Planting pits for soil fertilisation and moisture improvement [اوغندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
EBISANIYA (Runyankore language)
technologies_1587 - اوغندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
16/11/2013
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Planting pits in banana plantation filled with a mixture of manure, organic material and soil, to improve soil moisture and fertility and to enhance crop production and famer's income.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
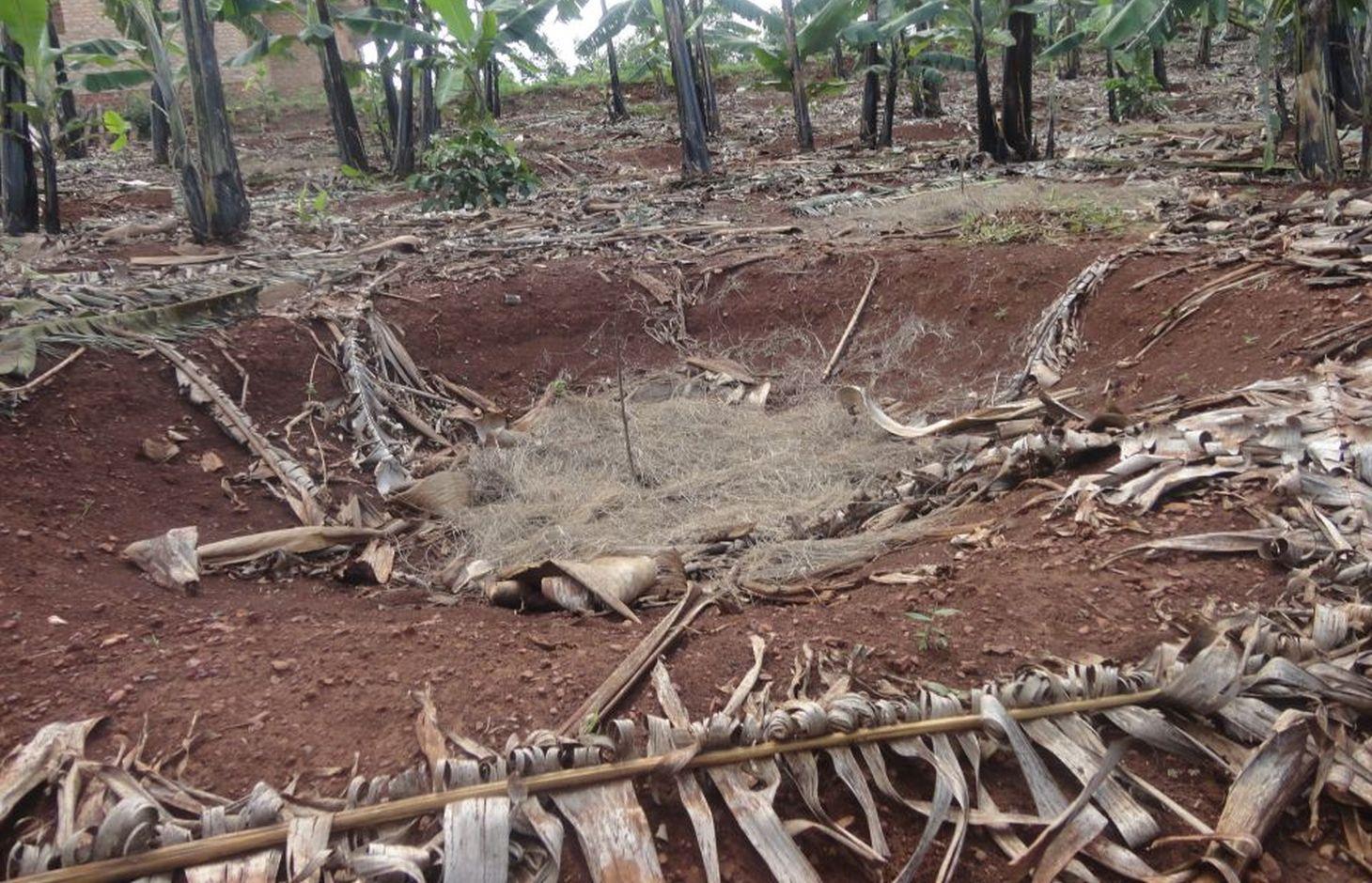
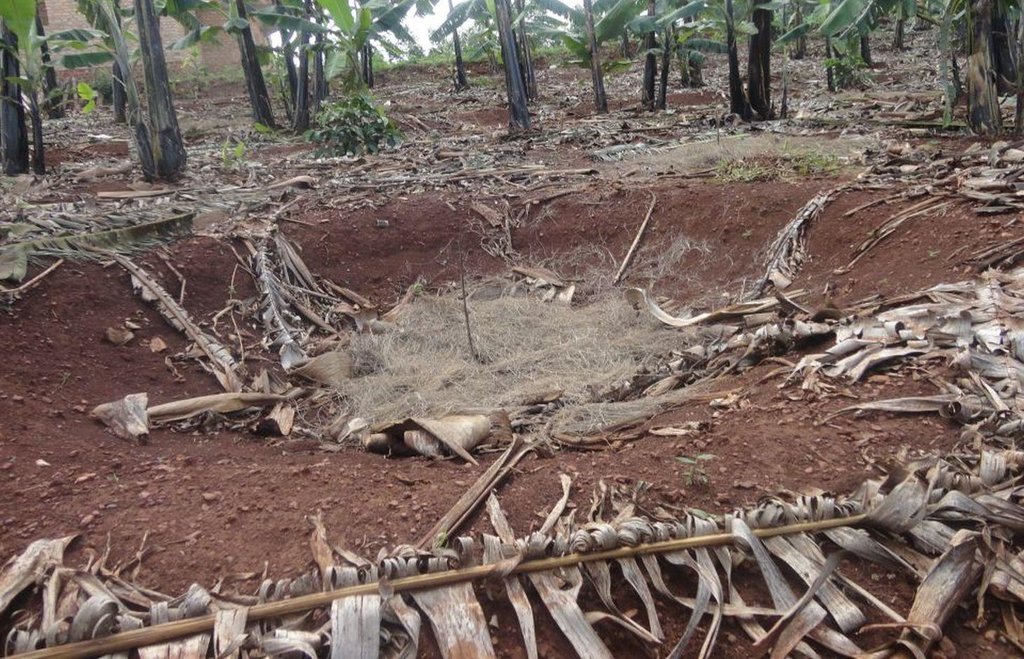
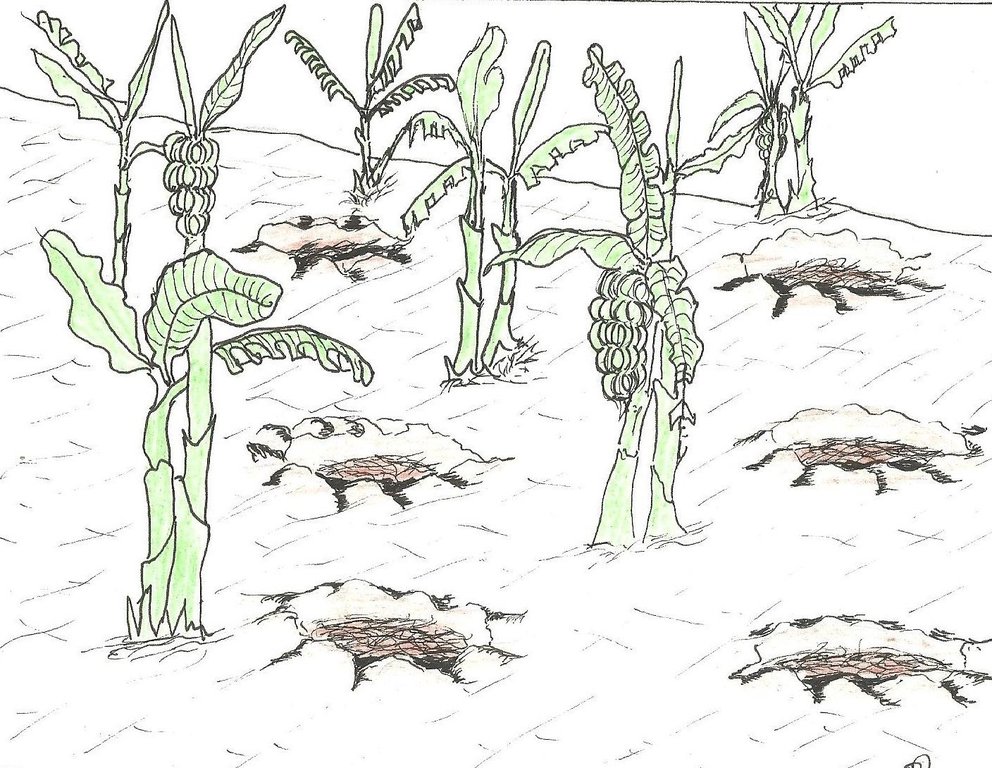
The planting pits are established between banana stems and filled with organic vegetative material mixed with decomposing manure to form a reservoir of nutrients for a long run. On gentle slopes covered with extensive banana plantations, the planting pits are dug at the center of banana stands. Before estbalishment of this technology, only the composting process was available for the conversion of organic domestic waste into manure. However, compost manure takes slightly longer to produce and is more bulky than conservation troughs making the latter easier to adopt. The technology can be applied to annual cropland as well. Application of the technology improves banana bunch size and plantation yield by over 300%.
