Crop-livestock integration to enhance soil productivity [ศรีลังกา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Head Soil Science
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley
technologies_6236 - ศรีลังกา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Kallora Shantha
ศรีลังกา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Gunasena Nimal
ศรีลังกา
co-compiler:
Rajapaksha Chandi
ศรีลังกา
co-compiler:
Beddegama Nilanthika
ศรีลังกา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Lands in Kandy, Badulla and Nuwara Eliya Districts in the Central Highlands of Sri Lankaชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - ศรีลังกา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity, and soil productivity technology improves nutrient recycling and soil productivity in the land and SLM practices are reducing land degradation
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [ศรีลังกา]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- ผู้รวบรวม: Bandara Rotawewa
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
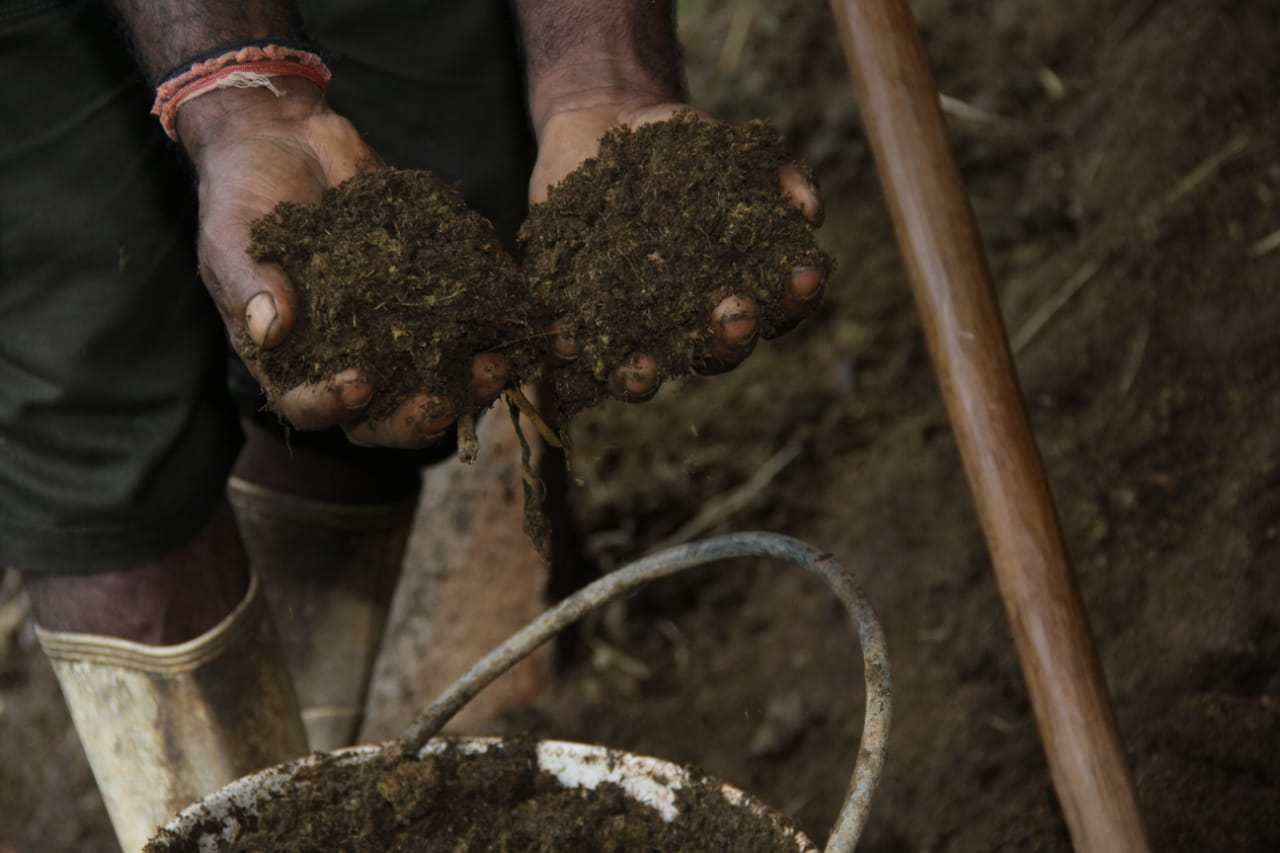
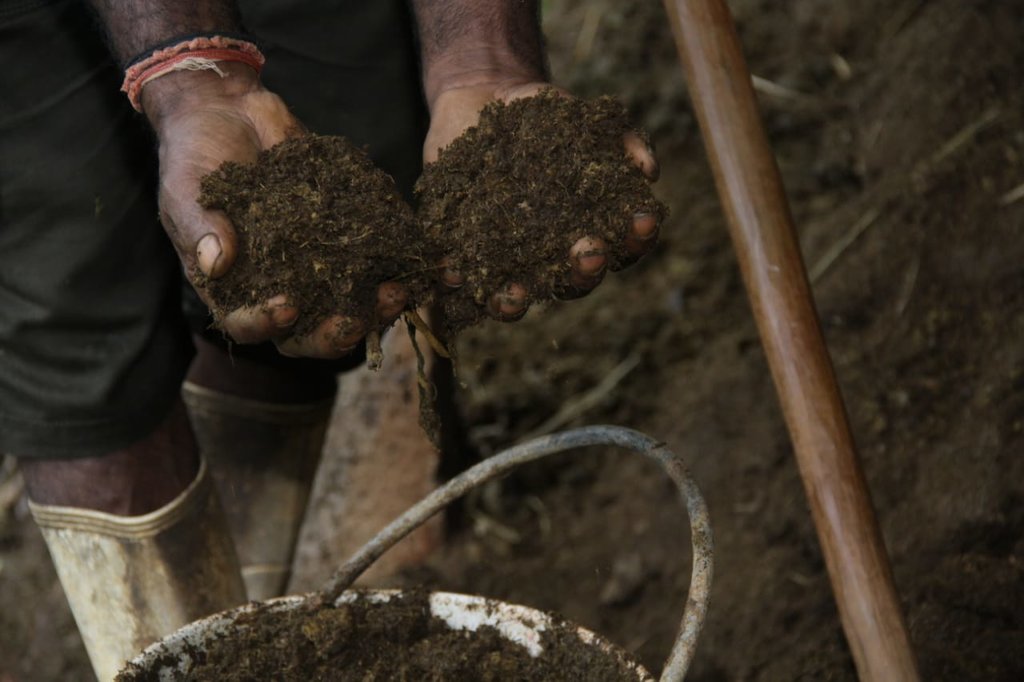
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity and soil productivity: solid and liquid organic fertilizers prepared from cow manure are incorporated to soil or sprayed on leaves of vegetables and tea.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
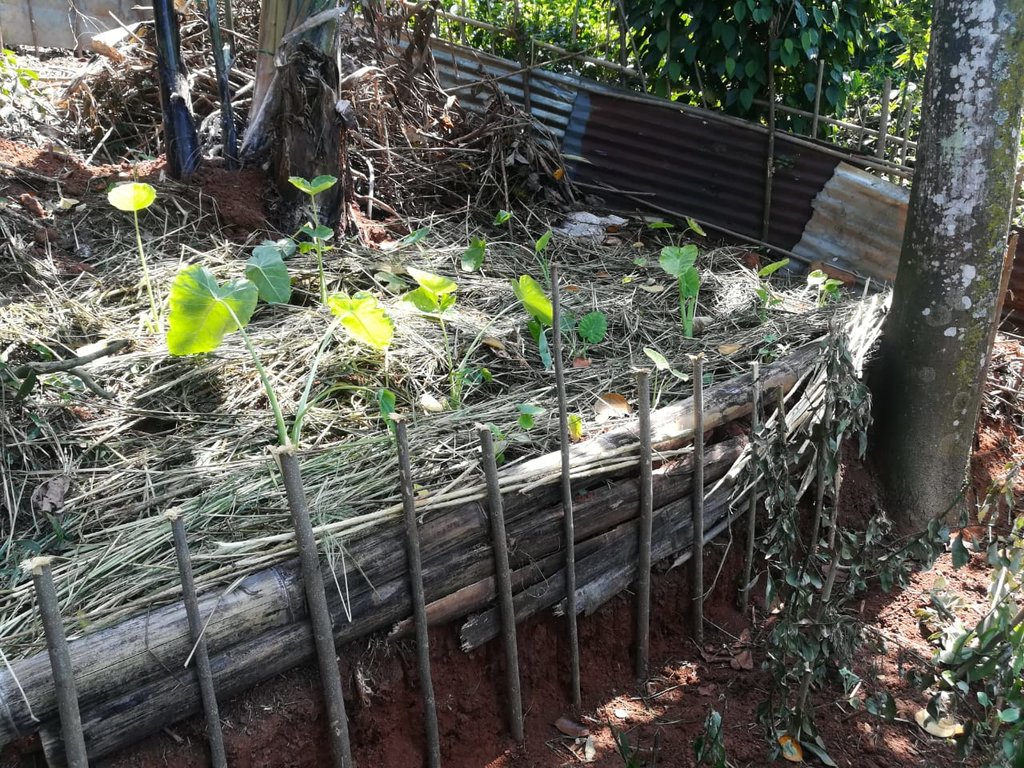
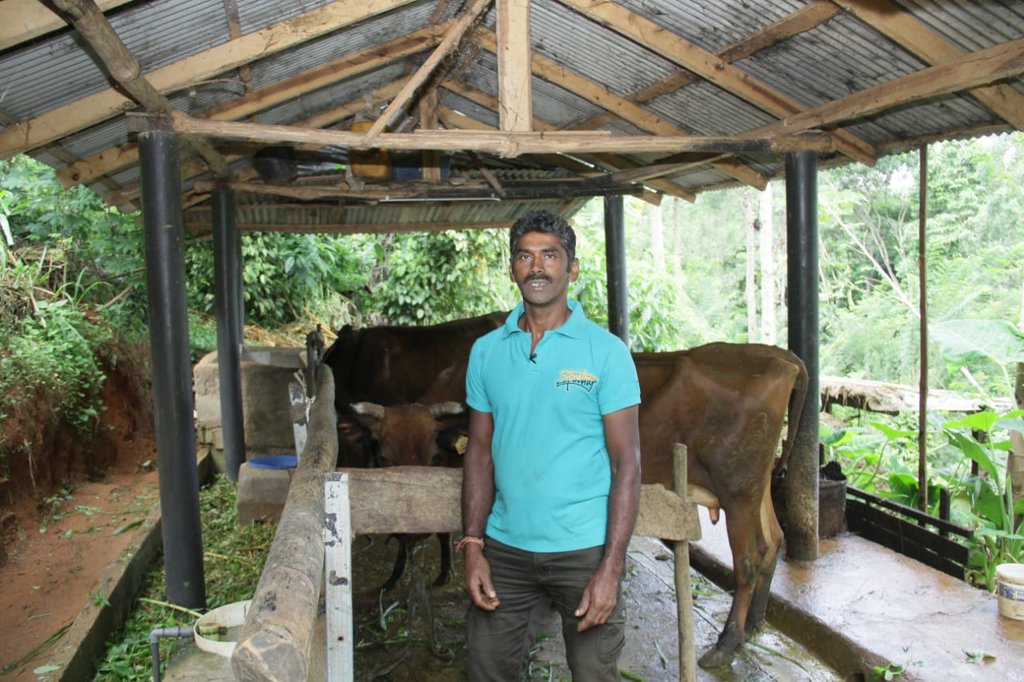
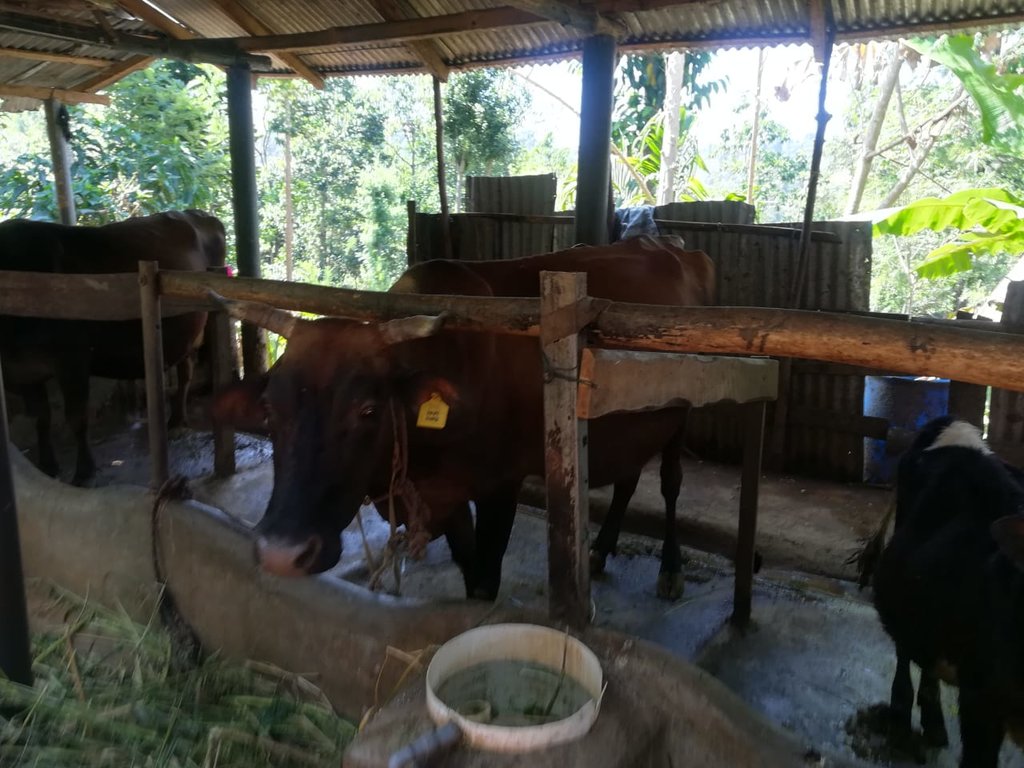
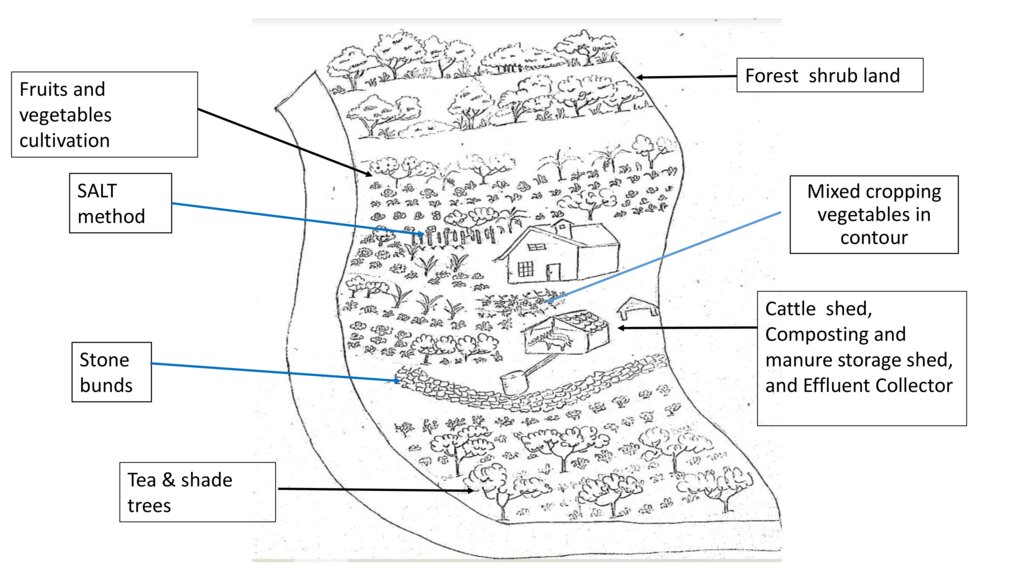
Dairy cattle farming is common in the Dolluwa area of the central province of Sri Lanka. Farmers typically have 3-4 cows on about 2-3 hectares for both milk consumption and sales. The landowner interviewed did not formerly adhere to best practices: cows were grazed in woodlands, and water and supplementary feed were not provided as needed. Housing was inadequate. Farm waste wasn’t properly recycled. The farm is located on steep land without adequate soil conservation for annual crops and tea. There was heavy dependence on chemical fertilizer. As a consequence, milk production was below average and crop yields had declined. Besides, there was reservoir pollution due to effluent washed downslope.
New technology was developed to increase milk and crop production by integrating animal–crop management strategies while enhancing nutrient circularity within the farm, and improving soil productivity and environmental quality.
