Crop-livestock integration to enhance soil productivity [ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Head Soil Science
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ William Critchley
technologies_6236 - ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Kallora Shantha
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Gunasena Nimal
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
co-compiler:
Rajapaksha Chandi
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
co-compiler:
Beddegama Nilanthika
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Lands in Kandy, Badulla and Nuwara Eliya Districts in the Central Highlands of Sri Lankaឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka (AGRI.PDN) - ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity, and soil productivity technology improves nutrient recycling and soil productivity in the land and SLM practices are reducing land degradation
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Bandara Rotawewa
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
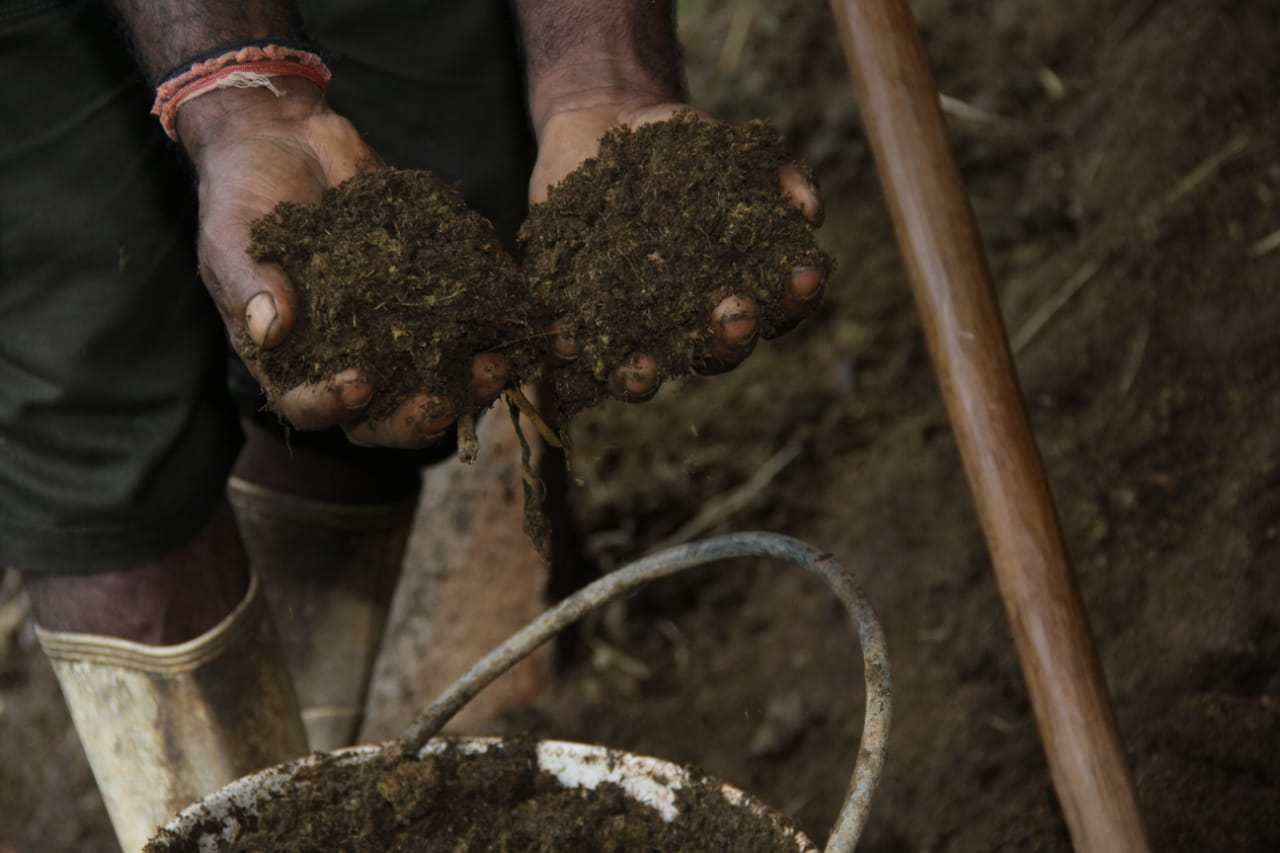
Crop-livestock integration improves nutrient circularity and soil productivity: solid and liquid organic fertilizers prepared from cow manure are incorporated to soil or sprayed on leaves of vegetables and tea.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
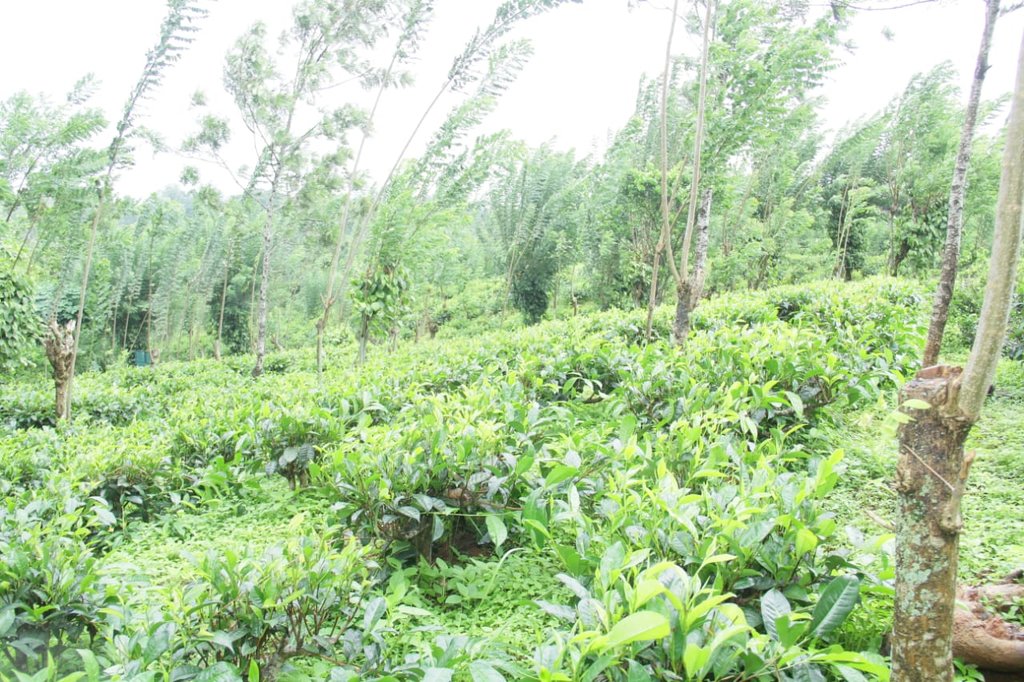
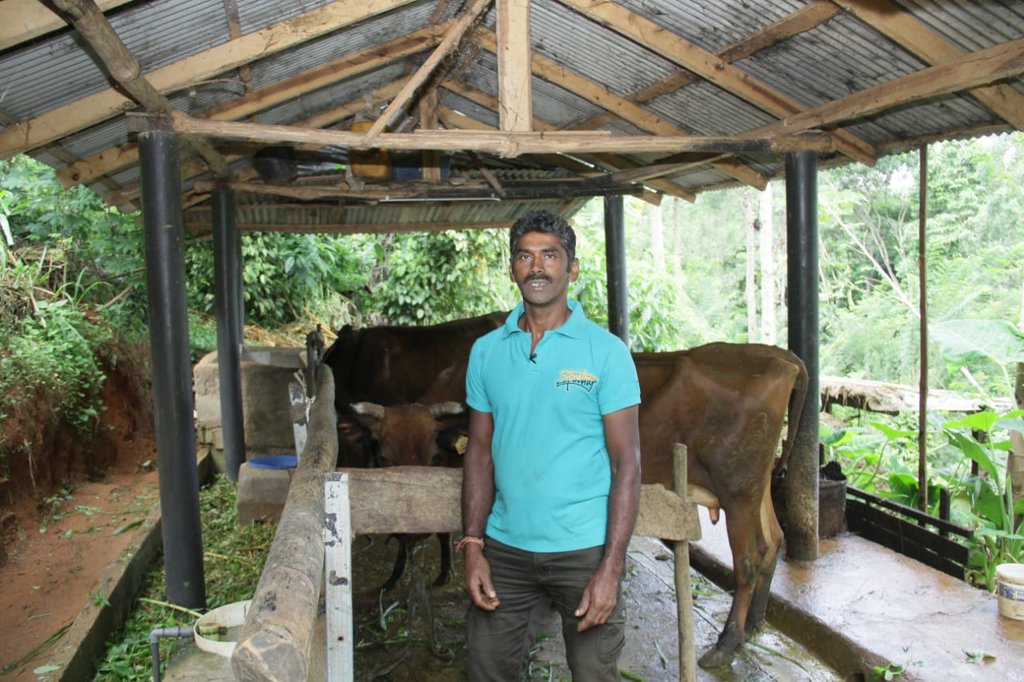
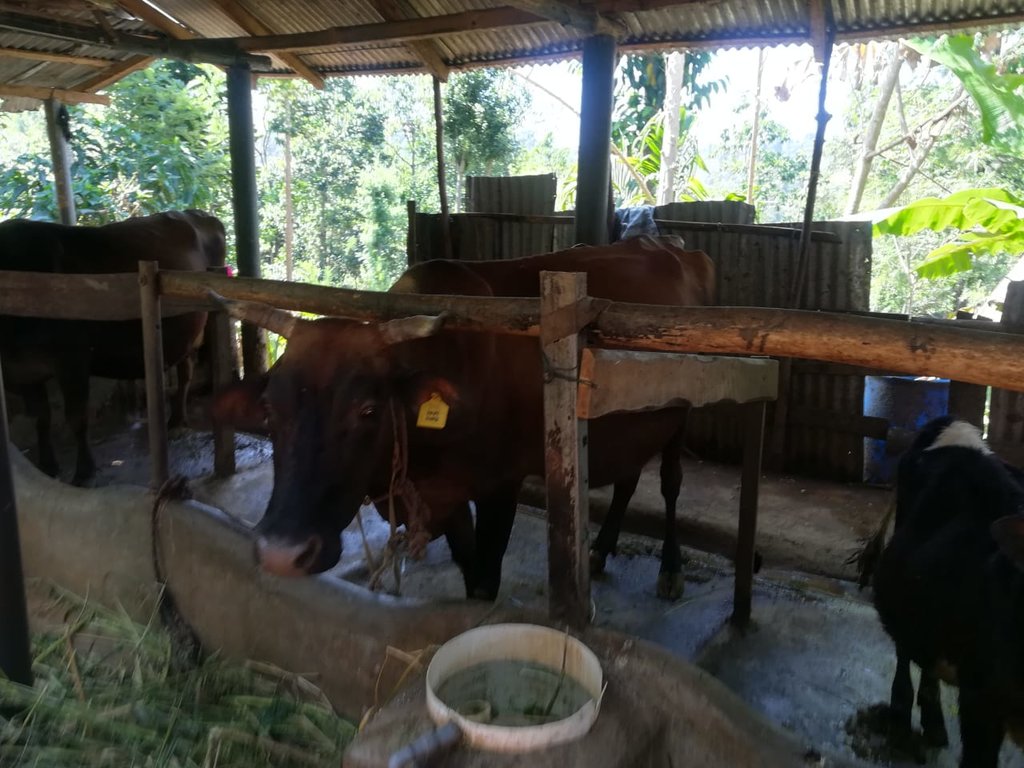
Dairy cattle farming is common in the Dolluwa area of the central province of Sri Lanka. Farmers typically have 3-4 cows on about 2-3 hectares for both milk consumption and sales. The landowner interviewed did not formerly adhere to best practices: cows were grazed in woodlands, and water and supplementary feed were not provided as needed. Housing was inadequate. Farm waste wasn’t properly recycled. The farm is located on steep land without adequate soil conservation for annual crops and tea. There was heavy dependence on chemical fertilizer. As a consequence, milk production was below average and crop yields had declined. Besides, there was reservoir pollution due to effluent washed downslope.