Purpose of the Technology: The main objective is to improve soil fertility. The planting pits also check runoff thereby reducing soil erosion, improving moisture infiltration and retention, and enabling the plantation to withstand the dry months. Cabbages, beans and other high value vegetables can be grown directly on top of the trough.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The planting pits are established using simple tools such as the hand hoe, spade, panga and wheelbarrow. The hoe is used to dig up the soil and soften it. The soil is then scooped out using a spade, to create a bowl-shaped trough. The panga is used to chop the remains of harvested bananas (stems and leaves) which are then, carried to the troughs using a wheel barrow. The planting pit is 0.45 m to 0.60 m deep depending on the amount of manure available and 0.6 m wide. Each trough is about 0.60 m from the nearest banana stand. It is filled with chopped banana stems, followed by a layer of manure and then covered with mulch to prevent excessive evaporation of moisture. The planting pit is then covered with soil. After 3 to 4 months, the vigor of the banana stems improves. If the trough is opened by digging, roots are observed to have grown through the walls of the planting pit from all directions.
During the rainy season, the trough slowly fills with sediment from surface erosion. Weeding at the trough is done by uprooting the weeds using hands or a hand hoe.
Natural / human environment: Over time, the banana stands grow towards the trough. To maintain the distance between the stands, the suckers nearest to the trough are pruned.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
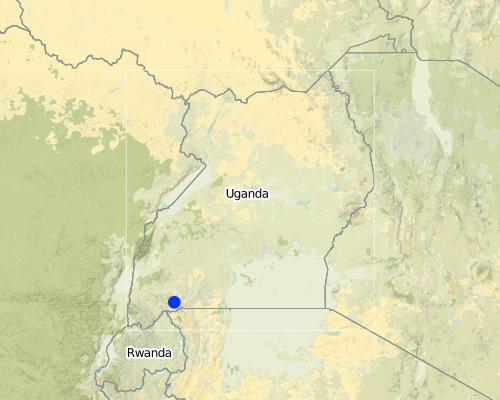
البلد:
اوغندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Uganda
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mbarara
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86269 30.62587; -0.86275 30.62622; -0.86279 30.62631; -0.86405 30.62522; -0.86393 30.62539, -0.86387 30.62503
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
In 2012, Kagera TAMP introduced the Farmer Field School methodology. The members of these schools have been experimenting on several SLM technologies since then and the troughs are one of the successful innovations
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop: Banana
Major food crop: Banana
Major other crops: Maize, beans, peas, Irish potatoes
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The light, sandy loam soil on a hilly slope has very little capacity to hold water. The soils are dry a few days after it rains. The banana plantation therefore suffers two problems: inadequate soil water for plant growth and low nutrient retention. The problem of soil erosion is critical in the area but is addressed more adequately by fanya ju retention trenches stabilized with Napier grass strips.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity of the land compared to past seasons.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.04 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A6:أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supp.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (No manure was being applied to replenish nutrients inspite of continuous banana harvesting)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Conservation troughs (0.4-0.6 m deep) are partially filled with a mixture of manure, undecomposed banana stems and other organic matter to add organic matter into the soil. They also capture rainfall runoff and help to maintain suitable soil moisture. The conservation trough should be dug about 0.6 m from banana plant so that the heat produced during decay does not affect the plant.
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara district. Uganda
Date: 29-Nov-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Self explanatory)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Basic training required on the construction methodology e.g. location selection, recommended dimentions of the trough (depth))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Reshaping surface
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): n/a
Construction material (earth): Troughs are developed by excavating soil; soil mixed with manure is used to fill the pit partially.
Construction material (stone): n/a
Construction material (wood): n/a
Construction material (concrete): n/a
Construction material (other): n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): n/a%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: n/a%
Lateral gradient along the structure: n/a%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity n/am3
Catchment area: n/am2
Beneficial area: n/am2
Slope of dam wall inside: n/a%;
Slope of dam wall outside: n/a%
Dimensions of spillways: n/am
Other specifications: n/a
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:n/a
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
UGX
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
2500,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
4.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Measuring and marking pit positions | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Wet season |
| 2. | Excavating pits | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Wet season |
| 3. | Mixing top soil with animal manure, filling mixture into pits, putting domestic and field organic residues into pits, covering pits | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Wet season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 7,0 | 7,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 91,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding by hand | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Wet season |
| 2. | Addition of manure and residues | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Once a year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 34,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe, wheel barrow
The calculations were made for the rainy season of September to November, 2013.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Availability of labour and animal manure are the most important factors affecting cost of the establishment activities. To reduce cost of labour it is recommended to apply Farmer Field Schools approach. To reduce cost of manure farmers can produce their own farmyard manure, e.g. by implementing zero-grazing technology.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
1400 mm spread over 2 seasons
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. Located at the Equator. A good supply of rain much of the year, but plenty of sunshine too
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1715 to 1740 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, concave) and ridges (ranked 2, convex)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Where the technology has been applied so far is on hilly slopes (< 30%) but the adjacent slopes where the technology is planned next is quite steep (> 45%))
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (The soils are generally shallow)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (Mulching had already introduced topsoil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: >50 m (Boreholes have been sank before to great lengths but have invariably dried up)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (Available only as trapped runoff behind rocky formations, but soon dries up)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, runoff)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
and own 20% of the land.
and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There has been an improvement in yields which translate into money generated per hectare. However, the farmers applying the technology have not yet diversified into other enterprises.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow)
Market orientation: Mixed (Surplus has grown to such a level that the commercial component has become inevitable)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
التعليقات:
Individual access to water rights is relatively new with the introduction of water harvesting.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8 Kg
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25 Kg
التعليقات/ حدد:
Bunch of bananas is bigger and heavier at harvest
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
67%
التعليقات/ حدد:
During the dry season or extended drought periods, only about 20% of the banana stands would have a fruiting stem; now well over two thirds of the stands do.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80 US$
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
200 US$
التعليقات/ حدد:
Monthly harvests for sale have increased from 20 to over 50 bunches
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Whereas extended drought posed food insecurity, this is no longer the case
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The earning power has increased greatly. Children are going to school because tuition fees are no longer burdensome and health needs are easily met. The farmers practicing the technology report making some savings from their incomes unlike before.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
The advantages of the technology to cropland are to be found underground. Therefore the technology is protected against most natural adversities above ground.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Costs at establishment are the only ones involved. There are no maintenance costs involved though pits need to be re-established every 2-3 years
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
22
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is a farmer initiative and no support has been received for the adoption of this technology.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
22 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: This is a farmer field school initiative and the district facilitator for Kagera TAMP (and also an Agricultural officer of the local government) provided guidance on positioning the pits for maximum utility.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Noticing the results in only 3 seasons, the other farmers (not members of farmer field school) are also adopting the technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
The technology requires the use of only the simplest of farm tools such as a hand hoe, a spade and a wheel barrow. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dissemination of the the technology through regular community meetings and a local language newsletter |
|
Demonstration of benefits is achieved quite quickly and therefore adoption by farmers is good. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Emphasize technology at farmer field school demonstration plots |
|
Technology bears similar benefits to composting but with a shorter list of activities How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption through demonstration |
|
Since the technology utilizes stem cuttings, whole stems are harvested reducing the risk of pests and diseases especially banana bacteria, that would be harbored by exposed rotting stems How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge dissemination through regular community meetings and local language newsletter |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The technology is labor intensive | Farmer Field Schools bring farmers together in a community level effort |
| The technology requires livestock manure in a predominantly cultivator community | Introduce zero-grazing livestock for manure production |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية