Environmental Friendly Pig Farm /Zero Waste Pig Farm [Thailand]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
หมูหลุมอินทรีย์ตามวิถึชุมชน
technologies_4252 - Thailand
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
สิงห์โตศรี นายสุพจน์
กลุ่มหมูหลุมอินทรีย์ ตามวิถีชุมชนตำบลดอนแร่
Thailand
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
-
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

ศูนย์ถ่ายทอดเทคโนโลยีการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม (Zero Waste Pig Farm Technology Transfer Center) [Thailand]
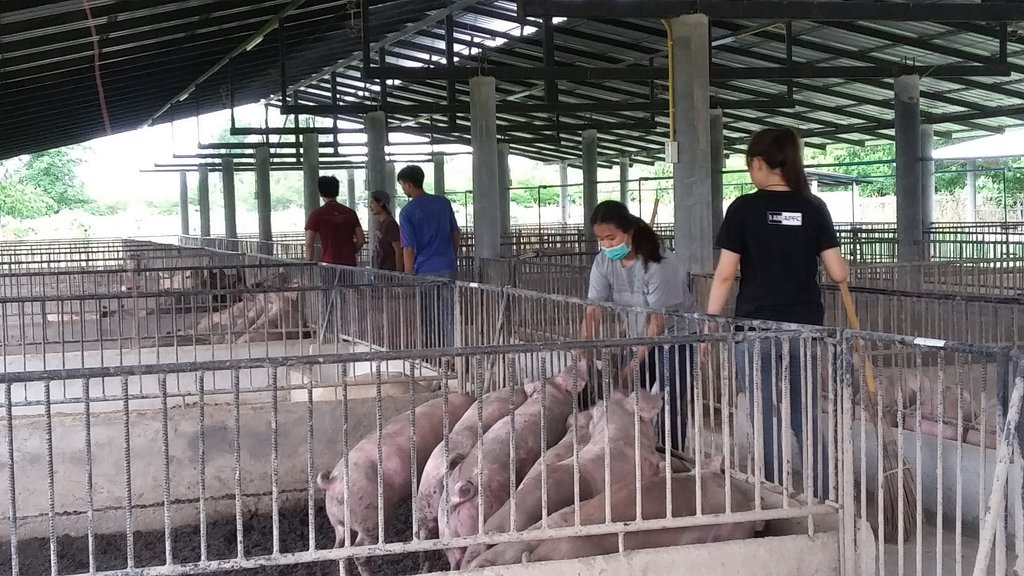
ศูนย์ถ่ายทอดเทคโนโลยีการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม เป็นศูนย์กลางการถ่ายทอดความรู้เรื่องการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม จากเกษตรกรผู้ประสบความสำเร็จไปยังเกษตรกรและผู้สนใจ รวมทั้งมีการสร้างเครือข่ายผู้เลี้ยงหมูหลุมให้เป็นเวทีการแลกเปลี่ยน เรียนรู้และแก้ไขปัญหาร่วมกัน
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
2. Description of the SLM Technology
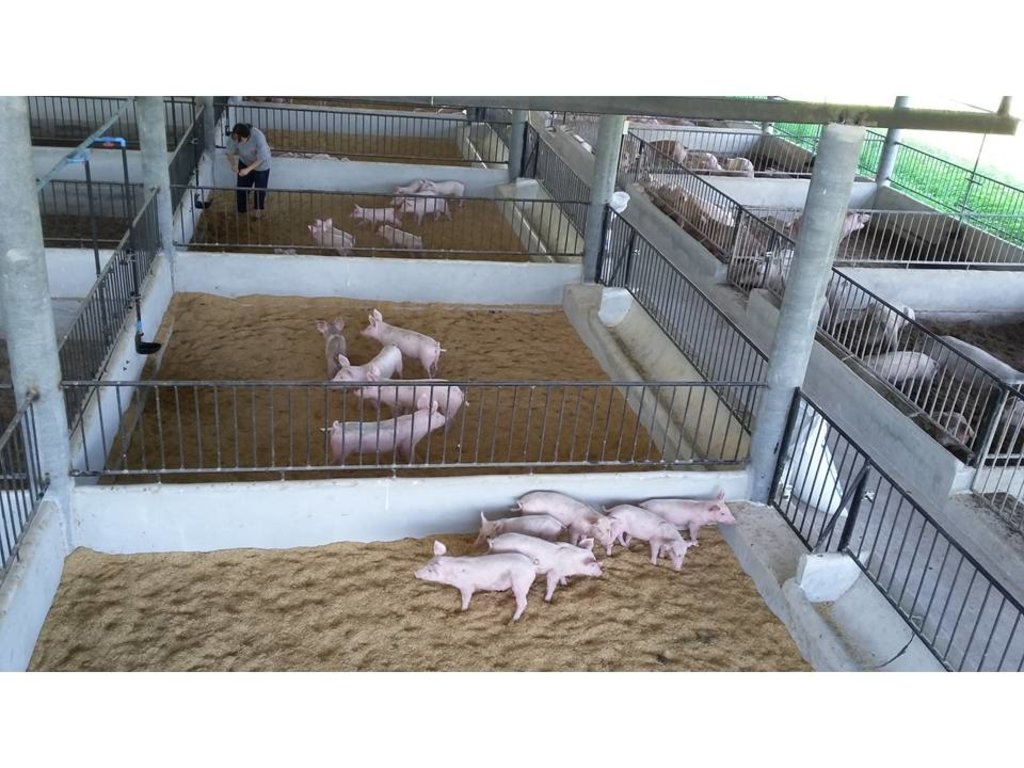
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
หมูหลุม เป็นการจัดการในการเลี้ยงสุกร ด้วยวิธีการจัดการคอกและการเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบผสมผสานกับการทำงานของจุลินทรีย์ที่ทำให้ได้ผลิตภัณฑ์หมูที่ปลอดภัย และสามารถกักเก็บของเสียจากคอกเป็นปุ๋ยอินทรีย์ นำไปใช้ให้เกิดประโยชน์ ตลอดจนไม่เกิดมลภาวะต่อชุมชน
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
(1) เทคโนโลยีนำไปใช้ที่ไหน(สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์ )
โดยทั่วไปการเลี้ยงสุกร ในชุมชน มักจะก่อให้เกิดมลภาวะอันเนื่องมาจาก ของเสียจากการเลี้ยงสุกรได้แก่ มูลสุกร น้ำเสียจากการเลี้ยงและกลิ่น ทำให้เกิดมลภาวะและความขัดแย้งในการใช้ประโยชน์จากที่ดินของชุมชน การจัดการเลี้ยงหมู แบบ หมูหลุม เป็นเทคโนโลยีทางเลือกในการลดปัญหาอันเนื่องมาจากการเลี้ยงหมูแบบเดิม ที่ส่งผลกระทบชีวิตความเป็นอยู่ สภาวะสิ่งแวดล้อมของชุมชนที่นำไปสู่ความขัดแย้งในการใช้ประโยชน์จากที่ดินของชุมชน
(2) อะไรคือลักษณะหรือองค์ประกอบที่สำคัญของเทคโนโลยี
การเลี้ยงหมูหลุม มีลักษณะการจัดการเฉพาะประกอบด้วย2 ส่วน คือ การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุมและการจัดการของเสียจากการเลี้ยงหมู
ก.การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม มีองค์ประกอบที่สำคัญ คือการจัดการโรงเรือนและวิธีการเลี้ยง
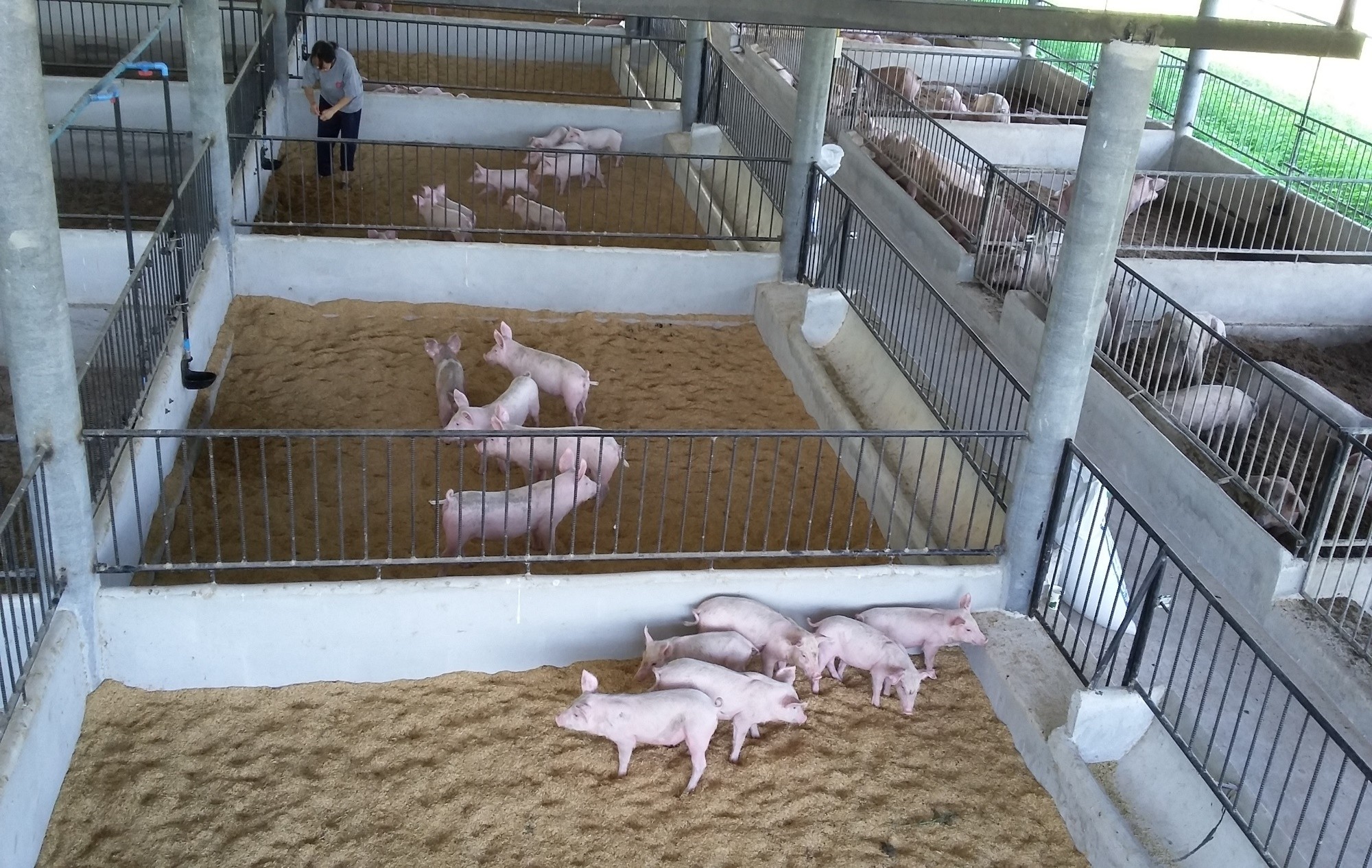
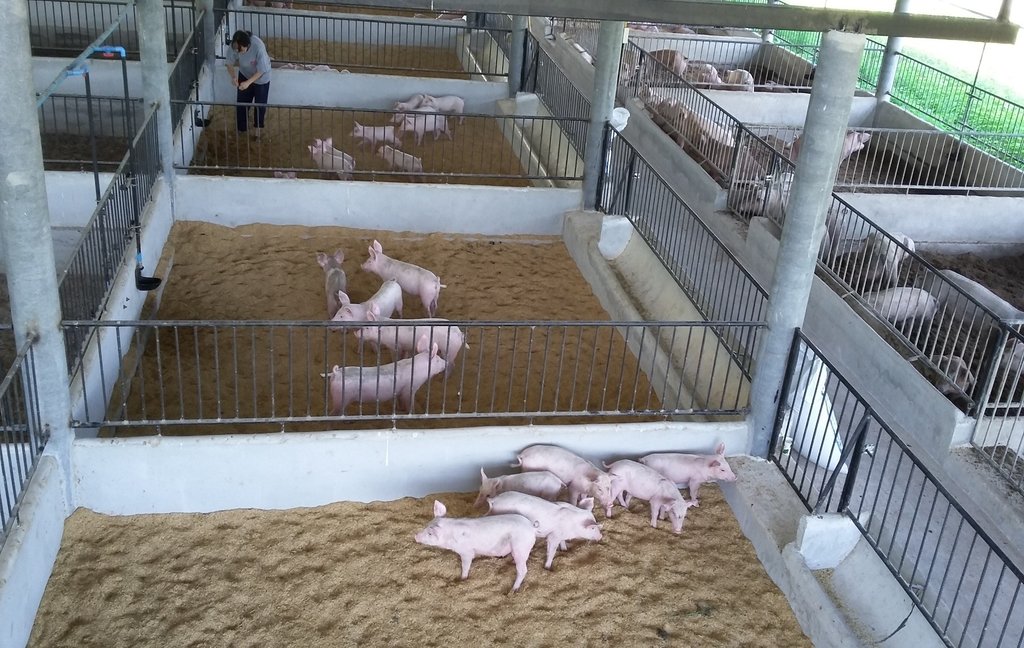
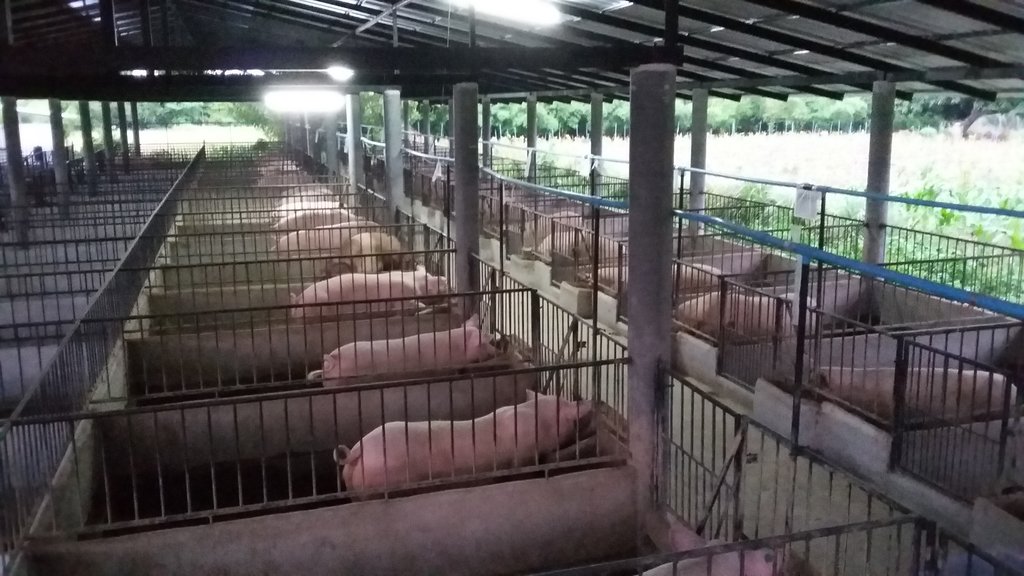