New technology was developed to increase milk and crop production by integrating animal–crop management strategies while enhancing nutrient circularity within the farm, and improving soil productivity and environmental quality.
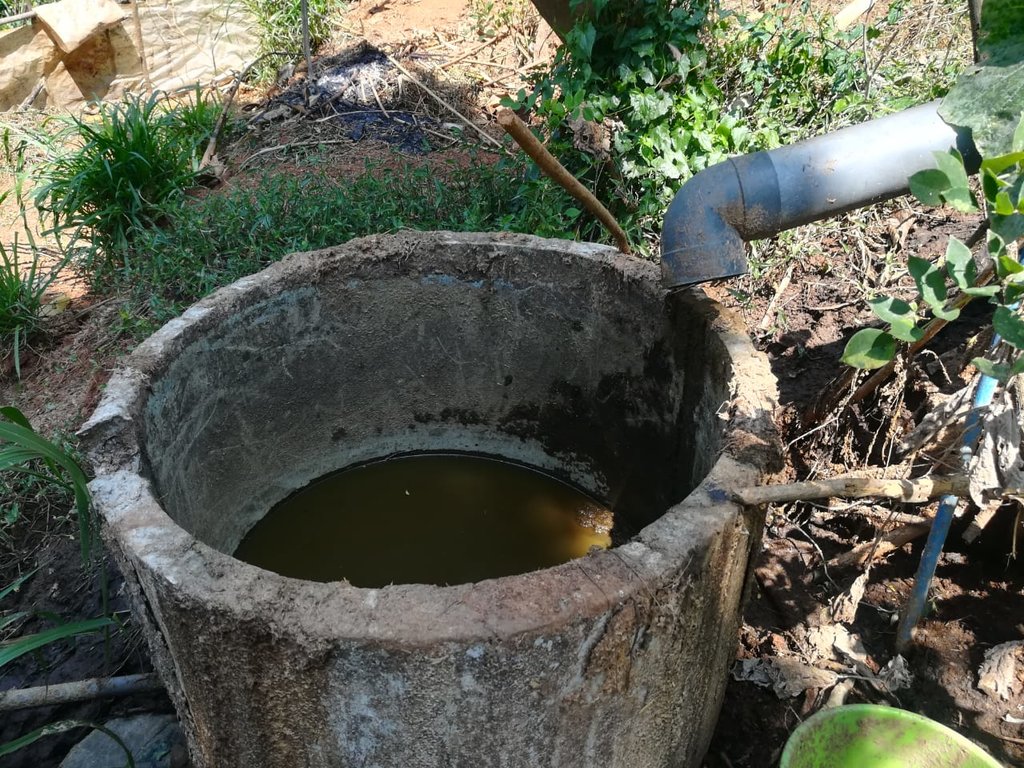
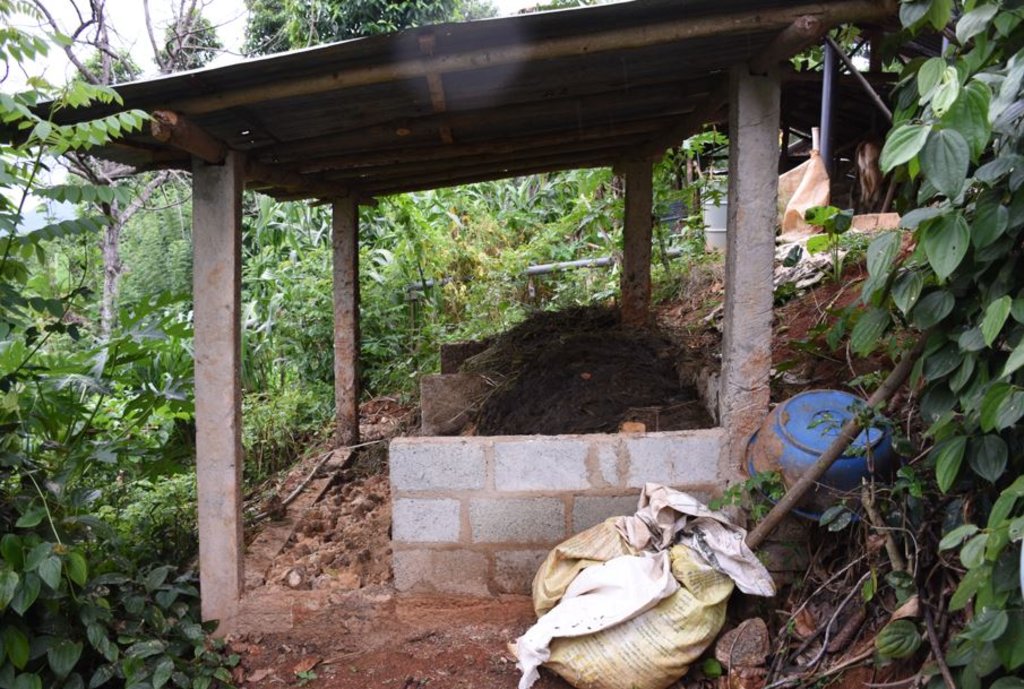
The landowner was first enrolled in the Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the UN’s FAO in 2018. The first priority was soil conservation for the steep areas under tea. SLM practices thus combined contour cropping and bunding. Following this, an integrated crop-livestock system was initiated. The RDALP and Fonterra Pvt. Ltd. helped the landowner to build a modern cowshed with infrastructure to provide feed and water. Thereafter, cows were stall-fed: grazing was completely stopped. Cow manure is collected and stored in heaps for 2-3 weeks before incorporating into soils. In the same shed, compost is prepared by mixing manure with crop residues and kitchen/ homegarden waste. Cattle urine and wastewater is directed to a cement tank where it is mixed with specific types of leaves; it is fermented and applied as liquid fertilizer and biopesticide. Manure is used mainly for fast-growing vegetables, while compost is applied to annuals, particularly at planting, and to tea once every three months. Liquid fertilizer is applied to tea seven days before harvesting.
This package requires adequate land for a cattle shed, and for a recycling system to prepare compost and liquid fertilizers. In addition, there must be enough labour for the whole process. The key inputs include materials for the shed, associated infrastructure, and a sprayer to apply liquid fertilizers.
The major benefit is recycling waste to generate useful products – while ensuring circularity of nutrients between crop and animal production systems: thus supporting a “bioeconomy”. Soil conservation practices and the nutrient sources described have improved soil fertility and productivity for overall sustainability. Milk yields have more than doubled, and the tea harvest more than trebled.
(1) Where is the Technology applied?
On steep terrain: tea is cultivated lower down and there are reservoirs in the valley.
(2) What are the purposes/ functions?
•Provide food security
•Increase efficiency of livestock production
•Promote overall nutrient cycling
•Partially substitute chemical fertilizers and pesticides with organic manure
•Generate high-quality organic manure and compost to improve soil fertility
•Control contamination of river water
(3) What are the benefits/ impacts of the Technology?
•Reduced susceptibility of crops to pests/ diseases
•Improved quality of food and water
•Slowed land degradation and restored soil fertility
•Reduced risks
•Economically feasible and rapid impact
(4) What do land users like/
•Reduced risk
•Increased income
•Reduction in cost of production
(5) ...dislike
•Damage to crops by wild animals.
•Higher cost for dairy farming (feed)
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Central province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Dolluwa
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2019
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) of the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations in 2018
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- Agro-pastoralism ( រួមបញ្ចូលទាំងដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
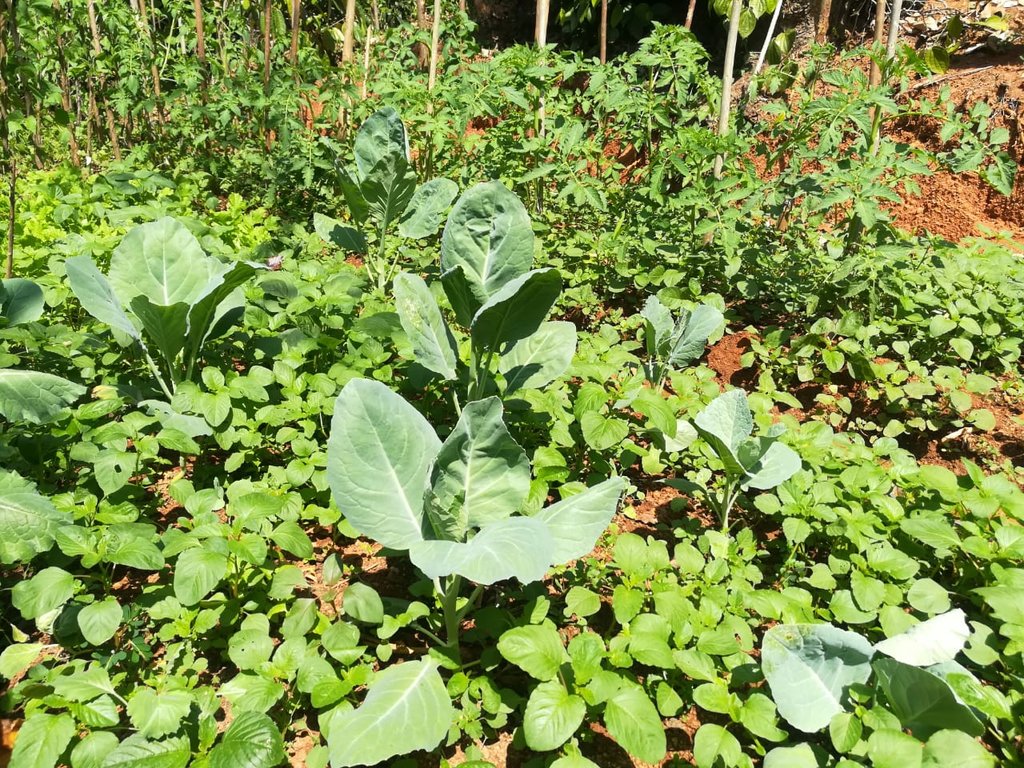
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ដំណាំយកផ្កា
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- រុក្ខជាតិឱសថ/ រុក្ខជាតិមានក្លិនក្រអូប/ រុក្ខជាតិការពារពីសត្វល្អិត និងពពួកជី
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងជ្វា ពពួកដំឡូង ត្រាវ ផ្សេងៗ
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងមី
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងបារាំង
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកស្លឹក (សាលាដ ស្ពៃក្តោប ផ្ទី ផ្សេងៗ)
- បន្លែ - ផ្សិត និងត្រាហ្វល
- បន្លែ - ផ្សេងៗ
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកមើម (ការ៉ុត ខ្ទឹមបារាំង ឆៃថាវម្យ៉ាង ផ្សេងៗ)
ប្រព័ន្ធដាំដុះដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ:
ដាំដំណាំបន្លែបន្តបន្ទាប់
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ) - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- areca
- ចេក/plantain/abaca
- ដំណាំយកផ្កា - មានរយៈពេលវែង
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- រុក្ខជាតិឱសថ/ រុក្ខជាតិមានក្លិនក្រអូប/ រុក្ខជាតិការពារពីសត្វល្អិត - មានរយៈពេលវែង
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែប៊ឺ
- កាកាវ
- ដូង (ផ្លែដូង ស្រកីដូង ស្លឹកដូង ។ល។)
- កាហ្វេ នៅពេលធំមានម្លប់
- ផ្លែស្វាយ/ផ្លែមង្ឃុត/ផ្លែត្របែក
- ផ្លែល្ហុង
- តែ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 3
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Vegetables are cultivated in three seasons per year
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំដែលដាំចន្លោះគ្នានោះ:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃល្បោះចម្រុះ/ ព្រៃស្រោង
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
- ផ្លែឈើ និងគ្រាប់ធញ្ញជាតិ
- ផលិតផលព្រៃផ្សេងៗ
- ការអភិរក្ស/ការការពារធម្មជាតិ
- ការពារពីគ្រោះធម្មជាតិ

លំនៅដ្ឋាន ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
- ដីលំនៅស្ថាន អគារ
- ខ្សែបណ្តាញថាមពល៖ បំពង់ហ្គាស បណ្តាញខ្សែអគ្គិសនី
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
cattle shed and compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
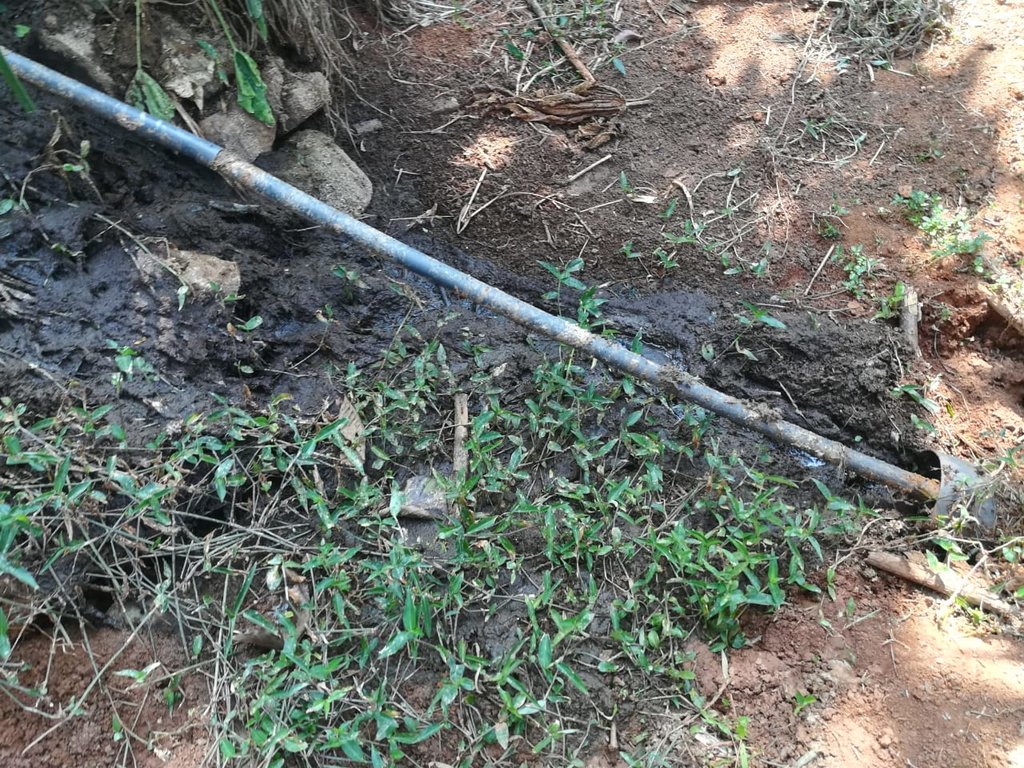
pipelines are used for reove effluents from the farm
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- Agro-pastoralism ( រួមបញ្ចូលទាំងដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ)

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកបារាំង
- រុក្ខជាតិឱសថ/ រុក្ខជាតិមានក្លិនក្រអូប/ រុក្ខជាតិការពារពីសត្វល្អិត និងពពួកជី
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងជ្វា ពពួកដំឡូង ត្រាវ ផ្សេងៗ
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងមី
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងបារាំង
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ឆៃថាវស្ករ
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកស្លឹក (សាលាដ ស្ពៃក្តោប ផ្ទី ផ្សេងៗ)
- បន្លែ - ត្រសក់ផ្អែម ល្ពៅ ពពួកបន្លែទ្រើង
- បន្លែ - ផ្សិត និងត្រាហ្វល
- បន្លែ - ផ្សេងៗ
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកមើម (ការ៉ុត ខ្ទឹមបារាំង ឆៃថាវម្យ៉ាង ផ្សេងៗ)
ប្រព័ន្ធដាំដុះដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ:
ដាំដំណាំបន្លែបន្តបន្ទាប់
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ) - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ចេក/plantain/abaca
- ដំណាំយកផ្កា - មានរយៈពេលវែង
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- រុក្ខជាតិឱសថ/ រុក្ខជាតិមានក្លិនក្រអូប/ រុក្ខជាតិការពារពីសត្វល្អិត - មានរយៈពេលវែង
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែប៊ឺ
- កាកាវ
- ពពួកក្រូច citrus
- ដូង (ផ្លែដូង ស្រកីដូង ស្លឹកដូង ។ល។)
- កាហ្វេ នៅពេលធំមានម្លប់
- ផ្លែស្វាយ/ផ្លែមង្ឃុត/ផ្លែត្របែក
- ផ្លែល្ហុង
- តែ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំដែលដាំចន្លោះគ្នានោះ:
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and flower crops
Vegetables and medicinal plant
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Legumes, leafy vegetables, rootcrops, root vegetables are rotated in same land, seasonally

លំនៅដ្ឋាន ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
- ដីលំនៅស្ថាន អគារ
- ខ្សែបណ្តាញថាមពល៖ បំពង់ហ្គាស បណ្តាញខ្សែអគ្គិសនី
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
A cattle shed and a compost shed are introduced through technology as settlements
Pipelines are used to remove effluents from the farm
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
Mainly water requirements are fulfilled by natural water sources in the land
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់/ ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកកង្វក់
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
- A6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់
A3: ប្រព័ន្ធភ្ជួររាស់ខុសៗគ្នា:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6: បញ្ជាក់ពីការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់:
A 6.4: រក្សាទុក

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
- S3: កម្ពស់ភ្លឺ ប្រឡាយ ផ្លូវទឹក
- S6: ជញ្ជាំង, របាំង, របងឈើខ្ពស់ៗ
- S8: អនាម័យ/ទំនប់ទឹកកង្វក់
- S9: រោងដំណាំ និងរោងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- S11: ផ្សេងៗ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
- M3: ប្លង់យោងទៅតាមធម្មជាតិ និងបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
- M6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងសំណល់ (កែឆ្នៃទ្បើងវិញ ប្រើប្រាស់ឡើងវិញ ឬបន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់)
មតិយោបល់:
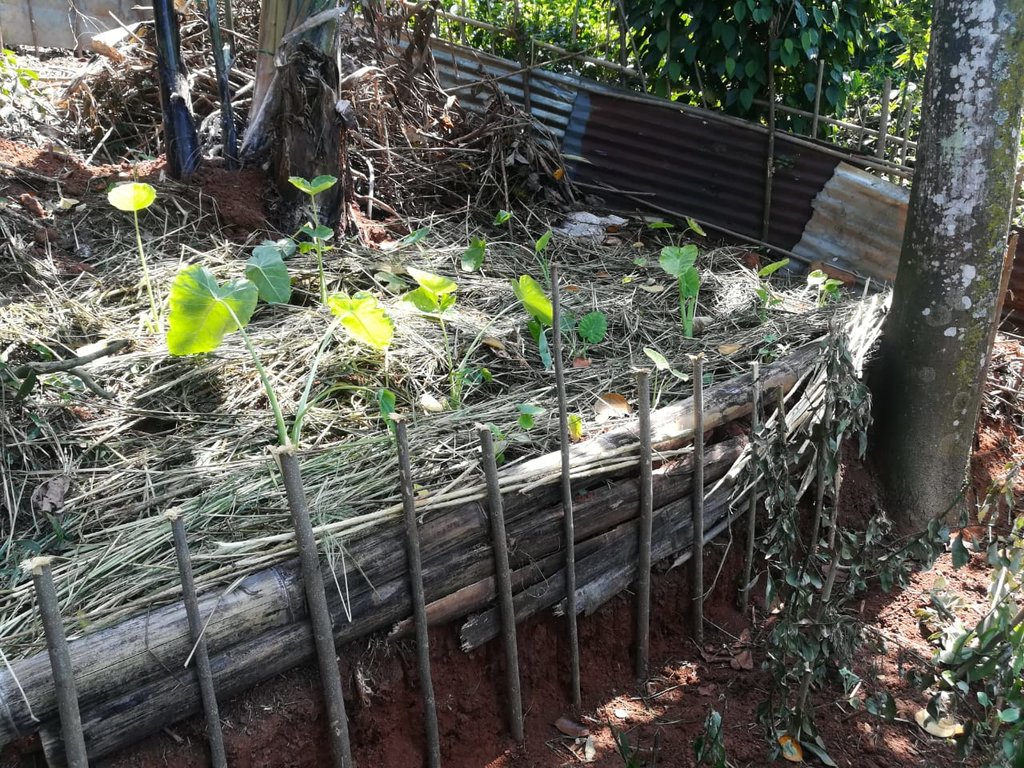
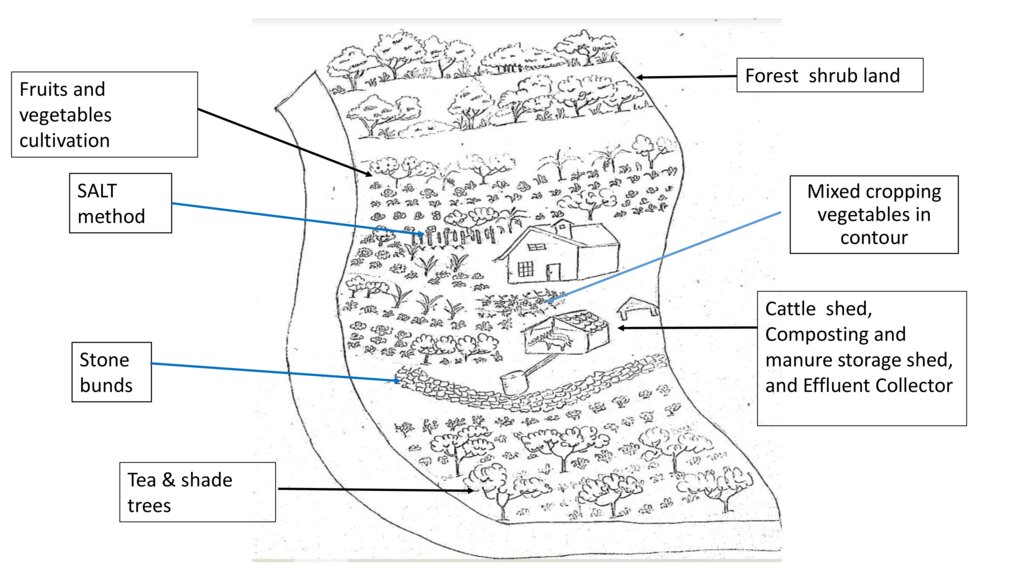
The land is very prone to soil erosion. Therefore several SLM measures were introduced to prevent soil erosion and improve the productivity of the land.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hp: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់:
Zero grazing reduced soil erosion by animal trampling
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Application of decomposed organic manure increased tea and vegetable production, proper disposal of farm waste prevents water pollution in reservoirs, prevention of application of chemical fertilizer reduces soil deterioration and water pollution
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
3.5 acre
បើសិនប្រើឯកតាតាមតំបន់ សូមបញ្ជាក់តម្លៃបម្លែងវាទៅជាហិកតា (ឧ. 1 ហិកតា = 2.47 អា)៖ 1 ហិកតា =:
1 hectare = 2.47 acres
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Sri Lankan Rupees
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
330,13
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
900.00 Sri Lankan Rupees
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of soil conservation measures | Before rainy season |
| 2. | Establishment of cattle shed | After establishment of soil conservation measures |
| 3. | Establishment of compost shed | Before rainy season |
| 4. | Establishment farm waste disposal system | After establishment of compost shed |
| 5. | Planting crops | With the onset of rain |
| 6. | Application of compost | At and after planting crops |
| 7. | Foliar application of liquid fertilizers | After planting crops |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Establishment of cattle shed | person days | 7,0 | 4400,0 | 30800,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Establishment of compost shed | person days | 6,0 | 2000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Establishment of disposal system | person days | 2,0 | 1200,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Prepearation of Stone bunds | person days | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 15,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Establishment of 'SALT' method (combined SLM measures on slopes) | person days | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 15,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Vegetable seeds | gram | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Gliricidia stalks | 1 stalk | 1000,0 | 3,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Compost | 1 bag | 25,0 | 125,0 | 3125,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Cattle manure | 1 bag | 25,0 | 125,0 | 3125,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Establishment of cattle shed (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1,0 | 118645,0 | 118645,0 | 16,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Establishment of compost preparation unit (roofing sheets, bricks, cement, sand..) | unit | 1,0 | 34560,0 | 34560,0 | 15,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Establishment of liquid waste disposal system (roofing sheets, cement, sand..) | unit | 1,0 | 16500,0 | 16500,0 | 40,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Large bins to collect liquid waste | 2,0 | 4500,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | cable | 18,0 | 890,0 | 16020,0 | ||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 260175,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 788,1 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Rehabilitation of degraded agriculture land project (RDALP) and local funds
មតិយោបល់:
The initial cost for establishing cattle shed with a filtering system and compost shed was higher. But the majority of the initial cost was covered by RDALP and local funds. Land users covered 30% of the establishment costs for soil conservation measures. Eg: the SALT method, stone bunds
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | After rainy season (twice a year) |
| 2. | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Before land preparation in each growing season |
| 3. | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Once in a year |
| 4. | Replace bins used to collect liquid waste | Whenever broken |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Cleaning of drains in tea land - removing weeds and sediments | Person days | 6,0 | 1200,0 | 7200,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Lopping of trees established as SALT and shade trees of tea land | Person days | 4,0 | 1200,0 | 4800,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Minor renovations of cattle shed and composing unit | Person days | 3,0 | 1200,0 | 3600,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Application of compost and cattle manure | bag | 25,0 | 125,0 | 3125,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Increase the area of the cattle shed (all included) | 1,0 | 17800,0 | 17800,0 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 36525,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 110,64 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Maintenance activities are fully covered by the land owner.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The cost involved in intensive labour is higher than for inputs on a daily basis
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
2500,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Average monthly rainfall from April to July under southwest monsoon is 120-200 mm. Average monthly rainfall from September to December under Northeast monsoon is 200-300 mm. First inter monsoon is from January to March with around 100 mm.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Gannoruwa, peradeniya
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Nilambe water reservoir is located in the valley and provides water for drinking and irrigation purposes. Part of the micro-catchment of the surface water body/reservoir is occupied by farms where intensive agriculture, homegardens and cattle rearing are practised. Limited soil conservation practices, overuse of agrochemicals and improper waste management have led to contamination of water
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
The forested and scrubland area is about tree species and species of shrubs. In addition, grass species as medicinal plants are also growing. Local and imported varieties of fruits avocado, guava, mango, banana, pomegranate, orange, lemon and tree and bush type of local fruits are grown. Local varieties of cardamom, cinnamon, pepper, nutmeg and other locally used spices such as coriander, mustard etc. have been grown in the home garden. Vegetables often grown include cabbage, beans, lettuce, cucumber, radish, tomato etc. In the tea land, two shade tree species, gliricidia and albizzia
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
The land belongs to a land user. Land use rights are passed down from generation to generation. Land use rights, water usage rights are based on a traditional legal system
មតិយោបល់:
Because of the traditional legal system land use rights, and water usage rights are not free for all. Land users are able to implement and maintain technology without any disturbance occurring due to land and water usage rights
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
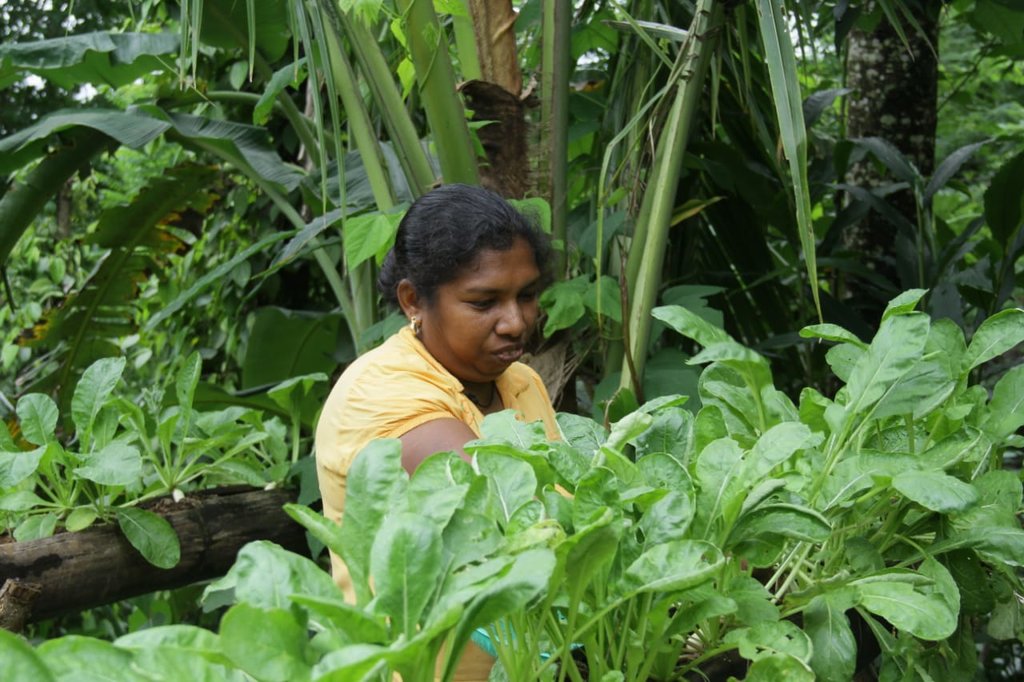
After introducing organic inputs, the production of tea and vegetables increased.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduction of the synthetic chemicals and supplement of balanced nutrients by organic inputs have enhanced crop quality.
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Supplement of quality feed and adequate water to the cattle shed increased milk production.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Integrated crop-livestock technology and crop diversification reduced the risk of production failure.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing this technology diversity of annual and perennial food crops were increased.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution.
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology proper disposal system for farm waste, zero application of chemical fertilizer prevent the water pollution
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers reduced the expenses for chemical fertilizers
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology, stall feeding improves milk production and compost application enhances the tea and vegetable cultivations.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Crop diversification and investment in mushroom production added new sources of income.
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After modernizing the dairy farm, all grazing was stopped, allowing more time to be spent on other tasks.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology milk, tea and vegetable production increased. Throughout the year foods are available for their own consumption.
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The approach was implemented on their own land. Natural water sources are available for their cultivation and dairy farming activity.
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Aesthetic view of homegarden improved.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Training programme and advisory services improved knowledge base on SLM.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
គុណភាពទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced application of synthetic chemicals and recycling of farm waste through a proper disposal system reduced contamination of water.
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines reduce surface runoff.
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improve in soil structure due to application of compost and cow manure facilitate water infiltration.
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mulching, application of crop residuals and organic manure reduce the evaporation from bare surfaces.
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Higher soil organic matter content increased soil moisture retention.
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology, landowners cultivated bare lands so that soil cover was improved.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Implementation of soil conservation measures (SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour line) reduced runoff.
ការកើនឡើងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
implementation of soil conservation reduced soil loss and thereby soil accumulation in the lower slope position of the land.
ដីប្រេះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As runoff is controlled by conservation measures, soil sealing is reduced.
ដីហាប់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mulching has reduced soil compaction.
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Nutrients are cycling within integrated crop-livestock technology.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The addition of cow manure and composts had improved soil organic matter content.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing technology, a landowner has cultivated all possible spaces on the land. Improving land cover by tea was also evident.
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Application of organic inputs increased biomass production of all crops.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
After implementing this technology diverse crops were introduced to the small unit of land.
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
An increase in earthworms and honey bees was observed.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
An increase in crop diversity may have introduced new habitats at a micro-scale level.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduced application of chemical fertilizer had led to less succulent crops and increased resistance to pests/ diseases. Natural pesticides sprayed mal also help keep crops healthy.
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Aerobic composting would help to reduce methane emissions. Control in excess urea application may also be led to a reduction in nitrous oxide emission.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
SLM measures such as SALT method, terraces, stone bunds and crops planted along contour lines prevent runoff and reduced downstream siltation.
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As an application of synthetic chemicals was reduced, and a proper farm waste disposal system was implemented, the removal of chemicals was controlled.
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Application of organic substances to soil and increased ground cover had improved filtering capacity.
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Restricted movements of the cows.
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Restricted movements of the cows.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Will have reduced the emission of methane and nitrous oxide from manure. A reduction in urea application would have reduced the emission of nitrous oxide.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវប្រាំង | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | ល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវប្រាំង | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | មធ្យម |
| ការមានបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិត/ដង្កូវ | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
According to the land user’s perspective implementation of this technology provided net benefits from tea, vegetables and dairy farming compared with establishment and maintenance cost. In the beginning, land users had to invest substantial amount of money to establish this technology. However, short-term and long-term returns could cover the cost involved in establishment and maintenance of the technology.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
The technology was introduced to about 10 farms but except one land user, others were unable to spend on developing technology irrespective of partial funds generated from other sources.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
No farmer was able to afford to develop technology by their own.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| After providing a proper shed for cows, it was possible to provide adequate feed and water for easy consumption of cows. This led to a significant increase in milk production. |
| Direct application of cow dung and liquid organic fertilizer for tea and vegetables led to an increase in crop yields and improved soil fertility. |
| As benefits are higher in monetary terms in comparison to the costs of investment for this technology, neighbourhood farmers who rear animals are encouraged to follow this technology. |
| Reduction in chemical fertilizer usage reduced the cost of production. |
| With the implementation of new technology, the number of pests and diseases incidences declined. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| This technology is easy to promote on the farmland due to the low cost involved and multiple benefits are visible. This technology has changed the attitudes of farmers that dairy farming could be profitable and support crop cultivation. |
| Before implementing this technology landowners had to work outside to earn money. As the income increase with the establishment of the technology, landowners could spend more time on other farming activities onsite . |
| Modernization of cattle farms enable zero-grazing so that land user was able to spend additional time for other farming activities. |
| The landowner does not need to depend on government or private sector funds to improve their farming activities. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Crops and fruits are often damaged by wild animals. Therefore the maximum profits cannot be achieved. | The landowner is with the opinion is that damage caused by wild animals could be stopped by constructing a steel fence around the land. However, farmer is unable to afford or such as the cost is very high. |
| Establishment of this technology requires considerable amount of money which is beyond the income and purchasing power of farmers with low income. | Providing partial funding by government or private sector organizations would help farmers to initiate the establishment of at least one or two components of technology. |
| Attitudes of neighboring farmers on dairy farming should be changed as a profit oriented business. | Introducing training programs and demonstrations at the successful farm would encourage other farmers to use the technology. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The landowner does not record profits that earn from his farming activities. He doesn’t have a good idea about the overall income of his farming activities per month. | The landowner should change attitudes toward income recordings. |
| People should be aware of these SLM technologies, SLM knowledge and benefits. | Government and private sector should invest in and implement SLM training programs. |
| Limited availability of modern technologies in cattle farming and crop cultivation affordable to middle income farmers. | Modernize farming with biogas technology, harvest tea with the cutter, prepare wormy compost and compost tea for tea cultivation. |
| Lack of properly established marketing channel for selling products. | Improve the product quality, or technology to develop value added products targeting supermarkets. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
01
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
02
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
02
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
02
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
06/02/2022
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Sustainable management practices for agricultural lands in the central highlands of Sri Lanka
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
rehabilitation of degraded agricultural land project office, food and agricultural organization of the United Nations Peradeniya Sri Lanka
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Project News: Fertile Soil
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Controlled livestock grazing for soil fertility improvement [Uganda]
វេបសាយ:
https://qcat.wocat.net/en/wocat/technologies/view/technologies_2761/
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Women practices SLM through Vanilla cultivation [ប្រទេសស្រីលង្កា]
Women in Central Highlands of Sri Lanka practice sustainable land management through vanilla cultivation and earn extra income for their families
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Bandara Rotawewa
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល