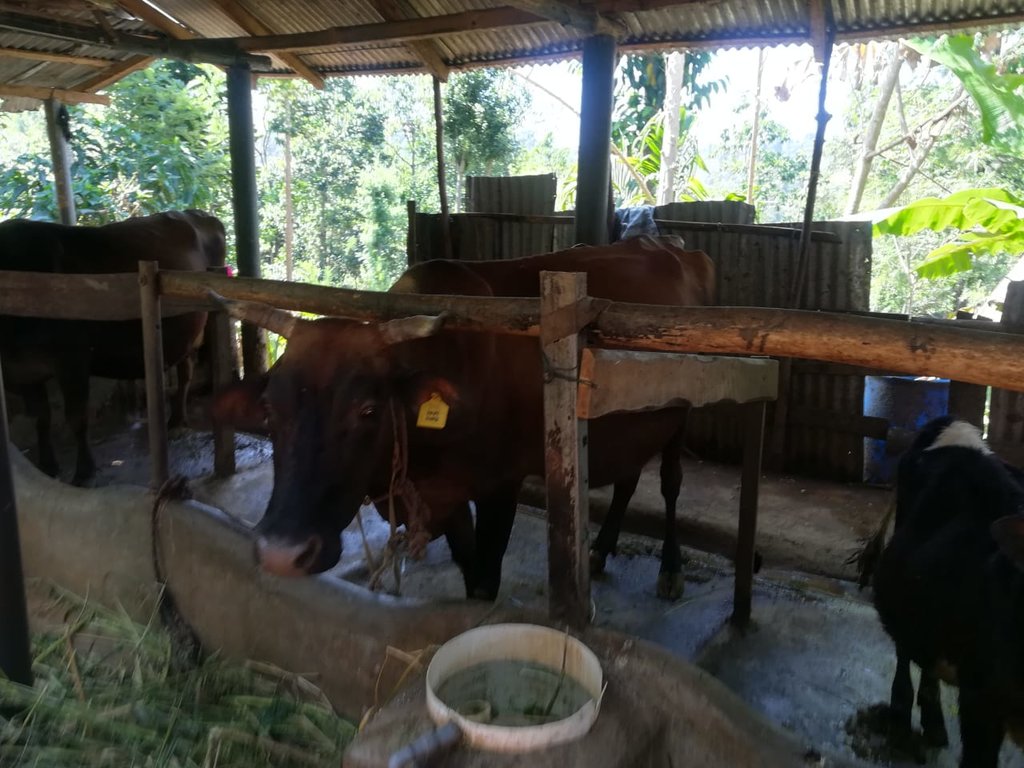
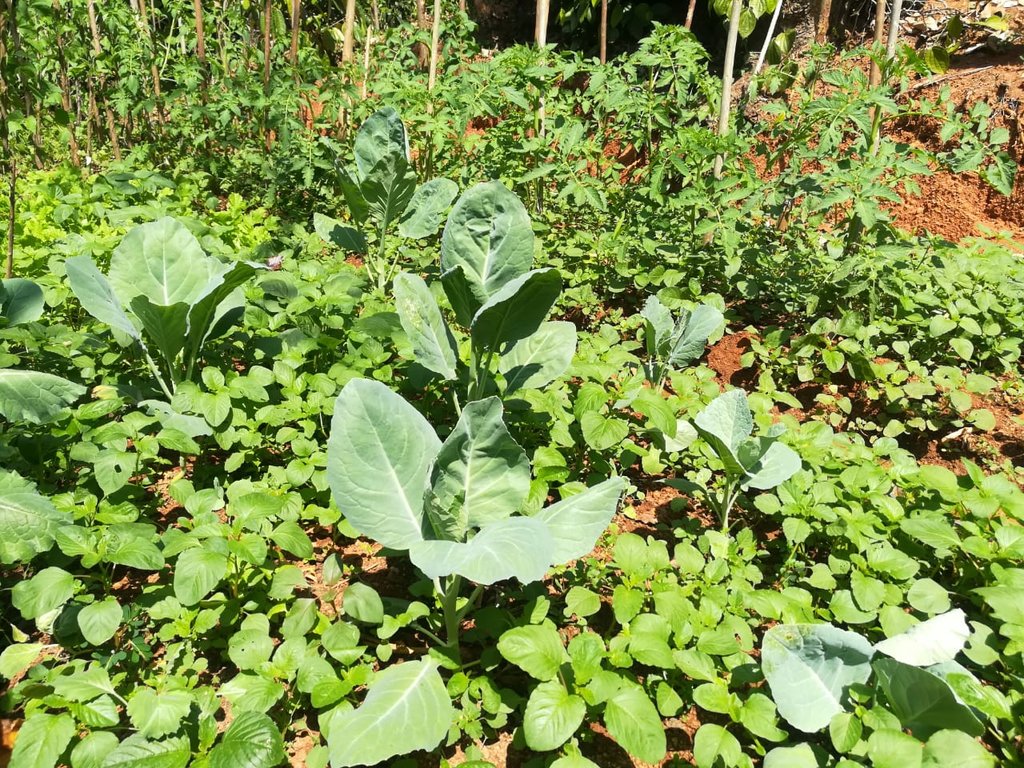
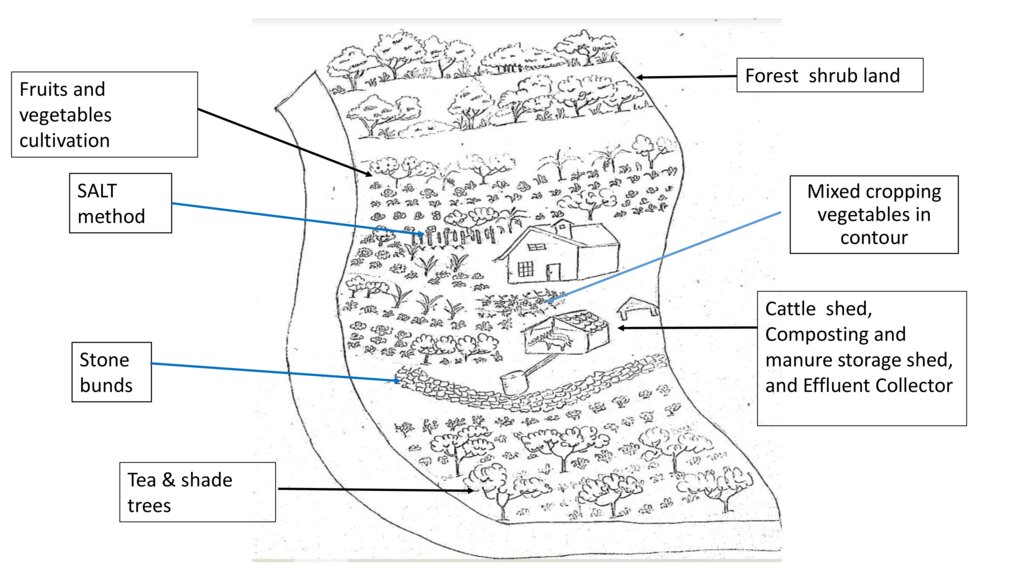
Dairy cattle farming is common in the Dolluwa area of the central province of Sri Lanka. Farmers typically have 3-4 cows on about 2-3 hectares for both milk consumption and sales. The landowner interviewed did not formerly adhere to best practices: cows were grazed in woodlands, and water and supplementary feed were not provided as needed. Housing was inadequate. Farm waste wasn’t properly recycled. The farm is located on steep land without adequate soil conservation for annual crops and tea. There was heavy dependence on chemical fertilizer. As a consequence, milk production was below average and crop yields had declined. Besides, there was reservoir pollution due to effluent washed downslope.
New technology was developed to increase milk and crop production by integrating animal–crop management strategies while enhancing nutrient circularity within the farm, and improving soil productivity and environmental quality.
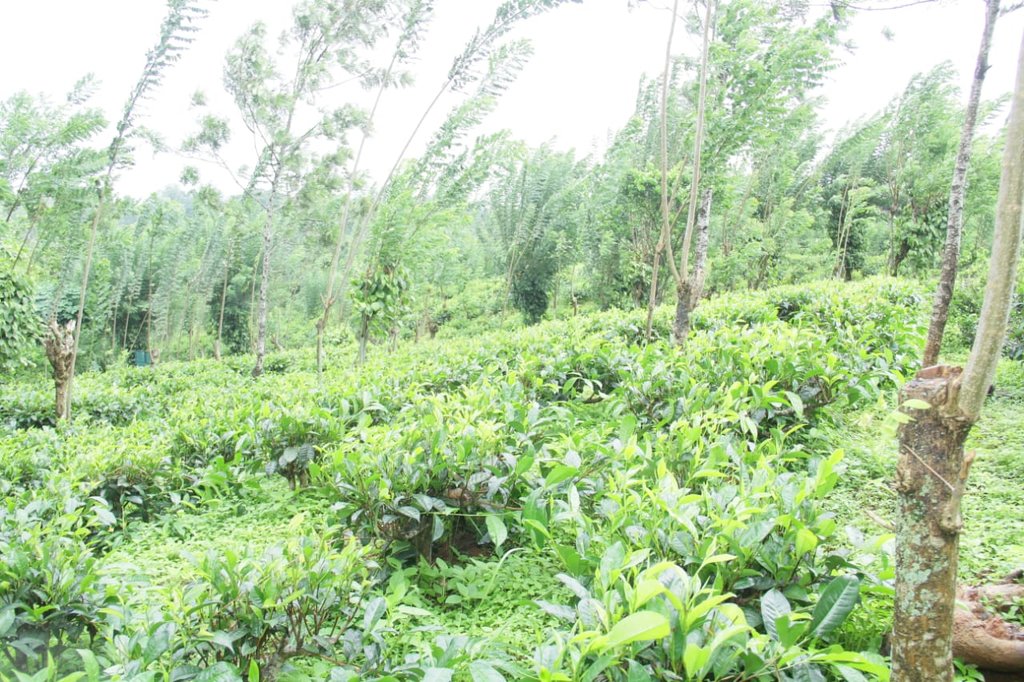
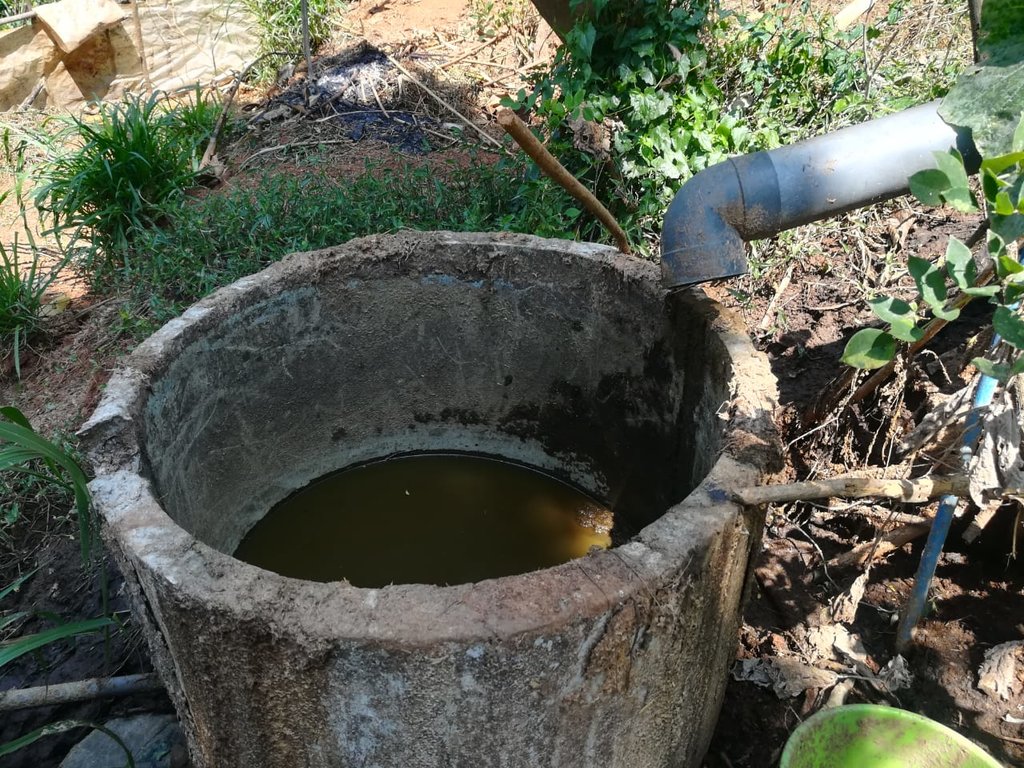
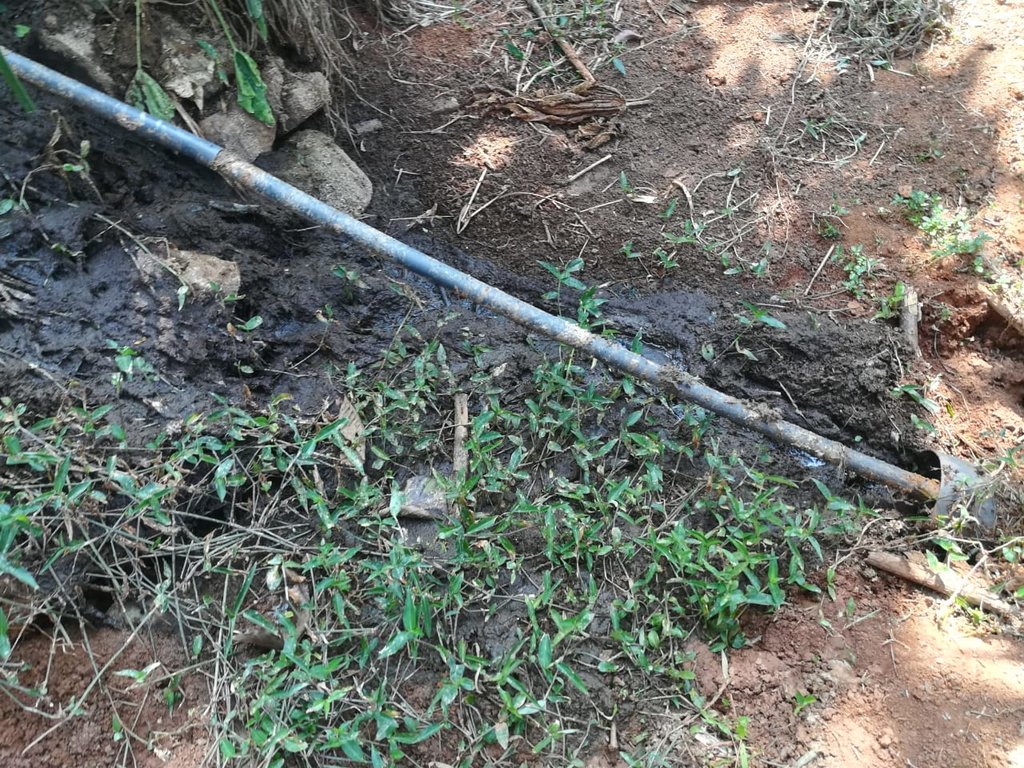
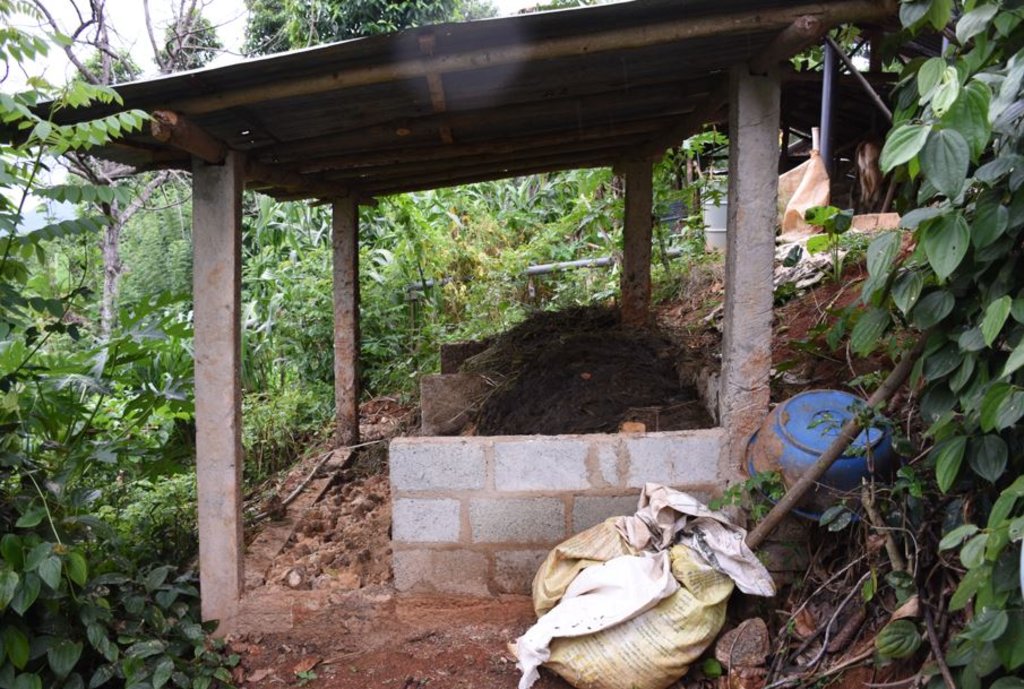
The landowner was first enrolled in the Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the UN’s FAO in 2018. The first priority was soil conservation for the steep areas under tea. SLM practices thus combined contour cropping and bunding. Following this, an integrated crop-livestock system was initiated. The RDALP and Fonterra Pvt. Ltd. helped the landowner to build a modern cowshed with infrastructure to provide feed and water. Thereafter, cows were stall-fed: grazing was completely stopped. Cow manure is collected and stored in heaps for 2-3 weeks before incorporating into soils. In the same shed, compost is prepared by mixing manure with crop residues and kitchen/ homegarden waste. Cattle urine and wastewater is directed to a cement tank where it is mixed with specific types of leaves; it is fermented and applied as liquid fertilizer and biopesticide. Manure is used mainly for fast-growing vegetables, while compost is applied to annuals, particularly at planting, and to tea once every three months. Liquid fertilizer is applied to tea seven days before harvesting.
This package requires adequate land for a cattle shed, and for a recycling system to prepare compost and liquid fertilizers. In addition, there must be enough labour for the whole process. The key inputs include materials for the shed, associated infrastructure, and a sprayer to apply liquid fertilizers.
The major benefit is recycling waste to generate useful products – while ensuring circularity of nutrients between crop and animal production systems: thus supporting a “bioeconomy”. Soil conservation practices and the nutrient sources described have improved soil fertility and productivity for overall sustainability. Milk yields have more than doubled, and the tea harvest more than trebled.
(1) Where is the Technology applied?
On steep terrain: tea is cultivated lower down and there are reservoirs in the valley.
(2) What are the purposes/ functions?
•Provide food security
•Increase efficiency of livestock production
•Promote overall nutrient cycling
•Partially substitute chemical fertilizers and pesticides with organic manure
•Generate high-quality organic manure and compost to improve soil fertility
•Control contamination of river water
(3) What are the benefits/ impacts of the Technology?
•Reduced susceptibility of crops to pests/ diseases
•Improved quality of food and water
•Slowed land degradation and restored soil fertility
•Reduced risks
•Economically feasible and rapid impact
(4) What do land users like/
•Reduced risk
•Increased income
•Reduction in cost of production
(5) ...dislike
•Damage to crops by wild animals.
•Higher cost for dairy farming (feed)
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
斯里兰卡
区域/州/省:
Central province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Dolluwa
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2019
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations in 2018
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 花卉作物
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 药用/芳香/杀虫植物和草药
- 根/块茎作物 - 红薯、山药、芋头/椰子,其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 木薯
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 蘑菇和块菌
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
年作制度:
连作蔬菜
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 槟榔属
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- 花卉作物 - 多年生
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- 药用、芳香、杀虫植物 - 多年生植物
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 可可
- 椰子(水果、椰壳、树叶等)
- 咖啡,采树荫栽培
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- 木瓜
- 茶叶
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Vegetables are cultivated in three seasons per year
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 混合落叶或常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- 自然保持/保护
- 自然灾害防护

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
- 能源:管道、电线
注释:
cattle shed and compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
pipelines are used for reove effluents from the farm
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 药用/芳香/杀虫植物和草药
- 根/块茎作物 - 红薯、山药、芋头/椰子,其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 木薯
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 根/块茎作物 - 甜菜
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- 蔬菜 - 香瓜、南瓜、南瓜或葫芦
- 蔬菜 - 蘑菇和块菌
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
年作制度:
连作蔬菜
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- 花卉作物 - 多年生
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- 药用、芳香、杀虫植物 - 多年生植物
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 可可
- 柑橘属
- 椰子(水果、椰壳、树叶等)
- 咖啡,采树荫栽培
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- 木瓜
- 茶叶
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
- 能源:管道、电线
注释:
A cattle shed and a compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
Pipelines are used to remove effluents from the farm
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
Mainly water requirements are fulfilled by natural water sources in the land
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 废物管理/废水管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A6:残株管理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6:对残株管理作出具体说明:
A 6.4:保留

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
- S8:卫生/废水结构物
- S9:动植物庇护所
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
注释:
The land is very prone to soil erosion. Therefore several SLM measures were introduced to prevent soil erosion and improve the productivity of the land.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Zero grazing reduced soil erosion by animal trampling
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Application of decomposed organic manure increased tea and vegetable production, proper disposal of farm waste prevents water pollution in reservoirs, prevention of application of chemical fertilizer reduces soil deterioration and water pollution
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
3.5 acre
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 hectare = 2.47 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Sri Lankan Rupees
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
330.13
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
900.00 Sri Lankan Rupees
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of soil conservation measures | Before rainy season |
| 2. | Establishment of cattle shed | After establishment of soil conservation measures |
| 3. | Establishment of compost shed | Before rainy season |
| 4. | Establishment farm waste disposal system | After establishment of compost shed |
| 5. | Planting crops | With the onset of rain |
| 6. | Application of compost | At and after planting crops |
| 7. | Foliar application of liquid fertilizers | After planting crops |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Establishment of cattle shed | person days | 7.0 | 4400.0 | 30800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of compost shed | person days | 6.0 | 2000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of disposal system | person days | 2.0 | 1200.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Prepearation of Stone bunds | person days | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 15.0 |
| 设备 | Establishment of 'SALT' method (combined SLM measures on slopes) | person days | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 15.0 |
| 植物材料 | Vegetable seeds | gram | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Gliricidia stalks | 1 stalk | 1000.0 | 3.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost | 1 bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Cattle manure | 1 bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Establishment of cattle shed (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 118645.0 | 118645.0 | 16.0 |
| 施工材料 | Establishment of compost preparation unit (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 34560.0 | 34560.0 | 15.0 |
| 施工材料 | Establishment of liquid waste disposal system (roofing sheets, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 16500.0 | 16500.0 | 40.0 |
| 施工材料 | Large bins to collect liquid waste | 2.0 | 4500.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | cable | 18.0 | 890.0 | 16020.0 | ||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 260175.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 788.1 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Rehabilitation of degraded agriculture land project (RDALP) and local funds
注释:
The initial cost for establishing cattle shed with a filtering system and compost shed was higher. But the majority of the initial cost was covered by RDALP and local funds. Land users covered 30% of the establishment costs for soil conservation measures. Eg: the SALT method, stone bunds
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | After rainy season (twice a year) |
| 2. | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Before land preparation in each growing season |
| 3. | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Once in a year |
| 4. | Replace bins used to collect liquid waste | Whenever broken |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | Person days | 6.0 | 1200.0 | 7200.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Person days | 4.0 | 1200.0 | 4800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Person days | 3.0 | 1200.0 | 3600.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Application of compost and cattle manure | bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Increase the area of the cattle shed (all included) | 1.0 | 17800.0 | 17800.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 36525.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 110.64 | |||||
注释:
Maintenance activities are fully covered by the land owner.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost involved in intensive labour is higher than for inputs on a daily basis
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2500.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average monthly rainfall from April to July under southwest monsoon is 120-200 mm. Average monthly rainfall from September to December under Northeast monsoon is 200-300 mm. First inter monsoon is from January to March with around 100 mm.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Gannoruwa, peradeniya
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Nilambe water reservoir is located in the valley and provides water for drinking and irrigation purposes. Part of the micro-catchment of the surface water body/reservoir is occupied by farms where intensive agriculture, homegardens and cattle rearing are practised. Limited soil conservation practices, overuse of agrochemicals and improper waste management have led to contamination of water
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The forested and scrubland area is about tree species and species of shrubs. In addition, grass species as medicinal plants are also growing. Local and imported varieties of fruits avocado, guava, mango, banana, pomegranate, orange, lemon and tree and bush type of local fruits are grown. Local varieties of cardamom, cinnamon, pepper, nutmeg and other locally used spices such as coriander, mustard etc. have been grown in the home garden. Vegetables often grown include cabbage, beans, lettuce, cucumber, radish, tomato etc. In the tea land, two shade tree species, gliricidia and albizzia
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The land belongs to a land user. Land use rights are passed down from generation to generation. Land use rights, water usage rights are based on a traditional legal system
注释:
Because of the traditional legal system land use rights, and water usage rights are not free for all. Land users are able to implement and maintain technology without any disturbance occurring due to land and water usage rights
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
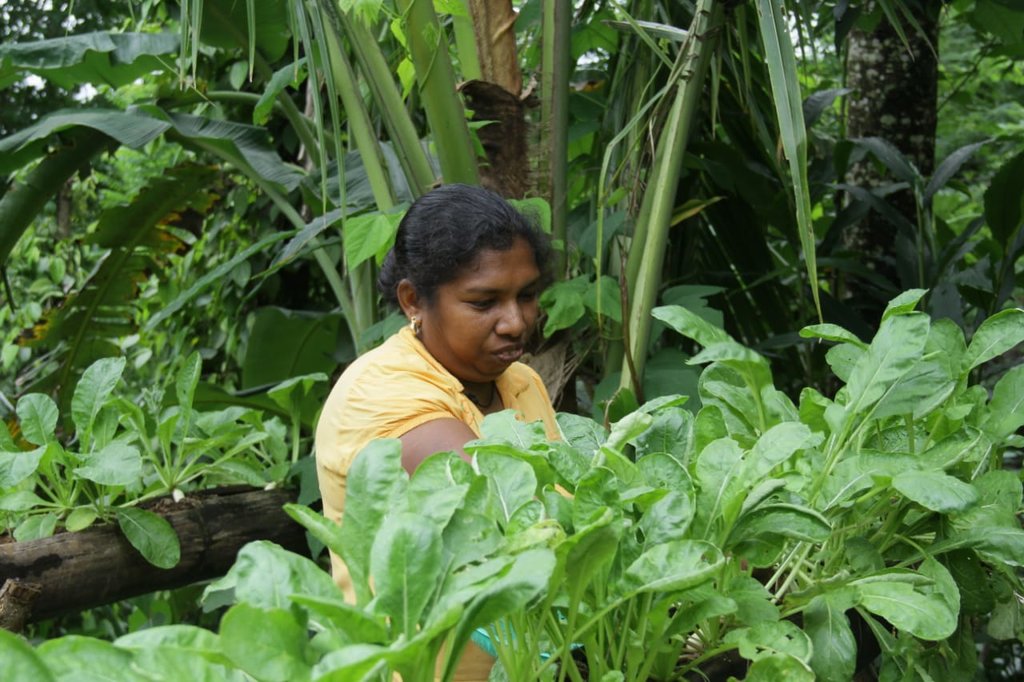
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
After introducing organic inputs, the production of tea and vegetables increased.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Reduction of the synthetic chemicals and supplement of balanced nutrients by organic inputs have enhanced crop quality.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Supplement of quality feed and adequate water to the cattle shed increased milk production.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Integrated crop-livestock technology and crop diversification reduced the risk of production failure.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
After implementing this technology diversity of annual and perennial food crops were increased.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution.
家畜用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers reduced the expenses for chemical fertilizers
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology, stall feeding improves milk production and compost application enhances the tea and vegetable cultivations.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Crop diversification and investment in mushroom production added new sources of income.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
After modernizing the dairy farm, all grazing was stopped, allowing more time to be spent on other tasks.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology milk, tea and vegetable production increased. Throughout the year foods are available for their own consumption.
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
The approach was implemented on their own land. Natural water sources are available for their cultivation and dairy farming activity.
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
Aesthetic view of homegarden improved.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Training programme and advisory services improved knowledge base on SLM.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Reduced application of synthetic chemicals and recycling of farm waste through a proper disposal system reduced contamination of water.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines reduce surface runoff.
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Improve in soil structure due to application of compost and cow manure facilitate water infiltration.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Mulching, application of crop residuals and organic manure reduce the evaporation from bare surfaces.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Higher soil organic matter content increased soil moisture retention.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology, landowners cultivated bare lands so that soil cover was improved.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Implementation of soil conservation measures (SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour line) reduced runoff.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
implementation of soil conservation reduced soil loss and thereby soil accumulation in the lower slope position of the land.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
As runoff is controlled by conservation measures, soil sealing is reduced.
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Mulching has reduced soil compaction.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Nutrients are cycling within integrated crop-livestock technology.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
The addition of cow manure and composts had improved soil organic matter content.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
After implementing technology, a landowner has cultivated all possible spaces on the land. Improving land cover by tea was also evident.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Application of organic inputs increased biomass production of all crops.
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
After implementing this technology diverse crops were introduced to the small unit of land.
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
An increase in earthworms and honey bees was observed.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
An increase in crop diversity may have introduced new habitats at a micro-scale level.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Reduced application of chemical fertilizer had led to less succulent crops and increased resistance to pests/ diseases. Natural pesticides sprayed mal also help keep crops healthy.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Aerobic composting would help to reduce methane emissions. Control in excess urea application may also be led to a reduction in nitrous oxide emission.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
SLM measures such as SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines prevent runoff and reduced downstream siltation.
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
As an application of synthetic chemicals was reduced, and a proper farm waste disposal system was implemented, the removal of chemicals was controlled.
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Application of organic substances to soil and increased ground cover had improved filtering capacity.
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Restricted movements of the cows.
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Restricted movements of the cows.
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Will have reduced the emission of methane and nitrous oxide from manure. A reduction in urea application would have reduced the emission of nitrous oxide.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 好 |
| 季雨量 | 旱季 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 适度 |
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
According to the land user’s perspective implementation of this technology provided net benefits from tea, vegetables and dairy farming compared with establishment and maintenance cost. In the beginning, land users had to invest substantial amount of money to establish this technology. However, short-term and long-term returns could cover the cost involved in establishment and maintenance of the technology.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
The technology was introduced to about 10 farms but except one land user, others were unable to spend on developing technology irrespective of partial funds generated from other sources.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
No farmer was able to afford to develop technology by their own.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| After providing a proper shed for cows, it was possible to provide adequate feed and water for easy consumption of cows. This led to a significant increase in milk production. |
| Direct application of cow dung and liquid organic fertilizer for tea and vegetables led to an increase in crop yields and improved soil fertility. |
| As benefits are higher in monetary terms in comparison to the costs of investment for this technology, neighbourhood farmers who rear animals are encouraged to follow this technology. |
| Reduction in chemical fertilizer usage reduced the cost of production. |
| With the implementation of new technology, the number of pests and diseases incidences declined. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This technology is easy to promote on the farmland due to the low cost involved and multiple benefits are visible. This technology has changed the attitudes of farmers that dairy farming could be profitable and support crop cultivation. |
| Before implementing this technology landowners had to work outside to earn money. As the income increase with the establishment of the technology, landowners could spend more time on other farming activities onsite . |
| Modernization of cattle farms enable zero-grazing so that land user was able to spend additional time for other farming activities. |
| The landowner does not need to depend on government or private sector funds to improve their farming activities. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Crops and fruits are often damaged by wild animals. Therefore the maximum profits cannot be achieved. | The landowner is with the opinion is that damage caused by wild animals could be stopped by constructing a steel fence around the land. However, farmer is unable to afford or such as the cost is very high. |
| Establishment of this technology requires considerable amount of money which is beyond the income and purchasing power of farmers with low income. | Providing partial funding by government or private sector organizations would help farmers to initiate the establishment of at least one or two components of technology. |
| Attitudes of neighboring farmers on dairy farming should be changed as a profit oriented business. | Introducing training programs and demonstrations at the successful farm would encourage other farmers to use the technology. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The landowner does not record profits that earn from his farming activities. He doesn’t have a good idea about the overall income of his farming activities per month. | The landowner should change attitudes toward income recordings. |
| People should be aware of these SLM technologies, SLM knowledge and benefits. | Government and private sector should invest in and implement SLM training programs. |
| Limited availability of modern technologies in cattle farming and crop cultivation affordable to middle income farmers. | Modernize farming with biogas technology, harvest tea with the cutter, prepare wormy compost and compost tea for tea cultivation. |
| Lack of properly established marketing channel for selling products. | Improve the product quality, or technology to develop value added products targeting supermarkets. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
01
- 与土地使用者的访谈
02
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
02
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
02
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
06/02/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sustainable management practices for agricultural lands in the central highlands of Sri Lanka
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
rehabilitation of degraded agricultural land project office, food and agricultural organization of the United Nations Peradeniya Sri Lanka
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Project News: Fertile Soil
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Controlled livestock grazing for soil fertility improvement [Uganda]
URL:
https://qcat.wocat.net/en/wocat/technologies/view/technologies_2761/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [斯里兰卡]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- 编制者: Bandara Rotawewa
模块
无模块