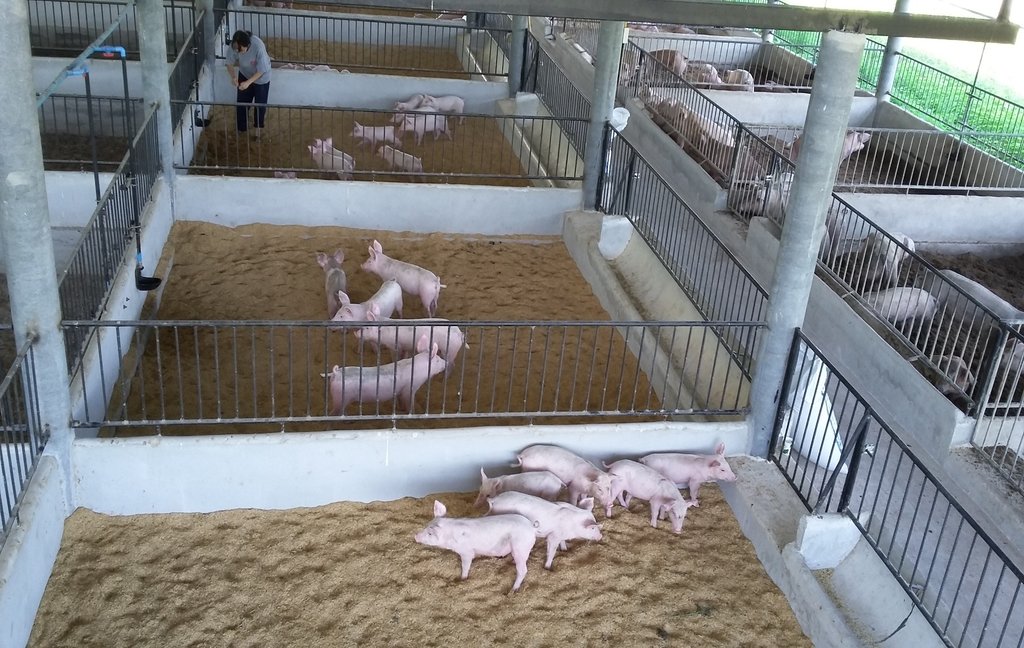
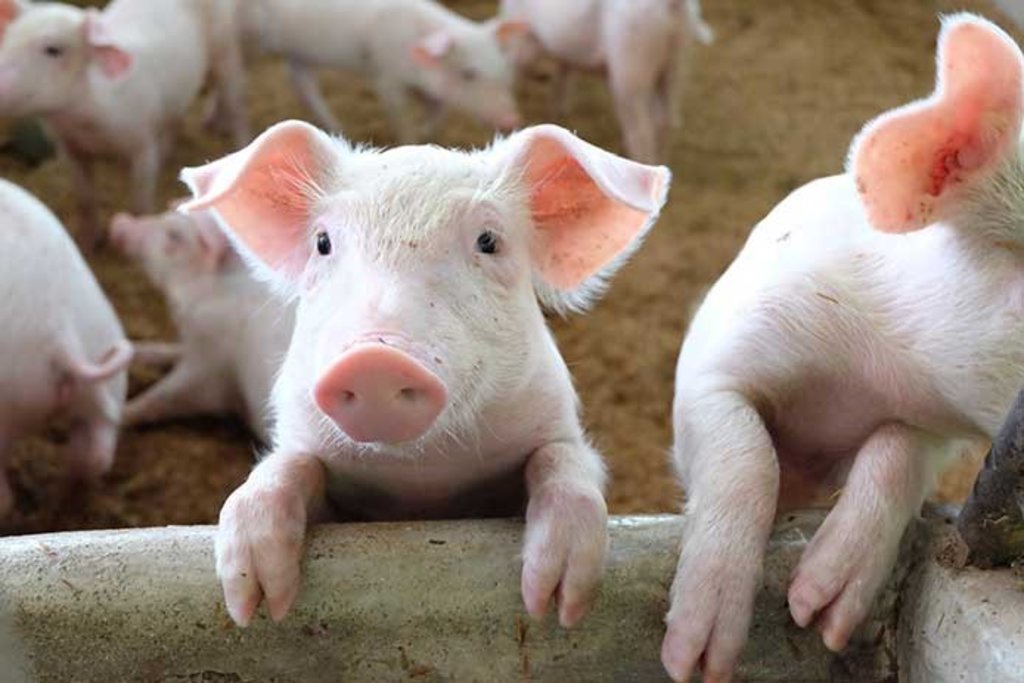
การจัดการโรงเรือน สร้างโรงเรือนบนพื้นที่ดอนที่ไม่มีน้ำท่วมขัง ใช้วัสดุที่หาได้ตามท้องถิ่น เช่น ไม้ไผ่ หญ้าคา เป็นต้น สร้างเป็นลักษณะเพิงหมาแหงนหรือหน้าจั่วโดยให้โรงเรือนมีการระบายอากาศที่ดี การทำคอกหมูหลุม ในการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม ให้ทำคอกบนพื้นดิน ไม่เทพื้นซีเมนต์ แต่จะขุดหลุมลึกประมาณ 60-70 เซนติเมตร แล้วรองก้นหลุมด้วยแกลบ ขี้เลื่อย หรือขุยมะพร้าว
วิธีการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม ประกอบด้วย. การจัดการเรื่อง อาหารได้แก่ อาหารข้นและอาหารหมัก วัตถุดิบต้องคัดเลือกว่ามาจากกระบวนการผลิตที่ไม่ใช้สารเคมี และมีการใช้สมุนไพรผงร่วมกับการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ ผสมน้ำ ให้สัตว์กินเพื่อส่งเสริมสุขภาพสัตว์ เป็นการป้องกันและรักษาโรค
พันธุ์สุกรที่นำมาเลี้ยงในลักษณะหมูหลุม ได้แก่สายพันธุ์ที่นิยมนำมาเลี้ยงจะเป็นลูกผสมสามสายพันธ์ คือ ดูร็อคเจอร์ซี่ + แลนด์เลซ + ลาร์จไวท์ โดยให้อยู่ในช่วงหย่านม ( ประมาณ 1 เดือน )
ข.การจัดการของเสียจากการเลี้ยงหมู ให้ใช้แกลบรองก้นหลุม แบ่งเป็น 2 ชั้น ชั้นละประมาณ 30 เซนติเมตร ระหว่างชั้น ใส่ดินแล้ว หว่านเกลือ แล้วรดน้ำหมักชีวภาพให้ชุ่ม จากนั้นทุกสัปดาห์ให้รดน้ำหมักชีวภาพเพื่อช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการย่อยสลายสิ่งปฏิกูลต่างๆ หลังจากเลี้ยงหมู ในแต่ละรอบของการเลี้ยง จะได้ปุ๋ยหมักมูลหมูหลุมพร้อมใช้
(3)อะไรคือจุดประสงค์หรือหน้าที่ของเทคโนโลยี
1.เพื่อให้การเลี้ยงหมูไม่ก่อให้เกิดมลภาวะและเป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อม
2.เพื่อให้ได้ปุ๋ยหมักมูลหมูหลุมที่มีคุณภาพ เพื่อนำไปใช้ในการผลิตสินค้าเกษตรอินทรีย์
3. เพื่อให้ได้ผลิตภัณฑ์จากสุกรที่ปลอดภัยจากสารพิษไม่เป็นอันตรายต่อผู้บริโภค
(4)กิจกรรมที่สำคัญหรือปัจจัยการผลิตที่จำเป็นในการจัดตั้งหรือบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี
ขั้นตอนการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม
1.สร้างโรงเรือน บนพื้นที่ดอนที่ไม่มีน้ำท่วมขัง ให้โรงเรือนมีการระบายอากาศที่ดี
2.สร้างคอกหมูหลุม ขนาดคอกกว้าง 4 x 4 เมตร สามารถเลี้ยงได้คอกละ8 ตัว
3. การเตรียมคอก
4.พันธุ์สุกร สายพันธ์ที่นิยมนำมาเลี้ยงจะเป็นลูกผสมสามสายพันธ์
5. อาหารหมูหลุม วัตถุดิบ ต้องคัดเลือกว่ามาจากกระบวนการผลิตที่ไม่ใช้สารเคมี
6. การป้องกันและรักษาโรค ใช้การฉีดพ่นน้ำหมักชีวภาพที่พื้นคอกและตัวหมูทุก 7 วันใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพผสมน้ำให้หมูกิน เมื่อมีอาการป่วยก็รักษาตามอาการโดยการใช้ยาสมุนไพร
7. การดูแลรักษา
(5)ประโยชน์ที่ได้รับหรือผลกระทบของเทคโนโลยีคืออะไรบ้าง
1)มีวัสดุและวัตถุดิบในพื้นที่ทำให้ช่วยลดต้นทุนการผลิต
2)ได้ปุ๋ยที่เป็นประโยชน์สามารถนำไปเป็นธาตุอาหารให้กับพืชได้
3)ได้ผลิตภัณฑ์เนื้อหมูที่ปลอดภัย
4)ไม่เป็นมลภาวะต่อสิ่งแวดล้อม และไม่มีกลิ่นรบกวนชุมชน
5)เป็นอาชีพที่สามารถดำรงชีพได้อย่างยั่งยืน
(6)อะไรบ้างที่ผู้ใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดินชอบหรือไม่ชอบเกี่ยวกับเทคโนโลยี
อะไรบ้างที่ผู้ใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดินชอบ
1.สามารถเลี้ยงในชุมชนได้ เนื่องจากไม่มีปัญหาเรื่องกลิ่นเหม็นจากมูลสุกรและ แมลงวัน
2.ได้ปุ๋ยอินทรีย์ที่มีคุณภาพ ใข้ปรับปรุง บำรุงดิน ที่ปลูกพืชอาหารสัตว์ในพื้นที่ และจำหน่ายเป็นรายได้เสริม
3.ประหยัดแรงงานเนื่องจากไม่ต้องใช้แรงงานในการเก็บกวาดมูล สุกร ทำความสะอาด คอกและล้างตัวสุกรรวมทั้งยังทำให้ประหยัดน้ำที่ใช้ในการเลี้ยงด้วย
อะไรบ้างที่ผู้ใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดินหรือไม่ชอบ
1.กระบวนการและการเลี้ยงหมูหลุมใช้เวลามากกว่าปกติ
2.ผลิตภัณฑ์จากหมูหลุมยังไม่เป็นที่รู้จักอย่างแพร่หลาย
3.ยังไม่มีการกำหนดมาตรฐานการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม จากภาครัฐ
4.การเลี้ยงหมูหลุม ต้องมีพื้นที่ปลูกพืชอาหารเพื่อเป็นวัตถุดิบอาหารให้หมูที่ปลอดภัย
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
-
Location:
-
Name of videographer:
-
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Thailand
Region/ State/ Province:
ราชบุรี
Further specification of location:
พื้นที่ตำบลดอนแร่ อ.เมือง จ.ราชบุรี
Comments:
นายสุพจน์ สิงห์โตศรี 95/1 ม.9 ต.ดอนแร่ อ.เมือง จ.ราชบุรี
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
1969
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
- การศึกษาดูงาน
Comments (type of project, etc.):
-
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Forest/ woodlands
- Tree plantation, afforestation
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- Mixed varieties
Comments:
-
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Comments:
-
3.4 Water supply
other (e.g. post-flooding):
- ใช้ในปศุสัตว์,สระน้ำ
Comments:
-
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated soil fertility management
- waste management/ waste water management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

management measures
- M6: Waste management (recycling, re-use or reduce)

other measures
Specify:
-
Comments:
การเลี้ยงหมูในคอกที่ทำให้ไม่มีของเสีย/ทำลายสิ่งแวดล้อม
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Hp: decline of surface water quality
Comments:
ถ้าทำปศุสัตว์แบบปกติจะทำให้เกิดมลภาวะต่อชุมชนและสิ่งแวดล้อม
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
นำปุ๋ยมูลหมูหลุมมาปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1.โรงเรือนหมูหลุม
สร้างโรงเรือนบนพื้นที่ดอนที่ไม่มีน้ำท่วมขัง ไม่เทพื้นซีเมนต์ ใช้วัสดุที่หาได้ตามท้องถิ่น เช่น ไม้ไผ่ หญ้าคา เป็นต้น สร้างเป็นลักษณะเพิงหมาแหงนหรือหน้าจั่ว โดยให้โรงเรือนมีการระบายอากาศที่ดี
2. การเตรียมคอก
การเลี้ยงแบบนี้จะเป็นพื้นอ่อนและโรงเรือนจะต้องสัมพันธ์กับจำนวนหมู โดยใช้มีขนาดคอกกว้าง 4 x 4 เมตร สามารถเลี้ยงได้คอกละ8 ตัว ส่วนแม่หมูจะใช้คอกเล็กกว่าหมูขุน จะใช้คอกขนาด 2x3 เมตร เริ่มด้วยการขุดพื้นคอกลึกลงไป 60 เซนติเมตร (หรือก่ออิฐขึ้นมาก็ได้) ในการมุงหลังคานั้นควรให้ตีนชายคากว้างกันไม่ให้น้ำฝนสาดเข้ามาในคอก และเมื่อตีฝาคอกแล้วต้องใช้อิฐบล็อกหรือไม้ไผ่กั้นรอบๆ คอกลึกลงไปจากพื้นดินประมาณ 40-50 เซนติเมตร เพื่อกันไม่ใช่หมูขุดนอกคอกได้ (การกั้นฝาคอกควรติดตั้งประตูปิด-เปิดได้ไว้ เพื่อความสะดวกในการนำหมูเข้า-ออก)
3.การเตรียมวัสดุพื้นคอก
ปูพื้นคอกโดยใช้แกลบหนา 60 เซ็นติเมตร แล้วใช้แกลือเม็ด ครึ่งลิตรโรยหน้าแล้วใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ ผสมน้ำ 20 ลิตร ราดให้ทั่ว ช่วงนี้วัสดุพื้นคอกจะยังร้อนจากการทำงานของจุลินทรีย์ ทิ้งไว้ประมาณ 7 วัน จึงนำหมูเข้าอยู่ได้ และควรราดน้ำหมักชีวภาพลงบนพื้นคอกเพิ่มเติมทุกๆ 5 – 7 วัน ครั้งละ 10ลิตร ภายหลังจากเริ่มเลี้ยงหมูแล้วเพื่อช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการย่อยสลายสิ่งปฏิกูลต่างๆ
แกลบจะทำหน้าที่ดูดซับความชื้นของเสียต่างๆ ลดการเกิดแก๊สจากการสะสมของเสีย พื้นแกลบนุ่มเดินสบายเท้าทำให้ไม่มีปัญหาเล็บเท้าฉีกขาด หมูชอบขุดคุ้ยดินที่เย็นสบาย นอกจากนั้นไม่ต้องใช้แรงงานและน้ำจำนวนมากในการทำความสะอาดโรงเรือน แกลบที่ใช้รองพื้นเมื่อหมูอายุครบกำหนด ยังได้ขายเป็นปุ๋ยคอกอีกด้วย สภาพแวดล้อมโดยรอบแห้งสะอาด ไม่มีสิ่งปฏิกูลให้เป็นแหล่งเพาะเชื้อโรค
4.พันธุ์สุกร
พันธุ์สุกรที่นำมาเลี้ยงในลักษณะหมูหลุม ได้แก่สายพันธุ์ที่นิยมนำมาเลี้ยงจะเป็นลูกผสมสามสายพันธ์ คือ ดูร็อคเจอร์ซี่ + แลนด์เลซ + ลาร์จไวท์ โดยให้อยู่ในช่วงหย่านม ( ประมาณ 1 เดือน )
5.อาหารหมูหลุม อาหารข้นและอาหารหมัก ผสมในอัตราส่วน อาหารข้น 50% และอาหารหมัก 50% เพื่อลดต้นทุนค่าอาหาร นอกจากนี้ยังมีการเสริมหญ้าสดให้กินทุกวันด้วย โดยให้กินประมาณครึ่งกิโลกรัม ต่อตัว สำหรับอาหารหมัก จะใช้พืชจากธรรมชาติมาหมัก คือ หยวกกล้วย 100 กิโลกรัม น้ำตาลทรายแดง 4 กิโลกรัม เกลือ 1 กิโลกรัม หมักทิ้งไว้ประมาณ 4-5 วัน วัตถุดิบที่นำมาผสมเป็นอาหาร ต้องคัดเลือกว่ามาจากกระบวนการผลิตที่ไม่ใช้สารเคมี
การผลิตอาหารหมักชีวภาพในการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม น้ำหมักชีวภาพเป็นเทคโนโลยีชีวภาพท้องถิ่นที่ชาวบ้านสามารถทำเองได้โดยการนำเอาพืชผักผลไม้ซากสัตว์ไปหมัก โดยจุลินทรีย์ที่มีในบรรยากาศและกากน้ำตาลเป็นอาหารของจุลินทรีย์หรือการใช้หัวเชื้อที่คัดเลือก การใช้สารสกัดจากสมุนไพร และสารสกัดจากพืช โดยกระบวนการการหมักบ่มด้วยจุลินทรีย์ที่มีลักษณะจำเพาะ ด้วยระยะเวลาและวิธีการหมักบ่มที่เหมาะสมจะได้ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่เป็นประโยชน์กับสัตว์การใช้สมุนไพรผงและการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ ผสมน้ำ ให้สัตว์กิน เป็นการส่งเสริมสุขภาพให้กับสัตว์ สามารถป้องกันและรักษาโรค นอกจากนี้ยังมีการใช้สมุนไพร ในการฆ่าเชื้อและต้านทานเชื้อก่อโรค
6.การให้อาหารและน้ำ
1.หมูเล็ก น้ำหนัก 15-30 กก.ใช้ อาหารข้น:อาหารหมัก=2:1
2.หมูรุ่น น้ำหนัก 30-60 กก.ใช้ อาหารข้น:อาหารหมัก=1:1
3.หมูใหญ่ น้ำหนัก 60-ส่งตลาดใช้ อาหารข้น:อาหารหมัก=1:2
4.แม่พันธุ์ พ่อพันธุ์ ใช้ อาหารข้น:อาหารหมัก=1:2
ส่วนการให้น้ำ ให้ตามปกติ และควรมีถ้วยรองน้ำเพื่อไม่ให้แฉอะแฉะ
7. การให้ยาและการป้องกันโรค
1. ในการเสริมสร้างความแข็งแรงให้กับหมู ใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพผสมน้ำให้หมูกิน แต่หากอาหารหรือน้ำไม่สะอาดพอ หมูอาจมีอาการท้องเสีย หรือขี้เหลวได้ (ซึ่งปกติไม่ค่อยเกิดบ่อยนัก) ต้องรักษาโดยนำใบฝรั่งสด ใบฟ้าทะลายโจรสด และเถาบอระเพ็ดเอาให้หมูกิน
2. ใช้ตาข่าย สำหรับกันยุงในเวลากลางคืน แต่หากเป็นพื้นที่ที่มีตัวริ้นชุกชุม ควรนำเอาตะไคร้หอมมาทุบแช่น้ำ แล้วฉีดพ่นให้หมูในช่วงหัวค่ำ
8. การดูแลหมูหลุม
1. ฉีดพ่นน้ำหมักชีวภาพที่พื้นคอกและตัวหมูทุก 7 วัน
2 .ทำความสะอาดบริเวณโรงเรือนทุกๆเดือน เติมขี้เถ้าแกลบ 1-2 กระสอบเดือนละครั้งต่อคอก
3. ตรวจสอบน้ำดื่มหมู เปลี่ยนที่เหลือสาดเข้าไปในคอกให้หญ้าสด,ผักสด ปริมาณ 1 ใน 3 ของอาหาร
Author:
-
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
27ไร่
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
-
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
32.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
300บาทต่อวัน
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม | 2 ครั้งต่อปี |
| 2. | การจัดการมูลจากหมูหลุม | 2 ครั้งต่อปี |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 1.การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม | แรง | 210.0 | 300.0 | 63000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 2.การจัดการอาหารหมูหลุม | แรง | 60.0 | 300.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 3.การจัดการมูลหมูหลุม | แรง | 300.0 | 300.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 4.การสร้างโรงเรือน | แรง | 120.0 | 300.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | 1.ค่าวัสดุการสร้างโรงเรือน | โรง | 1.0 | 84000.0 | 84000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 1.ค่าอาหารการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม | ตัว | 90.0 | 3800.0 | 342000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 2.ค่าพันธุ์ลูกสุกร | ตัว | 90.0 | 1500.0 | 135000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 768000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 24000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
-
Comments:
-
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม | 2 ครั้งต่อปี |
| 2. | 2. การจัดการอาหารหมูหลุม | 2 ครั้งต่อปี |
| 3. | 3. การจัดการมูลหมูหลุม | 2 ครั้งต่อปี |
Comments:
-
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | การจัดการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม | แรง | 210.0 | 300.0 | 63000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | การจัดกาอาหารรหมูหลุม | แรง | 60.0 | 300.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | การจัดการมูลหมูหลุม | แรง | 300.0 | 300.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 171000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 5343.75 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
-
Comments:
-
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ค่าแรง
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1210.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
อยู่ภายใต้อิทธิพลของลมมรสุมทีพัดเวียนประจําฤดูกาล 2 ชนิด คือพัดจากทิศตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือในฤดูหนาวเรียกว่าลมมรสุมตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือ อิทธิพลของลมนี้ทําให้ บริเวณจังหวัดราชบุรีมีอากาศหนาวเย็นและแห้งแล้ง กับมรสุมอีกชนิดหนึงคือมรสุมตะวันตกเฉียงใต้ ซึง พัดจากทิศตะวันตกเฉียงใต้เป็นส่วนใหญ่ในฤดูฝน ทําให้อากาศชุ่มชืนและมีฝนตกทัวไป
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
-
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
-
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
Comments and further specifications on topography:
ราชบุรีเป็นจังหวัดทีมีเทือกเขาใหญ่น้อยเป็ นอันมาก โดยเฉพาะทางด้านตะวันตก ของจังหวัดมีเทือกเขาตะนาวศรี เป็ นแนวยาวกันเขตแดนไทยกับพม่า ทางตอนกลางของจังหวัดมีทีราบลุ่ม แม่นํ าแม่กลอง ซึงเหมาะแก่การเพาะปลูก และทางด้านตะวันออกเฉียงใต้เป็ นทีราบตํา ซึงได้รับอิทธิพลจาก การหนุนเนืองของนําทะเล