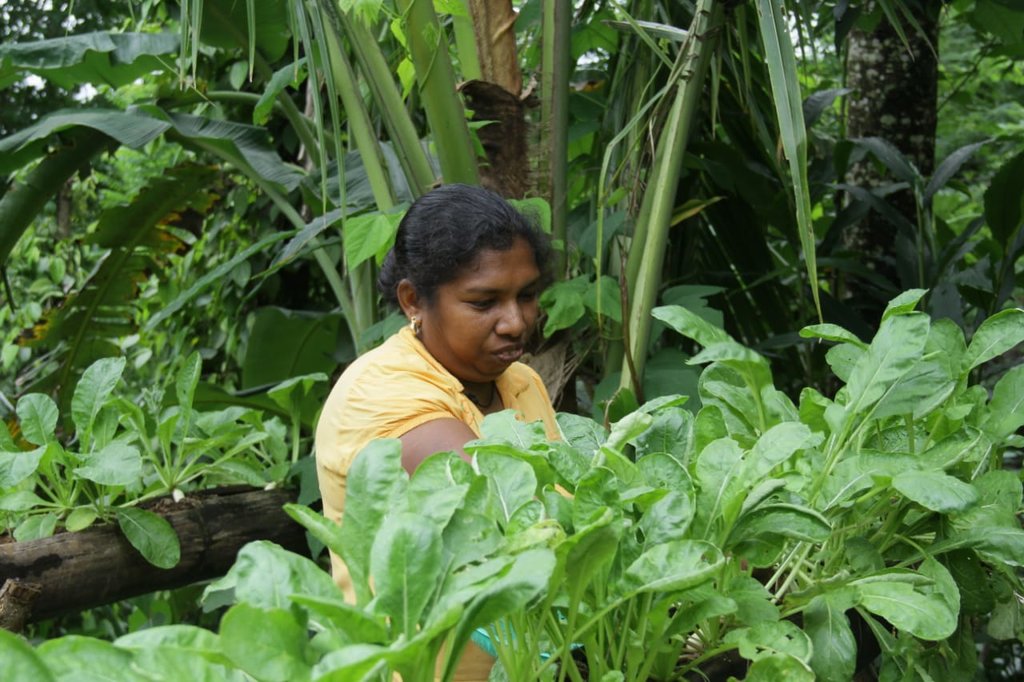
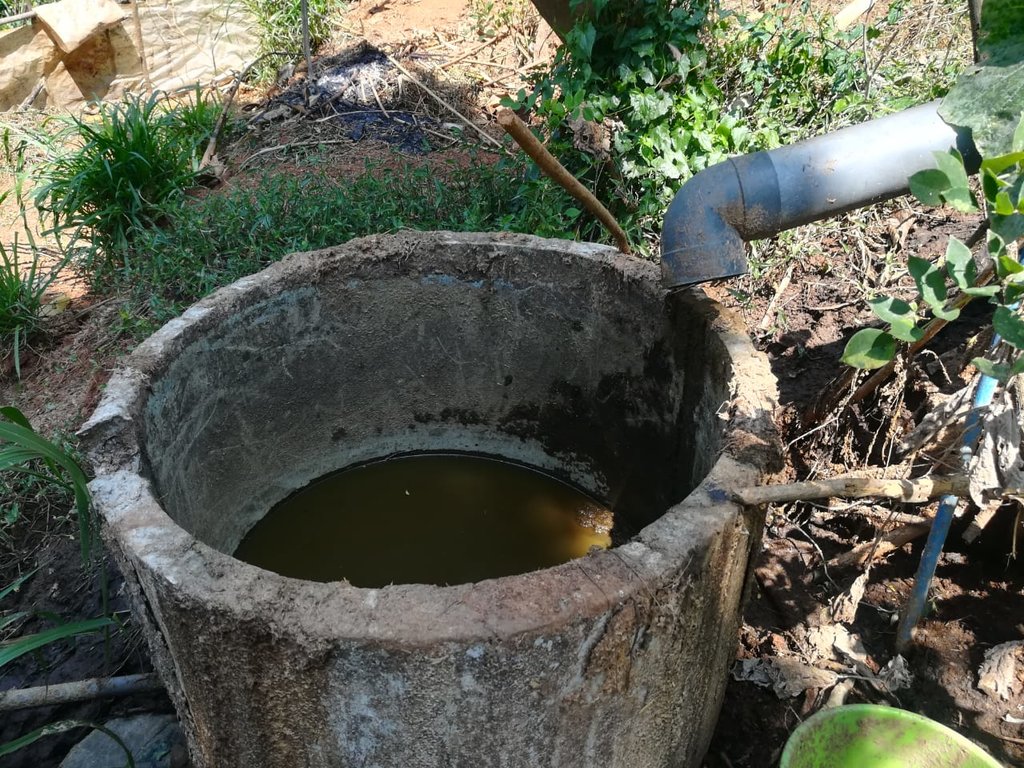
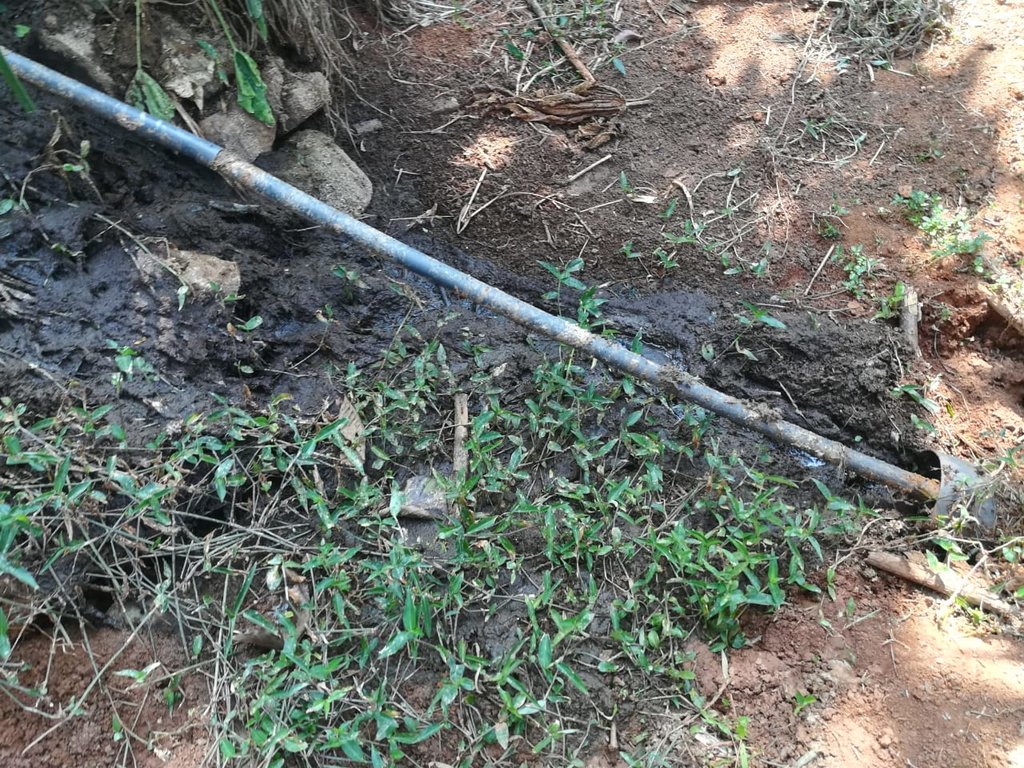
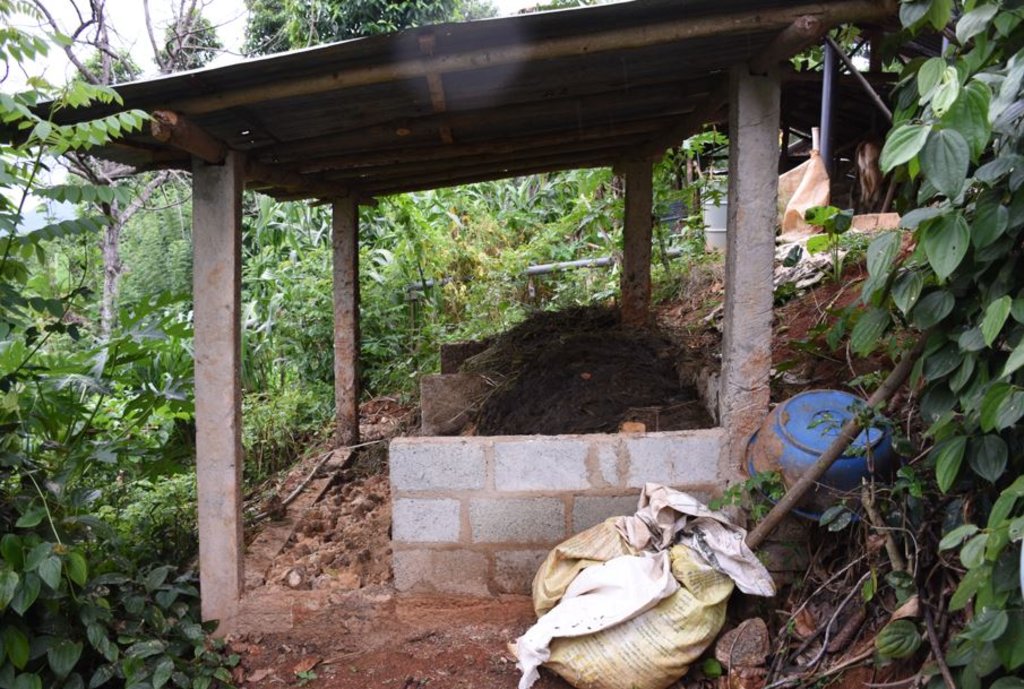
The landowner was first enrolled in the Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the UN’s FAO in 2018. The first priority was soil conservation for the steep areas under tea. SLM practices thus combined contour cropping and bunding. Following this, an integrated crop-livestock system was initiated. The RDALP and Fonterra Pvt. Ltd. helped the landowner to build a modern cowshed with infrastructure to provide feed and water. Thereafter, cows were stall-fed: grazing was completely stopped. Cow manure is collected and stored in heaps for 2-3 weeks before incorporating into soils. In the same shed, compost is prepared by mixing manure with crop residues and kitchen/ homegarden waste. Cattle urine and wastewater is directed to a cement tank where it is mixed with specific types of leaves; it is fermented and applied as liquid fertilizer and biopesticide. Manure is used mainly for fast-growing vegetables, while compost is applied to annuals, particularly at planting, and to tea once every three months. Liquid fertilizer is applied to tea seven days before harvesting.
This package requires adequate land for a cattle shed, and for a recycling system to prepare compost and liquid fertilizers. In addition, there must be enough labour for the whole process. The key inputs include materials for the shed, associated infrastructure, and a sprayer to apply liquid fertilizers.
The major benefit is recycling waste to generate useful products – while ensuring circularity of nutrients between crop and animal production systems: thus supporting a “bioeconomy”. Soil conservation practices and the nutrient sources described have improved soil fertility and productivity for overall sustainability. Milk yields have more than doubled, and the tea harvest more than trebled.
(1) Where is the Technology applied?
On steep terrain: tea is cultivated lower down and there are reservoirs in the valley.
(2) What are the purposes/ functions?
•Provide food security
•Increase efficiency of livestock production
•Promote overall nutrient cycling
•Partially substitute chemical fertilizers and pesticides with organic manure
•Generate high-quality organic manure and compost to improve soil fertility
•Control contamination of river water
(3) What are the benefits/ impacts of the Technology?
•Reduced susceptibility of crops to pests/ diseases
•Improved quality of food and water
•Slowed land degradation and restored soil fertility
•Reduced risks
•Economically feasible and rapid impact
(4) What do land users like/
•Reduced risk
•Increased income
•Reduction in cost of production
(5) ...dislike
•Damage to crops by wild animals.