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
-
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
-
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
-
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
-
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
-
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Specify:
-
Comments:
-
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
Comments:
-
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
ดีขึ้นเนื่องจกกมีการใช่ปุ๋ยหมักจากมูลหมูหลุมที่มีคุณภาพ
animal production
Quantity after SLM:
10%
Comments/ specify:
ลดการตายของประชากรหมูหลุม
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
มีตลาดหลากหลาย
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
มีการแปรรูปผลิตภัณฑ์ที่หลากหลาย
land management
Comments/ specify:
แบ่งพื้นที่จัดการได้เหมาะสม
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
water quality for livestock
Income and costs
farm income
diversity of income sources
workload
Comments/ specify:
เอาใจใส่ในการผลิตมากขึ้น
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
สามารผลิตได้อย่างยั่งยืน
health situation
Comments/ specify:
สุขภาพแข็งแรง
land use/ water rights
Comments/ specify:
มีการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดินอย่างเต็มที่
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
ทำให้ไม่มีกลิ่นเหม็นรบกวน
Ecological impacts
Soil
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
มีการนำมูลสุกรไปใช้ในพื้นที่
salinity
Comments/ specify:
ปรับปรุงดินด้วยมูลหมูหลุม
acidity
Comments/ specify:
มีการใช้มูลหมูหลุมปรับปรุงดิน
Other ecological impacts
ลดกลิ่นเหม็นในชุมชน
Comments/ specify:
ลดกลิ่นจากการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม
ไม่มีของเสียจากการเลี้ยงสัตว์
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
-
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | not well | |
| seasonal temperature | increase | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | not well at all |
Comments:
ระบุสัตว์ตายมากขึ้น
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
-
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
จำนวนสมาชิกในกลุ่ม 15 ครัวเรือน
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
-
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- changing markets
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
-คัดเลือกพันธุ์หมูหลุมให้เหมาะสม
-ลดหรือกำจัดกลิ่นเหม็นในการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| 1)มีวัสดุแลวัตถุดิบในพื้นที่ทำให้ช่วยลดต้นทุนการผลิต |
| 2)ได้ปุ๋ยที่เป็นประโยชน์สามารถนำไปเป็นธาตุอาหารให้กับพืชได้ |
| 3)ได้ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ปลอดภัย |
| 4)ไม่เป็นมลภาวะต่อสิ่งแวดล้อม ไม่มีกลิ่นรบกวนชุมชน |
| 5)สามารถเลี้ยงหมูหลุมในพื้นที่ชุมชนได้ |
| 6)เป็นอาชีพที่สามารถดำรงชีพได้อย่างยั่งยืน |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| 1)มีพื้นที่ที่เหมาะสมกับการใช้เทคโนโลยี |
| 2)ผู้ใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดินมีความรู้ความสามารถเป็นอย่างดี |
| 3)มีการปรับให้เหมาะสมกับสภาพแวดล้อมในชุมชน |
| 4)เป็นบุคคลที่น่าเชื่อถือเป็นที่ยอมรับในสังคมและชุมชน |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| 1.กระบวนการและการเลี้ยงหมูหลุมใช้เวลามากกว่าปกติ | 1ควรวิจัยหาเทคนิคและวิธีการตลอดจนเทคโนโลยีเข้ามาช่วย |
| 2) ผลิตภัณฑ์จากหมูหลุมยังไม่เป็นที่รู้จักอย่างแพร่หลาย | 2เสนอให้ทั้งภาครัฐและผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้องเผยแพร่ประชาสัมพันธ์ให้มากขึ้น |
| 3)ยังไม่มีการกำนดมาตรฐานการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม จากภาครัฐ | 3.ภาครัฐและหน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องควรพิจารณากำหนดให้มีมาตรฐาน การเลี้ยงหมูหลุมเพื่อสร้างความเชื่อมั่นให้กับผู้บริโภคทั้งในและต่างประเทศ |
| 4)การเลี้ยงหมูหลุม ต้องมีพื้นที่ปลูกพืชอาหารเพื่อเป็นวัตถุดิบอาหารให้หมูที่ปลอดภัย | 4ให้พิจารณาดำเนินการแบบกล่มและ/หรือชุมชนมีส่วนร่วม |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| - |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
-
Available from where? Costs?
-
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
-
URL:
-
7.4 General comments
-
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

ศูนย์ถ่ายทอดเทคโนโลยีการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม (Zero Waste Pig Farm Technology Transfer Center) [Thailand]
ศูนย์ถ่ายทอดเทคโนโลยีการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม เป็นศูนย์กลางการถ่ายทอดความรู้เรื่องการเลี้ยงหมูหลุม จากเกษตรกรผู้ประสบความสำเร็จไปยังเกษตรกรและผู้สนใจ รวมทั้งมีการสร้างเครือข่ายผู้เลี้ยงหมูหลุมให้เป็นเวทีการแลกเปลี่ยน เรียนรู้และแก้ไขปัญหาร่วมกัน
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
Modules
No modules