•Higher cost for dairy farming (feed)
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ศรีลังกา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Central province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Dolluwa
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2019
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations in 2018
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

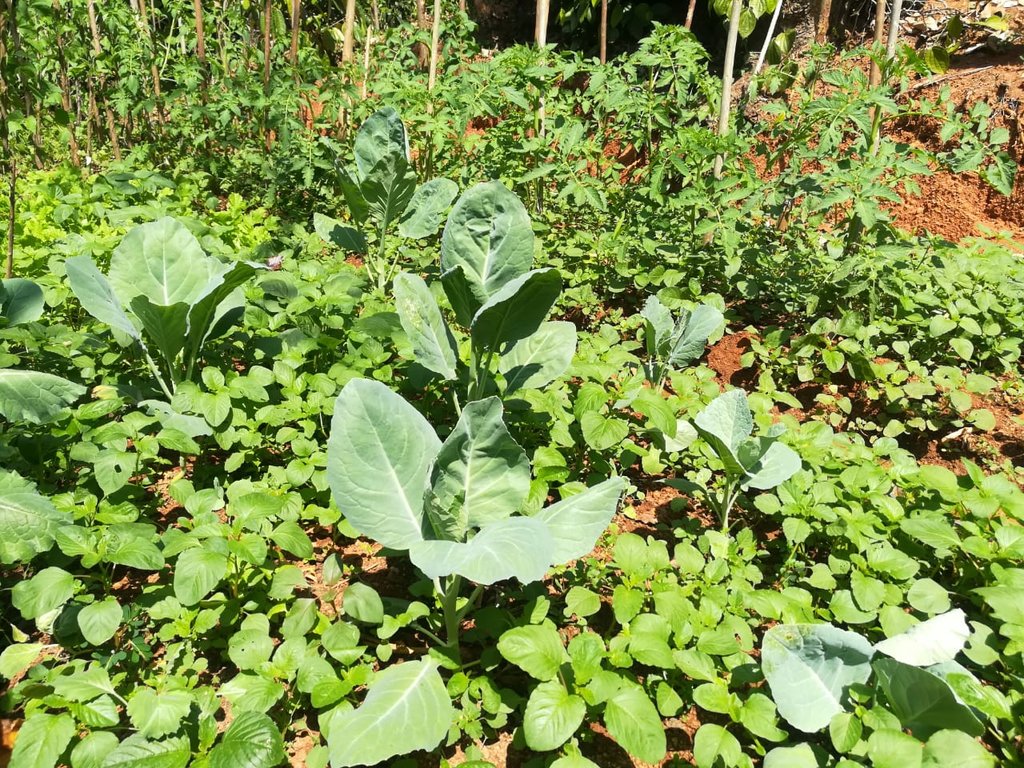
พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- flower crops
- legumes and pulses - beans
- medicinal/ aromatic/ pesticidal plants and herbs
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
- root/tuber crops - cassava
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- vegetables - mushrooms and truffles
- vegetables - other
- vegetables - root vegetables (carrots, onions, beet, other)
Annual cropping system:
Continuous vegetables
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- areca
- banana/plantain/abaca
- flower crops - perennial
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal plants - perennial
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- cacao
- coconut (fruit, coir, leaves, etc.)
- coffee, shade grown
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- papaya
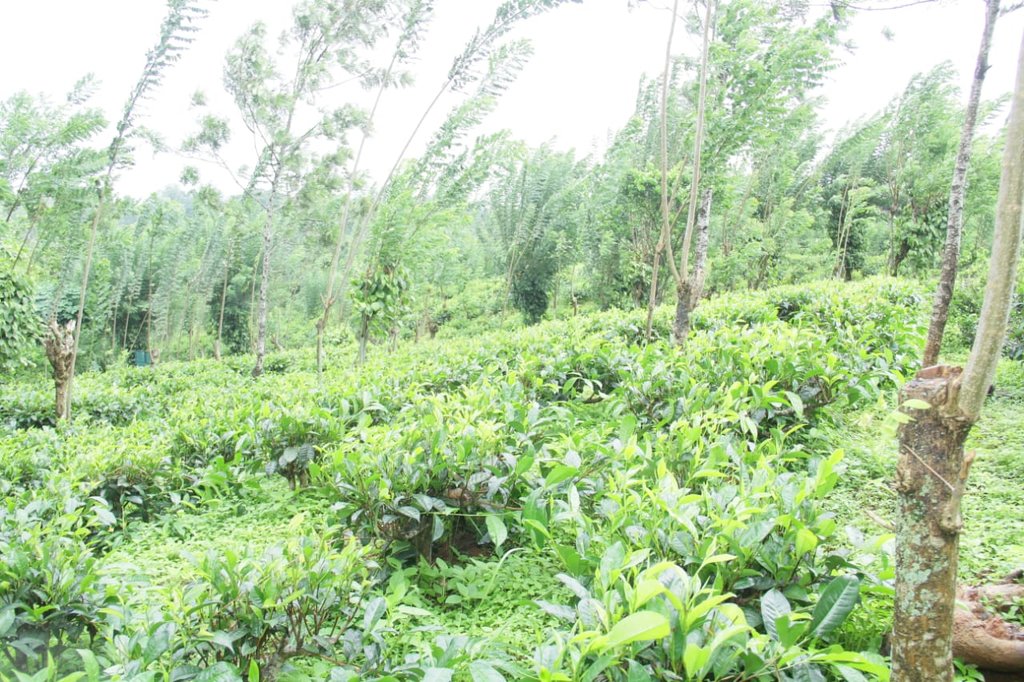
- tea
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 3
ระบุ:
Vegetables are cultivated in three seasons per year
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- mixed deciduous/ evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
- พลังงาน ท่อส่งก๊าซธรรมชาติ สายส่งไฟฟ้า
ข้อสังเกต:
cattle shed and compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
pipelines are used for reove effluents from the farm
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- medicinal/ aromatic/ pesticidal plants and herbs
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
- root/tuber crops - cassava
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- root/tuber crops - sugar beet
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- vegetables - melon, pumpkin, squash or gourd
- vegetables - mushrooms and truffles
- vegetables - other
- vegetables - root vegetables (carrots, onions, beet, other)
Annual cropping system:
Continuous vegetables
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- flower crops - perennial
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal plants - perennial
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- cacao
- citrus
- coconut (fruit, coir, leaves, etc.)
- coffee, shade grown
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- papaya
- tea
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
- พลังงาน ท่อส่งก๊าซธรรมชาติ สายส่งไฟฟ้า
ข้อสังเกต:
A cattle shed and a compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
Pipelines are used to remove effluents from the farm
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Mainly water requirements are fulfilled by natural water sources in the land
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การจัดการของเสีย / การจัดการน้ำเสีย
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
- A6: Residue management
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6: Specify residue management:
A 6.4: retained

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
- S8: การสุขาภิบาลหรือโครงสร้างเกี่ยวกับน้ำเสีย
- S9: ที่พักพิงสำหรับพืชและสัตว์
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
- M6: การจัดการของเสีย (การทำ รีไซเคิล การเอากลับมาใช้ใหม่หรือการลดปริมาณ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land is very prone to soil erosion. Therefore several SLM measures were introduced to prevent soil erosion and improve the productivity of the land.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Zero grazing reduced soil erosion by animal trampling
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Application of decomposed organic manure increased tea and vegetable production, proper disposal of farm waste prevents water pollution in reservoirs, prevention of application of chemical fertilizer reduces soil deterioration and water pollution
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
3.5 acre
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 hectare = 2.47 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Sri Lankan Rupees
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
330.13
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
900.00 Sri Lankan Rupees
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of soil conservation measures | Before rainy season |
| 2. | Establishment of cattle shed | After establishment of soil conservation measures |
| 3. | Establishment of compost shed | Before rainy season |
| 4. | Establishment farm waste disposal system | After establishment of compost shed |
| 5. | Planting crops | With the onset of rain |
| 6. | Application of compost | At and after planting crops |
| 7. | Foliar application of liquid fertilizers | After planting crops |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Establishment of cattle shed | person days | 7.0 | 4400.0 | 30800.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Establishment of compost shed | person days | 6.0 | 2000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Establishment of disposal system | person days | 2.0 | 1200.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Prepearation of Stone bunds | person days | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 15.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Establishment of 'SALT' method (combined SLM measures on slopes) | person days | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 15.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Vegetable seeds | gram | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Gliricidia stalks | 1 stalk | 1000.0 | 3.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost | 1 bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Cattle manure | 1 bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Establishment of cattle shed (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 118645.0 | 118645.0 | 16.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Establishment of compost preparation unit (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 34560.0 | 34560.0 | 15.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Establishment of liquid waste disposal system (roofing sheets, cement, sand..) | unit | 1.0 | 16500.0 | 16500.0 | 40.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Large bins to collect liquid waste | 2.0 | 4500.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | cable | 18.0 | 890.0 | 16020.0 | ||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 260175.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 788.1 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Rehabilitation of degraded agriculture land project (RDALP) and local funds
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The initial cost for establishing cattle shed with a filtering system and compost shed was higher. But the majority of the initial cost was covered by RDALP and local funds. Land users covered 30% of the establishment costs for soil conservation measures. Eg: the SALT method, stone bunds
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | After rainy season (twice a year) |
| 2. | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Before land preparation in each growing season |
| 3. | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Once in a year |
| 4. | Replace bins used to collect liquid waste | Whenever broken |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | Person days | 6.0 | 1200.0 | 7200.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Person days | 4.0 | 1200.0 | 4800.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Person days | 3.0 | 1200.0 | 3600.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Application of compost and cattle manure | bag | 25.0 | 125.0 | 3125.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Increase the area of the cattle shed (all included) | 1.0 | 17800.0 | 17800.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 36525.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 110.64 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Maintenance activities are fully covered by the land owner.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The cost involved in intensive labour is higher than for inputs on a daily basis
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
2500.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Average monthly rainfall from April to July under southwest monsoon is 120-200 mm. Average monthly rainfall from September to December under Northeast monsoon is 200-300 mm. First inter monsoon is from January to March with around 100 mm.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Gannoruwa, peradeniya
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Nilambe water reservoir is located in the valley and provides water for drinking and irrigation purposes. Part of the micro-catchment of the surface water body/reservoir is occupied by farms where intensive agriculture, homegardens and cattle rearing are practised. Limited soil conservation practices, overuse of agrochemicals and improper waste management have led to contamination of water
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The forested and scrubland area is about tree species and species of shrubs. In addition, grass species as medicinal plants are also growing. Local and imported varieties of fruits avocado, guava, mango, banana, pomegranate, orange, lemon and tree and bush type of local fruits are grown. Local varieties of cardamom, cinnamon, pepper, nutmeg and other locally used spices such as coriander, mustard etc. have been grown in the home garden. Vegetables often grown include cabbage, beans, lettuce, cucumber, radish, tomato etc. In the tea land, two shade tree species, gliricidia and albizzia
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
The land belongs to a land user. Land use rights are passed down from generation to generation. Land use rights, water usage rights are based on a traditional legal system
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Because of the traditional legal system land use rights, and water usage rights are not free for all. Land users are able to implement and maintain technology without any disturbance occurring due to land and water usage rights
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After introducing organic inputs, the production of tea and vegetables increased.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction of the synthetic chemicals and supplement of balanced nutrients by organic inputs have enhanced crop quality.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Supplement of quality feed and adequate water to the cattle shed increased milk production.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Integrated crop-livestock technology and crop diversification reduced the risk of production failure.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing this technology diversity of annual and perennial food crops were increased.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution.
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers reduced the expenses for chemical fertilizers
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology, stall feeding improves milk production and compost application enhances the tea and vegetable cultivations.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Crop diversification and investment in mushroom production added new sources of income.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After modernizing the dairy farm, all grazing was stopped, allowing more time to be spent on other tasks.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology milk, tea and vegetable production increased. Throughout the year foods are available for their own consumption.
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The approach was implemented on their own land. Natural water sources are available for their cultivation and dairy farming activity.
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Aesthetic view of homegarden improved.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Training programme and advisory services improved knowledge base on SLM.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced application of synthetic chemicals and recycling of farm waste through a proper disposal system reduced contamination of water.
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines reduce surface runoff.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improve in soil structure due to application of compost and cow manure facilitate water infiltration.
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulching, application of crop residuals and organic manure reduce the evaporation from bare surfaces.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Higher soil organic matter content increased soil moisture retention.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology, landowners cultivated bare lands so that soil cover was improved.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Implementation of soil conservation measures (SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour line) reduced runoff.
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
implementation of soil conservation reduced soil loss and thereby soil accumulation in the lower slope position of the land.
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As runoff is controlled by conservation measures, soil sealing is reduced.
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulching has reduced soil compaction.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Nutrients are cycling within integrated crop-livestock technology.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The addition of cow manure and composts had improved soil organic matter content.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing technology, a landowner has cultivated all possible spaces on the land. Improving land cover by tea was also evident.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Application of organic inputs increased biomass production of all crops.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
After implementing this technology diverse crops were introduced to the small unit of land.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
An increase in earthworms and honey bees was observed.
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
An increase in crop diversity may have introduced new habitats at a micro-scale level.
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced application of chemical fertilizer had led to less succulent crops and increased resistance to pests/ diseases. Natural pesticides sprayed mal also help keep crops healthy.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Aerobic composting would help to reduce methane emissions. Control in excess urea application may also be led to a reduction in nitrous oxide emission.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SLM measures such as SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines prevent runoff and reduced downstream siltation.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As an application of synthetic chemicals was reduced, and a proper farm waste disposal system was implemented, the removal of chemicals was controlled.
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Application of organic substances to soil and increased ground cover had improved filtering capacity.
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Restricted movements of the cows.
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Restricted movements of the cows.
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Will have reduced the emission of methane and nitrous oxide from manure. A reduction in urea application would have reduced the emission of nitrous oxide.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูฝน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูแล้ง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | ลดลง | ดี |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูแล้ง | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ปานกลาง |
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
According to the land user’s perspective implementation of this technology provided net benefits from tea, vegetables and dairy farming compared with establishment and maintenance cost. In the beginning, land users had to invest substantial amount of money to establish this technology. However, short-term and long-term returns could cover the cost involved in establishment and maintenance of the technology.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
The technology was introduced to about 10 farms but except one land user, others were unable to spend on developing technology irrespective of partial funds generated from other sources.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
No farmer was able to afford to develop technology by their own.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| After providing a proper shed for cows, it was possible to provide adequate feed and water for easy consumption of cows. This led to a significant increase in milk production. |
| Direct application of cow dung and liquid organic fertilizer for tea and vegetables led to an increase in crop yields and improved soil fertility. |
| As benefits are higher in monetary terms in comparison to the costs of investment for this technology, neighbourhood farmers who rear animals are encouraged to follow this technology. |
| Reduction in chemical fertilizer usage reduced the cost of production. |
| With the implementation of new technology, the number of pests and diseases incidences declined. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| This technology is easy to promote on the farmland due to the low cost involved and multiple benefits are visible. This technology has changed the attitudes of farmers that dairy farming could be profitable and support crop cultivation. |
| Before implementing this technology landowners had to work outside to earn money. As the income increase with the establishment of the technology, landowners could spend more time on other farming activities onsite . |
| Modernization of cattle farms enable zero-grazing so that land user was able to spend additional time for other farming activities. |
| The landowner does not need to depend on government or private sector funds to improve their farming activities. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Crops and fruits are often damaged by wild animals. Therefore the maximum profits cannot be achieved. | The landowner is with the opinion is that damage caused by wild animals could be stopped by constructing a steel fence around the land. However, farmer is unable to afford or such as the cost is very high. |
| Establishment of this technology requires considerable amount of money which is beyond the income and purchasing power of farmers with low income. | Providing partial funding by government or private sector organizations would help farmers to initiate the establishment of at least one or two components of technology. |
| Attitudes of neighboring farmers on dairy farming should be changed as a profit oriented business. | Introducing training programs and demonstrations at the successful farm would encourage other farmers to use the technology. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The landowner does not record profits that earn from his farming activities. He doesn’t have a good idea about the overall income of his farming activities per month. | The landowner should change attitudes toward income recordings. |
| People should be aware of these SLM technologies, SLM knowledge and benefits. | Government and private sector should invest in and implement SLM training programs. |
| Limited availability of modern technologies in cattle farming and crop cultivation affordable to middle income farmers. | Modernize farming with biogas technology, harvest tea with the cutter, prepare wormy compost and compost tea for tea cultivation. |
| Lack of properly established marketing channel for selling products. | Improve the product quality, or technology to develop value added products targeting supermarkets. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
01
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
02
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
02
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
02
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
06/02/2022
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Sustainable management practices for agricultural lands in the central highlands of Sri Lanka
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
rehabilitation of degraded agricultural land project office, food and agricultural organization of the United Nations Peradeniya Sri Lanka
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Project News: Fertile Soil
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Controlled livestock grazing for soil fertility improvement [Uganda]
URL:
https://qcat.wocat.net/en/wocat/technologies/view/technologies_2761/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [ศรีลังกา]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- ผู้รวบรวม: Bandara Rotawewa
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล